剑指 Offer 07. 重建二叉树
输入某二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果,请构建该二叉树并返回其根节点。
假设输入的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果中都不含重复的数字。
示例 1:
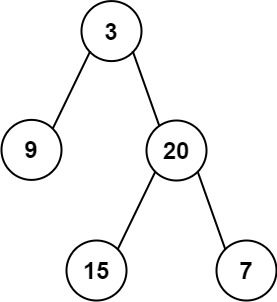
Input: preorder = [3,9,20,15,7], inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
Output: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
示例 2:
Input: preorder = [-1], inorder = [-1]
Output: [-1]
思路分析
首先要知道遍历后的数组都有什么样的特点
- 在前序遍历序列中,第一个元素为树的根节点
- 在中序遍历序列中,根节点的左边为左子树,根节点的右边为右子树
根据上面的理论知识可以清楚本题的解题策略,就是以 前序数组的第一个元素【根节点】为切割点,先切中序数组,根据中序数组,反过来在切前序数组。一层一层切下去,每次前序数组的第一个元素就是节点元素。

前序遍历的第一个元素就是他的头节点。知道了头节点,我们可以在中序遍历中找到头节点的位置index。通过index我们就可以求出来左子树在数组中的长度:index - inorder_start。(inorder_start是中序遍历的起点)。
-
获取树的头节点
int root_val = preorder[preorder_start](preorder_start是前序遍历的起始值)。然后我们直接构建二叉树 的根节点TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(root_val) -
构建左树:
root->left我们知道该二叉树的左子树的长度为left_length = index - inorder_start所以我们可以推出二叉树的左子树在前序遍历的位置是
[preorder_start+1,preorder_start+left_length]。
同理:二叉树的左子树在中序遍历的位置是[inorder_start, index - 1]。 -
构建右树:
root->right
二叉树的右子树在前序遍历的位置是[preorder_start+left_length+1,preorder_end]。
同理:二叉树右子树在中序遍历的位置是[index + 1 , inorder_end]。
代码如下:👇👇👇👇
class Solution {
public:
//递归代码
TreeNode* buildcore(const vector<int>& preorder, const vector<int>& inorder, int preorder_start, int preorder_end, int inorder_start, int inorder_end)
{
if(preorder_start>preorder_end||inorder_start>inorder_end)
{
return nullptr;
}
//前序遍历的第一个数字是根节点的值
int root_val = preorder[preorder_start];
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(root_val);
//区间里只有一个值,返回
if(preorder_start == preorder_end)
{
return root;
}
//中序遍历找到根节点的位置
int index = 0;
//可以等于,在范围内
while(index <= inorder_end && inorder[index] != root_val)
{
index++;
}
//如果index大于inorder_end,说明没找到,报错,题目所给的意思是肯定能找到,所以这里就不判断了。
//左右子树区间大小。
int left_length = index - inorder_start;
root->left = buildcore(preorder,inorder,preorder_start+1,preorder_start+left_length,inorder_start,index-1);
root->right = buildcore(preorder,inorder,preorder_start+left_length+1,preorder_end,index+1,inorder_end);
return root;
}
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder)
{
int n = preorder.size();
if(n==0)
{
return 0;
}
return buildcore(preorder,inorder,0,n-1,0,n-1);
}
};
106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
该题与上题类似,可以使用相同的解法递归解决。
思路分析
-
在后序遍历序列中,最后一个元素为树的根节点
-
在中序遍历序列中,根节点的左边为左子树,根节点的右边为右子树
以 后序数组的最后一个元素【根节点】为切割点,先切中序数组,根据中序数组,反过来在切后序数组。一层一层切下去,每次后序数组最后一个元素就是节点元素。
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* buildcore(const vector<int>& inorder, const vector<int>& postorder, int inorder_start, int inorder_end, int post_start, int post_end)
{
if(inorder_start>inorder_end||post_start>post_end)
{
return nullptr;
}
//后序遍历的最后一个值是根节点
int root_val = postorder[post_end];
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(root_val);
//遍历找根节点在中序遍历的的位置
int index = 0;
for(index = 0; index<= inorder_end; index++)
{
if(inorder[index] == root_val)
{
break;
}
}
//计算左子树的长度
int left_length = index - inorder_start;
//构建左子树
root->left = buildcore(inorder,postorder,inorder_start,index-1,post_start,post_start+left_length-1);
//构建右子树
root->right = buildcore(inorder,postorder,index+1,inorder_end,post_start+left_length,post_end-1);
return root;
}
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder)
{
int n = inorder.size();
if(n==0)
{
return nullptr;
}
return buildcore(inorder,postorder,0,n-1,0,n-1);
}
};


























 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










