- One tailed test
- Greater than type
- Less than type
- Two talied test
Not equal type:
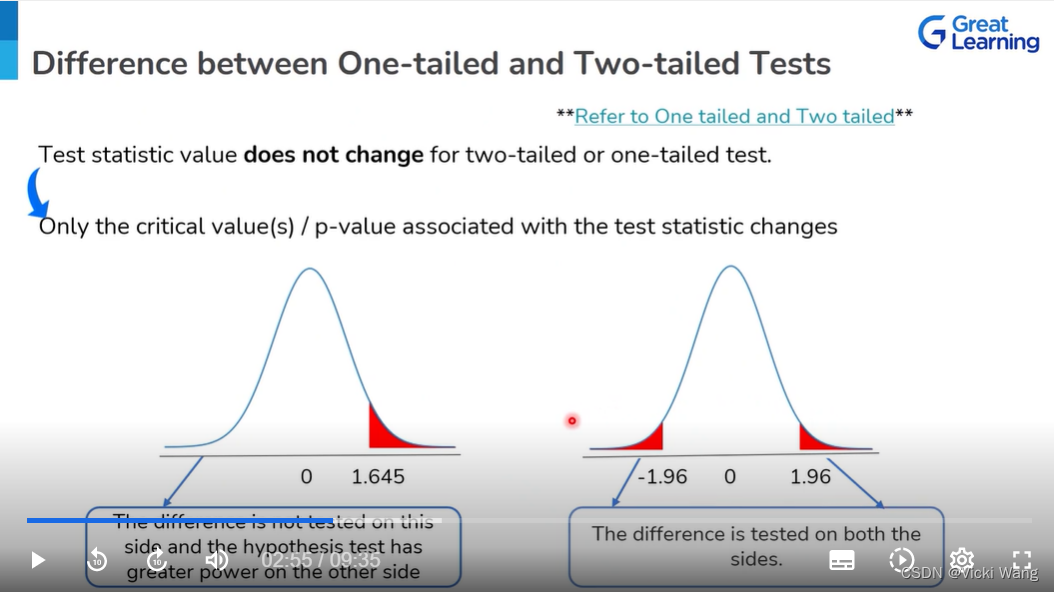
Difference between One-Tailed and Two-tailed Tests
Test statistic value does not change for two-tailed or one-tailed test.
Only the critical values/p-value associated with the test statistic changes
Example : one tailed and two-tailed
Suppose a soft-drink manufacturer's most selling product is 600ml coke with a standard deviation of 50ml.
A customer would like to test whether there is at least 600 ml coke in the bottle. He doubts that the amount of coke in the bottle is less than 600ml.
The null hypothesis formed by the customer is
The null hypothesis formed by the customer is
Against the alternative hypothesis
However the quality control team wants exactly 600ml coke in the bottle. The team wants to ensure that the amount of coke in the bottle is not different from 600ml.
The null hypothesis formed by the quality control team is
Against the alternative hypothesis
Thus the choice of one-sided vs two-sided alternative hypothesis depends on the nature of the problem
Two-tailed test example
Suppose you work on the quality control team of the company. It is known from experience that the mean amount of coke in a bottle is 600ml with a standard deviation of 50ml
You have collected 36 randomly sampled bottles. The mean amount of coke in the sample is 580ml.
You intend to test whether the amount of coke in the bottle s different from 600ml using 0.05 level of significance. Do you have enough Statistical evidence for it?
Hypothesis Test for Calculation Mean μ - Jupyter Notebook
Are the assumption of Z-test satisfied?
- Samples are drawn from a normal distribution - since the sample size is 36 (which is > 30), central limit theorem states that the distribution of sample means will be normal. If the sample size is less than 30, we would have been able to apply Z test on if we knew the population distribution was normal.
- Observations are from a sample random sample - we are informed that you have collected a simple random sample,
- Standard deviation is known - yes.
Voila! We can use Z test for this problem:





 本文对比了单尾和双尾检验的差异,强调了在不同情况下选择哪种检验取决于问题的性质。以软饮料公司为例,顾客怀疑瓶装可乐少于600ml,形成的是单尾检验的假设;而质量控制团队希望确保瓶装可乐精确为600ml,因此采用双尾检验。此外,文章通过一个案例展示了如何进行双尾检验的假设测试,以确定样本平均值与600ml的显著差异。
本文对比了单尾和双尾检验的差异,强调了在不同情况下选择哪种检验取决于问题的性质。以软饮料公司为例,顾客怀疑瓶装可乐少于600ml,形成的是单尾检验的假设;而质量控制团队希望确保瓶装可乐精确为600ml,因此采用双尾检验。此外,文章通过一个案例展示了如何进行双尾检验的假设测试,以确定样本平均值与600ml的显著差异。
















 1522
1522

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








