Micro Average vs Macro average
Precision and recall are then defined as:

Recall in this context is also referred to as the true positive rate or sensitivity, and precision is also referred to as positive predictive value (PPV);
other related measures used in classification include true negative rate and accuracy. True negative rate is also called specificity.


Additionally, the predicted positive condition rate (PPCR) identifies the percentage of the total population that is flagged;

Micro-average Method
In Micro-average method, you sum up the individual true positives, false positives, and false negatives of the system for different sets and the apply them to get the statistics.
For example, for a set of data, the system's
True positive (TP1) = 12
False positive (FP1) = 9
False negative (FN1) = 3
Then precision (P1) and recall (R1) will be:
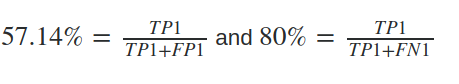
and for a different set of data, the system's
True positive (TP2) = 50
False positive (FP2) = 23
False negative (FN2) = 9
Then precision (P2) and recall (R2) will be 68.49 and 84.75
Now, the average precision and recall of the system using the Micro-average method is
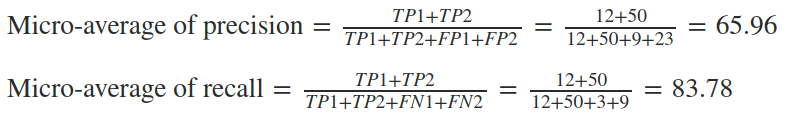
The Micro-average F-Score will be simply the harmonic mean of these two figures.
Macro-average Method
The method is straight forward. Just take the average of the precision and recall of the system on different sets.
For example, the macro-average precision and recall of the system for the given example is:
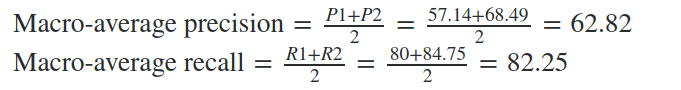
The Macro-average F-Score will be simply the harmonic mean of these two figures.
Suitability Macro-average method can be used when you want to know how the system performs overall across the sets of data.
You should not come up with any specific decision with this average. On the other hand, micro-average can be a useful measure when your dataset varies in size.
1 def precision_recall_f1_score(y_true, y_pred, average=None): 2 """ 3 The precision is the ratio ``tp / (tp + fp)`` where ``tp`` is the number of 4 true positives and ``fp`` the number of false positives. The precision is 5 intuitively the ability of the classifier not to label as positive a sample 6 that is negative. 7 The recall is the ratio ``tp / (tp + fn)`` where ``tp`` is the number of 8 true positives and ``fn`` the number of false negatives. The recall is 9 intuitively the ability of the classifier to find all the positive samples. 10 The F-beta score can be interpreted as a weighted harmonic mean of 11 the precision and recall, where an F-beta score reaches its best 12 value at 1 and worst score at 0. 13 14 :param y_true: 1d array-like, or label indicator array / sparse matrix Ground truth (correct) target values. 15 :param y_pred: 1d array-like, or label indicator array/sparse matrix Estimated targets as returned by a classifier. 16 :param average: [None (default), 'binary', 'micro', 'macro'] 17 :return: precision , recall, f1 18 """ 19 if len(y_true) != len(y_pred): 20 raise ValueError("y_true length is not equal y_pred length") 21 22 if average in ["binary", "micro"]: 23 matched = np.equal(y_pred, y_true).astype(int) 24 precision = np.sum(matched) / len(y_pred) 25 26 if not precision: 27 return 0.0, 0.0, 0.0 28 29 recall = np.sum(matched) / len(y_true) 30 f1 = 2 * precision * recall / (precision + recall) 31 32 return precision, recall, f1 33 34 elif average == "macro" or not average: 35 def judge(_tuple, ele): 36 mol, den = 0, 0 37 for one, two in _tuple: 38 if ele == one == two: 39 mol += 1 40 if ele == one: 41 den += 1 42 43 return mol, den 44 45 # precision 46 precision = 0.0 47 precision_none = dict() 48 pred_true = [(p, t) for p, t in zip(y_pred, y_true)] 49 element = set(y_pred) 50 for e in element: 51 molecular, denominator = judge(pred_true, e) 52 precision += 1/len(element) * (molecular / denominator) 53 precision_none[e] = molecular / denominator 54 55 # recall 56 recall = 0.0 57 recall_none = dict() 58 true_pred = [(t, p) for t, p in zip(y_true, y_pred)] 59 element = set(y_true) 60 for e in element: 61 molecular, denominator = judge(true_pred, e) 62 recall += 1 / len(element) * (molecular / denominator) 63 recall_none[e] = molecular / denominator 64 65 if average == "macro": 66 f = 2 * precision * recall / (precision + recall) 67 return precision, recall, f 68 69 else: 70 precision_ret, recall_ret, f_ret = list(), list(), list() 71 for idx, key in enumerate(set(list(precision_none.keys()) + list(recall_none.keys()))): 72 if key in precision_none.keys(): 73 precision_ret.append(precision_none[key]) 74 else: 75 precision_ret.append(0) 76 77 if key in recall_none.keys(): 78 recall_ret.append(recall_none[key]) 79 else: 80 recall_ret.append(0) 81 82 if not precision_ret[idx] and not recall_none[idx]: 83 f_ret.append(0) 84 else: 85 f_ret.append(2 * precision_ret[idx] * recall_ret[idx] / (precision_ret[idx] + recall_ret[idx])) 86 87 return precision_ret, recall_ret, f_ret 88 else: 89 raise ValueError("average value is error")
1 """ 2 test precision recall f1 3 true = [0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2] 4 pred = [0, 2, 1, 0, 0, 1] 5 # (0.2222222222222222, 0.3333333333333333, 0.26666666666666666) 6 # print(precision_recall_f1_score(true, pred, "macro")) 7 8 # ([0.6666666666666666, 0.0, 0.0], [1.0, 0.0, 0.0], [0.8, 0, 0]) 9 # print(precision_recall_f1_score(true, pred)) 10 11 # (0.33333333333333331, 0.33333333333333331, 0.33333333333333331) 12 # print(precision_recall_f1_score(true, pred, "micro")) 13 """
本文来自于:
Micro Average vs Macro average
感谢 Rahul Reddy Vemireddy!!!







 本文深入探讨了在多分类任务中,微平均与宏平均两种评估方法在精确率、召回率及F1分数计算上的差异。微平均适用于数据集大小不一的情况,通过汇总真阳性、假阳性和假阴性来计算总体性能;而宏平均则简单地取不同类别下精确率和召回率的平均值,用于评估模型在所有类别上的平均表现。
本文深入探讨了在多分类任务中,微平均与宏平均两种评估方法在精确率、召回率及F1分数计算上的差异。微平均适用于数据集大小不一的情况,通过汇总真阳性、假阳性和假阴性来计算总体性能;而宏平均则简单地取不同类别下精确率和召回率的平均值,用于评估模型在所有类别上的平均表现。

















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








