@Lingze师傅
该题目源码位于 yaklang仓库geek2023分支https://github.com/yaklang/yaklang/tree/geek2023
逆向
该题目使用 golang 编译,需要使用一定手段恢复符号。 恢复符号以后,将会看到以下内容: 调用 NewCodeMarshaller 并继续调用其 Unmarshal 方法,这是反序列化 yakc 文件也就是题目中的 marshalCode 文件,之后调用 NewWithSymbolTable 创建一个新的作用域。
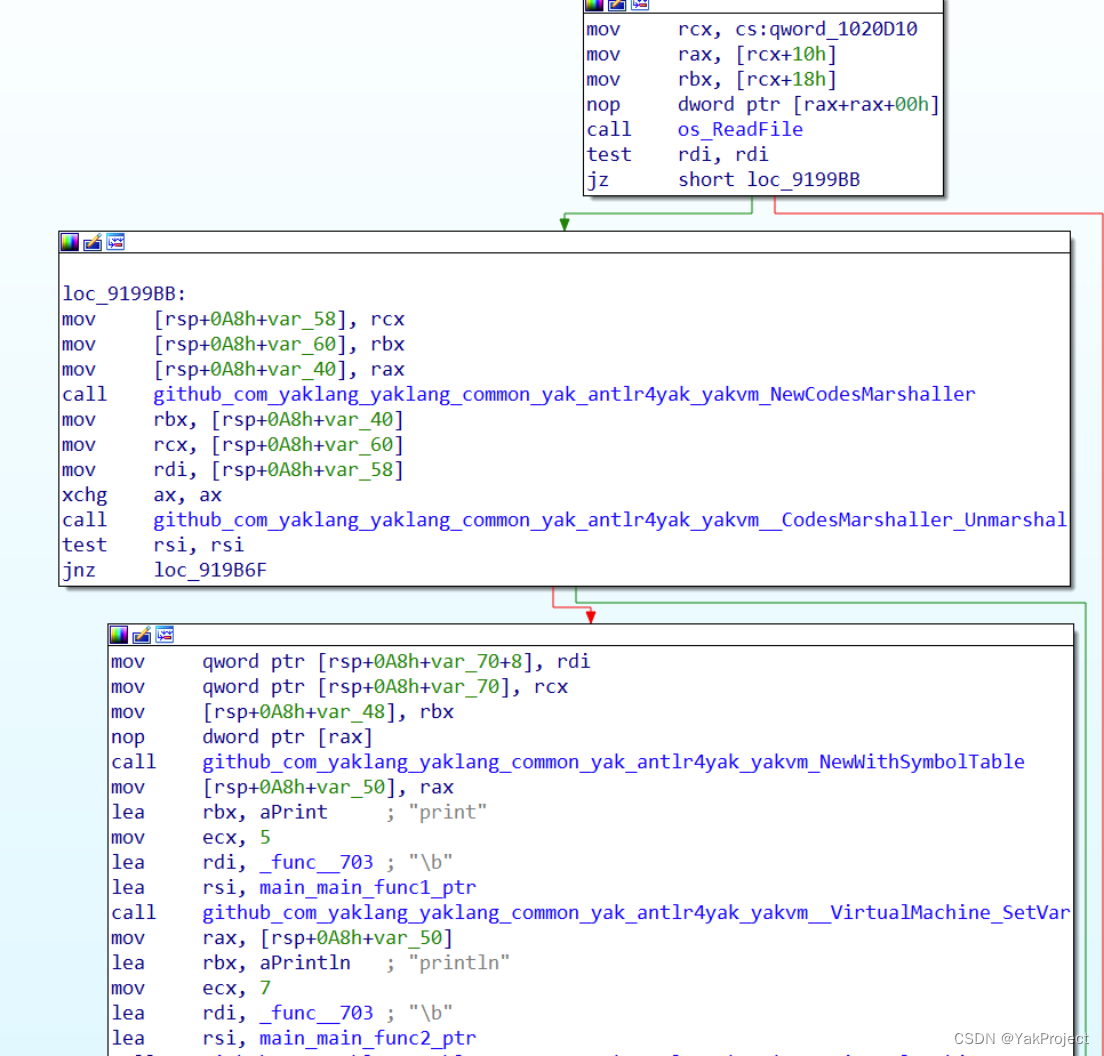
然后不断调用 SetVar 方法,设置如下的符号到对应的函数: print, println, get, string2int, len :
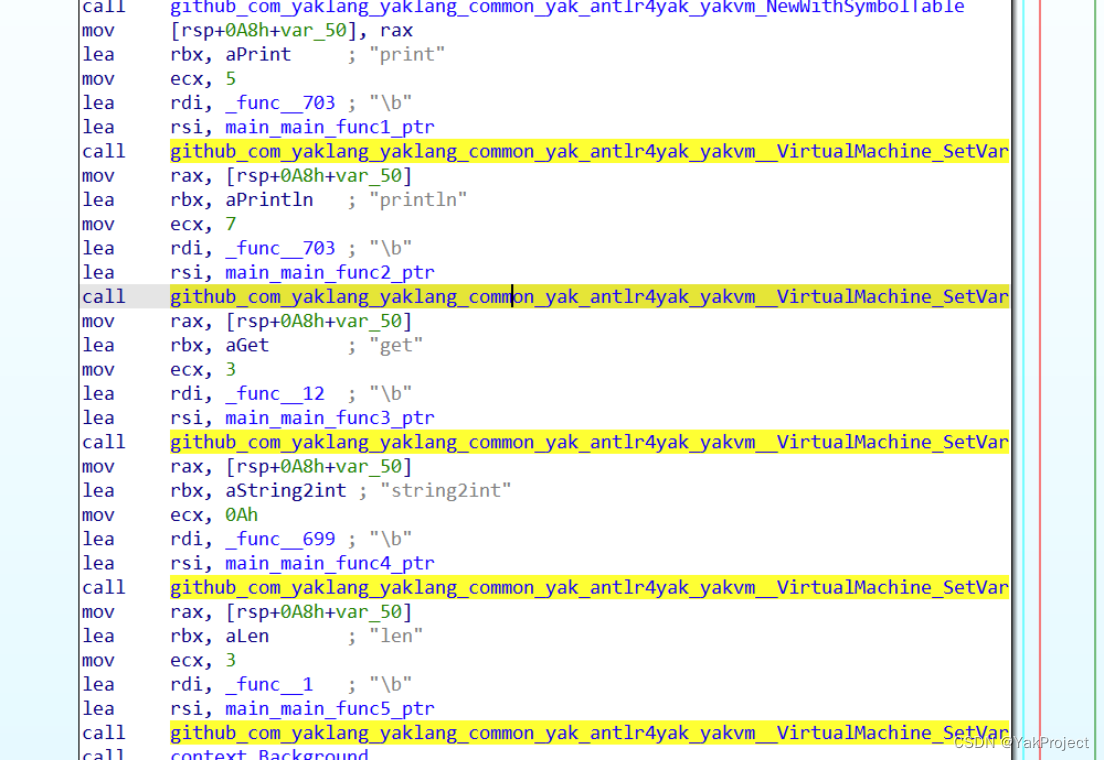
最后直接调用 Exec 方法,
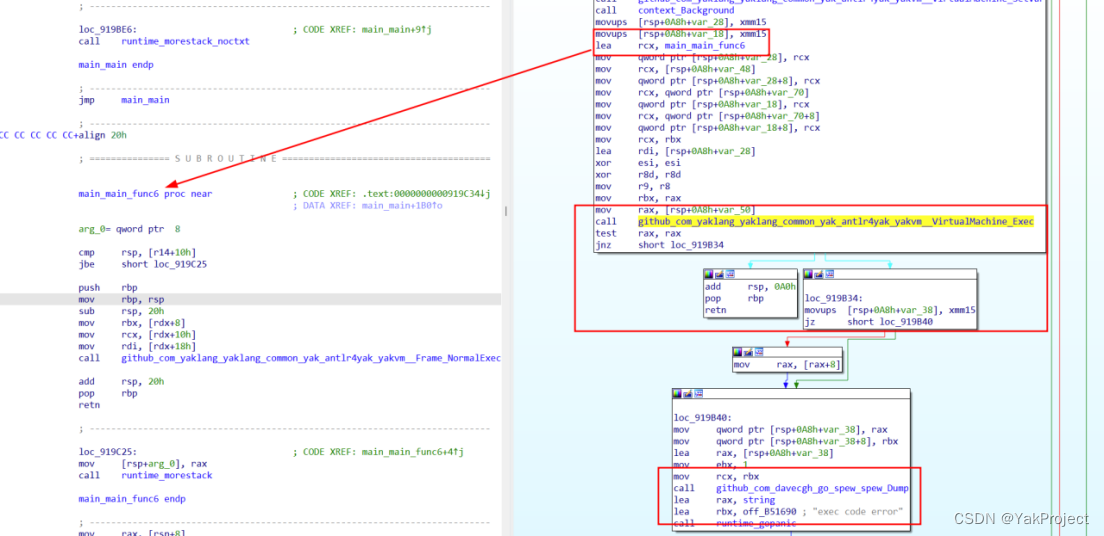
恢复符号以后发现该代码项目与题目 Readme 提示中的一致,主要代码都来自于https://github.com/yaklang/yaklang, 主要使用的是 YakVM 包https://github.com/yaklang/yaklang/tree/main/common/yak/antlr4yak的内容。 直接去看这些函数,在 main 分支的源码中都是存在的,也有很多对应的测试样例,可以了解这些 API 的使用。
VM
创建代码样例
直接去翻看这些 API 的参数和返回值,与逆向的数据进行对比,可以还原出这样的代码:
| Plain Text
func TestReverse(t *testing.T) {
bytes, err := os.ReadFile("./marshalCode")
if err != nil {
panic("read file error")
}
m := yakvm.NewCodesMarshaller()
table, code, err := m.Unmarshal(bytes)
if err != nil {
panic("unmarshal error")
}
yakvm.ShowOpcodes(code)
// run
vm := yakvm.NewWithSymbolTable(table)
// 这几个函数看名字就能知道啥意思,不影响对VM-OPcode的分析,或者逆向看代码也没有特别困难,基本都是直接调用api函数。
vm.SetVar("print", func(args ...interface{}) {
fmt.Print(args...)
})
vm.SetVar("println", func(args ...interface{}) {
fmt.Println(args...)
})
vm.SetVar("get", func() []byte {
var input string
fmt.Scanln(&input)
return []byte(input)
})
vm.SetVar("string2int", func(str string) int {
i, err := strconv.Atoi(str)
if err != nil {
return 0
}
return i
})
vm.SetVar("len", func(a []byte) int {
return len(a)
})
vm.Exec(context.Background(), func(frame *yakvm.Frame) {
frame.NormalExec(code)
})
} |
注意在这里直接使用 yakvm.ShowOpcodes(code) 这样的 API 即可直接打印出 Opcode 的反汇编版本。 同时,将所有注入的变量全部写一遍,都是直接打印数据。需要继续逆向一下各个子函数确定他们的意思,里头都是调用的 Golang 标准库 API,比较简单。
其实直接看着名字猜也可以猜到 (
可以补全整个测试样例,就可以开始 Golang 源码调试。这里多的就不赘述了可以直接看整个 VM 的实现。
逆向 Opcode
因为存在源码,所以几乎所有的 Opcode 都可以找到对应的运行操作和定义以及注释https://github.com/yaklang/yaklang/blob/main/common/yak/antlr4yak/yakvm/base.go 的,在其后的分析过程将不会详细解析每个 Opcode 的作用。函数参数和闭包捕获参考 func.gohttps://github.com/yaklang/yaklang/blob/main/common/yak/antlr4yak/yakvm/func.go#L245
通过之前的打印,可以得到一个线性的反汇编 Opcode。接下来将会分段讲解:
Opcode主函数
以下这段 Opcode 的作用是创建一个左值,这里先定义为 L1 内容位这些 push 的数据,类型为 byte[]。
| Plain Text
2:6->2:9 0:OP:type byte
2:4->2:97 1:OP:type slice
2:11->2:13 2:OP:push 137
2:15->2:17 3:OP:push 108
2:19->2:21 4:OP:push 159
2:23->2:25 5:OP:push 114
2:27->2:29 6:OP:push 185
2:31->2:32 7:OP:push 90
2:34->2:36 8:OP:push 174
2:38->2:39 9:OP:push 68
2:41->2:43 10:OP:push 160
2:45->2:46 11:OP:push 81
2:48->2:50 12:OP:push 179
2:52->2:53 13:OP:push 41
2:55->2:57 14:OP:push 186
2:59->2:60 15:OP:push 89
2:62->2:64 16:OP:push 168
2:66->2:67 17:OP:push 78
2:69->2:71 18:OP:push 229
2:73->2:75 19:OP:push 121
2:77->2:79 20:OP:push 149
2:81->2:83 21:OP:push 106
2:85->2:87 22:OP:push 147
2:89->2:91 23:OP:push 103
2:93->2:95 24:OP:push 156
2:97->2:99 25:OP:push 114
2:101->2:103 26:OP:push 133
2:105->2:106 27:OP:push 98
2:108->2:110 28:OP:push 146
2:112->2:114 29:OP:push 116
2:116->2:118 30:OP:push 181
2:4->2:97 25:OP:typedslice 23 // OP:OpNewSliceWithType
2:4->2:97 26:OP:list 1
2:0->2:0 27:OP:pushleftr 1
2:0->2:0 28:OP:list 1
2:0->2:97 29:OP:assign
L1 = []byte{137,108,159,114,185,90,174,68,160,81,179,41,186,89,168,78,229,121,149,106,147,103,156,114,133,98,146,116,181
} |
以下这一段是调用函数 print 并传入参数 "please input",最后扔掉返回值。
| Plain Text
3:0->3:4 30:OP:pushid print
3:6->3:25 31:OP:push please input flag:
3:5->3:26 32:OP:call vlen:1
3:0->3:26 33:OP:pop
print("please input") |
以下这段调用 get 函数:`
| Plain Text
4:4->4:6 34:OP:pushid get
4:7->4:8 35:OP:call vlen:0
4:4->4:8 36:OP:list 1
4:0->4:0 37:OP:pushleftr 2
4:0->4:0 38:OP:list 1
4:0->4:8 39:OP:assign
L2 = get() |
以下这段创建了新的作用域,一般情况下 if/for/switch/try 都会创建新的作用域,这段代码内部逻辑是判断+向后跳转,因此这应该是 if 结构:
| Plain Text
5:18->8:0 40:OP:new-scope 2
5:3->5:5 41:OP:pushid len
5:7->5:7 42:OP:pushr 2
5:6->5:8 43:OP:call vlen:1
5:12->5:14 44:OP:pushid len
5:16->5:16 45:OP:pushr 1
5:15->5:17 46:OP:call vlen:1
5:3->5:17 47:OP:gt
5:18->8:0 48:OP:jmpf -> 57
5:18->8:0 49:OP:new-scope 3
6:1->6:7 50:OP:pushid println
6:9->6:32 51:OP:push input string too long!
6:8->6:33 52:OP:call vlen:1
6:1->6:33 53:OP:pop
7:1->7:6 54:OP:return
5:18->8:0 55:OP:end-scope
5:18->8:0 56:OP:jmp -> 57
5:18->8:0 57:OP:end-scope
if len(L2) > len(L1) {
println("string too long!")
} |
以下这两段首先保存了一段 opcode 到一个左值中,其中这段 Opcode 是 Opcode 内定义的函数:
| Plain Text
12:8->21:0 58:OP:push function params[1] codes[54] (copy)
12:8->21:0 59:OP:list 1
12:0->12:4 60:OP:pushleftr 8
12:0->12:4 61:OP:list 1
12:0->21:0 62:OP:assign
25:4->25:8 63:OP:pushr 8
25:10->25:10 64:OP:pushr 2
25:9->25:11 65:OP:call vlen:1
25:4->25:11 66:OP:list 1
25:0->25:0 67:OP:pushleftr 2
25:0->25:0 68:OP:list 1
25:0->25:11 69:OP:assign
L8 = func_code_54
L2 = L8(L2)
28:9->33:0 70:OP:push function params[0] codes[40] (copy)
28:9->33:0 71:OP:list 1
28:0->28:4 72:OP:pushleftr 14
28:0->28:4 73:OP:list 1
28:0->33:0 74:OP:assign
36:0->36:4 75:OP:pushr 14
36:5->36:6 76:OP:call vlen:0
36:0->36:6 77:OP:pop
L14 = func_code_40
L14() |
这段 Opcode 的最后一段如下, 首先获取定义的函数,然后进入一个判断结构:
| Plain Text
38:11->48:0 78:OP:push function params[0] codes[52] (copy)
38:11->48:0 79:OP:list 1
38:0->38:7 80:OP:pushleftr 19
38:0->38:7 81:OP:list 1
38:0->48:0 82:OP:assign
// L19 = func_code_52
51:14->53:0 83:OP:new-scope 24
51:3->51:10 84:OP:pushr 19
51:11->51:12 85:OP:call vlen:0
51:14->53:0 86:OP:jmpf -> 94
51:14->53:0 87:OP:new-scope 25
52:1->52:5 88:OP:pushid print
52:7->52:24 89:OP:push yes! you get it!
52:6->52:25 90:OP:call vlen:1
52:1->52:25 91:OP:pop
// print("yes! you get it!")
51:14->53:0 92:OP:end-scope
51:14->53:0 93:OP:jmp -> 102
51:14->53:0 94:OP:end-scope
51:14->53:0 95:OP:new-scope 26
53:6->55:0 96:OP:new-scope 27
54:1->54:5 97:OP:pushid print
54:7->54:24 98:OP:push no this not flag
54:6->54:25 99:OP:call vlen:1
54:1->54:25 100:OP:pop
// print("no this not flag")
53:6->55:0 101:OP:end-scope
51:14->53:0 102:OP:end-scope
if L19() {
print("yes! you get it!")
}else {
print("no this not flag")
} |
Opcode 函数 1 func_code_54
| Plain Text
anonymous
12:15->21:0 0:OP:new-scope 5
13:1->19:1 1:OP:new-scope 6
13:1->19:1 2:OP:pushleftr 5
13:18->13:18 3:OP:pushr 3
13:1->19:1 4:OP:fast-assign
L5 = L3
13:1->19:1 5:OP:enter-for-range -> 47
13:1->19:1 6:OP:range-next
13:5->13:5 7:OP:pushleftr 6
13:8->13:8 8:OP:pushleftr 7
13:5->13:8 9:OP:list 2
13:1->19:1 10:OP:assign
L6, L7 = range L5
13:20->19:1 11:OP:new-scope 7
14:16->16:2 12:OP:new-scope 8
14:5->14:5 13:OP:pushr 6
14:9->14:9 14:OP:push 2
14:5->14:9 15:OP:mod
14:14->14:14 16:OP:push 0
14:5->14:14 17:OP:eq
// L6 % 2 == 0
14:16->16:2 18:OP:jmpf -> 31
14:16->16:2 19:OP:new-scope 9
15:10->15:10 20:OP:pushr 7
15:14->15:17 21:OP:push 240
15:10->15:17 22:OP:xor
15:10->15:17 23:OP:list 1
// L7 ^ 240
15:3->15:3 24:OP:pushr 3
15:5->15:5 25:OP:pushr 6
15:3->15:6 26:OP:list 2
// L3[L6]
15:3->15:6 27:OP:list 1
15:3->15:17 28:OP:assign
// L3[L6] = L7 ^ 240
14:16->16:2 29:OP:end-scope
14:16->16:2 30:OP:jmp -> 44
14:16->16:2 31:OP:end-scope
14:16->16:2 32:OP:new-scope 10
16:9->18:2 33:OP:new-scope 11
17:10->17:10 34:OP:pushr 7
17:14->17:17 35:OP:push 15
17:10->17:17 36:OP:xor
17:10->17:17 37:OP:list 1
// L7 ^ 15
17:3->17:3 38:OP:pushr 3
17:5->17:5 39:OP:pushr 6
17:3->17:6 40:OP:list 2
// L3[L6]
17:3->17:6 41:OP:list 1
17:3->17:17 42:OP:assign
// L3[L6] = L7 ^ 15
16:9->18:2 43:OP:end-scope
14:16->16:2 44:OP:end-scope
13:20->19:1 45:OP:end-scope
13:1->19:1 46:OP:exit-for-range -> 6
13:1->19:1 47:OP:pop
13:1->19:1 48:OP:end-scope
20:8->20:8 49:OP:pushr 3
20:8->20:8 50:OP:list 1
20:1->20:8 51:OP:return
// return L3
12:15->21:0 52:OP:end-scope
12:8->21:0 53:OP:return |
大概内容如下,函数的参数将会被定名为和父函数内所有值都不同名的一个 ID。
| Plain Text
func1 = (L3) => {
for L6, L6 = range arg1 {
if L6 % 2 == 0 {
L3[L6] = L6 ^ 240
}else {
L3[L6] = L6 ^ 15
}
}
return L3
} |
Opcode 函数 2 func_code_50
| Plain Text
anonymous
28:15->33:0 0:OP:new-scope 13
29:1->32:1 1:OP:new-scope 14
29:1->32:1 2:OP:pushleftr 10
29:18->29:18 3:OP:pushr 2
29:1->32:1 4:OP:fast-assign
// L10 = L2
29:1->32:1 5:OP:enter-for-range -> 36
29:1->32:1 6:OP:range-next
29:5->29:5 7:OP:pushleftr 11
29:8->29:8 8:OP:pushleftr 12
29:5->29:8 9:OP:list 2
29:1->32:1 10:OP:assign
// L11, L12 = range L10
29:20->32:1 11:OP:new-scope 15
30:6->30:6 12:OP:pushr 11
30:10->30:10 13:OP:push 2
30:6->30:10 14:OP:mul
30:6->30:10 15:OP:list 1
// L11 * 2
30:2->30:2 16:OP:pushleftr 13
30:2->30:2 17:OP:list 1
30:2->30:10 18:OP:assign
// L13 = L11 * 2
31:11->31:11 19:OP:pushr 12
31:10->31:11 20:OP:not
// ^L12
31:15->31:15 21:OP:pushr 13
31:10->31:15 22:OP:and
// L13 & ^L12
31:21->31:21 23:OP:pushr 12
31:26->31:26 24:OP:pushr 13
31:25->31:26 25:OP:not
31:21->31:26 26:OP:and
// ^L13 & L12
31:9->31:27 27:OP:or
31:9->31:27 28:OP:list 1
// (L13 & ^L12) | (L13 & ^L12)
31:2->31:2 29:OP:pushr 2
31:4->31:4 30:OP:pushr 11
31:2->31:5 31:OP:list 2
// L2[L11]
31:2->31:5 32:OP:list 1
31:2->31:27 33:OP:assign
// L2[L11] = (L13 & ^L12) | (L13 & ^L12)
29:20->32:1 34:OP:end-scope
29:1->32:1 35:OP:exit-for-range -> 6
29:1->32:1 36:OP:pop
29:1->32:1 37:OP:end-scope
28:15->33:0 38:OP:end-scope
28:9->33:0 39:OP:return |
大致内容如下,注意函数内使用和外部一样的 id,表示这个参数是尝试对外部变量的捕获,在此函数内对这个变量进行修改是可以将外部的该变量修改掉的。
| Plain Text
func2 = () => {
for L11, L12 := range L2 {
L13 = L11 * 2
L2[L11] = (L13 & ^L12) | (^L13 & L12)
}
} |
Opcode 函数 3 func_code_52
| Plain Text
anonymous
38:17->48:0 0:OP:new-scope 17
39:21->41:1 1:OP:new-scope 18
39:4->39:6 2:OP:pushid len
39:8->39:8 3:OP:pushr 2
39:7->39:9 4:OP:call vlen:1
// len(L2)
39:14->39:16 5:OP:pushid len
39:18->39:18 6:OP:pushr 1
39:17->39:19 7:OP:call vlen:1
// len(L1)
39:4->39:19 8:OP:neq
// Len(L2) != len(L1)
39:21->41:1 9:OP:jmpf -> 16
39:21->41:1 10:OP:new-scope 19
40:9->40:13 11:OP:push false
40:9->40:13 12:OP:list 1
40:2->40:13 13:OP:return
// return false
39:21->41:1 14:OP:end-scope
39:21->41:1 15:OP:jmp -> 16
39:21->41:1 16:OP:end-scope
42:1->46:1 17:OP:new-scope 20
42:1->46:1 18:OP:pushleftr 16
42:18->42:18 19:OP:pushr 2
42:1->46:1 20:OP:fast-assign
// L16 = L2
42:1->46:1 21:OP:enter-for-range -> 45
42:1->46:1 22:OP:range-next
42:5->42:5 23:OP:pushleftr 17
42:8->42:8 24:OP:pushleftr 18
42:5->42:8 25:OP:list 2
42:1->46:1 26:OP:assign
// L17, L18 = range L16
42:20->46:1 27:OP:new-scope 21
43:14->45:2 28:OP:new-scope 22
43:5->43:5 29:OP:pushr 18
// L18
43:10->43:10 30:OP:pushr 1
43:12->43:12 31:OP:pushr 17
43:11->43:13 32:OP:push false
43:11->43:13 33:OP:iterablecall off:1 op1: - op2: -
// L1[L17]
43:5->43:13 34:OP:neq
// L18 != L1[L17]
43:14->45:2 35:OP:jmpf -> 42
43:14->45:2 36:OP:new-scope 23
44:10->44:14 37:OP:push false
44:10->44:14 38:OP:list 1
44:3->44:14 39:OP:return
// return false
43:14->45:2 40:OP:end-scope
43:14->45:2 41:OP:jmp -> 42
43:14->45:2 42:OP:end-scope
42:20->46:1 43:OP:end-scope
42:1->46:1 44:OP:exit-for-range -> 22
42:1->46:1 45:OP:pop
42:1->46:1 46:OP:end-scope
47:8->47:11 47:OP:push true
47:8->47:11 48:OP:list 1
47:1->47:11 49:OP:return
// return true
38:17->48:0 50:OP:end-scope
38:11->48:0 51:OP:return |
大致内容如下:
| Plain Text
func3 = () => {
if len(L2)!=len(L1){
return false
}
L16 = L2
for L17, L18 = range L16{
if L18 != L1[L17] {
return false
}
}
return true
} |
伪代码展示:
| Plain Text
L1 = []byte{137,108,159,114,185,90,174,68,160,81,179,41,186,89,168,78,229,121,149,106,147,103,156,114,133,98,146,116,181
}
print("please input")
L2 = get()
if len(L2) > len(L1) {
println("string too long!")
}
L8 = func1
L2 = L8(L2)
L14 = func2
L14()
L19 = func3
if L19() {
print("yes! you get it!")
}else {
print("no this not flag")
}
func1 = (L3) => {
for L6, L6 = range arg1 {
if L6 % 2 == 0 {
L3[L6] = L6 ^ 240
}else {
L3[L6] = L6 ^ 15
}
}
return L3
}
func2 = () => {
for L11, L12 := range L2 {
L13 = L11 * 2
L2[L11] = (L13 & ^L12) | (^L13 & L12)
}
}
func3 = () => {
if len(L2)!=len(L1){
return false
}
L16 = L2
for L17, L18 = range L16{
if L18 != L1[L17] {
return false
}
}
return true
} |
解密得到 flag
| Plain Text
func TestGetFlag(t *testing.T) {
L1 := []byte{137, 108, 159, 114, 185, 90, 174, 68, 160, 81, 179, 41, 186, 89, 168, 78, 229, 121, 149, 106, 147, 103, 156, 114, 133, 98, 146, 116, 181}
Decode(L1)
fmt.Println(string(L1))
}
func Decode(flag []byte) {
for i, v := range flag {
v = v ^ byte(2*i)
if i%2 == 0 {
v = v ^ 0xf0
} else {
v = v ^ 0x0f
}
flag[i] = v
}
} |
Flag : yak{A_RE@LW0RLD_5TACKB@SE_VM}




 Yaklang项目逆向与Opcode分析获Flag
Yaklang项目逆向与Opcode分析获Flag





 博客围绕Yaklang仓库geek2023分支题目展开,先对使用golang编译的题目进行逆向,恢复符号后分析代码调用逻辑。接着创建代码样例,通过对比API参数和逆向数据还原代码。还对Opcode进行逆向分析,分段讲解其作用,最终解密得到Flag。
博客围绕Yaklang仓库geek2023分支题目展开,先对使用golang编译的题目进行逆向,恢复符号后分析代码调用逻辑。接着创建代码样例,通过对比API参数和逆向数据还原代码。还对Opcode进行逆向分析,分段讲解其作用,最终解密得到Flag。
















 1271
1271

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








