官网demo地址:
这篇讲了如何在地图上添加缓冲图形
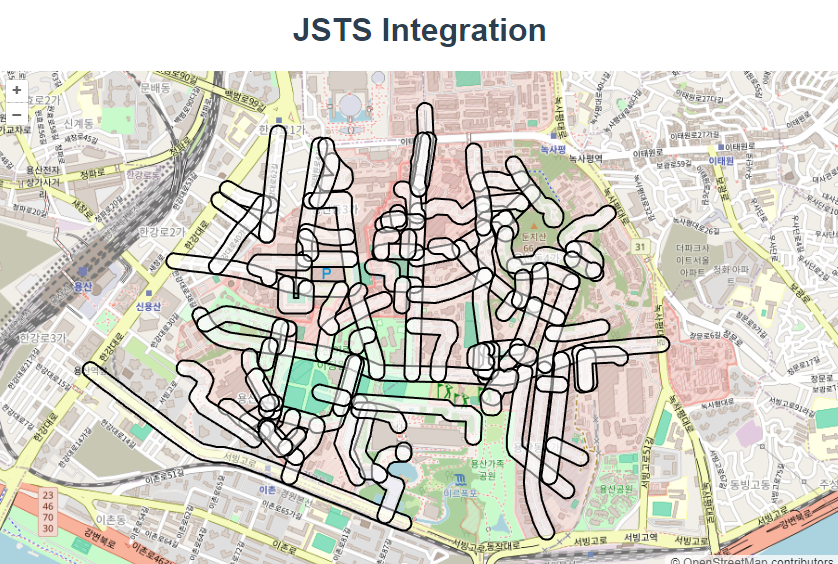
什么叫做缓冲几何?
几何缓冲(Geometric Buffering)是指在 GIS(地理信息系统)和计算几何中,围绕一个几何对象创建一个具有特定距离的区域。这种操作通常用于表示影响区域、保护区、可视范围等。例如,创建一个道路中心线的缓冲区,可以用于表示道路的影响范围。
缓冲几何的具体应用包括:
- 道路缓冲区:表示道路的影响范围,如交通噪音或安全距离。
- 河流缓冲区:用于表示河流两侧的生态保护区或防洪区。
- 设施缓冲区:用于表示设施(如学校、医院、加油站等)的服务范围或安全区。
首先,初始化地图
const rasterLayer = new TileLayer({
source: new OSM(),
});
const map = new Map({
layers: [rasterLayer, vectorLayer],
target: document.getElementById("map"),
view: new View({
center: fromLonLat([126.979293, 37.528787]),




 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 241
241

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








