背景:Elasticsearch关联查询的核心挑战
Elasticsearch(ES)的倒排索引(Inverted Index)架构使其无法原生支持关系型数据库的JOIN操作
- 根本问题:倒排索引存储"词项→文档ID"映射,破坏对象边界(如博客与评论的1:N关系)
- 典型场景:
- 关系型数据库(如MySQL):通过
blog_id关联blog表和comment表 - ES默认行为:将嵌套对象存储为扁平化数组,导致跨对象错误匹配
// 错误存储结构(破坏对象边界) { "title": "ES Guide", "comments.username": ["Li", "Fox"], // 所有用户名合并 "comments.content": ["Great!", "Thanks"] }
- 关系型数据库(如MySQL):通过
要点
- ES关联查询需特殊方案弥补倒排索引缺陷
- 默认
object[]类型导致查询失真(如搜索"Li的含Thanks评论"返回错误结果)
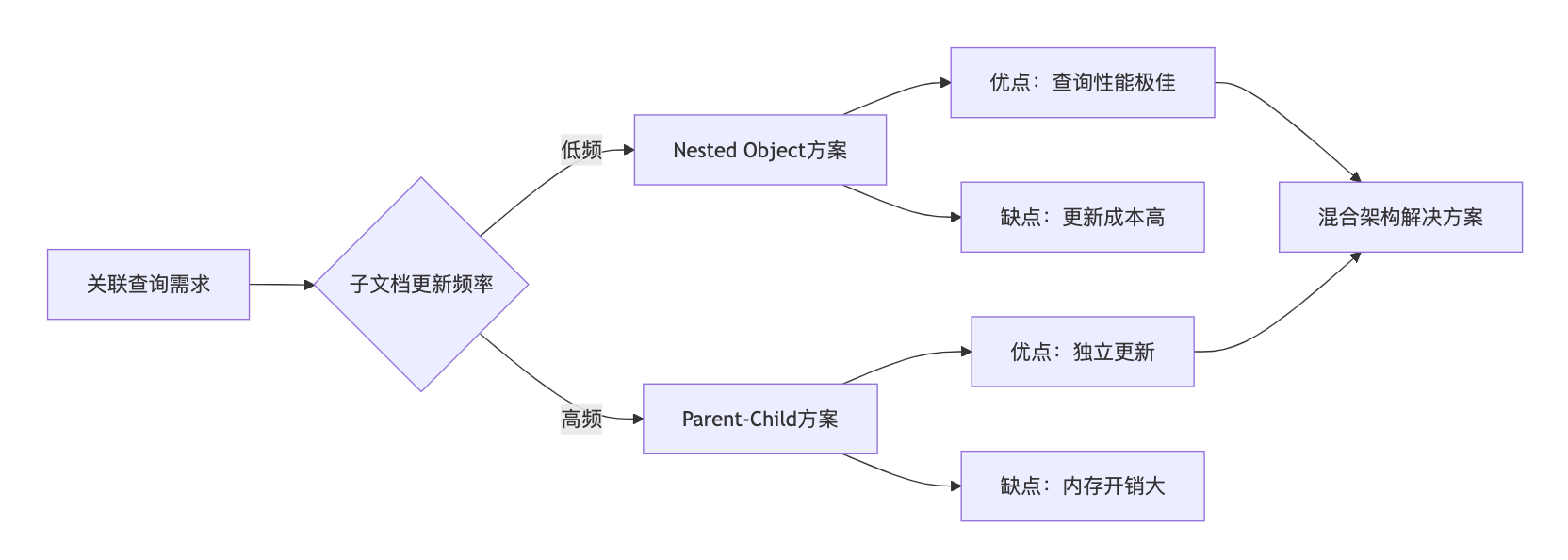
两种核心解决方案
| 维度 | Nested Object | Parent-Child |
|---|---|---|
| 读写性能 | 读取性能高(父子同文档) | 写入性能高(父子独立更新) |
| 更新开销 | 需重建整个文档(评论更新=全量重写博客) | 可独立更新子文档 |
| 内存消耗 | 无额外开销 | 需维护join关系的内存结构 |
| 适用场景 | 子文档更新少、查询频繁(如商品标签) | 子文档频繁更新(如订单-订单日志) |
| 查询灵活性 | 支持复杂子对象过滤 | 支持跨父子双向过滤 |
黄金准则:优先选择nested,仅在子文档高频更新时使用parent-child
1 ) 方案1:Nested Object(嵌套对象)
- 问题背景与错误示例
- 错误根源:未声明
nested类型的数组字段(如评论列表),ES默认将其存储为扁平化的object数组。// 错误映射导致的存储结构(隐式扁平化) { "title": "ES关联查询", "author": "John", "comments.name": ["Alice", "Bob"], // 所有用户名合并到同一数组 "comments.content": ["Good", "Thanks"] // 所有评论内容合并到同一数组 } - 查询缺陷:查询语句要求返回用户
Alice且评论含Thanks的博客:
错误返回结果:{ "query": { "bool": { "must": [ {"match": {"comments.name": "Alice"}}, {"match": {"comments.content": "Thanks"}} ] } } }Bob的评论含Thanks但Alice的评论不含,因扁平化存储破坏了对象边界。
- Nested Object 解决方案
-
映射定义:显式声明
nested类型保留对象独立性:PUT /blog_index_nested { "mappings": { "properties": { "title": {"type": "text"}, "author": {"keyword"}, "comments": { "type": "nested", // 关键声明 "properties": { "username": {"type": "keyword"}, "date": {"type": "date"}, "content": {"type": "text"} } } } } } -
正确查询语法:
{ "query": { "nested": { "path": "comments", // 指定nested字段路径 "query": { "bool": { "must": [ {"match": {"comments.username": "Alice"}}, {"match": {"comments.content": "Thanks"}} ] } } } } }执行效果:仅返回
username和content同时匹配的子对象所属文档 -
底层原理:
- 独立存储:每个
nested对象作为隐藏子文档存储,与父文档隔离 - 关联机制:查询时对每个
nested对象单独匹配,再通过内部_id关联回父文档
- 独立存储:每个
| 优势 | 劣势 |
|---|---|
| 读取性能高:父子数据物理相邻,减少IO开销 | 更新成本高:修改任一评论需全文档重写 |
| 查询精准:独立存储保障对象边界一致性 | 扩展性差:数组过大影响写入效率 |
2 ) 方案2:Parent-Child(父子文档)
- 核心概念与版本限制
join数据类型:ES 6.x+ 支持,替代旧版本多type父子模型。- 映射定义:
PUT /blog_index_parent_child { "mappings": { "properties": { "blog_join_field": { "type": "join", // 声明join类型 "relations": { "blog": "comment" // 父类型:子类型 } }, "title": {"type": "text"}, "content": {"type": "text"} } } }
- 文档操作规范
-
父文档创建:
POST /blog_index_parent_child/_doc/1 { "title": "ES关联实战", "blog_join_field": "blog" // 标记为父文档 } -
子文档创建:需指定
routing确保与父文档同分片POST /blog_index_parent_child/_doc/comment1?routing=1 { "username": "Alice", "content": "Great article!", "blog_join_field": { "name": "comment", // 标记为子文档 "parent": "1" // 关联父文档ID } } -
专用查询:
查询类型 用途 示例 parent_id获取父文档的所有子文档 {"parent_id": {"type": "log", "id": "1"}}has_child检索含匹配子文档的父文档 {"has_child": {"type": "log", "query": {...}}}has_parent检索匹配父文档的子文档 {"has_parent": {"parent_type": "order", ...}}
要点
- Nested:读写性能高,但更新需全文档重写
- Parent-Child:支持独立更新,但内存开销大
优缺点分析
| 优势 | 劣势 |
|---|---|
| 更新独立:父子文档可单独修改 | 内存开销大:维护Join关系消耗Heap |
| 扩展灵活:支持海量子文档 | 查询延迟高:跨文档检索性能较低 |
案例:NestJS工程实践
1 ) 方案1:Nested Object实现博客评论系统
ES配置:
PUT /blogs
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"title": {"type": "text"},
"comments": {
"type": "nested",
"properties": {
"user": {"type": "keyword"},
"text": {"type": text}
}
}
}
}
}
NestJS服务层代码(使用@nestjs/elasticsearch):
import { Injectable } from '@nestjs/common';
import { ElasticsearchService } from '@nestjs/elasticsearch';
@Injectable()
export class BlogService {
constructor(private readonly esService: ElasticsearchService) {}
// 创建含嵌套评论的博客
async createBlogWithComments(blogData: {
title: string;
comments: Array<{ user: string; text: string }>;
}) {
return this.esService.index({
index: 'blogs',
body: blogData,
});
}
// 嵌套查询:检索用户特定评论
async searchUserComments(user: string, keyword: string) {
return this.esService.search({
index: 'blogs',
body: {
query: {
nested: {
path: 'comments',
query: {
bool: {
must: [
{ match: { 'comments.user': user } },
{ match: { 'comments.text': keyword } },
],
},
},
},
},
},
});
}
}
或参考如下:
// 1. 定义Elasticsearch映射与模型
import { Injectable } from '@nestjs/common';
import { ElasticsearchService } from '@nestjs/elasticsearch';
@Injectable()
export class BlogService {
constructor(private readonly esService: ElasticsearchService) {}
async createIndex() {
await this.esService.indices.create({
index: 'blogs',
body: {
mappings: {
properties: {
title: { type: 'text' },
author: { type: 'keyword' },
comments: {
type: 'nested',
properties: {
username: { type: 'keyword' },
content: { type: 'text' },
date: { type: 'date' }
}
}
}
}
}
});
}
// 2. 嵌套评论查询
async searchBlogsByComment(keyword: string, user: string) {
const { body } = await this.esService.search({
index: 'blogs',
body: {
query: {
nested: {
path: 'comments',
query: {
bool: {
must: [
{ match: { 'comments.username': user } },
{ match: { 'comments.content': keyword } }
]
}
}
}
}
}
});
return body.hits.hits;
}
}
2 ) 方案2:Parent-Child实现订单日志系统
ES配置:
PUT /blog_system
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"relation": {
"type": "join",
"relations": {"blog": "comment"}
}
}
}
}
NestJS服务层代码:
import { Injectable } from '@nestjs/common';
import { ElasticsearchService } from '@nestjs/elasticsearch';
@Injectable()
export class CommentService {
constructor(private readonly esService: ElasticsearchService) {}
// 添加子评论
async addComment(blogId: string, comment: { user: string; text: string }) {
return this.esService.index({
index: 'blog_system',
id: `comment_${Date.now()}`,
routing: blogId, // 关键路由设置
body: {
...comment,
relation: { name: 'comment', parent: blogId },
},
});
}
// Has_child查询:检索含特定评论的博客
async findBlogsByComment(keyword: string) {
return this.esService.search({
index: 'blog_system',
body: {
query: {
has_child: {
type: 'comment',
query: { match: { text: keyword } },
},
},
},
});
}
}
或参考如下:
// 1. 父子文档映射配置
async initOrderIndex() {
await this.esService.indices.create({
index: 'orders',
body: {
mappings: {
properties: {
order_join_field: {
type: 'join',
relations: { order: 'log' }
},
order_id: { type: 'keyword' },
amount: { type: 'float' }
}
}
}
});
}
// 2. 添加订单日志(子文档)
async addOrderLog(orderId: string, log: { action: string; timestamp: Date }) {
await this.esService.index({
index: 'orders',
id: `log_${Date.now()}`,
routing: orderId, // 关键:与父文档同分片
body: {
action: log.action,
timestamp: log.timestamp,
order_join_field: {
name: 'log',
parent: orderId // 关联父文档ID
}
}
});
}
// 3. 查询订单的最新日志
async getLatestLogs(orderId: string) {
const { body } = await this.esService.search({
index: 'orders',
body: {
query: {
parent_id: {
type: 'log',
id: orderId
}
},
sort: [{ timestamp: { order: 'desc' } }],
size: 10
}
});
return body.hits.hits;
}
3 ) 方案3:混合架构(冷热数据分离)(Nested + Parent-Child)
适用场景:高频查询基础数据 + 低频更新扩展数据。
- ES Mapping:
PUT /hybrid_blogs { "mappings": { "properties": { "title": {"type": "text"}, "author": {"type": "keyword"}, "top_comments": { // 嵌套存储热评 "type": "nested", "properties": {...} }, "relation": { // 父子存储全量评论 "type": "join", "relations": {"blog": "all_comments"} } } } }
NestJS混合查询服务:
import { Injectable } from '@nestjs/common';
import { ElasticsearchService } from '@nestjs/elasticsearch';
@Injectable()
export class HybridService {
constructor(private readonly esService: ElasticsearchService) {}
// 获取博客及其热评(Nested)
async getBlogWithHotComments(blogId: string) {
return this.esService.get({
index: 'hybrid_blogs',
id: blogId,
});
}
// 分页查询全量评论(Parent-Child)
async paginateAllComments(blogId: string, page: number) {
return this.esService.search({
index: 'hybrid_blogs',
body: {
query: {
has_parent: {
parent_type: 'blog',
query: { match: { _id: blogId } },
},
},
from: (page - 1) * 10,
size: 10,
},
});
}
}
或参考如下
- 热数据(频繁更新字段)使用
parent-child - 冷数据(稳定字段)使用
nested或普通字段// 映射示例 { "product": { "properties": { "name": {"type": "text"}, "price": {"type": "float"}, "reviews": {"type": "nested"}, // 低频更新的评论 "inventory_join": { // 高频更新的库存 "type": "join", "relations": {"product": "inventory_log"} } } } }
要点
- 混合方案平衡性能:Nested处理稳定数据,Parent-Child处理动态数据
- 路由一致性是Parent-Child的生命线
配置优化与生产级考量
1 )分片策略
- Parent-Child需强制
routing:写入子文档时指定routing=父文档IDrouting参数必须设为父文档ID,避免跨分片查询POST /orders/_doc/log123?routing=order_456
- Nested Object建议增大
index.mapping.nested_objects.limit(默认10000),防止数组溢出
2 ) 性能调参
PUT /blogs/_settings
{
"index": {
"max_inner_result_window": 50000, // 扩大nested查询返回限制
"mapping": {
"nested_objects": {
"limit": 10000 // 单个文档允许的nested对象数
}
}
}
}
或
// 在索引设置中调整
PUT /_settings
{
"index": {
"query": {
"bool": {
"max_nested_depth": 20 // 增加嵌套深度限制
}
}
}
}
3 ) 关键性能参数
# elasticsearch.yml
indices.query.bool.max_clause_count: 8192 # 提升查询复杂度
indices.memory.index_buffer_size: 30% # 增加索引缓冲区
4 ) 内存与监控
- Parent-Child:监控
join字段的堆内存占用 - Parent-Child 场景增加
indices.query.bool.max_clause_count(默认1024) - Nested:警惕单个文档超1000子对象时的性能衰减
6 ) 安全与韧性
- 启用TLS加密:
xpack.security.transport.ssl.enabled: true - NestJS集成重试机制:
ElasticsearchModule.register({ node: 'https://es-cluster:9200', maxRetries: 5, // 查询失败重试 requestTimeout: 60000 })
7 ) 内存管理
避坑指南:
- Nested对象数量超过
100时需测试集群性能 - 禁用Parent-Child的
_all字段(ES 6.x前版本) - 定期监控
join字段内存占用
Nested Object 与 Parent-Child 对比与应用场景
| 维度 | Nested Object | Parent-Child | 推荐场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 数据模型 | 嵌入式存储(单文档) | 分离式存储(多文档) | - |
| 写入性能 | 低(整文档更新) | 高(局部更新) | 子文档频繁更新 → Parent-Child |
| 读取性能 | 高(无跨文档操作) | 低(内存Join计算) | 高频查询 → Nested Object |
| 适用数据量 | 中小规模(<1000子项) | 大规模(>10万子项) | 按数据量选择 |
| 典型用例 | 博客评论、订单商品 | 用户-日志、产品-库存 | - |
通用建议:优先使用Nested Object(因性能优势),仅在子文档更新极频繁时选用Parent-Child
选型指南与最佳实践
| 维度 | Nested Object | Parent-Child |
|---|---|---|
| 读写性能 | 读优⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️ | 写优⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️ |
| 更新开销 | 全文档重写 | 独立更新 |
| 适用场景 | 商品标签/博客评论 | 订单日志/实时库存 |
| 数据规模 | 子对象<1000 | 子文档>10万 |
黄金准则:
- 优先选择
Nested Object(性能优势) - 仅在子文档分钟级高频更新时用
Parent-Child - 禁用以下场景:
- 跨索引关联 → 改用应用层JOIN
- 嵌套层级>2 → 重构数据模型
终极架构建议:
- 热数据(评论摘要)用Nested Object实现毫秒查询
- 冷数据(全量日志)用Parent-Child支持动态扩展
- 通过消息队列(如Kafka)保证混合数据一致性
通过精准选择关联模型,可在ES中实现每秒10万级关联查询,规避传统数据库JOIN瓶颈
总结:关联关系处理黄金策略
- 首选Nested当:
- 子对象数量有限(百级内)
- 更新频率低于读取频率
- 需强一致性查询(如评论精准过滤)
- 选择Parent-Child当:
- 子文档数量无限(如日志流)
- 父子需独立更新
- 接受最终一致性查询
- 禁用方案:
- 跨索引关联 → 改用应用层JOIN或
_lookup特性 - 深层嵌套(>2层)→ 数据模型需重构
- 跨索引关联 → 改用应用层JOIN或
通过精准选择关联模型,可在ES中实现高效关联查询,规避关系型数据库的JOIN短板。






















 1372
1372

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










