文章目录
成员变量
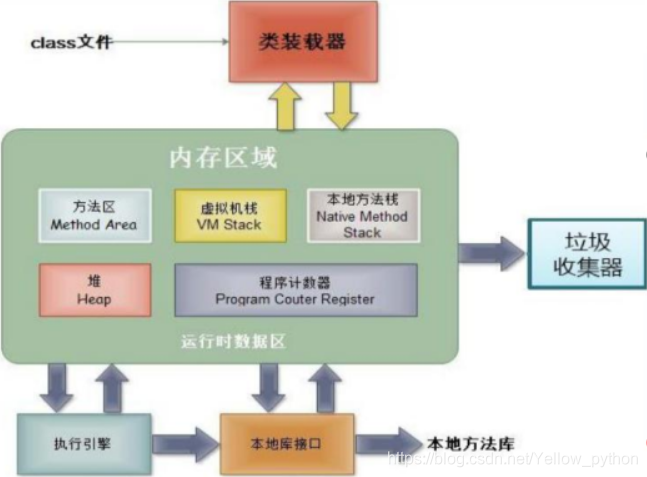
成员变量的内存图
| 区域名称 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| 程序计数器 | 程序计数器是CPU中的寄存器,它包含每一个线程下一条要执行的指令的地址 |
| 本地方法栈 | 当程序中调用了native的本地方法时,本地方法执行期间的内存区域 |
| 方法区 | 存储已被虚拟机加载的类信息、常量、静态变量、即时编译器编译后的代码等数据。 |
| 堆内存 | 存储对象(包括数组对象),new出来的那些 |
| 虚拟机栈 | 存储正在执行的每个Java方法的局部变量表等。局部变量表存放了编译期可知长度的各种基本数据类型、对象引用,方法执行完,自动释放 |
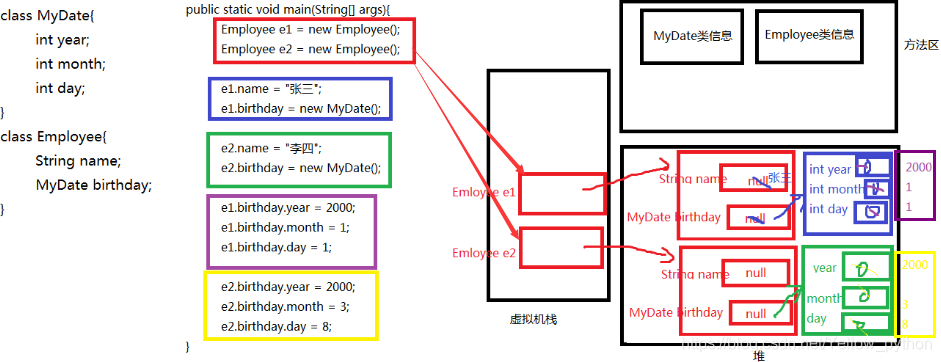
class MyDate{
int year;
int month;
int day;
}
class Employee{
String name;
MyDate birthday;
}
public class Hello{
public static void main(String[] args){
//创建两个员工对象
Employee e1 = new Employee();
Employee e2 = new Employee();
//为两个员工对象的成员变量赋值
e1.name = "张三";
e1.birthday = new MyDate();
e2.name = "李四";
e2.birthday = new MyDate();
e1.birthday.year = 2000;
e1.birthday.month = 1;
e1.birthday.day = 1;
e2.birthday.year = 2000;
e2.birthday.month = 3;
e2.birthday.day = 8;
}
}
上面代码的内存图
构造方法、方法重载、方法重写、继承、多态
- 构造方法:constructor
- 方法重载:overload
- 方法重写:override
- 继承:extends(extend的第三人称单数形式)
- 多态:polymorphic
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建对象
Dogface d = new Dogface("小兵");
Hero h = new Hero("先知", 200, 15, 15);
// 互相攻击
d.attack(h); // 多态
h.attack(d); // 本态
// 打印现有血量
System.out.println(d.name + "现有血量为:" + d.hp); // 小兵现有血量为:70
System.out.println(h.name + "现有血量为:" + h.hp); // 先知现有血量为:190
}
}
class Dogface {
// 类里面的变量(下面3个是普通成员变量)
String name;
int hp = 100;
int ad = 10;
// 构造器(类似Python的__init__)
Dogface(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
// 构造器重载(overload)
Dogface(String name, int hp, int ad) {
this.name = name;
this.hp = hp;
this.ad = ad;
}
// 方法(method,类似Python的函数)
public void attack(Dogface other) {
other.hp -= ad;
}
}
// 继承(extends)
class Hero extends Dogface {
int ap = 0;
Hero(String name, int hp, int ad, int ap) {
super(name, hp, ad); // 继承父类特性
this.ap = ap; // 子类新特性
}
// 重写方法(override,关键词可写可不写,建议写)
@Override
public void attack(Dogface other) {
super.attack(other); // 调用父类方法
other.hp -= ap;
}
}
代码块
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new A();
new A();
}
}
class A {
{
System.out.println("代码块");
}
static {
System.out.println("静态代码块");
}
}
打印结果
静态代码块
代码块
代码块
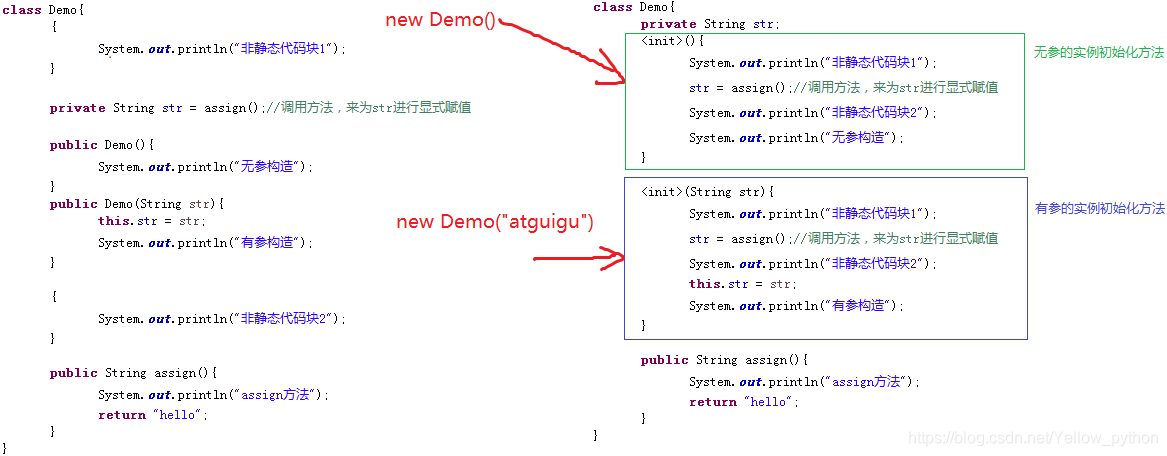
对象初始化
实例化初始化方法
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new A();
}
}
class A {
{
System.out.println("1、代码块");
}
private int a = setA();
A() {
System.out.println("2、构造方法");
}
public int setA() {
System.out.println("3、赋值");
return 1;
}
{
System.out.println("4、代码块");
}
}
/*
打印结果
1、代码块
3、赋值
4、代码块
2、构造方法
*/
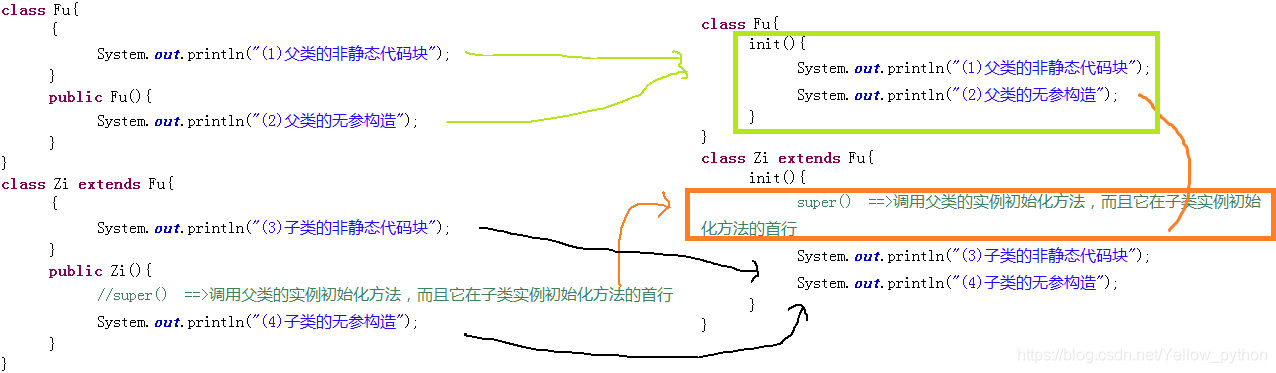
父子类实例化初始化方法
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new B();
}
}
class A {
{
System.out.println("1、A代码块");
}
private int a = setA();
A() {
System.out.println("2、A构造方法");
}
public int setA() {
System.out.println("3、A赋值");
return 1;
}
}
class B extends A {
{
System.out.println("4、B代码块");
}
private int b = setB();
B() {
System.out.println("5、B构造方法");
}
public int setB() {
System.out.println("6、B赋值");
return 2;
}
}
/*
打印结果
1、A代码块
3、A赋值
2、A构造方法
4、B代码块
6、B赋值
5、B构造方法
*/
类初始化
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new A();
}
}
class A {
{
System.out.println("1、代码块");
}
static {
System.out.println("2、静态代码块");
}
private int a = setA();
private static int b = 2;
A() {
System.out.println("3、构造方法,打印a值:" + a);
}
public int setA() {
System.out.println("4、a现值" + a);
return b;
}
}
/*
打印结果
2、静态代码块
1、代码块
4、a现值0
3、构造方法,打印a值:2
*/
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new B();
}
}
class A {
{
System.out.println("1、A代码块");
}
int a = setA();
static {
System.out.println("2、A静态代码块");
}
A() {
System.out.println("3、A构造方法,并打印a:" + a);
}
public int setA() {
System.out.println("4、A的a赋值前:" + a);
return 1;
}
}
class B extends A {
{
System.out.println("5、B代码块");
}
int b = setB();
static {
System.out.println("6、B静态代码块");
}
B() {
System.out.println("7、B构造方法,并打印a值:" + a + "和b值:" + b);
}
public int setB() {
System.out.println("8、B的b赋值前" + b);
return 2;
}
}
/*
打印结果
2、A静态代码块
6、B静态代码块
1、A代码块
4、A的a赋值前:0
3、A构造方法,并打印a:1
5、B代码块
8、B的b赋值前0
7、B构造方法,并打印a值:1和b值:2
*/
封装
packaging
| 修饰符 | 本类 | 本包 | 其他包子类 | 其他包非子类 | 其他模块 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| private | √ | × | × | × | × |
| 缺省 | √ | √ | × | × | × |
| protected | √ | √ | √ | × | × |
| public | √ | √ | √ | √ | 默认不可以,可以建立依赖 |
| 名称 | 修饰允许 |
|---|---|
| 外部类 | public和缺省 |
| 成员变量 | public,protected,缺省,private |
| 成员方法 | public,protected,缺省,private |
| 构造器 | public,protected,缺省,private |
JavaBean:Java语言编写类的一种标准规范
- 类必须是具体的和公共的
- 具有无参数的构造方法
- 成员变量私有化,并提供用来操作成员变量的
set和get方法
public class ClassName{
//成员变量
//构造方法
//无参构造方法【必须】
//有参构造方法【建议】
//getXxx()
//setXxx()
//其他成员方法
}
public class Student {
// 成员变量
private String name;
private int age;
// 构造方法
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
// get/set成员方法
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
//其他成员方法列表
public String getInfo(){
return "姓名:" + name + ",年龄:" + age;
}
}
类型转换
数据类型转换
double i2f = 2; //自动类型转换
int f2i = (int)2.3; //强制类型转换
System.out.println(i2f); // 2.0
System.out.println(f2i); // 2
引用数据类型转换
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建对象
Animal a = new Animal();
Cat c = new Cat();
// 向上转型(upcasting):子类 -> 父类(猫 -> 动物)
Animal c2a = c;
c2a.eat(); // 吃鱼
//c2a.attack(); // 没有这个方法
// 向下转型(downcasting):父类 -> 子类(动物 -> 猫)
Cat a2c = (Cat) c2a;
a2c.eat(); // 吃鱼
a2c.attack(); // 喵喵拳
// 编译通过,但运行报错
//Cat c2 = (Cat) a; // ClassCastException
}
}
class Animal {
public void eat() {
System.out.println("吃");
}
}
class Cat extends Animal {
public void eat() {
System.out.println("吃鱼");
}
public void attack() {
System.out.println("喵喵拳");
}
}
判断实例是否属于某类(instance of)
instance of(类似Python的is instance)
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建对象
Animal a = new Animal();
Cat c = new Cat();
// 猫属于动物
System.out.println(a instanceof Animal); // true
System.out.println(a instanceof Cat); // false
System.out.println(c instanceof Animal); // true
System.out.println(c instanceof Cat); // true
}
}
class Animal {}
class Cat extends Animal {}
修饰符
静态(static):类方法、静态属性、静态代码块
static(类似Python的@classmethod)
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cat.attack();
}
}
class Cat {
static void attack() {
System.out.print("喵爪");
}
}
静态方法没有多态,也没有重写
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal a = new Cat();
a.attack(); // 打印【攻击】而不是【喵爪】
}
}
abstract class Animal {
static void attack() {
System.out.print("攻击");
}
}
class Cat extends Animal{
static void attack() {
System.out.print("喵爪");
}
}
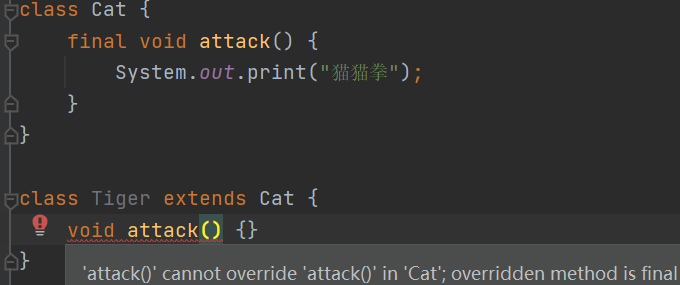
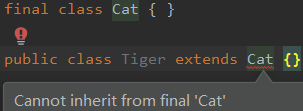
最终(final)
子类不能重写父类的最终方法
子类不能继承final类
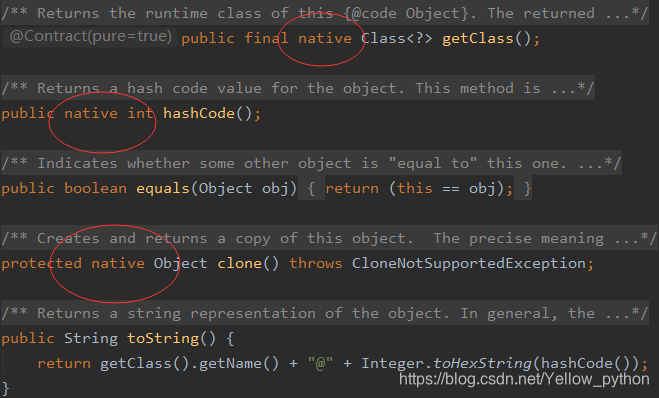
原生的(native)
- 只能修饰方法
- 表示这个方法的方法体代码不是用Java语言实现的,而是由C/C++语言编写的。
- 但是对于Java程序员来说,可以当做Java的方法一样去正常调用它,或者子类重写它。
一些源码
抽象(abstract):抽象方法、抽象类
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Graph[] g = new Graph[2];
g[1] = new Circle(1.0);
System.out.println(g[1].Area());
}
}
// 抽象类
abstract class Graph {
// 抽象方法,抽象方法必须在抽象类中,没有方法体
abstract double Area();
}
class Circle extends Graph {
double radius;
Circle(double radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
@Override
double Area() {
return Math.PI * radius * radius;
}
}
接口(interface):比抽象类更抽象
IDE可以创建接口
// 接口:翅膀
public interface Wing {
// 默认的【public、abstract】可省略
public abstract void fly();
// default修饰的方法,有方法体,由实现类的对象来调用
public default void lay() {
System.out.println("default方法:下蛋");
}
// static修饰的方法,有方法体;调用方法:Wing.information()
public static void information() {
System.out.println("static方法:翅膀");
}
}
// 抽象类:动物
abstract class Animal {
private String name;
Animal(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "名字:" + this.name;
}
}
// 鸟类:继承1个抽象类,实现n个接口
class Bird extends Animal implements Wing {
Bird(String name) {
super(name);
}
@Override
public void fly() {
System.out.println("implement方法:树上飞");
}
}
// 运行,打印
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Bird b = new Bird("鹏");
System.out.println(b); // 名字:鹏
b.fly(); // implement方法:树上飞
b.lay(); // default方法:下蛋
Wing.information(); // static方法:翅膀
}
}
枚举(enumerate)
IDE可以创建枚举
public enum Gender {
BOY("男"), GIRL("女");
private String str;
Gender(String str) { this.str = str; }
@Override
public String toString() { return str; }
}
// 打印
System.out.println(Gender.BOY); // 男
System.out.println(Gender.GIRL); // 女
// 遍历
for (Gender g : Gender.values()) { System.out.print(g); } // 男女
内部类
// 外部类:外部类里面有内部类
public class Outer{
// 成员内部类
class Inner {}
// 静态成员内部类
static class staticInner {}
public void myMethod() {
// 局部内部类
class localInner {}
}
}
成员内部类
// 心脏
interface Heart {
void beat();
}
// 青蛙
public class Frog {
String name;
boolean live;
private Heart heart = new FrogHeart();
Frog(String name, boolean live) {
this.name = name;
this.live = live;
}
private class FrogHeart implements Heart {
@Override
public void beat() {
System.out.print(name);
// 直接访问外部类成员
if (live) {
System.out.println("心脏在跳动");
} else {
System.out.println("心脏不跳了");
}
}
}
public Heart getHeart() {
System.out.println("取出" + name + "心脏");
return heart;
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Frog f1 = new Frog("青蛙1号", true);
Heart b1 = f1.getHeart();
b1.beat();
Frog f2 = new Frog("青蛙2号", false);
Heart b2 = f2.getHeart();
b2.beat();
}
}
打印结果
取出青蛙1号心脏
青蛙1号心脏在跳动
取出青蛙2号心脏
青蛙2号心脏不跳了
局部内部类
// 接口(将会被局部内部类实现)
interface Shoot {
void shoot(String bullet);
}
// Hello是外部类
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 局部内部类(有名)
class Gun implements Shoot {
@Override
public void shoot(String bullet) {
System.out.println("射" + bullet);
}
}
(new Gun()).shoot("箭");
// 局部内部类(匿名)
(new Shoot() {
@Override
public void shoot(String bullet) {
System.out.println("射" + bullet);
}
}).shoot("枪");
// 接口参数,必须传入接口的实现类对象
shoot((new Shoot() {
@Override
public void shoot(String bullet) {
System.out.println("射" + bullet);
}
}), "水");
// IDE优化
shoot((bullet -> System.out.println("射" + bullet)), "水");
}
// 方法的参数要求:传入接口的实现类对象
private static void shoot(Shoot s, String bullet) {
s.shoot(bullet);
}
}
/*
打印结果
射箭
射枪
射水
射水
*/
根父类(Object)
其它类的父类
import java.util.Objects;
class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object[] a = new Object[2];
a[0] = new Object();
a[1] = new Hero("剑圣", 6);
for (Object o : a) {
// toString
System.out.println(o);
// hashCode
System.out.println(o.hashCode());
// getClass
System.out.println(o.getClass());
// equals
System.out.println(o.equals(new Hero("剑圣", 6)));
System.out.println("-------------------------------------");
}
// finalize
System.gc();
}
}
class Hero {
String name;
int lv;
Hero(String name, int lv) {
this.name = name;
this.lv = lv;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Hero:name=" + name;
}
@Override
protected void finalize() {
System.out.println("__del__");
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Hero hero = (Hero) o;
return lv == hero.lv && Objects.equals(name, hero.name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, lv);
}
}
/*
打印结果
java.lang.Object@677327b6
1735600054
class java.lang.Object
false
-------------------------------------
Hero:name=剑圣
20943637
class agu.com.hell0.Hero
true
-------------------------------------
__del__
__del__
*/
| python | str | class | del | hash | eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| java | toString | getClass | finalize | hashCode | equals |
class Hero:
def __init__(self, name, lv=1):
self.name = name
self.lv = lv
def __str__(self):
return 'toString:' + self.name
def __del__(self):
print('finalize')
def __hash__(self):
return hash(self.name)
def __eq__(self, other):
return (self is other) and \
(self.__class__ == other.__class__) and \
(hash(self) == hash(other)) and \
(self.name == other.name)
h = Hero('剑圣')
print(h)
# toString:剑圣
print(hash(h), hash(h.name) == hash(h))
# 445903300893569928 True
print(h == Hero('剑圣', 6))
# finalize
# True
# finalize
包装类
用包装类来包装基本数据类型,方便用API
| 基本数据类型 | 包装类(java.lang包) | 缓存对象 |
|---|---|---|
| byte | Byte | -128~127 |
| short | Short | -128~127 |
| int | Integer | -128~127 |
| long | Long | -128~127 |
| float | Float | 没有 |
| double | Double | 没有 |
| char | Character | 0~127 |
| boolean | Boolean | true和false |
| void | Void |
装箱、拆箱
- 装箱:把基本数据类型转为包装类对象
- 拆箱:把包装类对象拆为基本数据类型
int i = 99;
String s = "100";
// int -> Integer
Integer integer2 = i; // 自动装箱
// Integer -> i
int v1 = integer; // 自动拆箱
// String -> Integer
Integer s1 = Integer.valueOf(s);
// String -> int
int si = Integer.parseInt(s);
// int -> String
String is1 = Integer.toString(i);
String is2 = "" + i;
// Integer -> String
String is3 = integer.toString();
String is4 = "" + integer;
缓存对象
Integer i = 1;
Integer j = 1;
System.out.println(i == j);//true
Integer i = 128;
Integer j = 128;
System.out.println(i == j);//false
Integer i = new Integer(1);//新new的在堆中
Integer j = 1;//这个用的是缓冲的常量对象,在方法区
System.out.println(i == j);//false
Integer i = new Integer(1);//新new的在堆中
Integer j = new Integer(1);//另一个新new的在堆中
System.out.println(i == j);//false
注解(annotation)
系统预定义的常用注解
-
检测被修饰的方法为有效的重写方法,如果不是,则报编译错误
只能标记在 方法上
它会被编译器程序读取 -
抑制编译警告
可用于修饰 类、属性、方法、构造、局部变量、参数
它会被编译器程序读取 -
表示
反对使用
可用于修饰 属性、方法、构造、类、包、局部变量、参数
它会被编译器程序读取
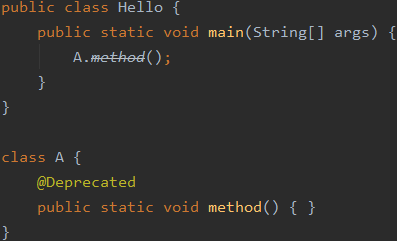
@Override
@SuppressWarnings
@Deprecated
自写注解
| 元注解 | 说明 | 例如 |
|---|---|---|
@Target | 描述注解的使用范围 | TYPE、FIELD、METHOD、CONSTRUCTOR、PACKAGE… |
@Retention | 描述注解的生命周期 | SOURCE(源代码)、CLASS(字节码)、RUNTIME(运行时) |
@Documented | 该被javadoc工具记录 | |
@Inherited | 允许子类继承父类中 |
IDE可以创建
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface Table {
String value();
}
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface Column {
String name();
String type();
}
@Table("t_user")
class User {
@Column(name = "identification", type = "int")
private String id;
@Column(name = "username", type = "varchar(20)")
private String name;
@Column(name = "password", type = "char(6)")
private String pwd;
}
附录
| en | 🔉 | cn |
|---|---|---|
| native | ˈneɪtɪv | adj. 本地出生的;天生的;土著的;天然的;n. 本地人; |
| bean | /biːn/ | n. 豆;嘴峰;毫无价值的东西;vt. 击…的头部 |
| construct | /kənˈstrʌkt/ | v. 建造;n. 构想 |
| constructor | /kənˈstrʌktər/ | n. 构造函数 |
| overload | /ˌoʊvərˈloʊd/ | v. (使)过载,超载;(使)负担过重;(使)电力系统超负荷;n. 超载量 |
| override | /ˌoʊvərˈraɪd/ | vt. 推翻;不顾;践踏;n. 代理佣金 |
| extend | /ɪkˈstend/ | v 延伸 |
| polymorphic | /pɑlɪ’mɔrfɪk/ | adj. [生物] 多态的;[生物] 多形的;多形态的; |
| retention | rɪˈtenʃn | n. 保留;滞留;记忆力 |
| annotation | ˌænəˈteɪʃn | n. 注释;注解 |
| protected | prəˈtektɪd | adj. 受保护的 |
| inherit | ɪnˈherɪt | vt. 继承 |
-Xms | 初始堆内存大小 | |
-Xmx | 最大堆内存大小 |






















 143
143

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










