以下所有题解都参照了他人的解法,主要是灵神
图论
200. 岛屿数量(中等)

方法一、深度搜索
class Solution {
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
int n = grid.length,m = grid[0].length,res = 0;
int [][] visited = new int[n][m];
for(int i = 0; i < n;i++){
for(int j = 0;j < m;j++){
if(grid[i][j]== '1'){
DFS(grid,i,j);
res++;
}
}
}
return res;
}
public void DFS(char[][] grid,int x,int y){
if(x<0 || x >= grid.length || y < 0 || y >= grid[0].length || grid[x][y] == '0'){
return;
}
grid[x][y] = '0';
DFS(grid,x-1,y);
DFS(grid,x+1,y);
DFS(grid,x,y-1);
DFS(grid,x,y+1);
}
}方法二、广度搜索
class Solution {
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
int n = grid.length,m = grid[0].length,res = 0;
int [][] visited = new int[n][m];
for(int i = 0; i < n;i++){
for(int j = 0;j < m;j++){
if(grid[i][j]== '1'){
BFS(grid,i,j);
res++;
}
}
}
return res;
}
public void BFS(char[][] grid, int x, int y){
Deque<int[]> list = new LinkedList<>();
list.add(new int[]{x,y});
while(!list.isEmpty()){
int[] cur = list.remove();
x = cur[0];
y = cur[1];
if(x >=0 && x < grid.length && y >=0 && y < grid[0].length && grid[x][y] == '1'){
grid[x][y] = '0';
list.add(new int[]{x-1,y});
list.add(new int[]{x+1,y});
list.add(new int[]{x,y-1});
list.add(new int[]{x,y+1});
}
}
}
}994. 腐烂的橘子(中等)

方法一、广搜
一开始看成char数组了。。强调四个方向明显广搜
class Solution {
private static final int[][] dic={{-1,0},{1,0},{0,-1},{0,1}};
public int orangesRotting(int[][] grid) {
//bfs需要记录:新增的橘子数
int n = grid.length,m = grid[0].length,fresh = 0;
List<int[]> q = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){
for(int j = 0;j < m;j++){
if(grid[i][j] == 1)fresh++;
if(grid[i][j] == 2)q.add(new int[]{i,j});
}
}
int ans = 0;
while(!q.isEmpty() && fresh>0){
ans++;
List<int[]> tmp = q;
q = new ArrayList<>();
for(int[] pos : tmp){
for(int[] d : dic){
int x = pos[0] + d[0],y = pos[1] + d[1];
if(x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < m && grid[x][y] == 1){
grid[x][y] = 2;
fresh--;
q.add(new int[]{x,y});
}
}
}
}
return fresh == 0 ? ans : -1;
}
}207. 课程表(中等)
方法一、DFS
链表一条路走到黑所以是dfs,其实就是建图然后判断成环,这里的建有向图用了链表的方式,而不是矩阵。之所以不用之前快慢指针,是因为比较复杂,那个只适用于单条链表。中途出了一个比较大的问题,第一个for循环写成0-numCourses了,其实pre数组未必那么长
class Solution {
public boolean canFinish(int numCourses, int[][] prerequisites) {
int[] color = new int[numCourses];
List<Integer>[] map = new ArrayList[numCourses];
Arrays.setAll(map,i->new ArrayList<>());
for(int[] p : prerequisites){
map[p[1]].add(p[0]);//对于pre每个前置课程对应的链表,后面加
}
for(int i = 0;i < numCourses;i++){
if(DFS(i,map,color)){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public boolean DFS(int x,List<Integer>[] list,int[] color){
color[x] = 1;//访问中
for(int a : list[x]){
if(color[a] == 1 || (color[a] == 0 && DFS(a,list,color))){
return true;
};
}
color[x] = 2;//递归完了恢复现场
return false;
}
}
208. 实现 Trie (前缀树)(中等)

方法一、二十六叉树
主要难度是设计新的数据结构
class Node{
Node[] son = new Node[26];
boolean end;
}
class Trie {
private Node root;
public Trie() {
root = new Node();
root.end = true;
}
public void insert(String word) {
Node cur = root;
int n = word.length();
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){
int c = word.charAt(i)-'a';
if(cur.son[c] == null){
cur.son[c] = new Node();
}
cur = cur.son[c];
}
cur.end = true;
}
private int find(String word){
Node cur = root;
int n = word.length();
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){//遍历
int c = word.charAt(i)-'a';
if(cur.son[c] == null)return 0;
cur = cur.son[c];
}
if(cur.end){//正好结尾
return 2;
}else{
return 1;
}
}
public boolean search(String word) {
return find(word) == 2;
}
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
return find(prefix) > 0;
}
}碎碎念
之后就不每次都放复杂度了,除非两个方法性能差很多
①学会了方向数组,bfs更简洁
②学会了这种技巧
List<Integer>[] g = new ArrayList[numCourses];
Arrays.setAll(g, i -> new ArrayList<>());
作者:灵茶山艾府
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/course-schedule/solutions/2992884/san-se-biao-ji-fa-pythonjavacgojsrust-by-pll7/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。③一直感觉Deque模拟栈、linkedlist模拟队列很神奇,所以搜了搜
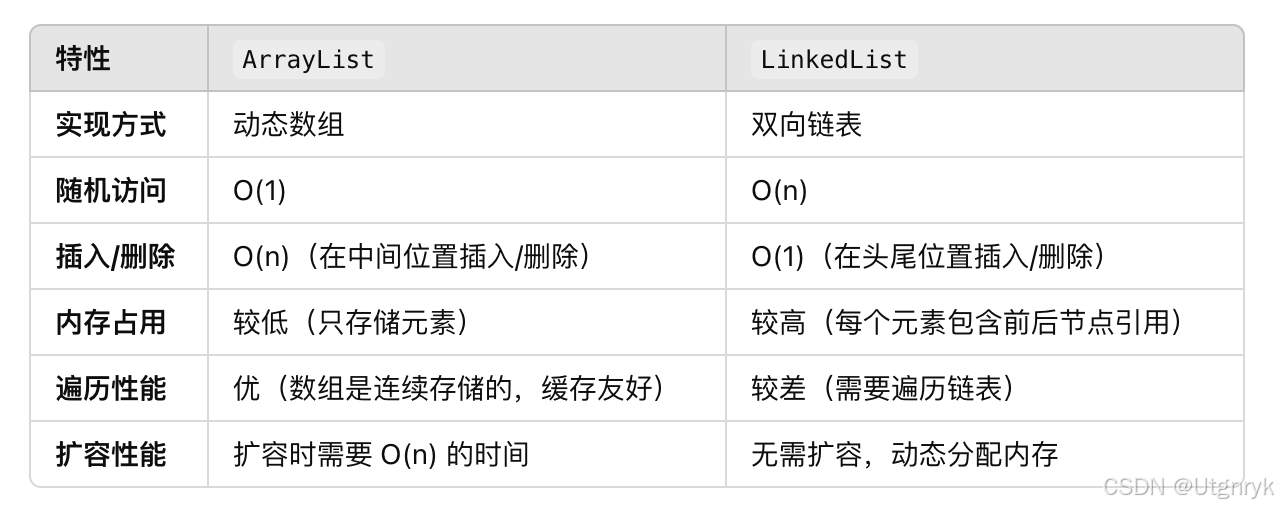
总结:deque更高效灵活,stack设计比较过时

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








