论文地址:Simple-BEV: What Really Matters for Multi-Sensor BEV Perception?
项目地址:https://github.com/aharley/simple_bev
阅读代码前的准备
1.环境搭建
# 虚拟环境中安装pytorch1.12+cuda11.3
conda install pytorch=1.12.0 torchvision=0.13.0 cudatoolkit=11.3 -c pytorch
# 下载相关依赖包
pip install -r requirements.txt2.预训练模型下载
# 下载camera-only的预训练模型
sh get_rgb_model.sh
# 下载camera-plus-radar的预训练模型
sh get_rad_model.sh3.准备nuScenes数据集
nuScenes
|---trainval
|---maps
|---samples
|---sweeps
|---v1.0-trainval 数据集的一些参数:
translation和rotation就是对应的平移和旋转关系
模型搭建与前向传播
先看一下README.md
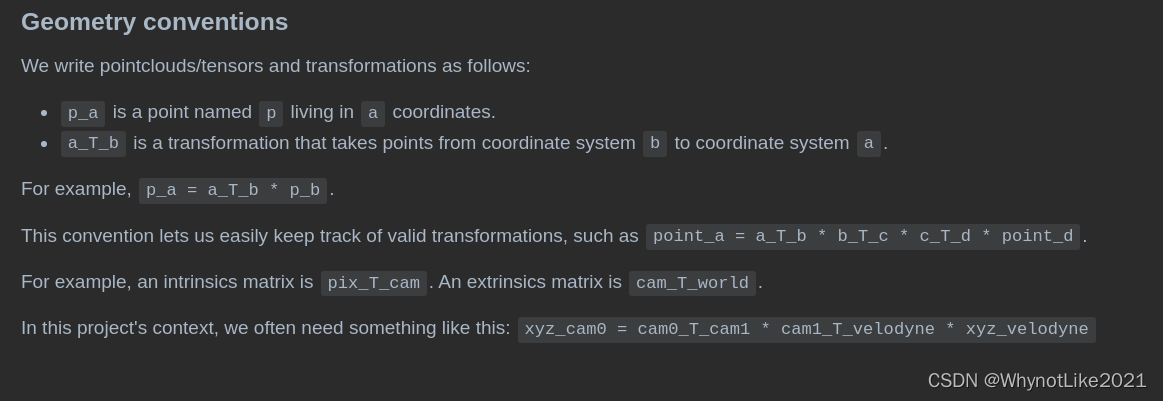
规定了一些变量命名标准, (最开始没看, 都有点看不懂一些变量的含义)
注意: pix_T_cam是内参矩阵(自车坐标系, 一般是以后轴中心为原点, 车头朝向为X轴)
顺便温习一下转置矩阵和逆矩阵
Segnet类初始化:
class Segnet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, Z, Y, X, vox_util=None,
use_radar=False,
use_lidar=False,
use_metaradar=False,
do_rgbcompress=True,
rand_flip=False,
latent_dim=128,
encoder_type="res101"):
super(Segnet, self).__init__()
assert (encoder_type in ["res101", "res50", "effb0", "effb4"])
self.Z, self.Y, self.X = Z, Y, X
self.use_radar = use_radar
self.use_lidar = use_lidar
self.use_metaradar = use_metaradar
self.do_rgbcompress = do_rgbcompress
self.rand_flip = rand_flip
self.latent_dim = latent_dim
self.encoder_type = encoder_type
self.mean = torch.as_tensor([0.485, 0.456, 0.406]).reshape(1,3,1,1).float().cuda()
self.std = torch.as_tensor([0.229, 0.224, 0.225]).reshape(1,3,1,1).float().cuda()
# Encoder
self.feat2d_dim = feat2d_dim = latent_dim
if encoder_type == "res101":
self.encoder = Encoder_res101(feat2d_dim)
elif encoder_type == "res50":
self.encoder = Encoder_res50(feat2d_dim)
elif encoder_type == "effb0":
self.encoder = Encoder_eff(feat2d_dim, version='b0')
else:
# effb4
self.encoder = Encoder_eff(feat2d_dim, version='b4')
# BEV compressor
if self.use_radar:
if self.use_metaradar:
self.bev_compressor = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(feat2d_dim*Y + 16*Y, feat2d_dim, kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=1, bias=False),
nn.InstanceNorm2d(latent_dim),
nn.GELU(),
)
else:
self.bev_compressor = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(feat2d_dim*Y+1, feat2d_dim, kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=1, bias=False),
nn.InstanceNorm2d(latent_dim),
nn.GELU(),
)
elif self.use_lidar:
self.bev_compressor = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(feat2d_dim*Y+Y, feat2d_dim, kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=1, bias=False),
nn.InstanceNorm2d(latent_dim),
nn.GELU(),
)
else:
if self.do_rgbcompress:
self.bev_compressor = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(feat2d_dim*Y, feat2d_dim, kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=1, bias=False),
nn.InstanceNorm2d(latent_dim),
nn.GELU(),
)
else:
# use simple sum
pass
# Decoder
self.decoder = Decoder(
in_channels=latent_dim,
n_classes=1,
predict_future_flow=False
)
# Weights
self.ce_weight = nn.Parameter(torch.tensor(0.0), requires_grad=True)
self.center_weight = nn.Parameter(torch.tensor(0.0), requires_grad=True)
self.offset_weight = nn.Parameter(torch.tensor(0.0), requires_grad=True)
# set_bn_momentum(self, 0.1)
if vox_util is not None:
self.xyz_memA = utils.basic.gridcloud3d(1, Z, Y, X, norm=False)
self.xyz_camA = vox_util.Mem2Ref(self.xyz_memA, Z, Y, X, assert_cube=False)
else:
self.xyz_camA = NoneSegnet类的前向传播过程:
关键部分进行了注释
主要涉及unproject_image_to_mem()函数方法, 下面根据论文的Architecture部分进行细读
def forward(self, rgb_camXs, pix_T_cams, cam0_T_camXs, vox_util, rad_occ_mem0=None):
'''
B = batch size, S = number of cameras, C = 3, H = img height, W = img width
rgb_camXs: (B,S,C,H,W)
pix_T_cams: (B,S,4,4)
cam0_T_camXs: (B,S,4,4)
vox_util: vox util object
rad_occ_mem0:
- None when use_radar = False, use_lidar = False
- (B, 1, Z, Y, X) when use_radar = True, use_metaradar = False
- (B, 16, Z, Y, X) when use_radar = True, use_metaradar = True
- (B, 1, Z, Y, X) when use_lidar = True
'''
B, S, C, H, W = rgb_camXs.shape # 输出是(1, 6, 3, 448, 800)
assert(C==3)
# reshape tensors
__p = lambda x: utils.basic.pack_seqdim(x, B)
__u = lambda x: utils.basic.unpack_seqdim(x, B)
rgb_camXs_ = __p(rgb_camXs) # 输出是(6, 3, 448, 800)
pix_T_cams_ = __p(pix_T_cams) # 输出是(6, 4, 4)
cam0_T_camXs_ = __p(cam0_T_camXs) # 输出是(6, 4, 4)
# 对cam0_T_camXs_求逆,形状不变
camXs_T_cam0_ = utils.geom.safe_inverse(cam0_T_camXs_)
# rgb encoder
device = rgb_camXs_.device
rgb_camXs_ = (rgb_camXs_ + 0.5 - self.mean.to(device)) / self.std.to(device)
if self.rand_flip:
B0, _, _, _ = rgb_camXs_.shape
self.rgb_flip_index = np.random.choice([0,1], B0).astype(bool)
rgb_camXs_[self.rgb_flip_index] = torch.flip(rgb_camXs_[self.rgb_flip_index], [-1])
feat_camXs_ = self.encoder(rgb_camXs_) # 输出是(6, 128, 56, 100)
if self.rand_flip:
feat_camXs_[self.rgb_flip_index] = torch.flip(feat_camXs_[self.rgb_flip_index], [-1])
_, C, Hf, Wf = feat_camXs_.shape
sy = Hf/float(H)
sx = Wf/float(W)
Z, Y, X = self.Z, self.Y, self.X
# unproject image feature to 3d grid
featpix_T_cams_ = utils.geom.scale_intrinsics(pix_T_cams_, sx, sy) # 输出是(6, 4, 4)
if self.xyz_camA is not None:
xyz_camA = self.xyz_camA.to(feat_camXs_.device).repeat(B*S,1,1) # 输出是(6, 320000, 3)
else:
xyz_camA = None
feat_mems_ = vox_util.unproject_image_to_mem(
feat_camXs_,
utils.basic.matmul2(featpix_T_cams_, camXs_T_cam0_),
camXs_T_cam0_, Z, Y, X,
xyz_camA=xyz_camA) # 输出是(6, 128, 200, 8, 200)
feat_mems = __u(feat_mems_) # B, S, C, Z, Y, X (1, 6, 128, 200, 8, 200)
mask_mems = (torch.abs(feat_mems) > 0).float()
feat_mem = utils.basic.reduce_masked_mean(feat_mems, mask_mems, dim=1) # B, C, Z, Y, X
if self.rand_flip:
self.bev_flip1_index = np.random.choice([0,1], B).astype(bool)
self.bev_flip2_index = np.random.choice([0,1], B).astype(bool)
feat_mem[self.bev_flip1_index] = torch.flip(feat_mem[self.bev_flip1_index], [-1])
feat_mem[self.bev_flip2_index] = torch.flip(feat_mem[self.bev_flip2_index], [-3])
if rad_occ_mem0 is not None:
rad_occ_mem0[self.bev_flip1_index] = torch.flip(rad_occ_mem0[self.bev_flip1_index], [-1])
rad_occ_mem0[self.bev_flip2_index] = torch.flip(rad_occ_mem0[self.bev_flip2_index], [-3])
# bev compressing
if self.use_radar:
assert(rad_occ_mem0 is not None)
if not self.use_metaradar:
feat_bev_ = feat_mem.permute(0, 1, 3, 2, 4).reshape(B, self.feat2d_dim*Y, Z, X)
rad_bev = torch.sum(rad_occ_mem0, 3).clamp(0,1) # squish the vertical dim
feat_bev_ = torch.cat([feat_bev_, rad_bev], dim=1)
feat_bev = self.bev_compressor(feat_bev_)
else:
feat_bev_ = feat_mem.permute(0, 1, 3, 2, 4).reshape(B, self.feat2d_dim*Y, Z, X)
rad_bev_ = rad_occ_mem0.permute(0, 1, 3, 2, 4).reshape(B, 16*Y, Z, X)
feat_bev_ = torch.cat([feat_bev_, rad_bev_], dim=1)
feat_bev = self.bev_compressor(feat_bev_)
elif self.use_lidar:
assert(rad_occ_mem0 is not None)
feat_bev_ = feat_mem.permute(0, 1, 3, 2, 4).reshape(B, self.feat2d_dim*Y, Z, X)
rad_bev_ = rad_occ_mem0.permute(0, 1, 3, 2, 4).reshape(B, Y, Z, X)
feat_bev_ = torch.cat([feat_bev_, rad_bev_], dim=1)
feat_bev = self.bev_compressor(feat_bev_)
else: # rgb only
if self.do_rgbcompress:
feat_bev_ = feat_mem.permute(0, 1, 3, 2, 4).reshape(B, self.feat2d_dim*Y, Z, X) # 输出是(1, 1024, 200, 200)
feat_bev = self.bev_compressor(feat_bev_) # 输出是(1, 128, 200, 200)
else:
feat_bev = torch.sum(feat_mem, dim=3)
# bev decoder
# 得到{dict:6}
out_dict = self.decoder(feat_bev, (self.bev_flip1_index, self.bev_flip2_index) if self.rand_flip else None)
raw_e = out_dict['raw_feat']
feat_e = out_dict['feat']
seg_e = out_dict['segmentation']
center_e = out_dict['instance_center']
offset_e = out_dict['instance_offset']
return raw_e, feat_e, seg_e, center_e, offset_e论文Architecture部分:
1. 利用ResNet-101骨干网提取特征, 输入(H, W)=(448, 800)
2. 对最后一层输出进行上采样, 并将其与第三层输出连接起来, 并应用两个具有实例归一化和ReLU激活的卷积层, 得到特征图, 形状为C*(H/8)*(W/8)
class Encoder_res101(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, C):
super().__init__()
self.C = C # self.C=128,在Segnet类中初始化定义
resnet = torchvision.models.resnet101(pretrained=True)
# 这里应该是拿出resnet101的前三层, 作为self.backbone
self.backbone = nn.Sequential(*list(resnet.children())[:-4])
# 这里是resnet101的最后一层
self.layer3 = resnet.layer3
self.depth_layer = nn.Conv2d(512, self.C, kernel_size=1, padding=0)
# 这里的1536是x1与x2拼接起来,1024+512=1536
self.upsampling_layer = UpsamplingConcat(1536, 512)
def forward(self, x):
# 传入self.backbone得到第三层的输出
x1 = self.backbone(x) # 输出是(6, 512, 56, 100)
# 将x1传入self.layer3得到最后一层的输出
x2 = self.layer3(x1) # 输出是(6, 1024, 28, 50)
x = self.upsampling_layer(x2, x1) # 输出是(6, 512, 56, 100)
x = self.depth_layer(x) # 输出是(6, 128, 56, 100)
return x
class UpsamplingConcat(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, scale_factor=2):
super().__init__()
self.upsample = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=scale_factor, mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
# 两个具有实例归一化和ReLU激活的卷积层
self.conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.InstanceNorm2d(out_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(out_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.InstanceNorm2d(out_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
)
def forward(self, x_to_upsample, x):
x_to_upsample = self.upsample(x_to_upsample)
# 上采样之后的拼接操作
x_to_upsample = torch.cat([x, x_to_upsample], dim=1) # 输出是(6, 1536, 56, 100)
return self.conv(x_to_upsample)3. 将预定义的3D坐标volume投影到所有特征图中, 并对特征进行双线性采样, 从而从每个相机中生成3D特征volume, 然后通过判断3D坐标是否落在相机视锥内, 来同时计算每个相机的二进制"有效"volume
def unproject_image_to_mem(self, rgb_camB, pixB_T_camA, camB_T_camA, Z, Y, X, assert_cube=False, xyz_camA=None):
# rgb_camB is B x C x H x W
# pixB_T_camA is B x 4 x 4
# rgb lives in B pixel coords
# we want everything in A memory coords
# this puts each C-dim pixel in the rgb_camB
# along a ray in the voxelgrid
B, C, H, W = list(rgb_camB.shape)
if xyz_camA is None:
xyz_memA = utils.basic.gridcloud3d(B, Z, Y, X, norm=False, device=pixB_T_camA.device)
xyz_camA = self.Mem2Ref(xyz_memA, Z, Y, X, assert_cube=assert_cube)
xyz_camB = utils.geom.apply_4x4(camB_T_camA, xyz_camA) # 输出是(6, 320000, 3)
z = xyz_camB[:,:,2]
xyz_pixB = utils.geom.apply_4x4(pixB_T_camA, xyz_camA) # 输出是(6, 320000, 3)
normalizer = torch.unsqueeze(xyz_pixB[:,:,2], 2) # 输出是(6, 320000, 1)
EPS=1e-6
# z = xyz_pixB[:,:,2]
xy_pixB = xyz_pixB[:,:,:2]/torch.clamp(normalizer, min=EPS) # 输出是(6, 320000, 2)
# this is B x N x 2
# this is the (floating point) pixel coordinate of each voxel
x, y = xy_pixB[:,:,0], xy_pixB[:,:,1]
# these are B x N
x_valid = (x>-0.5).bool() & (x<float(W-0.5)).bool()
y_valid = (y>-0.5).bool() & (y<float(H-0.5)).bool()
z_valid = (z>0.0).bool()
valid_mem = (x_valid & y_valid & z_valid).reshape(B, 1, Z, Y, X).float() # 输出是(6, 1, 200, 8, 200)
if (0):
# handwritten version
values = torch.zeros([B, C, Z*Y*X], dtype=torch.float32)
for b in list(range(B)):
values[b] = utils.samp.bilinear_sample_single(rgb_camB[b], x_pixB[b], y_pixB[b])
else:
# native pytorch version
y_pixB, x_pixB = utils.basic.normalize_grid2d(y, x, H, W)
# since we want a 3d output, we need 5d tensors
z_pixB = torch.zeros_like(x)
xyz_pixB = torch.stack([x_pixB, y_pixB, z_pixB], axis=2) # 输出是(6, 320000, 3)
rgb_camB = rgb_camB.unsqueeze(2)
xyz_pixB = torch.reshape(xyz_pixB, [B, Z, Y, X, 3]) # 输出是(6, 200, 8, 200, 3)
values = F.grid_sample(rgb_camB, xyz_pixB, align_corners=False) # 输出是(6, 128, 200, 8, 200)
values = torch.reshape(values, (B, C, Z, Y, X)) # 输出是(6, 128, 200, 8, 200)
values = values * valid_mem
return values4. 在volume集合上取一个有效的加权平均值, 将表示简化为单个3Dvolume的特征, 形状为C*Z*Y*X
def reduce_masked_mean(x, mask, dim=None, keepdim=False):
# x and mask are the same shape, or at least broadcastably so < actually it's safer if you disallow broadcasting
# returns shape-1
# axis can be a list of axes
for (a,b) in zip(x.size(), mask.size()):
# if not b==1:
assert(a==b) # some shape mismatch!
# assert(x.size() == mask.size())
prod = x*mask # 输出是(1, 6, 128, 200, 8, 200)
if dim is None: # dim=1
numer = torch.sum(prod)
denom = EPS+torch.sum(mask)
else:
numer = torch.sum(prod, dim=dim, keepdim=keepdim) # 输出是(1, 128, 200, 8, 200)
denom = EPS+torch.sum(mask, dim=dim, keepdim=keepdim) # 输出是(1, 128, 200, 8, 200)
mean = numer/denom # 输出是(1, 128, 200, 8, 200)
return mean5. 重新排列3D特征volume尺寸, C*X*Y*X -> (CxY)*Z*X, 生成高维BEV特征图, 将RGB特征和雷达特征连接, 并应用3*3卷积核压缩CxY维
self.bev_compressor = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(feat2d_dim*Y, feat2d_dim, kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=1, bias=False),
nn.InstanceNorm2d(latent_dim),
nn.GELU(),
)
feat_bev_ = feat_mem.permute(0, 1, 3, 2, 4).reshape(B, self.feat2d_dim*Y, Z, X) # 输出是(1, 1024, 200, 200)
feat_bev = self.bev_compressor(feat_bev_) # 输出是(1, 128, 200, 200)6. 使用Resnet-18的三个模块处理BEV特征, 生成三个特征图, 然后使用具有双线性上采样的加性跳跃连接, 最后应用特征任务的头
class Decoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, n_classes, predict_future_flow):
super().__init__()
backbone = resnet18(pretrained=False, zero_init_residual=True)
self.first_conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3, bias=False)
self.bn1 = backbone.bn1
self.relu = backbone.relu
self.layer1 = backbone.layer1
self.layer2 = backbone.layer2
self.layer3 = backbone.layer3
self.predict_future_flow = predict_future_flow
shared_out_channels = in_channels
self.up3_skip = UpsamplingAdd(256, 128, scale_factor=2)
self.up2_skip = UpsamplingAdd(128, 64, scale_factor=2)
self.up1_skip = UpsamplingAdd(64, shared_out_channels, scale_factor=2)
self.feat_head = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(shared_out_channels, shared_out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.InstanceNorm2d(shared_out_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(shared_out_channels, shared_out_channels, kernel_size=1, padding=0),
)
self.segmentation_head = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(shared_out_channels, shared_out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.InstanceNorm2d(shared_out_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(shared_out_channels, n_classes, kernel_size=1, padding=0),
)
self.instance_offset_head = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(shared_out_channels, shared_out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.InstanceNorm2d(shared_out_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(shared_out_channels, 2, kernel_size=1, padding=0),
)
self.instance_center_head = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(shared_out_channels, shared_out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.InstanceNorm2d(shared_out_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(shared_out_channels, 1, kernel_size=1, padding=0),
nn.Sigmoid(),
)
if self.predict_future_flow:
self.instance_future_head = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(shared_out_channels, shared_out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.InstanceNorm2d(shared_out_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(shared_out_channels, 2, kernel_size=1, padding=0),
)
def forward(self, x, bev_flip_indices=None):
b, c, h, w = x.shape
# (H, W)
skip_x = {'1': x}
x = self.first_conv(x) # 输出是(1, 64, 100, 100)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
# (H/4, W/4)
x = self.layer1(x) # 输出是(1, 64, 100, 100)
skip_x['2'] = x
x = self.layer2(x) # 输出是(1, 128, 50, 50)
skip_x['3'] = x
# (H/8, W/8)
x = self.layer3(x) # 输出是(1, 256, 25, 25)
# First upsample to (H/4, W/4)
x = self.up3_skip(x, skip_x['3']) # 输出是(1, 128, 50, 50)
# Second upsample to (H/2, W/2)
x = self.up2_skip(x, skip_x['2']) # 输出是(1, 64, 100, 100)
# Third upsample to (H, W)
x = self.up1_skip(x, skip_x['1']) # 输出是(1, 128, 200, 200)
if bev_flip_indices is not None:
bev_flip1_index, bev_flip2_index = bev_flip_indices
x[bev_flip2_index] = torch.flip(x[bev_flip2_index], [-2]) # note [-2] instead of [-3], since Y is gone now
x[bev_flip1_index] = torch.flip(x[bev_flip1_index], [-1])
feat_output = self.feat_head(x) # 输出是(1, 128, 200, 200)
segmentation_output = self.segmentation_head(x) # 输出是(1, 1, 200, 200)
instance_center_output = self.instance_center_head(x) # 输出是(1, 1, 200, 200)
instance_offset_output = self.instance_offset_head(x) # 输出是(1, 2, 200, 200)
instance_future_output = self.instance_future_head(x) if self.predict_future_flow else None
return {
'raw_feat': x,
'feat': feat_output.view(b, *feat_output.shape[1:]),
'segmentation': segmentation_output.view(b, *segmentation_output.shape[1:]),
'instance_center': instance_center_output.view(b, *instance_center_output.shape[1:]),
'instance_offset': instance_offset_output.view(b, *instance_offset_output.shape[1:]),
'instance_flow': instance_future_output.view(b, *instance_future_output.shape[1:])
if instance_future_output is not None else None,
}
class UpsamplingAdd(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, scale_factor=2):
super().__init__()
self.upsample_layer = nn.Sequential(
nn.Upsample(scale_factor=scale_factor, mode='bilinear', align_corners=False),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.InstanceNorm2d(out_channels),
)
def forward(self, x, x_skip):
x = self.upsample_layer(x)
return x + x_skip



 该文介绍了一个用于多传感器BEV感知的模型Simple-BEV,它结合了摄像头和雷达数据。模型首先通过ResNet提取特征,然后通过上采样和卷积层压缩特征。接着,将不同传感器的数据融合并压缩到BEV表示。在nuScenes数据集上进行训练,适用于自动驾驶场景的理解。
该文介绍了一个用于多传感器BEV感知的模型Simple-BEV,它结合了摄像头和雷达数据。模型首先通过ResNet提取特征,然后通过上采样和卷积层压缩特征。接着,将不同传感器的数据融合并压缩到BEV表示。在nuScenes数据集上进行训练,适用于自动驾驶场景的理解。
















 2090
2090










