文章目录
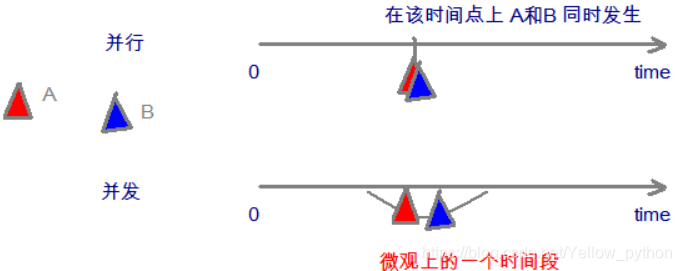
- 并行(parallel):多个事件在同一时刻发生。指在同一时刻,有多条指令在多个处理器上同时执行。
- 并发(concurrency):多个事件在同一个时间段内发生。指在同一个时刻只能有一条指令执行,但多个进程的指令被快速轮换执行,使得在宏观上具有多个进程同时执行的效果。
并发示例:
晚上你和妹子网聊,妹子一直秒回,你就以为妹子只在和你聊天。其实妹子在和很多人聊天,但是切换很快,你感觉不出来。
1、Java多线程入门代码
1.1、Thread
- 继承Thread类
- 重写
public void run(),写入业务逻辑 - 创建对象,
对象.start()来启动线程
class MySleep {
public static void sleep() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
class MyThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
System.out.print(i);
MySleep.sleep();
}
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
(new MyThread()).start();
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
System.out.print(i);
MySleep.sleep();
}
}
}
打印结果
001122334455667788
1.2、Runnable
- 实现Runnable接口
- 实现
public void run(),写入业务逻辑 - 借助Thread对象来
start
class MySleep {
static void sleep() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
class MyThread implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
System.out.print(i);
MySleep.sleep();
}
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t = new Thread(new MyThread());
t.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
System.out.print(i);
MySleep.sleep();
}
}
}
打印结果
001122334455667788
2、源码截取
2.1、Runnable
- 只包含一个抽象方法的接口
public interface Runnable {
public abstract void run();
}
2.2、Thread
- 实现Runnable接口
- 可使用静态方法sleep
- 构造时可传入Runnable实现类的对象
- 实现了Runnable的抽象方法:调用Runnable实现类对象的run方法
- start方法开启一个新线程来执行run方法
public class Thread implements Runnable {
// 静态方法:睡眠(单位:毫秒)
public static native void sleep(long millis) throws InterruptedException;
// 其中1个构造器,可传入Runnable实现类的对象
private Runnable target;
public Thread(Runnable target) {
this.target = target;
}
// 重写Runnable的run方法
@Override
public void run() {
// 执行Runnable实现类对象的run方法
if (target != null) {
target.run();
}
}
// 使线程开始执行
public synchronized void start() {
// 两个线程并发运行:
// 当前线程从start方法的调用返回
// 另一个线程执行其run方法
}
}
3、Thread常用API
Thread t = new Thread();
// toString
System.out.println(t); // Thread[Thread-0,5,main]
// 线程的优先级
System.out.println(t.getPriority()); // 5
// 线程的名字
System.out.println(t.getName()); // Thread-0
// 线程组
System.out.println(t.getThreadGroup()); // java.lang.ThreadGroup[name=main,maxpri=10]
// 线程的标识符
System.out.println(t.getId()); // 12
3.1、sleep
自写sleep,复制用
class Sleep {
public static void sleep(long millisecond) {
try {
Thread.sleep(millisecond);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
随机睡眠
import java.util.Random;
class Sleep {
static void sleep(long millisecond) {
try {
Thread.sleep(millisecond);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
static void sleep() {
sleep(10);
}
static void sleepRandomly(int bound) {
Random random = new Random();
try {
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(bound));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
static void sleepRandomly() {
sleepRandomly(100);
}
}
3.2、join
- 设置最大等待时间,等待当前线程,直至线程死亡或者等待时间结束
- 等待时间设为0则永久等待
class Thread1 extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
sleep(100L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread1 t = new Thread1();
t.start();
t.join(500L);
//t.join(99999L);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
Thread.sleep(100);
System.out.println("----" + i);
}
}
}
4、线程安全
线程锁:使用synchronized来锁定某个公共对象
class Cook extends Thread {
private static int apples = 10; // 苹果总数
private static final Object lock = new Object(); // 锁
private void box(long millis) {
if (millis > 0) {
try {
//System.out.println("准备礼盒,需要一定时间");
sleep(millis);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
box(1000L);
//box(0L);
synchronized (lock) {
if (apples > 0) {
System.out.print(getName() + "出售1个盒装苹果;");
System.out.println("剩余苹果数:" + --apples);
} else {
break;
}
}
}
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cook c1 = new Cook();
Cook c2 = new Cook();
Cook c3 = new Cook();
c1.start();
c2.start();
c3.start();
}
}
class Cook implements Runnable {
private static int apples = 10; // 苹果总数
private void box(long millis) {
if (millis > 0) {
try {
//System.out.println("准备礼盒,需要一定时间");
Thread.sleep(millis);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
box(1000L);
//box(0L);
synchronized (this) {
if (apples > 0) {
System.out.print("出售1个盒装苹果;");
System.out.println("剩余苹果数:" + --apples);
} else {
break;
}
}
}
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cook c = new Cook();
Thread t1 = new Thread(c);
Thread t2 = new Thread(c);
Thread t3 = new Thread(c);
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
}
synchronized可以写到方法名的前面
非静态方法被锁的是this
静态方法被锁的是当前类.class
class Cook implements Runnable {
private static int apples = 10; // 苹果总数
private void box(long millis) {
if (millis > 0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(millis);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (apples > 0) {
box(1000L);
//box(0L);
sell();
}
}
private synchronized void sell() {
if (apples > 0) {
String name = Thread.currentThread().toString();
System.out.print(name + "出售1个盒装苹果;");
System.out.println("剩余苹果数:" + --apples);
}
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cook c = new Cook();
Thread t1 = new Thread(c);
Thread t2 = new Thread(c);
Thread t3 = new Thread(c);
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
}
5、单例设计模式
1、事先创建好一个单例对象
class Singleton {
public static final Singleton SINGLETON = new Singleton();
private Singleton() {}
}
2、需要时才创建单例对象
class Singleton {
private static Singleton instance;
private Singleton() {}
public static Singleton getInstance() {
if (instance == null) {
instance = new Singleton();
}
return instance;
}
}
3、多线程情况下,会有安全问题
class Sleep {
public static void sleep(long millisecond) {
try {
Thread.sleep(millisecond);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
class Singleton {
private static Singleton instance;
private Singleton() {
}
public static Singleton getInstance() {
if (instance == null) {
Sleep.sleep(1000);
instance = new Singleton();
}
return instance;
}
}
public class Hello {
private static Singleton s1;
private static Singleton s2;
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
// 内部类
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> s1 = Singleton.getInstance());
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> s2 = Singleton.getInstance());
t1.start();
t2.start();
t1.join();
t2.join();
System.out.println(s1 == s2); // false
}
}
4、加上synchronized
class Sleep {
public static void sleep(long millisecond) {
try {
Thread.sleep(millisecond);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
class Singleton {
private static Singleton instance;
private Singleton() {
}
synchronized public static Singleton getInstance() {
Sleep.sleep(5000); // 假设需要一系列准备工作
if (instance == null) {
Sleep.sleep(1000); // 假设造一个实例出来要较长时间
instance = new Singleton();
}
return instance;
}
}
public class Hello {
private static Singleton s1;
private static Singleton s2;
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
// 内部类
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> s1 = Singleton.getInstance());
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> s2 = Singleton.getInstance());
t1.start();
t2.start();
t1.join();
t2.join();
System.out.println(s1 == s2); // true(跑了12秒)
}
}
5、缩小线程锁范围,提高效率
class Sleep {
public static void sleep(long millisecond) {
try {
Thread.sleep(millisecond);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
class Singleton {
private static Singleton instance;
private Singleton() {
}
public static Singleton getInstance() {
Sleep.sleep(5000); // 假设需要一系列准备工作
if (instance == null) {
synchronized (Singleton.class) {
if (instance == null) {
Sleep.sleep(1000); // 假设造一个实例出来要较长时间
instance = new Singleton();
}
}
}
return instance;
}
}
public class Hello {
private static Singleton s1;
private static Singleton s2;
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
// 内部类
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> s1 = Singleton.getInstance());
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> s2 = Singleton.getInstance());
t1.start();
t2.start();
t1.join();
t2.join();
System.out.println(s1 == s2); // true(跑了6秒)
}
}
6、使用内部类
class Singleton {
private Singleton() {}
private static class Inner {
public static final Singleton INSTANCE = new Singleton();
}
public static Singleton getInstance() {
return Inner.INSTANCE;
}
}
6、死锁
至少2个锁
class Merchant implements Runnable {
private Object goods;
private Object money;
Merchant(Object goods, Object money) {
this.goods = goods;
this.money = money;
}
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (goods) {
System.out.println("商家说:先给钱");
synchronized (money) {
System.out.println("商家发货");
}
}
}
}
class Customer implements Runnable {
private Object goods;
private Object money;
Customer(Object goods, Object money) {
this.goods = goods;
this.money = money;
}
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (money) {
System.out.println("顾客说:先发货");
synchronized (goods) {
System.out.println("顾客给钱");
}
}
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object g = new Object();
Object m = new Object();
Merchant s = new Merchant(g, m);
Customer c = new Customer(g, m);
new Thread(s).start();
new Thread(c).start();
}
}
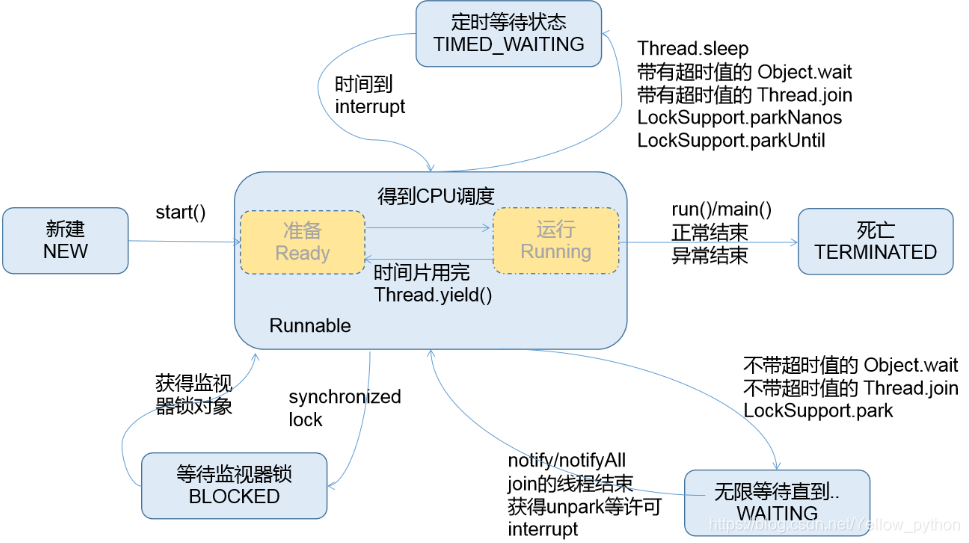
7、Java线程声明周期
public enum State {
NEW,
RUNNABLE,
BLOCKED,
WAITING,
TIMED_WAITING,
TERMINATED;
}
java.lang.Thread.State
8、线程间通信(wait和notify):生产者和消费者
单个生产者和单个消费者
import java.util.Random;
class Sleep {
static void sleepRandomly() {
Random random = new Random();
try {
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(100));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
// 消息队列
class MessageQueue {
// 容量
private int capacity = 10;
// 出队
synchronized void dequeue() {
// wait和notify要写在同步代码块中,其调用的对象是锁对象
if (capacity <= 0) {
System.out.println("====队列空了,等入队====");
try {
// 当前线程进入等待状态,等待其它线程唤醒
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("出队,剩余量:" + --capacity);
// 随机唤醒一个线程
this.notify();
}
// 入队
synchronized void enqueue() {
if (capacity >= 10) {
System.out.println("----队列满了,等出队----");
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("入队,剩余量:" + ++capacity);
this.notify();
}
}
class Producer extends Thread {
private MessageQueue mq;
Producer(MessageQueue mq) {
this.mq = mq;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
Sleep.sleepRandomly();
mq.enqueue();
}
}
}
class Consumer extends Thread {
private MessageQueue mq;
Consumer(MessageQueue mq) {
this.mq = mq;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
Sleep.sleepRandomly();
mq.dequeue();
}
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MessageQueue mq = new MessageQueue();
Producer producer = new Producer(mq);
Consumer consumer = new Consumer(mq);
producer.start();
consumer.start();
}
}
多个生产者和多个消费者:notifyAll
import java.util.Random;
class Sleep {
static void sleep(long millisecond) {
try {
Thread.sleep(millisecond);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
static void sleepRandomly(int bound) {
Random random = new Random();
try {
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(bound));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
static void sleepRandomly() {
sleepRandomly(200);
}
}
// 消息队列
class MessageQueue {
// 容量
private int capacity;
private int maxCapacity;
MessageQueue(int capacity, int maxCapacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
this.maxCapacity = maxCapacity;
}
// 出队
synchronized void dequeue(String name) {
while (capacity <= 0) {
System.out.println("========队列空了,等生产========");
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println(name + "消费1个,剩余量:" + --capacity);
// 唤醒其它所有线程
this.notifyAll();
}
// 入队
synchronized void enqueue(String name) {
while (capacity >= maxCapacity) {
System.out.println("--------队列满了,等消费--------");
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println(name + "生产1个,剩余量:" + ++capacity);
this.notifyAll();
}
}
class Producer extends Thread {
private MessageQueue mq;
Producer(MessageQueue mq) {
System.out.println("生产者名称:" + getName());
this.mq = mq;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
Sleep.sleepRandomly();
mq.enqueue(getName());
}
}
}
class Consumer extends Thread {
private MessageQueue mq;
Consumer(MessageQueue mq) {
System.out.println("消费者名称:" + getName());
this.mq = mq;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
Sleep.sleepRandomly();
mq.dequeue(getName());
}
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MessageQueue mq = new MessageQueue(2, 4);
new Producer(mq).start();
new Producer(mq).start();
new Consumer(mq).start();
new Consumer(mq).start();
}
}





 本文深入探讨Java多线程的基础知识,包括线程创建、线程安全、生命周期、线程间通信等内容,并通过实例讲解如何避免死锁及实现高效的线程通信。
本文深入探讨Java多线程的基础知识,包括线程创建、线程安全、生命周期、线程间通信等内容,并通过实例讲解如何避免死锁及实现高效的线程通信。

















 3万+
3万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










