Java基础
基础介绍
JAVA_SE 、EE、ME 三者的区别
Java SE(Java Platform,Standard Edition),应该先说这个,因为这个是标准版本。
Java EE (Java Platform,Enterprise Edition),java 的企业版本,做大型企业服务的。
Java ME(Java Platform,Micro Edition),java的微型版本,做嵌入式,硬件设备的。
注:运行Java程序,需要安装JDK——标准库,JRE——运行环境
基础语法
数据类型使用
整数类型:byte,short,int,long
浮点类型:float,double
字符型:char
布尔型:true,false
引用数据类型:类(class),接口(interface),数组
public static void main(String[] args) {}
Java程序入口
System.out.println(“Hello world”);
字符串末尾加了换行字符\n的打印方法
System.out.print(“Hello world”);
字符串末尾没加换行字符\n的打印方法
float f = (float)0.1;
float f1 = 0.1f;
float类型在Java中定义的都默认是double类型,所以需要转译
f就是区别double类型
char sex= ‘男’;
字符类型定义
String name = “张三”;
字符串类型定义
System.out.println(“a=”+a+" b="+b+" c="+c);
打印多个数据
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello world");
int a;
a = 10;
int b;
b = 20;
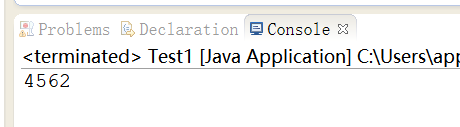
int c = a+b;
System.out.println("a="+a);
System.out.println("b="+b);
System.out.println("c="+c);
System.out.println("a="+a+" b="+b+" c="+c);
System.out.println(a+"+"+b+"="+c);
float f = (float)0.1;
float f1 = 0.1f;
double d = 0.2;
System.out.println("f="+f);
System.out.println("f1="+f1);
System.out.println("d="+d);
String name;
name = "张三";
char sex= '男';
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(sex);
}
}
数据类型相互转换
byte->short->int->long->float->double
char->int->long->float->double
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char i = 97;
System.out.println(i);
}
}
执行结果:

字符串转换为整数
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "123";
int str1 = Integer.parseInt(str);
System.out.println(str1+2);
}
}
执行结果:

整数转换为字符串
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 456;
System.out.println(i + "" +2);
}
}
执行结果:
转译字符 \
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("姓名:\"木易\" \\");
}
}
执行结果:

java中的关键字
abstract ; boolean ; break ; byte ; case ; catch ; char ; class ; continue ; default ; do ; double ; else ; extend ; false ; final ; finally ; float ; for ; if ; implement ; import ; instanceof ; int ; interface ; long ; native ; new ; null ; package ; private ; protected ; public ; return ; short ; static ; synchronized ; super ; this ; throw ; throws ; transient ; true ; try ; void ; volatile ; while ;
字符串的对比
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "abc";
String s2 = new String("abc");
System.out.println(s1 == s2);
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));
}
}
执行结果:

位移运算
1.左移运算<< 左移右移都是移动二进制数
0000-0000 0000-0000 0000-0000 0000-1100 =12 向左移动一位变为(右边缺几位就补几个0)
0000-0000 0000-0000 0000-0000 0001 1000 =24 再向左移一位
0000-0000 0000-0000 0000-0000 0011 0000 =48
由此,我们可以得到,其实m向左移n位后,m=m*2^n;即每向左移一位,该数就会增到一倍。
2.右移运算>> 右移运算和左移运算类似,但是也有一个区别。
0000-0000 0000-0000 0000-0000 0000-1100 =12 向右移一位
0000-0000 0000-0000 0000-0000 0000-0110 =6再向右移一位
0000-0000 0000-0000 0000-0000 0000-0011 =3再向右移动一位
0000-0000 0000-0000 0000-0000 0000-0001 =1
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 12;
i = i << 1;
System.out.println(i);
}
}
执行结果:

异或运算
思路:
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
System.out.println("a="+a+"-------b="+b);
a = a+b;
b = a-b;
a = a-b;
System.out.println("a="+a+"-------b="+b);
}
}
加异或运算符:
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
System.out.println("a="+a+"-------b="+b);
a = a^b;
b = a^b;
a = a^b;
System.out.println("a="+a+"-------b="+b);
}
}
执行结果:

三目运算符
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int score = 70;
String result = (score >= 60)?"及格":"不及格";
System.out.println(result);
}
}
执行结果:

基本的优先级需要记住:
单目乘除为关系,逻辑三目后赋值。
单目:单目运算符+ –(负数) ++ – 等
乘除:算数单目运算符* / % + -
为:位移单目运算符<< >>
关系:关系单目运算符> < >= <= == !=
逻辑:逻辑单目运算符&& || & | ^
三目:三目单目运算符A > B ? X : Y
后:无意义,仅仅为了凑字数
赋值:赋值=
流程控制
if,else if,else条件选择语句
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int score = 90;
if(score >= 90){
System.out.println("优秀!");
}else if(score >= 70 && score <90){
System.out.println("良好!");
}else if(score >= 60 && score <70){
System.out.println("及格!");
}else{
System.out.println("不及格!");
}
}
}
执行结果:

switch,case分支语句
switch语句 , java的分支结构语句:
switch (支持的判断类型变量) {
case “值1”:
语句1;
break;
case “值2”:
语句2;
break;
…
default:
语句;
break;
}
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char sex ='女';
switch(sex){
case '男':
System.out.println("这是男!");
break;
case '女':
System.out.println("这是女!");
break;
default:
System.out.println("不是男,也不是女!");
}
}
}
执行结果:

While与dowhile循环
while循环:
while(循环条件){
循环操作
}
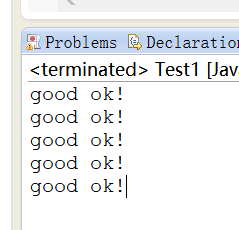
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 0;
while(i < 5){
System.out.println("good ok!");
i++;
}
}
}
执行结果:
do…while循环:
do{
循环操作
}while(循环条件);
do while循环是不管条件成不成立都先执行一次
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 6;
do{
System.out.println("good ok!");
i++;
}while(i < 5);
}
}
执行结果:

for循环:
for(初始化条件(一般为数据的初始化); 判断条件(一般与前面初始化的数据有关); 条件改变(一般改变那个数据)){
执行的操作
}
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i;
for(i=0;i<5;i++){
System.out.println("good ok!");
}
}
}
字符串循环:
info.substring(0);
截取字符串
s.length()
计算字符串大小
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String info = "我顿时凌乱了";
for(String s = info.substring(0);s.length()>0;s = s.substring(1)){
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
执行结果:

for循环嵌套:
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i=0;i<5;i++){
for(int j=i;j<4;j++){
System.out.print(" ");
}
for(int k=0;k<=i;k++){
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
执行结果:

求1!,2!…,10!的和:
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum = 0;
for(int i=1;i<=10;i++){
int s =1;
for(int j=1;j<=i;j++){
s *=j;
}
System.out.println(i+"的阶乘是:"+s);
sum +=s;
}
System.out.println("10的阶乘是:"+sum);
}
}
执行结果:

乘法表:
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i=1;i<=9;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=i;j++){
System.out.print(j+"x"+i+"="+i*j+"\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
执行结果:

循环关键字:break,continue,return
Java提供了continue和break来控制循环结构,除此之外,return可以结束整个方法,也可以间接的实现结束循环。
break:跳出循环体
break加标识符:
outer:可以随便写,只要不是关键字
break outer;
这样可以直接结束掉外部,内部循环
continue:忽略循环体本次循环后面的内容
return:方法结束,所以可以间接结束循环
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
outer:
for(int i=1;i<=5;i++){
System.out.println("外部i:"+i);
for(int j=11;j<=15;j++){
System.out.println(" 内部j:"+j);
if(j == 13){
break outer;
}
}
}
}
}
执行结果:

数组
array.length
计算数组的元素个数
数组的定义:
第一种写法:
int a[] = {1,2,6};
第二种写法:
int array[] = new int[3];
第三种写法:
int b[] = null;
b = new int[4];
代码示例:
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[] = {1,2,6};
System.out.println(a[0]);
System.out.println(a[1]);
System.out.println(a[2]);
int array[] = new int[3];
int i;
for(i=0;i<array.length;i++){
array[i] = i;
}
for(i=0;i<array.length;i++){
System.out.println(array[i]);
}
}
}
执行结果:

方法调用
类似C语言里的函数
第一种调用方式:
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
myPrint();
putAInt(20);
}
static void myPrint()
{
System.out.println("Hello world!");
}
static void putAInt(int a)
{
System.out.println("输出了一个数:"+a);
}
}
第二种调用方式:
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test1 t = new Test1();
t.myPrint();
t.putAInt(20);
}
void myPrint()
{
System.out.println("Hello world!");
}
void putAInt(int a)
{
System.out.println("输出了一个数:"+a);
}
}
执行结果:

























 360
360

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








