一,前言
ListView和GridView作为一个常用的控件,基本上每一个app都要用到,本文透过相关资料,试图为大家解开Android开发中的那些疑问,同时也探讨Android部分源代码的本质。
本文引用的资料,由于时间关系,不多做翻译。
阅读本文前,我认为读者应该具备基本的Android相关知识,如Activity/View的基本原理及使用。
系统框架
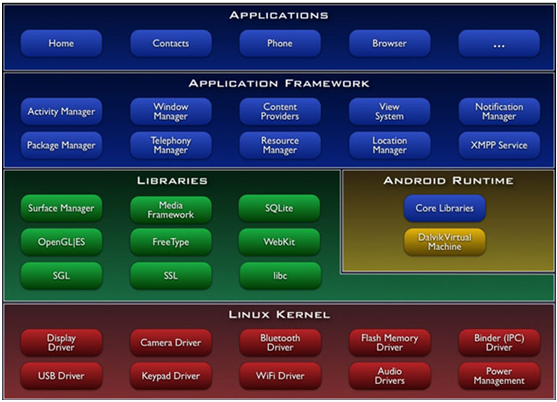
从Android的系统框架结构上看,我们这次要了解的是处于Application Framework层的View部分.
类层次关系
从类的层次关系上可以明显看到,ViewGroup是View的子类,而ListView和GridView则分别继承自AdapterView.
ViewGroup:
http://developer.android.com/reference/android/view/ViewGroup.html
A ViewGroup is a special view that can contain other views (called children.) The view group is the base class for layouts and views containers. This class also defines the ViewGroup.LayoutParams class which serves as the base class for layouts parameters.
Also see ViewGroup.LayoutParams for layout attributes.
顾名思义,ViewGroup是一个或者多个View的组合,它提供Layout服务,把多个View组合成一个复杂视图。
ViewGroup里面有一个重要的概念:Layout,定义其子视图的Layout。
Layout:
http://developer.android.com/guide/topics/ui/declaring-layout.html
A layout defines the visual structure for a user interface, such as the UI for an activity or app widget. You can declare a layout in two ways:
Declare UI elements in XML . Android provides a straightforward XML vocabulary that corresponds to the View classes and subclasses, such as those for widgets and layouts.
Instantiate layout elements at runtime . Your application can create View and ViewGroup objects (and manipulate their properties) programmatically.
Layout是一个定义UI控件的可视结构体,可以用XML声明或运行时实例化,下图展示了Layout和View之间的关系。
以下以最常用的LinearLayout作例子,描述Layout的本质,其它几种Layout本质也是一样,需要了解的朋友参阅相关资料即可:
http://developer.android.com/guide/topics/ui/layout/linear.html
LinearLayout is a view group that aligns all children in a single direction, vertically or horizontally. You can specify the layout direction with the android:orientation attribute.
请注意其描述中的:single direction,这个就是LinearLayout所遵循的规则和限制。
再对比Linear Layout和Relative Layout的差异,本质上是一样的,只是应用的场景不同。
根据上面的资料,我们不难得出ViewGroup和View之间的关系:
http://www.cnblogs.com/duguguiyu/archive/2010/03/27/1698515.html
通过上面的一系列的分析,我们基本知道了有关于Android中一个View的来龙去脉,接下来我们会对AdapterView和ListView进行一步的讲解。继承层次:
ListView继承自AdapterView的子类AbsListView,而且ListView跟GridView是兄弟关系。
AdapterView:
1,不管ListView,还是GridView,还是Gallery,它的本质是存储着一分表格形式的数据。而这份数据如何进行展现,根据指定的Adapter,它会呈现成列表,表格或图库的模式。
2,AdapterView有具体处理用户输入的能力,所以相应的它可以设置listener。
ListView:
从上面的分析中,继续往下解剖之后,剩下的事情很简单,就是ListView是一个使用了某一种Adapter的线性列表视图,只要指定具体的Adapter(如ArrayAdapter),就呈现出具体的样式。
看到这里,我相信大家会更明白,为什么ListView需要绑定一个Adapter;以及往后如果需要对类似的View进行扩展的时候,应该如何做。
引入childView:
由于每一个Layout,本身就是View的子类,所以,当我们需要指定自已的View,可以很简单的在xml里面指定一个layout,然后find它,把它转换成layout,然后把自定义的view加到layout里面,范例代码如下:
LayoutInflater inflater = (LayoutInflater) context
.getSystemService(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE);
View rowView = inflater.inflate(R.layout.list_analystics, parent, false);
DemoStatistics statistics = new DemoStatistics();
View subView = statistics.setData(context);
LinearLayout ly = (LinearLayout) rowView.findViewById(R.id.statistics);
ly.addView(subView);
return rowView;
}
相关的源代码在线查看资源有:
http://grepcode.com/file/repository.grepcode.com/java/ext/com.google.android/android/1.6_r2/android/widget/AdapterView.java?av=f
本文参考了大量的网上资料,因为比较多,不一一列出。





 本文深入解析Android开发中的ListView和GridView控件,详细解释它们的类层次关系、核心概念及其在系统框架中的作用。文章还介绍了如何通过XML声明或运行时实例化布局,并以LinearLayout为例展示布局的本质。此外,文章探讨了AdapterView与ListView的继承关系,解释了为何ListView需要绑定Adapter以及如何扩展View类。最后,提供了创建自定义View的方法和相关源代码链接。
本文深入解析Android开发中的ListView和GridView控件,详细解释它们的类层次关系、核心概念及其在系统框架中的作用。文章还介绍了如何通过XML声明或运行时实例化布局,并以LinearLayout为例展示布局的本质。此外,文章探讨了AdapterView与ListView的继承关系,解释了为何ListView需要绑定Adapter以及如何扩展View类。最后,提供了创建自定义View的方法和相关源代码链接。
















 652
652

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








