官网demo地址:
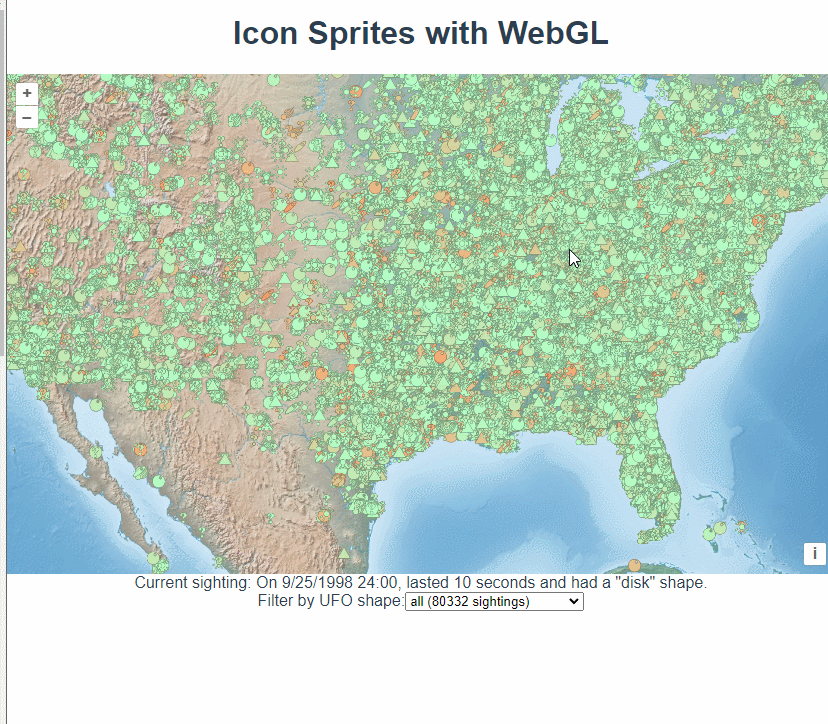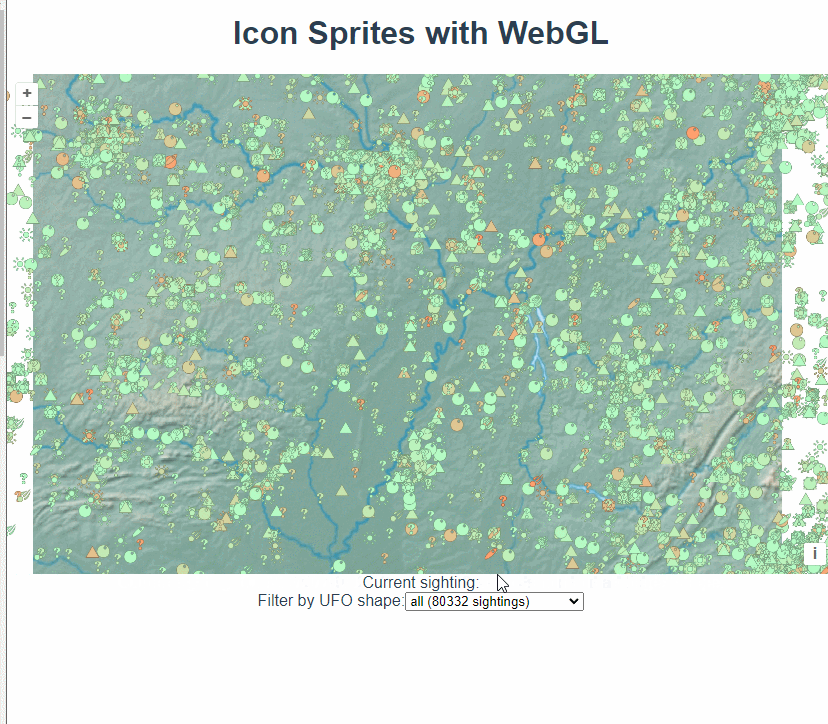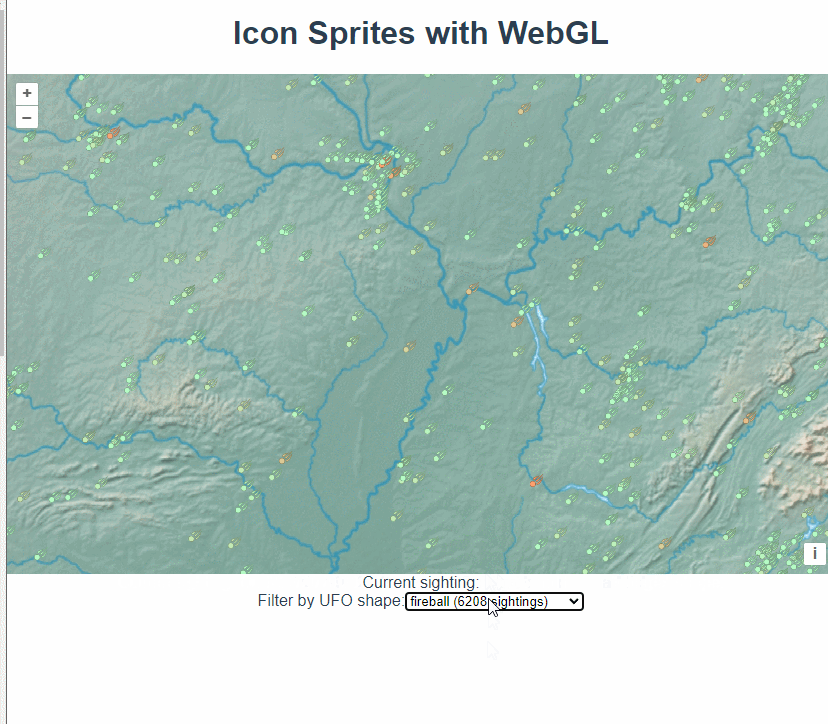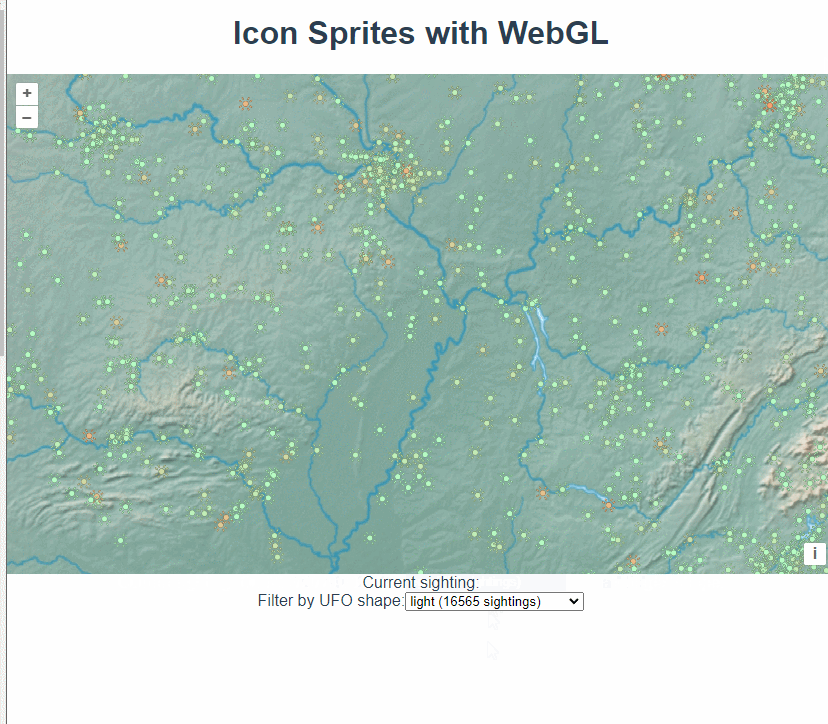
这篇讲的是使用webgl加载海量的数据点。
首先忘地图上添加了底图。
const rasterLayer = new Tile({
source: new OGCMapTile({
url: "https://maps.gnosis.earth/ogcapi/collections/NaturalEarth:raster:HYP_HR_SR_OB_DR/map/tiles/WebMercatorQuad",
crossOrigin: "",
}),
});
const map = new Map({
layers: [rasterLayer],
target: document.getElementById("map"),
view: new View({
center: [0, 4000000],
zoom: 2,
}),
});然后请求一个文件,获取点数据。
const client = new XMLHttpRequest();
client.open(
"GET",
"https://openlayers.org/en/latest/examples/data/csv/ufo_sighting_data.csv"
);
client.addEventListener("load", function () {
const csv = client.responseText;
});
client.send();请求回来的数据是这样的。

所以要对数据进行一些切割处理,最终生成feature
const shapeTypes = {};
const features = [];
let prevIndex = csv.indexOf("\n") + 1;
let curIndex;
while ((curIndex = csv.indexOf("\n", prevIndex)) !== -1) {
const line = csv.substring(prevIndex, curIndex).split(",");
prevIndex = curIndex + 1;
const coords = [parseFloat(line[5]), parseFloat(line[4])];
const shape = line[2];
shapeTypes[shape] = (shapeTypes[shape] || 0) + 1;
features.push(
new Feature({
datetime: line[0],
year: parseInt(/[0-9]{4}/.exec(line[0])[0], 10),
shape: shape,
duration: line[3],
geometry: new Point(fromLonLat(coords)),
})
);
}
shapeTypes["all"] = features.length;




 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 1454
1454

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








