 看见数据范围知,只能使用小于(nlogn)的算法。
看见数据范围知,只能使用小于(nlogn)的算法。
询问x到y的最大载重,意思为从x到y开车,这条路径需要在所有从x到y的路径中的最小值,让最小值最大,考虑生成最大树,从已知相连接的两点之间,只选择路径最大的那条,生成一棵树,那么从x到y,就算绕路走,也走最大的那唯一的一条路。
目前有prim(时间复杂度mlogn)和kru(时间复杂度mlogm)两种算法生成最大树。(m为边的数量,n为点的数量),不知道为啥这题选kru?我也不知道
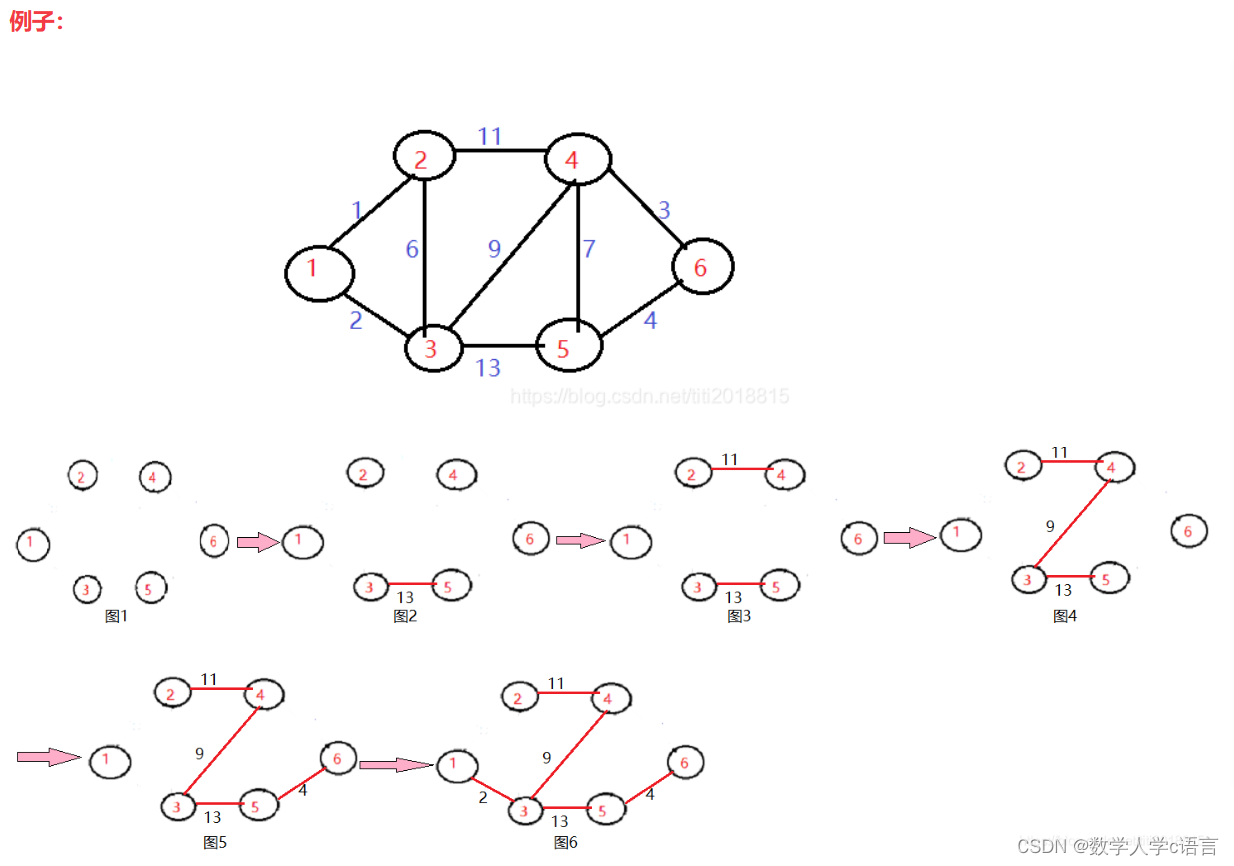 生成最大树后,如果查询q次最大承载力,暴力的算法可能复杂度达到qn,所以使用LCA优化寻找速度,例如查(1,2**10+2)的最大承载力,可以先查(1,2**10)再查(2**10,2**10+2)。
生成最大树后,如果查询q次最大承载力,暴力的算法可能复杂度达到qn,所以使用LCA优化寻找速度,例如查(1,2**10+2)的最大承载力,可以先查(1,2**10)再查(2**10,2**10+2)。
洛谷可以ac,acwing报错。
from collections import defaultdict, deque
class trie:
def __init__(self, value):
self.v = []
for i in range(n+1):
self.v.append(i)
self.edge = defaultdict(dict)
self.leth = value
self.f = [ [0]*20 for _ in range(n+1) ]
self.w = [ [0]*20 for _ in range(n+1) ]
self.d = [0]*(n+1)
def add_path(self, x, y, w):
x1 = self.find_father(x)
y1 = self.find_father(y)
if x1 != y1:
self.leth -= 1
self.v[x1] = y1
self.edge[x][y] = w
self.edge[y][x] = w
if not self.leth:
return True
def find_father(self, x):
if self.v[x] == x:
return x
self.v[x] = self.find_father(self.v[x])
return self.v[x]
def create(self):
self.vis = [0]*(n+1)
for i in range(1, n+1):
if self.vis[i] == 0:
self.dfs(i,0)
def dfs(self, now, fa):
self.vis[now] = 1
self.f[now][0] = fa
if fa == 0:
self.w[now][0] = float('inf')
else:
self.w[now][0] = self.edge[now][fa]
self.d[now] = self.d[fa] + 1
for i in range(1, 20):
self.f[now][i] = self.f[self.f[now][i-1]][i-1]
self.w[now][i] = min( self.w[now][i-1], self.w[ self.f[now][i-1] ][i-1] )
for nex in self.edge[now]:
if nex == fa :continue
self.dfs(nex, now)
def lca(self, x, y):
x1 = self.find_father(x)
y1 = self.find_father(y)
if x1 != y1:
return -1
dx, dy = self.d[x], self.d[y]
ans = float('inf')
# 让x更深
if dx < dy:
dx, dy = dy, dx
x, y = y, x
# x向上跑到与y相同深度
for i in range(19, -1, -1):
if self.d[self.f[x][i]] >= dy:
ans = min(ans, self.w[x][i])
x = self.f[x][i]
if x == y: return ans
# x,y同时跑到lca下面两个节点
for i in range(19, -1, -1):
if self.f[x][i] != self.f[y][i]:
ans = min(ans, self.w[x][i], self.w[y][i])
x, y = self.f[x][i], self.f[y][i]
ans = min(ans, self.w[x][0], self.w[y][0])
return ans
n, m = map(int,input().split())
dic = defaultdict(dict)
v1 = []
for idx in range(m):
x, y, z = map(int,input().split())
v1.append([z,x,y])
v1.sort(reverse = True)
root = trie(n-1)
for w, x, y in v1:
if root.add_path(x, y, w):
break
# LCA
root.create()
# questions
q = int(input())
for _ in range(q):
x, y = map(int,input().split())
print(root.lca(x, y))







 文章介绍了如何使用Prim算法和Kruskal算法生成最大树,以解决查询路径最大承载力的问题。通过LCA优化,查询效率大大提高。Trie结构用于存储和操作数据,有助于降低查询复杂度。
文章介绍了如何使用Prim算法和Kruskal算法生成最大树,以解决查询路径最大承载力的问题。通过LCA优化,查询效率大大提高。Trie结构用于存储和操作数据,有助于降低查询复杂度。
















 1269
1269

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








