E-Element(在集合中使用,因为集合中存放的是元素)
示例:
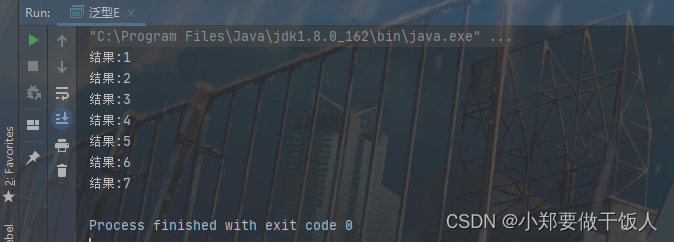
public class 泛型E {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer[] stringArray = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7};
printArray(stringArray);
}
/**
*
*/
public static <E> void printArray(E[] inputArray) {
//输出数组元素
for (E result : inputArray) {
System.out.println("结果:"+ result);
}
}
}
T-Type(Java类)
例一:
public class 泛型T {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("最大值:"+ maximum(3,4,5));
}
public static <T extends Comparable<T>> T maximum(T x, T y, T z) {
//假设x是初始最大值
T max = x;
//y更大
if (y.compareTo(max) > 0) {
max = y;
}
//z更大
if (z.compareTo(max)>0){
max = z;
}
return max;
}
}

例二:
public class 泛型T1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Box<Integer> integerBox = new Box<Integer>();
Integer method = integerBox.method(new Integer(10));
System.out.println(method);
//System.out.println(integerBox.get());
Box<String> stringBox = new Box<String>();
Integer zhangSan = stringBox.method(new String("zhangSan"));
System.out.println(zhangSan);
//System.out.println(stringBox.get());
}
}
class Box<T> {
private T t;
public Integer method(T t){
Integer as = 0;
if (t.equals("zhangSan")){
as = 1;
}
if (t.equals(10)){
as = 2;
}
return as;
}
public void add(T t){
this.t = t;
}
// public void add(T t) {
// this.t = t;
// }
public T get() {
return t;
}
}

例三:
package com.zzx.泛型.T;
/**
* @Author Zhengzx
* @Date 2022/9/8 16:01
* @Title
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class People extends model<People>{
private String phone;
private String address;
public String getPhone() {
return phone;
}
public void setPhone(String phone) {
this.phone = phone;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "People{" +
"phone='" + phone + '\'' +
", address='" + address + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
class model<T>{
private String id;
private String name;
private String age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(String age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
}
class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
People people = new People();
people.setId("11");
people.setName("张三");
people.setAge("23");
people.setPhone("110");
people.setAddress("五道口男子职业技术学院");
System.out.println(people.toString());
}
}

?-类型通配符
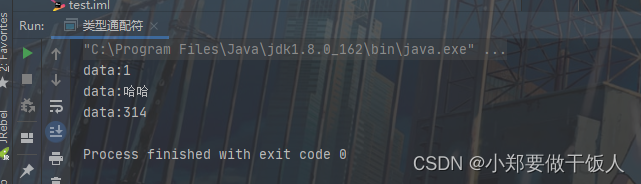
public class 类型通配符 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> integerList = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> stringList = new ArrayList<>();
List<Number> numberList = new ArrayList<>();
integerList.add(1);
stringList.add("哈哈");
numberList.add(314);
getData(integerList);
getData(stringList);
getData(numberList);
}
public static void getData(List<?> data){
System.out.println("data:" + data.get(0));
}
}

























 10万+
10万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










