Arc of Dream
Time Limit: 2000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65535/65535 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 1542 Accepted Submission(s): 517
Problem Description
An Arc of Dream is a curve defined by following function:
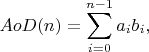
where
a0 = A0
ai = ai-1*AX+AY
b0 = B0
bi = bi-1*BX+BY
What is the value of AoD(N) modulo 1,000,000,007?
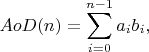
where
a0 = A0
ai = ai-1*AX+AY
b0 = B0
bi = bi-1*BX+BY
What is the value of AoD(N) modulo 1,000,000,007?
Input
There are multiple test cases. Process to the End of File.
Each test case contains 7 nonnegative integers as follows:
N
A0 AX AY
B0 BX BY
N is no more than 1018, and all the other integers are no more than 2×109.
Each test case contains 7 nonnegative integers as follows:
N
A0 AX AY
B0 BX BY
N is no more than 1018, and all the other integers are no more than 2×109.
Output
For each test case, output AoD(N) modulo 1,000,000,007.
Sample Input
1 1 2 3 4 5 6 2 1 2 3 4 5 6 3 1 2 3 4 5 6
Sample Output
4 134 1902构造矩阵,上图: AC代码:
AC代码:#include <iostream> #include <cmath> #include <cstdlib> #include <cstring> #include <cstdio> #include <queue> #include <stack> #include <ctime> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> #define ll __int64 #define L(rt) (rt<<1) #define R(rt) (rt<<1|1) using namespace std; const int INF = 2000000000; const int maxn = 7; const int mod = 1e9+7; struct Mat { ll mat[maxn][maxn]; void zero() { memset(mat, 0, sizeof(mat)); } void unit() { zero(); for(int i = 0; i < maxn; i++) mat[i][i] = 1; } } A, T; ll n, A0, B0, AX, BX, AY, BY; Mat operator * (const Mat &a, const Mat &b) { Mat tmp; for(int i = 0; i < maxn; i++) for(int j = 0; j < maxn; j++) { ll sum = 0; for(int k = 0; k < maxn; k++) sum += a.mat[i][k] * b.mat[k][j] % mod; tmp.mat[i][j] = sum % mod; } return tmp; } Mat operator ^ (Mat x, ll n) { Mat tmp; tmp.unit(); while(n) { if(n & 1) tmp = tmp * x; x = x * x; n >>= 1; } return tmp; } void init(){ A.zero(); A.mat[0][0] = A0 * B0 % mod, A.mat[1][0] = A0 % mod, A.mat[2][0] = B0 % mod; A.mat[3][0] = AY * BY % mod, A.mat[4][0] = AY % mod, A.mat[5][0] = BY % mod, A.mat[6][0] = 0; T.zero(); T.mat[0][0] = AX * BX % mod, T.mat[0][1] = AX * BY % mod, T.mat[0][2] = BX * AY % mod; T.mat[1][1] = AX % mod, T.mat[2][2] = BX % mod; for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++) T.mat[i][i + 3] = 1; for(int i = 3; i < maxn; i++) T.mat[i][i] = 1; T.mat[6][0] = 1; } int main() { while(cin>>n) { cin>>A0>>AX>>AY; cin>>B0>>BX>>BY; if(!n) { cout<<0<<endl; continue; } init(); Mat ans = (T ^ n) * A; cout<<ans.mat[6][0]<<endl; } return 0; }























 4669
4669

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








