前言
Jetson平台的GPU如果有足够的显存,,可以实现多个模型并发推理,并且推理时间相比推理单个模型不会有明显下降,任能保证较高的实时性。而目前类似像瑞芯微这样主流的NPU方案(如RK3588、RK3568等)在多模型并发推理方面,并不支持严格意义上的多模型同时计算(即真正的硬件并行)。
所以要完成真正意义上的多模型并发推理,还是选择GPU作为推理平台。
本文选择Jetson的orin nx 16g作为并发推理测试平台,这个显存主够并发推理四个量化为FP16/INT8的Yolo模型。
(除了Jetson,本文的流程与代码也适用于带Nvidia GPU的电脑)
准备工作
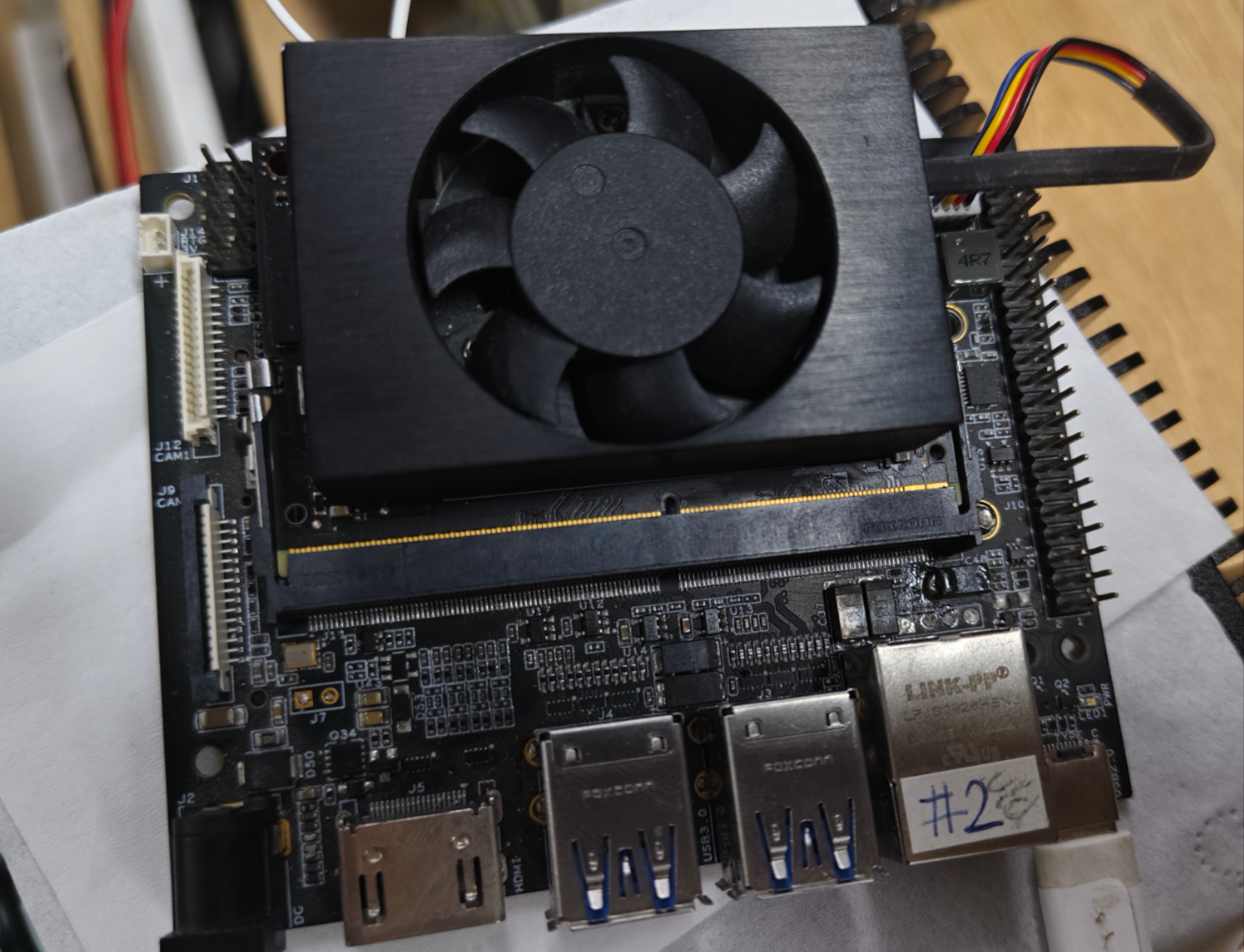
首先就是要准备一个带Nvidia GPU的设备,本文的硬件平台如下:
https://jp.seeedstudio.com/reComputer-J4012-w-o-power-adapter-p-5628.html

如果是jetson的话,预装的Jetpack上都会自带CUDA、Tensorrt、Opencv等用于加速推理Yolo的工具。
还需要我们手动安pycuda,终端输入:
sudo apt-get install python3-pip
pip3 install Cython
pip3 install pycuda --user
接下来把需要推理的.onnx模型转为Tensorrt的.engine格式,本文以yolov8n.onnx为例。一般安装好Tensorrt后,转换工具会在/usr/src/tensorrt/bin这个路径,搜索trtexec这个执行文件就能看到。
以量化为FP16为例,生成静态batch size的engine
./trtexec --onnx=<onnx_file> \
--explicitBatch \
--saveEngine=<tensorRT_engine_file> \
--workspace=<size_in_megabytes> \
--fp16
其中,--workspace根据你的显存大小设置,可以是2048、4096 或更高。
--explicit_batch 批处理模式是指在模型构建阶段,明确指定每个输入张量的批次大小,及静态固定的输入张量。你可以在Netron上查看你的onnx模型是固定输入还是动态输入。
--onnx输入的onnx模型的路径。
-saveEngine输出engine文件的路径
--fp16可以替换为int8等其他精度
如果要生成动态batchsize的engine,静态输入的模型不要参考这个指令
./trtexec --onnx=<onnx_file> \
--minShapes=input:<shape_of_min_batch> \
--optShapes=input:<shape_of_opt_batch> \
--maxShapes=input:<shape_of_max_batch> \
--workspace=<size_in_megabytes> \
--saveEngine=<engine_file> \
--fp16
官方的yolov8预训练模型是静态输入。如果不知道.pt模型如何转为.onnx可以参考这篇文章
https://docs.pytorch.org/tutorials/beginner/onnx/export_simple_model_to_onnx_tutorial.html
转换后的onnx如果版本太高,想切换onnx文件的版本和其opset的版本,可以用这个脚本:
https://github.com/jjjadand/ONNX_Downgrade
本文选用两个yolov8-det和yolov8-pose,分别进行fp16和int8精度的量化,最后得到四个.engine,转换的过程必须要在你的部署设备上进行,因为加载.engine和转换得到engine的硬件环境需要严格一致。最终得到两个F16和两个INT8的Tensorrt格式模型:
实时并发推理四个YOLO
本文选用USB 摄像头作为输入,终端输入下面指令查看摄像头映射的设备名:
ls /dev/video*
查看摄像头支持的帧率和分辨率,以video设备为例:
sudo apt install v4l-utils
v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --list-formats-ext
把下面的代码配置改为符合你的摄像头的参数,以及输入的.engine文件名也需要修改为你的。
import cv2
import time
import numpy as np
import pycuda.autoinit
import pycuda.driver as cuda
import tensorrt as trt
# ==== 配置 ====
cam_width = 640
cam_len = 480
MODEL_INPUT_SIZE = 640
CONF_THRESHOLD = 0.3
CONF_THRESHOLD_POSE = 0.1
POSE_KPT_THRESHOLD = 0.2
NMS_THRESHOLD = 0.1
# now not enable, GStreamer 管道(针对 Jetson 优化),modify base on your camera
# gst_str = (
# "v4l2src device=/dev/video0 ! "
# "video/x-raw, width=640, height=480, framerate=30/1 ! "
# "videoconvert ! "
# "video/x-raw, format=BGR ! appsink"
# )
# 类别列表(检测用)
CLASSES = ["person", "bicycle", "car", "motorcycle", "airplane", "bus", "train", "truck",
"boat", "traffic light", "fire hydrant", "stop sign", "parking meter", "bench",
"bird", "cat", "dog", "horse", "sheep", "cow", "elephant", "bear", "zebra",
"giraffe", "backpack", "umbrella", "handbag", "tie", "suitcase", "frisbee",
"skis", "snowboard", "sports ball", "kite", "baseball bat", "baseball glove",
"skateboard", "surfboard", "tennis racket", "bottle", "wine glass", "cup",
"fork", "knife", "spoon", "bowl", "banana", "apple", "sandwich", "orange",
"broccoli", "carrot", "hot dog", "pizza", "donut", "cake", "chair", "couch",
"potted plant", "bed", "dining table", "toilet", "tv", "laptop", "mouse",
"remote", "keyboard", "cell phone", "microwave", "oven", "toaster", "sink",
"refrigerator", "book", "clock", "vase", "scissors", "teddy bear", "hair drier",
"toothbrush"]
COLORS = np.random.uniform(0, 255, size=(len(CLASSES), 3))
# COCO 姿态关键点连线(17 点)
SKELETON = [
(0,1),(0,2),(1,3),(2,4),
(5,6),(5,7),(7,9),(6,8),(8,10),
(5,11),(6,12),(11,12),(11,13),(13,15),(12,14),(14,16)
]
# ==== 工具函数 ====
def load_engine(path):
logger = trt.Logger(trt.Logger.WARNING)
with open(path, "rb") as f, trt.Runtime(logger) as rt:
return rt.deserialize_cuda_engine(f.read())
def allocate_buffers(engine):
inputs, outputs, bindings = [], [], []
stream = cuda.Stream()
for binding in engine:
shape = engine.get_binding_shape(binding)
size = trt.volume(shape)
dtype = trt.nptype(engine.get_binding_dtype(binding))
host_mem = cuda.pagelocked_empty(size, dtype)
device_mem = cuda.mem_alloc(host_mem.nbytes)
bindings.append(int(device_mem))
(inputs if engine.binding_is_input(binding) else outputs).append((host_mem, device_mem))
return inputs[0], outputs[0], bindings, stream
def preprocess(img):
h0, w0 = img.shape[:2]
r = min(MODEL_INPUT_SIZE/w0, MODEL_INPUT_SIZE/h0)
w, h = int(w0*r), int(h0*r)
resized = cv2.resize(img, (w,h), interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
padded = np.full((MODEL_INPUT_SIZE, MODEL_INPUT_SIZE,3), 114, dtype=np.uint8)
padded[:h,:w] = resized
blob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(padded, 1/255.0, (MODEL_INPUT_SIZE,MODEL_INPUT_SIZE), swapRB=False)
return padded, blob, {"scale": r, "original_shape": (h0,w0)}
# def postprocess_det(output, meta):
# # output: np.array (anchors,84)
# scale = meta["scale"]
# # 提取
# boxes = output[:, :4]
# scores = output[:,5:]
# cls_ids = np.argmax(scores, axis=1)
# confs = scores[np.arange(len(scores)), cls_ids]
# keep = confs>CONF_THRESHOLD
# boxes, confs, cls_ids = boxes[keep], confs[keep], cls_ids[keep]
# if boxes.shape[0]==0: return []
# # cx,cy,w,h → x1,y1,x2,y2
# cx,cy,w,h = boxes[:,0], boxes[:,1], boxes[:,2], boxes[:,3]
# x1 = ((cx - w/2)/scale).astype(int)
# y1 = ((cy - h/2)/scale).astype(int)
# x2 = ((cx + w/2)/scale).astype(int)
# y2 = ((cy + h/2)/scale).astype(int)
# xyxy = np.stack([x1,y1,x2,y2],axis=1)
# # NMS
# idxs = nms_numpy(xyxy, confs, NMS_THRESHOLD)
# return [(xyxy[i], confs[i], cls_ids[i]) for i in idxs]
def postprocess_det(output, meta):
h_orig, w_orig = meta["original_shape"]
scale = meta["scale"]
boxes_raw = output[:, :4] # (N, 4)
scores = output[:, 4:] # (N, num_classes), 4 or 5
#print("scores shape:", scores.shape)
#for i in range(5):
#print(f"cls{i} max score: {np.max(scores[:, i])}")
cls_ids = np.argmax(scores, axis=1) # (N,)
confs = scores[np.arange(len(output)), cls_ids]
keep = confs > CONF_THRESHOLD
boxes_raw = boxes_raw[keep]
confs = confs[keep]
cls_ids = cls_ids[keep]
if len(boxes_raw) == 0:
return []
# (cx,cy,w,h) -> (x1,y1,x2,y2),注意只考虑缩放,不补偿 padding
cx, cy, w, h = boxes_raw[:, 0], boxes_raw[:, 1], boxes_raw[:, 2], boxes_raw[:, 3]
x1 = ((cx - w / 2) / scale).astype(int)
y1 = ((cy - h / 2) / scale).astype(int)
x2 = ((cx + w / 2) / scale).astype(int)
y2 = ((cy + h / 2) / scale).astype(int)
boxes = np.stack([x1, y1, x2, y2], axis=1)
# NMS
indices = cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes(boxes.tolist(), confs.tolist(), CONF_THRESHOLD, NMS_THRESHOLD)
results = []
if len(indices) > 0:
for i in indices.flatten():
results.append((boxes[i], confs[i], cls_ids[i]))
return results
def nms_numpy(boxes, scores, iou_thres=0.5):
x1,y1,x2,y2 = boxes[:,0],boxes[:,1],boxes[:,2],boxes[:,3]
areas = (x2-x1)*(y2-y1)
order = scores.argsort()[::-1]
keep=[]
while order.size>0:
i = order[0]; keep.append(i)
if order.size==1: break
xx1 = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[order[1:]])
yy1 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[order[1:]])
xx2 = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[order[1:]])
yy2 = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[order[1:]])
w = np.maximum(0.0, xx2-xx1)
h = np.maximum(0.0, yy2-yy1)
inter = w*h
iou = inter/(areas[i]+areas[order[1:]]-inter)
inds = np.where(iou<=iou_thres)[0]
order = order[inds+1]
return keep
def postprocess_pose(output, meta):
"""
带 NMS 的 Vectorized CPU 后处理 YOLOv8-Pose 输出。
output: np.ndarray, shape (N, 5 + 3*K)
meta: dict, 包含 'scale'
返回: list of persons,每个是长度 K 的 (x,y) or None
"""
scale = meta["scale"]
N, C = output.shape
K = (C - 5) // 3
if N == 0:
return []
# --- 1. 提取 bbox 和 objectness ---
cx = output[:, 0]
cy = output[:, 1]
w = output[:, 2]
h = output[:, 3]
obj_conf = output[:, 4]
# 转成原图坐标的 x1,y1,x2,y2
x1 = (cx - w * 0.5) / scale
y1 = (cy - h * 0.5) / scale
x2 = (cx + w * 0.5) / scale
y2 = (cy + h * 0.5) / scale
boxes = np.stack([x1, y1, x2, y2], axis=1)
# --- 2. obj_conf 阈值过滤 ---
mask0 = obj_conf >= CONF_THRESHOLD_POSE
if not np.any(mask0):
return []
boxes = boxes[mask0]
scores = obj_conf[mask0]
selected = output[mask0] # shape = (M, 5+3K)
# --- 3. NMS 去重 ---
keep = nms_numpy(boxes, scores, iou_thres=NMS_THRESHOLD)
if len(keep) == 0:
return []
sel = selected[keep] # shape = (M2, 5+3K)
# --- 4. Vectorized 后处理关键点 ---
M2 = sel.shape[0]
kp = sel[:, 5:].reshape(M2, K, 3) # (M2, K, 3)
x_rel = kp[:, :, 0]
y_rel = kp[:, :, 1]
c_rel = kp[:, :, 2]
valid = c_rel >= POSE_KPT_THRESHOLD
xs = (x_rel / scale).astype(np.int32)
ys = (y_rel / scale).astype(np.int32)
xs[~valid] = -1
ys[~valid] = -1
# --- 5. 构造返回列表 ---
persons = [
[(int(xs[i, j]), int(ys[i, j])) if valid[i, j] else None
for j in range(K)]
for i in range(M2)
]
return persons
def main():
# 1. 加载4个 TRT 引擎
det_engine = load_engine("yolov8n.engine")
det2_engine = load_engine("yolov8n-int8.engine")
pose_engine= load_engine("yolov8n-pose.engine")
pose2_engine= load_engine("yolov8n-pose-int8.engine")
# 2. 创建上下文、缓冲
det_ctx = det_engine.create_execution_context()
det2_ctx = det_engine.create_execution_context()
pose_ctx = pose_engine.create_execution_context()
pose2_ctx = pose_engine.create_execution_context()
(h_din, d_din), (h_dout, d_dout), det_bind, det_stream = allocate_buffers(det_engine)
(h_din2, d_din2), (h_dout2, d_dout2), det2_bind, det2_stream = allocate_buffers(det2_engine)
(h_pin, d_pin), (h_pout, d_pout), pose_bind, pose_stream = allocate_buffers(pose_engine)
(h_pin2, d_pin2), (h_pout2, d_pout2), pose2_bind, pose2_stream = allocate_buffers(pose2_engine)
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
cap.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH, cam_width)
cap.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT, cam_len)
#cap = cv2.VideoCapture(gst_str, cv2.CAP_GSTREAMER)
if not cap.isOpened():
print("[ERROR] Camera pipeline failed to open. Check GStreamer string or camera device.")
while True:
ret, frame = cap.read()
if not ret: break
start_time = time.time() # ← 帧开始时间
# 预处理
start_pre = time.time() # ← pre开始时间
img_padded, blob, meta = preprocess(frame)
np.copyto(h_din, blob.ravel()); np.copyto(h_pin, blob.ravel())
np.copyto(h_din2, blob.ravel()); np.copyto(h_pin2, blob.ravel())
over_pre = time.time() #
print("pre time:", over_pre - start_pre)
# 4路并发推理
start_infer = time.time() # infer开始时间
cuda.memcpy_htod_async(d_din, h_din, det_stream)
det_ctx.execute_async_v2(det_bind, stream_handle=det_stream.handle)
cuda.memcpy_dtoh_async(h_dout, d_dout, det_stream)
cuda.memcpy_htod_async(d_pin, h_pin, pose_stream)
pose_ctx.execute_async_v2(pose_bind, stream_handle=pose_stream.handle)
cuda.memcpy_dtoh_async(h_pout, d_pout, pose_stream)
cuda.memcpy_htod_async(d_din2, h_din2, det2_stream)
det2_ctx.execute_async_v2(det2_bind, stream_handle=det2_stream.handle)
cuda.memcpy_dtoh_async(h_dout2, d_dout2, det2_stream)
cuda.memcpy_htod_async(d_pin2, h_pin2, pose2_stream)
pose2_ctx.execute_async_v2(pose2_bind, stream_handle=pose2_stream.handle)
cuda.memcpy_dtoh_async(h_pout2, d_pout2, pose2_stream)
det_stream.synchronize()
pose_stream.synchronize()
det2_stream.synchronize()
pose2_stream.synchronize()
over_infer = time.time() # ←
print("infer time:",over_infer - start_infer)
# 5. 解析结果
start_post = time.time() # ← post始时间
#det_model x2 post
anchors = h_dout.size // 84
det_out = h_dout.reshape(1,84,-1).transpose(0,2,1).squeeze(0)
anchors2 = h_dout2.size // 84
det2_out = h_dout2.reshape(1,84,-1).transpose(0,2,1).squeeze(0)
#print(det_out)
dets = postprocess_det(det_out, meta)
dets2 = postprocess_det(det2_out, meta)
#print(dets)
# 姿态x2 post
pose_ch = h_pout.size // anchors
pose_out= h_pout.reshape(1,pose_ch,-1).transpose(0,2,1).squeeze(0)
pose2_ch = h_pout.size // anchors
pose2_out= h_pout2.reshape(1,pose2_ch,-1).transpose(0,2,1).squeeze(0)
people = postprocess_pose(pose_out, meta)
people2 = postprocess_pose(pose2_out, meta)
# 6. 可视化:检测 + 姿态
# 6.1 检测框
for box, conf, cid in dets:
color = COLORS[cid]; x1,y1,x2,y2 = box
cv2.rectangle(frame, (x1,y1),(x2,y2), color, 2)
for box, conf, cid in dets:
color = COLORS[cid]; x1,y1,x2,y2 = box
cv2.rectangle(frame, (x1,y1),(x2,y2), color, 2)
# 6.2 姿态关键点 + 骨架
for pts in people:
# 画点
for p in pts:
if p: cv2.circle(frame, p, 3, (0,255,255), -1)
# 画连线
for i,j in SKELETON:
if pts[i] and pts[j]:
cv2.line(frame, pts[i], pts[j], (0,200,0), 2)
for pts in people2:
# 画点
for p in pts:
if p: cv2.circle(frame, p, 3, (0,155,155), -1)
# 画连线
for i,j in SKELETON:
if pts[i] and pts[j]:
cv2.line(frame, pts[i], pts[j], (100,100,0), 2)
over_post = time.time() #
print("post time:",over_post - start_post)
# === 计算 FPS ===
elapsed = time.time() - start_time
print("all time:",elapsed) #print all time
fps = 1.0 / elapsed if elapsed > 0 else 0
cv2.putText(frame, f"FPS: {fps:.2f}", (10, 25),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.75, (0, 255, 0), 2)
cv2.imshow("Det+Pose", frame)
if cv2.waitKey(1)&0xFF==ord("q"):
break
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
del det_ctx
del pose_ctx
del det2_ctx
del pose2_ctx
print("[INFO] All TensorRT contexts released.")
if __name__=="__main__":
main()
- 代码中注释了使用Gstreamer的方式读取摄像头,因为笔者测试后发现没有明显快于opencv默认的摄像头读取API。
- 代码是基于官方yolov8推理的,所以
CLASSES和SKELETON两个列表是根据yolo官方的预训数据练来写的, - 如果使用的是自行训练的yolo模型,你需要把这两个列表换位你训练的检测类别和骨架。
最后的测试结果为,在并发推理四个yolov8模型的情况下,算上预处理+推理+后处理的时间,帧率稳定在35帧左右。
如果只算推理时间的话,大概是50帧左右。
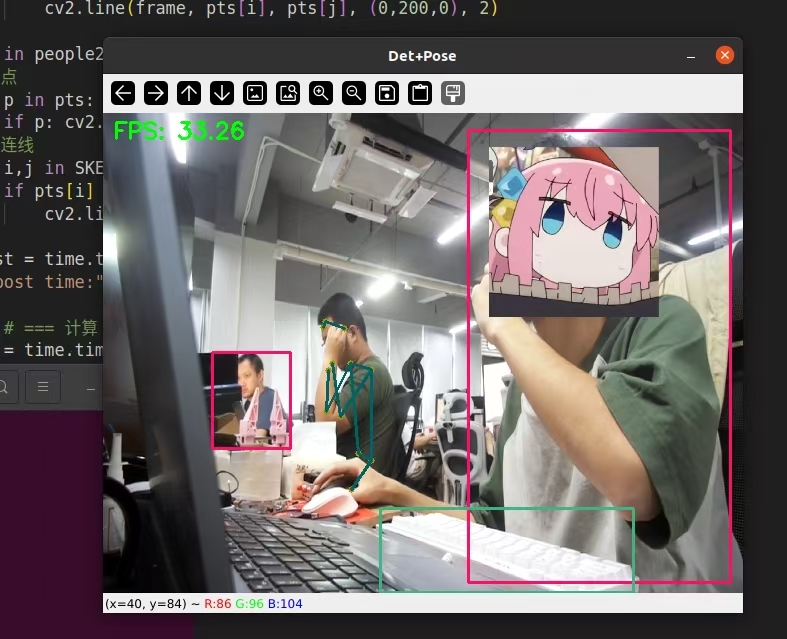
- 推理单个模型,算上预处理+推理+后处理帧率为80fps左右
- 注意,并发推理多个模型,需要有足够的显存,显存不够的话只能考虑量化模型,或者减少并发推理的模型数量。
小结
预处理和后处理在并发推理多个模型的时候,其实也会占用不少时间,如果不想自己手写CUDA算子在GPU上加速的话,也可以用numpy的SIMD在cpu上加速,但并发模型较多的情况下还是建议预处理和后处理用CUDA来写。





















 1591
1591

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








