剑指 Offer 52. 两个链表的第一个公共节点
输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共节点。
如下面的两个链表:
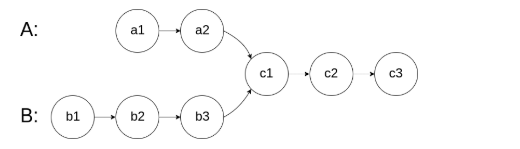
在节点 c1 开始相交。
示例 1:
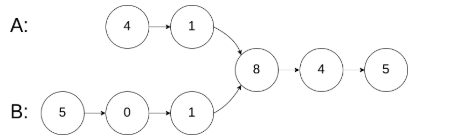
输入: intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
输出: Reference of the node with value = 8
输入解释: 相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个列表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,0,1,8,4,5]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
示例 2:
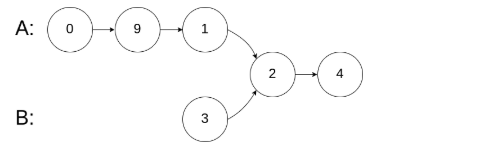
输入: intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
输出: Reference of the node with value = 2
输入解释: 相交节点的值为 2 (注意,如果两个列表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [0,9,1,2,4],链表 B 为 [3,2,4]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 1 个节点。
示例 3:
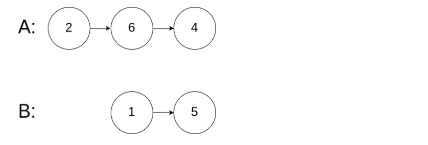
输入: intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
输出: null
输入解释: 从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [2,6,4],链表 B 为 [1,5]。由于这两个链表不相交,所以 intersectVal 必须为 0,而 skipA 和 skipB 可以是任意值。
解释: 这两个链表不相交,因此返回 null。
注意:
如果两个链表没有交点,返回 null.在返回结果后,两个链表仍须保持原有的结构。可假定整个链表结构中没有循环。程序尽量满足 O(n) 时间复杂度,且仅用 O(1) 内存。
本题与主站 160 题相同:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists/
解题思路
- 用两个指针分别从两个链表头部开始扫描,每次分别走一步;
如果指针走到null,则从另一个链表头部开始走;- 当两个指针相同时,
- 如果指针不是
null,则指针位置就是相遇点; - 如果指针是
null,则两个链表不相交;
- 如果指针不是
我还是别偷懒画个图吧,一目了然:
1. 两个链表不相交:
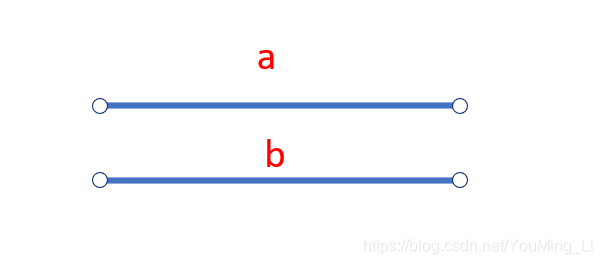
a,b分别代表两个链表的长度,则第一个指针走了a + b步,第二个指针走了b + a步,即两个指针分别走 a+b 步后都变成 null,Java中用“==”判断两个null是否相等会返回true。
2. 两个链表相交:
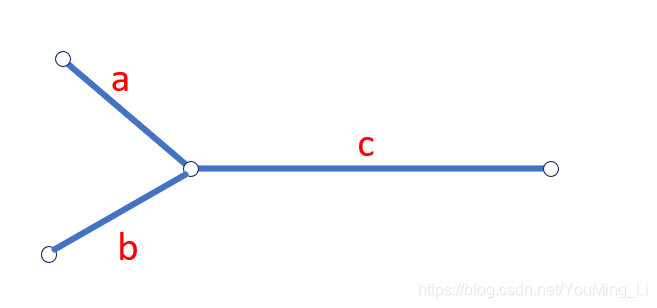
-
a
=
b
a = b
a=b 时,两个指针都走了
a步就相遇了。 -
a
≠
b
a \not= b
a=b 时,第一个指针走了
a + c + b步,第二个指针走了b + c + a步,即两个指针分别走a + b + c步后在两链表交汇处相遇。
时间复杂度: 每个指针走的长度不大于两个链表的总长度,所以时间复杂度是 O ( n ) O(n) O(n)。
Java代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if(headA == null || headB == null) return null;
ListNode cur1 = headA,cur2 = headB;
//cur1走到尽头时,再从headB开始走,cur2走到尽头时,再从headA开始走
//最后cur1和cur2要么在相交点相遇,要么在结尾的null相遇
//两个null用==判断也会返回true
while(cur1 != cur2){
cur1 = cur1 == null ? headB : cur1.next;
cur2 = cur2 == null ? headA : cur2.next;
}
return cur1;
}
}
Go代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func getIntersectionNode(headA, headB *ListNode) *ListNode {
//cur1走到尽头时,再从headB开始走,cur2走到尽头时,再从headA开始走
//最后cur1和cur2要么在相交点相遇,要么在结尾的null相遇
if headA == nil || headB == nil {
return nil
}
cur1,cur2 := headA,headB
for cur1 != cur2 {
if cur1 == nil {
cur1 = headB
} else {
cur1 = cur1.Next
}
if cur2 == nil {
cur2 = headA
} else {
cur2 = cur2.Next
}
}
return cur1
}





 本文介绍了一种高效算法来找到两个链表的第一个公共节点,通过双指针技巧实现O(n)的时间复杂度和O(1)的空间复杂度。
本文介绍了一种高效算法来找到两个链表的第一个公共节点,通过双指针技巧实现O(n)的时间复杂度和O(1)的空间复杂度。
















 713
713










