结构型模式:②桥接模式(Bridge Pattern)
核心思想
1.将类的 “抽象部分” 与 “实现部分” 解耦,通过 “组合关系”(桥接)替代 “继承关系”,使两者可以独立扩展、互不影响:
1.1抽象部分:定义上层逻辑(如 “产品类型”:普通手机、游戏手机),持有实现部分的引用;
1.2实现部分:定义底层具体实现(如 “品牌”:华为、苹果),提供统一接口供抽象部分调用;
2.核心本质:用 “对象组合” 替代 “多层继承”,避免因两者组合导致的 “类爆炸”(例如不用桥接时,需定义华为普通机、华为游戏机、苹果普通机、苹果游戏机等大量子类)。
C语言编写(结构体 + 函数指针模拟)
实现关键要点
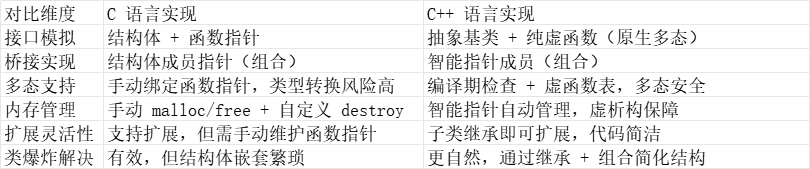
1.接口模拟:用 “结构体 + 函数指针” 分别定义抽象接口(Phone)和实现接口(Brand),模拟类的方法和多态。
2.桥接核心:抽象接口(Phone)通过成员指针 brand 持有实现接口(Brand)的实例,形成 “组合关系”,替代继承。
3.解耦逻辑:抽象部分的方法(如 normal_phone_show)通过桥接调用实现部分的方法(brand->show_brand),抽象与实现互不依赖具体类型,仅依赖接口。
4.独立扩展:
4.1扩展实现(新增品牌:小米):仅需创建新的 Brand 实例,无需修改抽象部分;
4.2扩展抽象(新增产品:折叠屏手机):仅需创建新的 Phone 实例,无需修改实现部分。
5.避免类爆炸:若不用桥接,需定义 华为普通机、华为游戏机、苹果普通机 等 N*M 个子类;用桥接后,仅需 N 个抽象类 + M 个实现类。
6.内存管理:抽象接口的 destroy 函数需同时销毁桥接的实现实例,避免内存泄漏。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
// -------------------------- 1. 实现部分(Implementor):品牌接口 --------------------------
// 品牌抽象接口:定义实现部分的统一方法(供抽象部分调用)
typedef struct Brand {
// 品牌的核心方法:展示品牌信息
void (*show_brand)(struct Brand* self);
char name[32]; // 品牌名称
void (*destroy)(struct Brand* self);
} Brand;
// 品牌接口的销毁通用实现
void brand_destroy(Brand* brand) {
if (brand != NULL) {
free(brand);
}
}
// -------------------------- 具体实现1:华为品牌 --------------------------
void huawei_show_brand(Brand* self) {
printf("品牌:%s(自研芯片,鸿蒙系统)\n", self->name);
}
Brand* create_huawei_brand() {
Brand* huawei = (Brand*)malloc(sizeof(Brand));
strncpy(huawei->name, "华为", sizeof(huawei->name));
huawei->show_brand = huawei_show_brand;
huawei->destroy = brand_destroy;
return huawei;
}
// -------------------------- 具体实现2:苹果品牌 --------------------------
void apple_show_brand(Brand* self) {
printf("品牌:%s(A系列芯片,iOS系统)\n", self->name);
}
Brand* create_apple_brand() {
Brand* apple = (Brand*)malloc(sizeof(Brand));
strncpy(apple->name, "苹果", sizeof(apple->name));
apple->show_brand = apple_show_brand;
apple->destroy = brand_destroy;
return apple;
}
// -------------------------- 2. 抽象部分(Abstraction):产品类型接口 --------------------------
// 产品抽象接口:持有品牌接口指针(桥接核心),定义抽象逻辑
typedef struct Phone {
// 产品的核心方法:展示产品信息(抽象逻辑)
void (*show_product)(struct Phone* self);
Brand* brand; // 持有实现部分的引用(桥接:组合品牌接口)
char type[32]; // 产品类型(普通/游戏)
void (*destroy)(struct Phone* self);
} Phone;
// 产品接口的销毁通用实现(需同时销毁品牌)
void phone_destroy(Phone* phone) {
if (phone != NULL) {
phone->brand->destroy(phone->brand); // 销毁桥接的品牌
free(phone);
}
}
// -------------------------- 具体抽象1:普通手机 --------------------------
void normal_phone_show(Phone* self) {
printf("产品类型:%s\n", self->type);
// 调用桥接的品牌实现(抽象依赖实现,通过桥接调用)
self->brand->show_brand(self->brand);
printf("核心功能:日常通讯、拍照、轻度娱乐\n\n");
}
Phone* create_normal_phone(Brand* brand) {
Phone* normal = (Phone*)malloc(sizeof(Phone));
strncpy(normal->type, "普通手机", sizeof(normal->type));
normal->show_product = normal_phone_show;
normal->brand = brand; // 绑定品牌(桥接关系建立)
normal->destroy = phone_destroy;
return normal;
}
// -------------------------- 具体抽象2:游戏手机 --------------------------
void game_phone_show(Phone* self) {
printf("产品类型:%s\n", self->type);
// 调用桥接的品牌实现(同一抽象逻辑可搭配不同实现)
self->brand->show_brand(self->brand);
printf("核心功能:高帧率游戏、散热优化、快充\n\n");
}
Phone* create_game_phone(Brand* brand) {
Phone* game = (Phone*)malloc(sizeof(Phone));
strncpy(game->type, "游戏手机", sizeof(game->type));
game->show_product = game_phone_show;
game->brand = brand; // 绑定品牌(桥接关系建立)
game->destroy = phone_destroy;
return game;
}
// -------------------------- 测试代码(客户端) --------------------------
int main() {
// 1. 华为普通手机(抽象:普通手机 + 实现:华为品牌)
Brand* huawei = create_huawei_brand();
Phone* huawei_normal = create_normal_phone(huawei);
printf("=== 华为普通手机 ===\n");
huawei_normal->show_product(huawei_normal);
// 2. 苹果游戏手机(抽象:游戏手机 + 实现:苹果品牌)
Brand* apple = create_apple_brand();
Phone* apple_game = create_game_phone(apple);
printf("=== 苹果游戏手机 ===\n");
apple_game->show_product(apple_game);
// 3. 扩展:新增小米品牌(仅扩展实现部分,不影响抽象)
Brand* xiaomi = (Brand*)malloc(sizeof(Brand));
strncpy(xiaomi->name, "小米", sizeof(xiaomi->name));
xiaomi->show_brand = [](Brand* self) { printf("品牌:%s(骁龙芯片,MIUI系统)\n", self->name); };
xiaomi->destroy = brand_destroy;
Phone* xiaomi_game = create_game_phone(xiaomi);
printf("=== 小米游戏手机 ===\n");
xiaomi_game->show_product(xiaomi_game);
// 4. 资源释放
huawei_normal->destroy(huawei_normal);
apple_game->destroy(apple_game);
xiaomi_game->destroy(xiaomi_game);
return 0;
}
C++语言实现(类 + 继承 + 多态)
C++ 支持原生类、继承和多态,通过 “抽象基类 + 纯虚函数” 定义接口,用 “成员变量指针” 实现桥接(组合关系),代码更简洁、类型更安全。
关键要点
1.接口定义:用 “抽象基类 + 纯虚函数” 分别定义抽象接口(Phone)和实现接口(Brand),强制子类实现核心方法,保证多态安全。
2.桥接核心:抽象基类 Phone 持有实现基类 Brand 的智能指针(std::shared_ptr),通过组合建立桥接关系,替代多层继承。
3.多态调用:客户端通过抽象基类指针 / 引用调用,实际执行具体子类的实现(如 NormalPhone::ShowProduct 和 Huawei::ShowBrand),实现抽象与实现的动态绑定。
4.独立扩展:
4.1扩展实现(新增品牌:小米):仅需新增 Xiaomi 类继承 Brand,无需修改抽象部分;
4.2扩展抽象(新增产品:折叠屏手机):仅需新增 FoldPhone 类继承 Phone,无需修改实现部分;
4.3组合灵活:任意抽象与实现可搭配(如 FoldPhone + Huawei、GamePhone + Xiaomi)。
5.内存安全:使用智能指针(std::shared_ptr/std::unique_ptr)自动管理内存,避免手动 delete 导致的泄漏,且虚析构确保子类析构被正确调用。
6.开闭原则:新增功能时不修改原有代码,仅新增子类,符合设计模式的开闭原则。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <memory> // 智能指针,自动管理内存
// -------------------------- 1. 实现部分(Implementor):品牌抽象基类 --------------------------
// 品牌接口:定义实现部分的统一接口(纯虚函数)
class Brand {
public:
virtual ~Brand() = default; // 虚析构:确保子类析构被调用
virtual void ShowBrand() const = 0; // 纯虚函数:强制子类实现
std::string GetName() const { return name_; }
protected:
explicit Brand(std::string name) : name_(std::move(name)) {}
private:
std::string name_;
};
// -------------------------- 具体实现1:华为品牌 --------------------------
class Huawei : public Brand {
public:
Huawei() : Brand("华为") {}
void ShowBrand() const override {
std::cout << "品牌:" << GetName() << "(自研芯片,鸿蒙系统)" << std::endl;
}
};
// -------------------------- 具体实现2:苹果品牌 --------------------------
class Apple : public Brand {
public:
Apple() : Brand("苹果") {}
void ShowBrand() const override {
std::cout << "品牌:" << GetName() << "(A系列芯片,iOS系统)" << std::endl;
}
};
// -------------------------- 2. 抽象部分(Abstraction):产品抽象基类 --------------------------
// 产品接口:持有品牌接口指针(桥接核心),定义抽象逻辑
class Phone {
public:
// 构造函数:传入品牌实例(建立桥接关系)
explicit Phone(std::shared_ptr<Brand> brand) : brand_(std::move(brand)) {}
virtual ~Phone() = default;
virtual void ShowProduct() const = 0; // 纯虚函数:抽象逻辑接口
std::string GetType() const { return type_; }
protected:
std::shared_ptr<Brand> brand_; // 桥接核心:组合实现部分(智能指针管理内存)
std::string type_; // 产品类型
};
// -------------------------- 具体抽象1:普通手机 --------------------------
class NormalPhone : public Phone {
public:
explicit NormalPhone(std::shared_ptr<Brand> brand) : Phone(std::move(brand)) {
type_ = "普通手机";
}
void ShowProduct() const override {
std::cout << "产品类型:" << GetType() << std::endl;
brand_->ShowBrand(); // 调用桥接的实现部分(多态调用)
std::cout << "核心功能:日常通讯、拍照、轻度娱乐" << std::endl << std::endl;
}
};
// -------------------------- 具体抽象2:游戏手机 --------------------------
class GamePhone : public Phone {
public:
explicit GamePhone(std::shared_ptr<Brand> brand) : Phone(std::move(brand)) {
type_ = "游戏手机";
}
void ShowProduct() const override {
std::cout << "产品类型:" << GetType() << std::endl;
brand_->ShowBrand(); // 调用桥接的实现部分(同一抽象逻辑搭配不同实现)
std::cout << "核心功能:高帧率游戏、散热优化、快充" << std::endl << std::endl;
}
};
// -------------------------- 测试代码(客户端) --------------------------
int main() {
// 1. 华为普通手机(抽象:NormalPhone + 实现:Huawei)
std::shared_ptr<Brand> huawei = std::make_shared<Huawei>();
std::unique_ptr<Phone> huawei_normal = std::make_unique<NormalPhone>(huawei);
std::cout << "=== 华为普通手机 ===" << std::endl;
huawei_normal->ShowProduct();
// 2. 苹果游戏手机(抽象:GamePhone + 实现:Apple)
std::shared_ptr<Brand> apple = std::make_shared<Apple>();
std::unique_ptr<Phone> apple_game = std::make_unique<GamePhone>(apple);
std::cout << "=== 苹果游戏手机 ===" << std::endl;
apple_game->ShowProduct();
// 3. 扩展:新增小米品牌(仅扩展实现部分,抽象部分无改动)
class Xiaomi : public Brand {
public:
Xiaomi() : Brand("小米") {}
void ShowBrand() const override {
std::cout << "品牌:" << GetName() << "(骁龙芯片,MIUI系统)" << std::endl;
}
};
std::shared_ptr<Brand> xiaomi = std::make_shared<Xiaomi>();
std::unique_ptr<Phone> xiaomi_game = std::make_unique<GamePhone>(xiaomi);
std::cout << "=== 小米游戏手机 ===" << std::endl;
xiaomi_game->ShowProduct();
// 4. 扩展:新增折叠屏手机(仅扩展抽象部分,实现部分无改动)
class FoldPhone : public Phone {
public:
explicit FoldPhone(std::shared_ptr<Brand> brand) : Phone(std::move(brand)) {
type_ = "折叠屏手机";
}
void ShowProduct() const override {
std::cout << "产品类型:" << GetType() << std::endl;
brand_->ShowBrand();
std::cout << "核心功能:大屏办公、折叠便携、多任务" << std::endl << std::endl;
}
};
std::unique_ptr<Phone> huawei_fold = std::make_unique<FoldPhone>(huawei);
std::cout << "=== 华为折叠屏手机 ===" << std::endl;
huawei_fold->ShowProduct();
return 0;
}
设计原则
1.优先 “组合” 而非 “继承”:通过组合建立桥接,降低耦合;
2.依赖倒置原则:抽象依赖抽象(Phone 依赖 Brand 接口),不依赖具体实现;
3.开闭原则:扩展功能通过新增子类,而非修改原有代码。
桥接模式核心总结(C vs C++)





















 1970
1970

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








