文章目录
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext是用来加载xml配置文件的Context,而AnnotationConfigApplicationContext是用来加载注解配置的Context。虽然直接父类不同,但是都有一个共同的祖先类AbstractApplicationContext。以及同样有一个组合对象BeanFactory提供容器作用。
一、ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext继承关系图:

ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 构造器源码:
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, ApplicationContext parent) {
//null
super(parent);
setConfigLocations(configLocations);
//默认true
if (refresh) {
refresh();
}
}
1.构造器
首先调用super方法,所以看父类构造器,沿着继承体系一直向上调用,直到AbstractApplicationContext:
public AbstractApplicationContext() {
this.resourcePatternResolver = getResourcePatternResolver();
}
public AbstractApplicationContext(ApplicationContext parent) {
this();
setParent(parent);
}
默认的无参构造函数中调用getResourcePatternResolver()方法设置配置文件路径:
protected ResourcePatternResolver getResourcePatternResolver() {
return new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver(this);
}
PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver支持Ant风格的路径解析。
2. 设置配置文件路径
调用setConfigLocations方法设置配置文件路径,即AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext.setConfigLocations()
public void setConfigLocations(String... locations) {
if (locations != null) {
Assert.noNullElements(locations, "Config locations must not be null");
this.configLocations = new String[locations.length];
for (int i = 0; i < locations.length; i++) {
this.configLocations[i] = resolvePath(locations[i]).trim();
}
} else {
this.configLocations = null;
}
}
2.1resolvePath() 方法:
protected String resolvePath(String path) {
return getEnvironment().resolveRequiredPlaceholders(path);
}
此方法的目的在于将占位符(placeholder)解析成实际的地址。比如可以这么写: new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(“classpath:config.xml”);那么classpath:就是需要被解析的。
2.2 getEnvironment()方法
getEnvironment()方法来自于ConfigurableApplicationContext接口,源码很简单,如果为空就调用createEnvironment创建一个。AbstractApplicationContext.createEnvironment():
protected ConfigurableEnvironment createEnvironment() {
return new StandardEnvironment();
}
2.3 resolveRequiredPlaceholders()方法
resolveRequiredPlaceholders()用来处理路径Placeholder:
@Override
public String resolveRequiredPlaceholders(String text) throws IllegalArgumentException {
//text即配置文件路径,比如classpath:config.xml
return this.propertyResolver.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(text);
}
propertyResolver成员变量是一个PropertySourcesPropertyResolver对象:
private final ConfigurablePropertyResolver propertyResolver =
new PropertySourcesPropertyResolver(this.propertySources);
PropertySourcesPropertyResolver关系继承图:
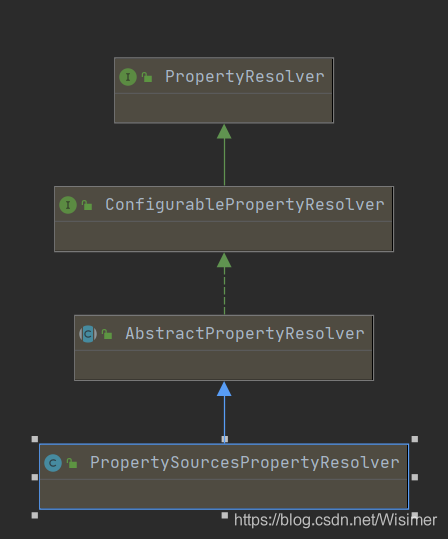
PropertyResolver这个接口就是用来解析PropertyResource的。
3. Environment接口
StandardEnvironment 继承关系图:

Environmen接口代表了当前应用所处的环境。从此接口的方法可以看出,其主要和profile、Property相关:
public interface Environment extends PropertyResolver {
String[] getActiveProfiles();
String[] getDefaultProfiles();
boolean acceptsProfiles(String... profiles);
boolean acceptsProfiles(Profiles profiles);
}
AbstractEnvironment构造器:
private final MutablePropertySources propertySources = new MutablePropertySources(this.logger);
public AbstractEnvironment() {
customizePropertySources(this.propertySources);
}
StandardEnvironment.customizePropertySources()方法:
/** System environment property source name: {@value} */
public static final String SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "systemEnvironment";
/** JVM system properties property source name: {@value} */
public static final String SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "systemProperties";
@Override
protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
propertySources.addLast(new MapPropertySource
(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, getSystemProperties()));
propertySources.addLast(new SystemEnvironmentPropertySource
(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, getSystemEnvironment()));
}
4. PropertySource和PropertySources
这里的Property指的是程序运行时的一些参数,引用注释:
properties files, JVM system properties, system environment variables, JNDI, servlet context parameters, ad-hoc Properties objects,Maps, and so on.
(1)MutablePropertySources 继承关系图:

默认的MutablePropertySources实现内部含有一个CopyOnWriteArrayList作为存储载体,所以PropertySources其实是作为一个容器保存了多个PropertySource。
(2)PropertySource
PropertySource代表了键值对的Property来源。PropertySource继承关系图:
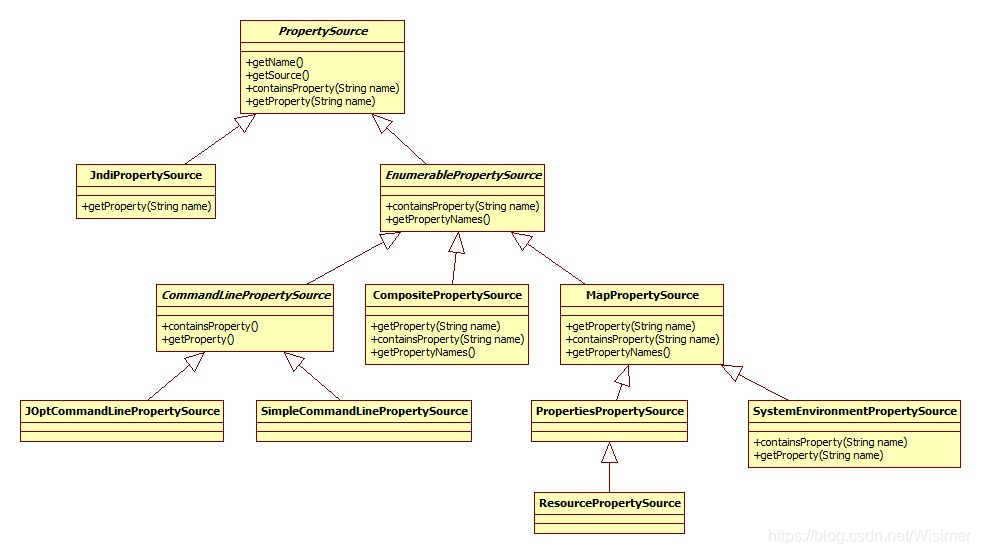
在StandardEnvironment.customizePropertySources()方法中向propertySources容器中添加了MapPropertySource和SystemEnvironmentPropertySource两种PropertySource。
- MapPropertySource通过
AbstractEnvironment.getSystemProperties()获取:
@Override
public Map<String, Object> getSystemProperties() {
try {
return (Map) System.getProperties();
}
catch (AccessControlException ex) {
return (Map) new ReadOnlySystemAttributesMap() {
@Override
protected String getSystemAttribute(String attributeName) {
try {
return System.getProperty(attributeName);
}
catch (AccessControlException ex) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info(format("Caught AccessControlException when accessing system " +
"property [%s]; its value will be returned [null]. Reason: %s",
attributeName, ex.getMessage()));
}
return null;
}
}
};
}
}
这里的实现很有意思,如果安全管理器阻止获取全部的系统属性,那么会尝试获取单个属性的可能性,如果还不行就抛异常了。
- SystemEnvironmentPropertySource通过
AbstractEnvironment.getSystemEnvironment()获取:
getSystemEnvironment方法也是一个套路,不过最终调用的是System.getenv,可以获取jvm和OS的一些版本信息。
4. Profile
Spring Profile特性是从3.1开始的,其主要是为了解决这样一种问题: 线上环境和测试环境使用不同的配置或是数据库或是其它。有了Profile便可以在 不同环境之间无缝切换。Spring容器管理的所有bean都是和一个profile绑定在一起的。使用了Profile的配置文件示例:

application.yml:
spring:
# 环境 dev|test|pro
profiles:
active: dev
二、AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext继承关系图:

1. 构造函数:
用来注册内部处理器类
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext() {
StartupStep createAnnotatedBeanDefReader = this.getApplicationStartup().start("spring.context.annotated-bean-reader.create");
this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this);
createAnnotatedBeanDefReader.end();
this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this);
}
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Class<?>... componentClasses) {
this();
register(componentClasses);
refresh();
}
默认的构造函数中StartupStep实际是记录性能用的,可以不看,AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader和ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner两个类的实例化其实是完成了Spring内部定义的BeanFactory后处理器的注册以及初始化注解bean定义解析器和类路径bean定义扫描器。
2. register()方法
注册Java配置类
@Override
public void register(Class<?>... componentClasses) {
StartupStep registerComponentClass = this.getApplicationStartup().start("spring.context.component-classes.register")
.tag("classes", () -> Arrays.toString(componentClasses));
this.reader.register(componentClasses);
registerComponentClass.end();
}
register方法是通过注解bean读取器AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader来实现的。
reader.register()方法按指定的配置bean注册信息:
public void register(Class<?>... componentClasses) {
for (Class<?> componentClass : componentClasses) {
registerBean(componentClass);
}
}
registerBean()内部实际调用doRegisterBean()方法:
<T> void doRegisterBean(Class<T> annotatedClass, @Nullable Supplier<T> instanceSupplier, @Nullable String name,
@Nullable Class<? extends Annotation>[] qualifiers, BeanDefinitionCustomizer... definitionCustomizers) {
// 其实就是创建BeanDefinition了,只是多了一个注解的属性metadata
AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition abd = new AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition(annotatedClass);
// @Conditional注解的判断在这里,如果不符合条件,就不注册了
if (this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(abd.getMetadata())) {
return;
}
// 回调用的
abd.setInstanceSupplier(instanceSupplier);
// 解析bean的作用域,scope,没有设置默认单例
ScopeMetadata scopeMetadata = this.scopeMetadataResolver.resolveScopeMetadata(abd);
abd.setScope(scopeMetadata.getScopeName());
// 解析bean的名称
String beanName = (name != null ? name : this.beanNameGenerator.generateBeanName(abd, this.registry));
// 设置abd的Lazy, primary DependsOn, Role ,Description这五个属性
AnnotationConfigUtils.processCommonDefinitionAnnotations(abd);
// 特定限定符处理
if (qualifiers != null) {
for (Class<? extends Annotation> qualifier : qualifiers) {
if (Primary.class == qualifier) {
abd.setPrimary(true);
}
else if (Lazy.class == qualifier) {
abd.setLazyInit(true);
}
else {
abd.addQualifier(new AutowireCandidateQualifier(qualifier));
}
}
}
for (BeanDefinitionCustomizer customizer : definitionCustomizers) {
customizer.customize(abd);
}
// 定义一个BeanDefinitionHolder,就是beanName和BeanDefinition的映射
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(abd, beanName);
// 是否有代理
definitionHolder = AnnotationConfigUtils.applyScopedProxyMode(scopeMetadata, definitionHolder, this.registry);
// 往容器注册BeanDefinition,同时注册别名
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry);
}
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition()方法实现:
public static void registerBeanDefinition(BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
// 根据主名称注册bean定义信息
String beanName = definitionHolder.getBeanName();
/**
* GenericApplicationContext类实现了BeanDefinitionRegistry接口,
* 并且在 GenericApplicationContext类中维护了一个DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory (卧槽, 终于见到bean工厂了)
*
* 该步骤实际调用的是GenericApplicationContext类中的registerBeanDefinition()方法
*{@link org.springframework.context.support.GenericApplicationContext#registerBeanDefinition(String,BeanDefinition)}
*/
registry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, definitionHolder.getBeanDefinition());
// 如果该bean有别名的话, 为bean名称注册别名
String[] aliases = definitionHolder.getAliases();
if (aliases != null) {
for (String alias : aliases) {
registry.registerAlias(beanName, alias);
}
}
}
3. refresh()方法用来刷新上下文
注册普通BeanDefinition
解析请看https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/Wisimer/article/details/110949420
THE END.





 本文介绍了Spring框架中两种上下文加载方式:ClassPathXmlApplicationContext和AnnotationConfigApplicationContext。前者用于加载XML配置文件,后者用于加载注解配置。文章详细解析了它们的构造函数、核心方法及其实现原理。
本文介绍了Spring框架中两种上下文加载方式:ClassPathXmlApplicationContext和AnnotationConfigApplicationContext。前者用于加载XML配置文件,后者用于加载注解配置。文章详细解析了它们的构造函数、核心方法及其实现原理。
















 2699
2699

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








