一、从尾到头打印单链表
- 方法一:非递归
void SLitsPrintTailToHead(SListNode* pHead)
{
assert(pHead);
SListNode* end = NULL;
while (end != pHead)
{
SListNode* cur = pHead;
while (cur->_next != end)
{
cur = cur->_next;
}
printf("%d ", cur->_data);
end = cur;
}
printf("\n");
}
- 方法二:递归
void SLitsPrintTailToHead(SListNode* pHead)
{
if (pHead == NULL)
{
return;
}
SLitsPrintTailToHeadR(pHead->_next);
printf("%d ", pHead->_data);
}
二、删除一个无头单链表的非尾节点(不能遍历链表)
方法:替换法删除
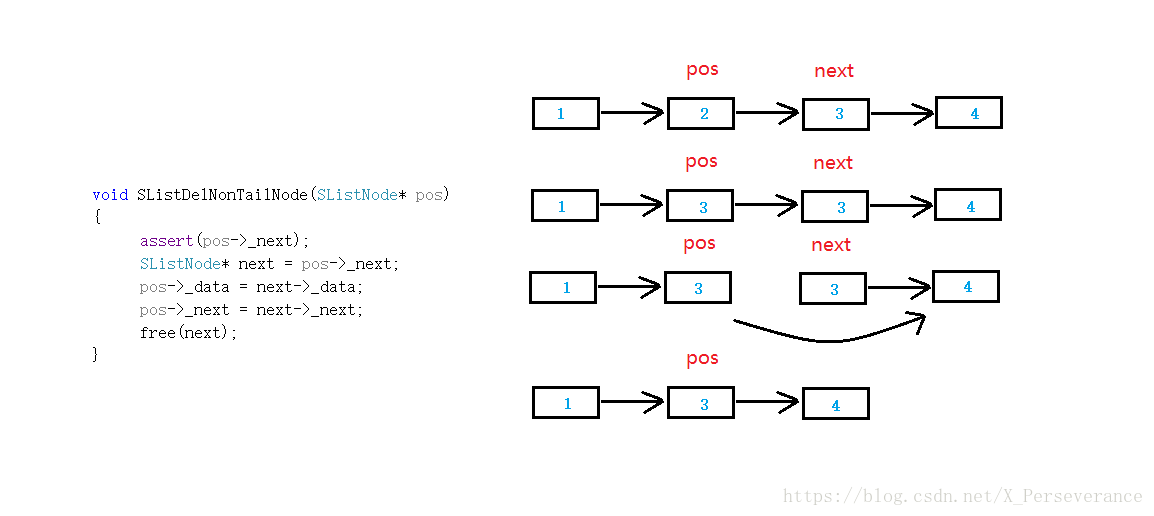
void SListDelNonTailNode(SListNode* pos)
{
assert(pos->_next);
SListNode* next = pos->_next;
pos->_data = next->_data;
pos->_next = next->_next;
free(next);
}
三、在无头单链表的一个节点前插入一个节点(不能遍历链表)
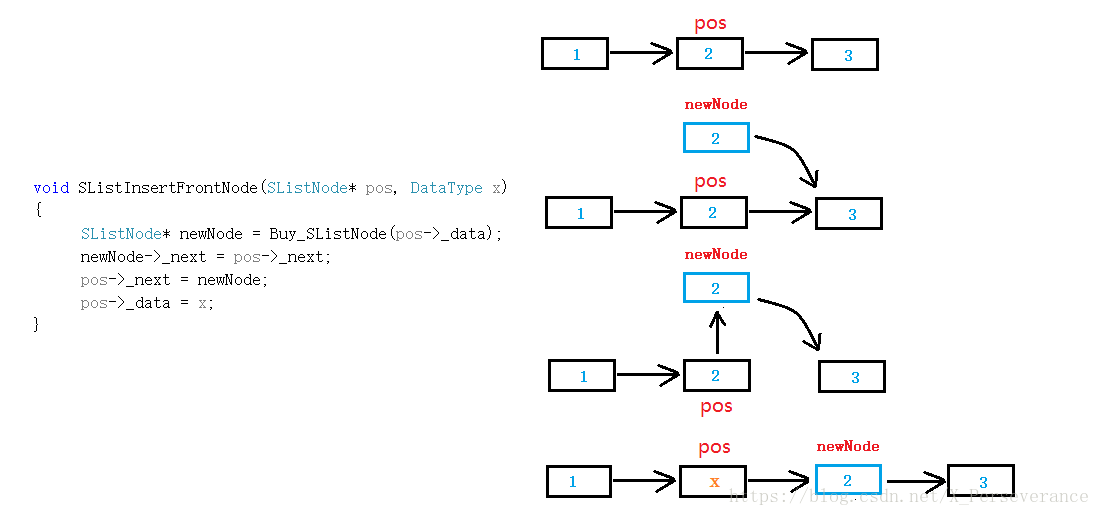
方法:替换法插入
void SListInsertFrontNode(SListNode* pos, DataType x)
{
SListNode* newNode = Buy_SListNode(pos->_data);
newNode->_next = pos->_next;
pos->_next = newNode;
pos->_data = x;
}
四、单链表实现约瑟夫环(JosephCircle)
SListNode* SListJosephCircle(SListNode* pHead, int k)
{
SListNode* cur = pHead;
SListNode* tail = pHead;
while (tail->_next)
{
tail = tail->_next;
}
tail->_next = pHead; // 构成环
while (cur->_next != cur)
{
int count = k;
while (--count)
{
cur = cur->_next;
}
SListNode* next = cur->_next;
cur->_data = next->_data;
cur->_next = next->_next;
free(next);
}
return cur;
}
五、逆置/反转单链表
- 方法一:
SListNode* SListReverse(SListNode* list)
{
SListNode* cur = list;
SListNode* newhead = NULL;
while (cur)
{
SListNode* next = cur->_next;
cur->_next = newhead;
newhead = cur;
cur = next;
}
return newhead;
}
- 方法二:
SListNode* SListReverse(SListNode* list)
{
SListNode* n1 = list;
SListNode* n2 = n1->_next;
SListNode* n3 = n2->_next;
while (n2)
{
n2->_next = n1;
n1 = n2;
n2 = n3;
if (n3)
{
n3 = n3->_next;
}
}
list->_next = NULL;
return n1;
}
六、单链表排序(冒泡排序)
void SListBubbleSort(SListNode* list)
{
if (list == NULL)
{
return;
}
SListNode* tail = NULL;
while ((list->_next) != tail)
{
int flag = 0;
SListNode* cur = list;
SListNode* next = cur->_next;
while (next != tail)
{
if (cur->_data > next->_data)
{
flag = 1;
DataType tmp = cur->_data;
cur->_data = next->_data;
next->_data = tmp;
}
cur = cur->_next;
next = next->_next;
}
if (flag == 0)
{
break;
}
tail = cur;
}
}
七、合并两个有序链表,合并后依然有序
SListNode* SListMerge(SListNode* list1, SListNode* list2)
{
assert(list1&&list2);
SListNode* list = NULL;
SListNode* tail = NULL;
if (list1->_data < list2->_data)
{
list = tail = list1;
list1 = list1->_next;
}
else
{
list = tail = list2;
list2 = list2->_next;
}
while (list1&&list2)
{
if (list1->_data < list2->_data)
{
tail->_next = list1;
list1 = list1->_next;
}
else
{
tail->_next = list2;
list2 = list2->_next;
}
tail = tail->_next;
}
if (list1)
{
tail->_next = list1;
}
if (list2)
{
tail->_next = list2;
}
return list;
}
八、查找单链表的中间节点,要求只能遍历一次链表
方法:设置快慢指针
SListNode* SListFindMidNode(SListNode* list)
{
if (list == NULL || list->_next == NULL)
{
return list;
}
else
{
SListNode* slow = list;
SListNode* fast = list->_next->_next;
while (fast)
{
slow = slow->_next;
fast = fast->_next;
if (fast)
{
fast = fast->_next;
}
}
return slow;
}
}
九、查找单链表的倒数第k个节点,要求只能遍历一次链表
方法:设置快慢指针
SListNode* SListFindTailKNode(SListNode* list, size_t k)
{
SListNode* slow = list;
SListNode* fast = list;
while (k--)
{
if (fast)
fast = fast->_next;
else
return NULL;
}
while (fast)
{
slow = slow->_next;
fast = fast->_next;
}
return slow;
}
十、删除链表的倒数第K个结点
void SListDelTailKNode(SListNode** plist, size_t k)
{
SListNode* pos = SListFindTailKNode(*plist, k);
SList_Erase(plist, pos);
}
十一、判断单链表是否带环?若带环,求环的长度?求环的入口点?
(1)是否带环
SListNode* SListIsCycle(SListNode* list)
{
SListNode* slow = list;
SListNode* fast = list;
while (fast&&fast->_next)
{
slow = slow->_next;
fast = fast->_next->_next;
if (fast == slow)
{
return slow;
}
}
return NULL;
}
(2)环长度
int SListCycleLen(SListNode* meetNode)
{
SListNode* cur = meetNode;
int count = 1;
while((cur->_next) != meetNode)
{
count++;
cur = cur->_next;
}
return count;
}
(3)环入口点
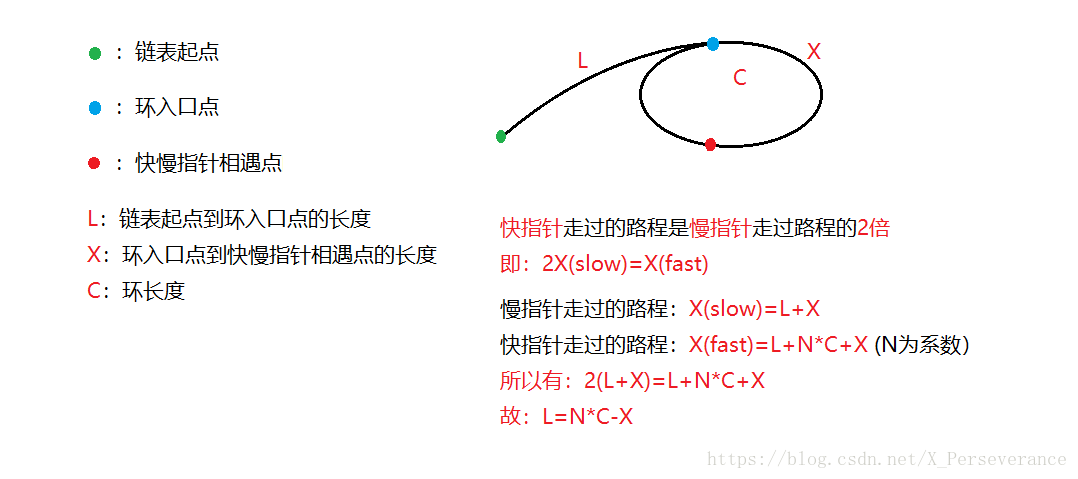
SListNode* SListEntryNode(SListNode* list, SListNode* meetNode)
{
SListNode* cur1 = list;
SListNode* cur2 = meetNode;
while (cur1 != cur2)
{
cur1 = cur1->_next;
cur2 = cur2->_next;
}
return cur1;
}
十二、判断两个链表是否相交?若相交,求交点?
(1)是否相交
int SListIsCrossNode(SListNode* list1, SListNode* list2)
{
assert(list1&&list2);
SListNode* meet1 = SListIsCycle(list1);
SListNode* meet2 = SListIsCycle(list2);
//一:都不带环
//判断两个链表最后一个结点是否相等
if (meet1 == NULL&&meet2 == NULL)
{
SListNode* cur1 = list1;
SListNode* cur2 = list2;
while (cur1&&cur1->_next)
{
cur1 = cur1->_next;
}
while (cur2&&cur2->_next)
{
cur2 = cur2->_next;
}
if (cur1 == cur2)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return 0;
}
}
//二:都带环
//判断两个相遇点是否在同一个环内
else if (meet1 != NULL&&meet2 != NULL)
{
SListNode* cur = meet1;
while (cur->_next != meet1)
{
if (cur == meet2)
{
return 1;
}
cur = cur->_next;
}
if (cur == meet2)
{
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
//三:一个带环,另一个不带环
//肯定不相交
else
{
return 0;
}
}
(2)求交点
【1】适应于两链表都不带环相交时,求交点
SListNode* SListCrossNode_1(SListNode* list1, SListNode* list2)
{
assert(list1&&list2);
SListNode* tail = list1;
SListNode* meet = NULL;
while (tail->_next)
{
tail = tail->_next;
}
tail->_next = list2;
meet = SListIsCycle(list1);
return SListEntryNode(list1, meet);
}
【2】适应于两链表都不带环相交或者是都带环且在环外相交时,求交点
SListNode* SListCrossNode_2(SListNode* list1, SListNode* list2)
{
SListNode* longlist = NULL;
SListNode* shortlist = NULL;
SListNode* cur1 = list1;
SListNode* cur2 = list2;
int count1 = 0;
int count2 = 0;
int gap = 0;
SListNode* meetNode = SListIsCycle(list1);
//若都不带环,meetNode为NULL;若都带环,meetNode为环内一个节点
while (cur1 != meetNode)
{
count1++;
cur1 = cur1->_next;
}
while (cur2 != meetNode)
{
count2++;
cur2 = cur2->_next;
}
longlist = list1;
shortlist = list2;
if (count1 < count2)
{
longlist = list2;
shortlist = list1;
}
gap = abs(count1 - count2);
while (gap--)
{
longlist = longlist->_next;
}
while (shortlist != longlist)
{
shortlist = shortlist->_next;
longlist = longlist->_next;
}
return shortlist;
}
【3】适应于都带环且在环内相交
void SListCrossNode_3(SListNode* list1, SListNode* list2)
{
SListNode* meetNode1 = SListIsCycle(list1);
printf("交点1是:%d\n", SListEntryNode(list1, meetNode1)->_data);
SListNode* meetNode2 = SListIsCycle(list2);
printf("交点2是:%d\n", SListEntryNode(list2, meetNode2)->_data);
}
十三、求两个已排序单链表中相同的数据
void UnionSet(SListNode* list1, SListNode* list2)
{
assert(list1&&list2);
SListNode* cur1 = list1;
SListNode* cur2 = list2;
while (cur1 && cur2)
{
if (cur1->_data < cur2->_data)
{
cur1 = cur1->_next;
}
else if (cur1->_data > cur2->_data)
{
cur2 = cur2->_next;
}
else
{
printf("%d ", cur1->_data);
cur1 = cur1->_next;
cur2 = cur2->_next;
}
}
}
十四、复杂链表的复制
一个链表的每个节点,有一个指向next指针指向下一个节点,还有一个random指针指向这个链表中的一个随机节点或者NULL,现在要求实现复制这个链表,返回复制后的新链表。
typedef struct ComplexListNode
{
int _data;
struct ComplexListNode* _next;
struct ComplexListNode* _random;
} ComplexListNode;
ComplexListNode * CopyComplexList(ComplexListNode * list)
{
if (list == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
//第一步:复制节点
ComplexListNode * cur = list;
while (cur)
{
ComplexListNode * newnode = Buy_SListNode(cur->_data);
newnode->_next = cur->_next;
cur->_next = newnode;
newnode->_random = NULL;
cur = cur->_next->_next;
}
//第二步:复制random指针
cur = list;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_random)
{
cur->_next->_random = cur->_random->_next;
}
else
{
cur->_next->_random = NULL;
}
cur = cur->_next->_next;
}
//第三步:拆分,重新连接
cur = list;
ComplexListNode * newlist = list->_next;
ComplexListNode * newcur = newlist;
while (cur)
{
cur->_next = cur->_next->_next;
if (newcur->_next)
{
newcur->_next = newcur->_next->_next;
}
else
{
newcur->_next = NULL;
}
cur = cur->_next;
newcur = newcur->_next;
}
return newlist;
}
注:部分嵌套函数请参照(单链表)





















 766
766

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








