隐式图的搜索问题
实验内容:
编写九宫重排问题的启发式搜索(A*算法)求解程序。
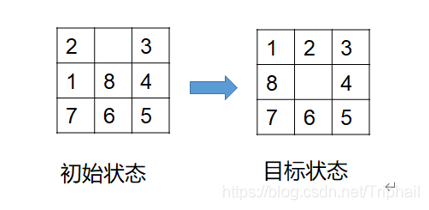
在3х3组成的九宫棋盘上,放置数码为1~8的8个棋子,棋盘中留有一个空格,空格周围的棋子可以移动到空格中,从而改变棋盘的布局。根据给定初始布局和目标布局,编程给出一个最优的走法序列。输出每个状态的棋盘。
对于九宫重排问题的解决,首先要考虑是否有答案。每一个状态可认为是一个1×9的矩阵,问题即通过矩阵的变换,可以变换为目标状态对应的矩阵。由数学知识可知,可计算这两个有序数列的逆序值,如果两者都是偶数或奇数,则可通过变换到达,否则,这两个状态不可达。这样,就可以在具体解决问题之前判断出问题是否可解,从而可以避免不必要的搜索。
如果初始状态可以到达目标状态,那么采取什么样的方法呢?常用的状态空间搜索有深度优先和广度优先。广度和深度优先搜索有一个很大的缺陷就是他们都是在一个给定的状态空间中穷举。这在状态空间不大的情况下是很合适的算法,可是当状态空间十分大,且不预测的情况下就不可取了。他的效率实在太低,甚至不可完成。由于九宫重排问题状态空间共有9!个状态,如果选定了初始状态和目标状态,有9!/2个状态要搜索,考虑到时间和空间的限制,在这里要求采用A*算法求解。
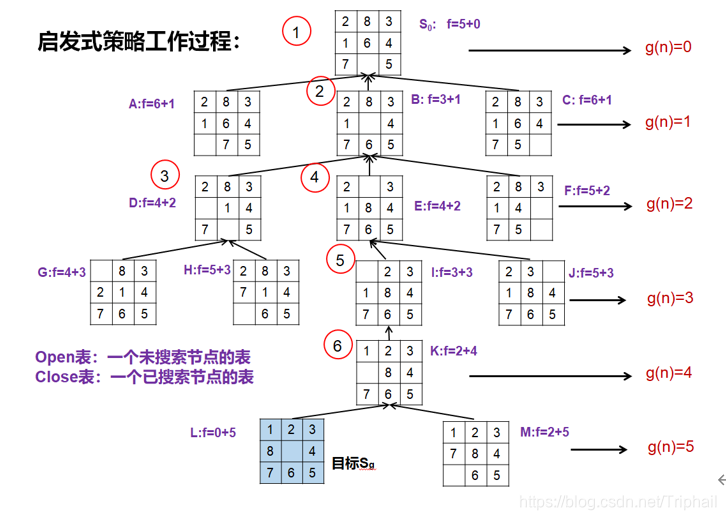
A*算法是启发式搜索算法,启发式搜索就是在状态空间中对每一个搜索分支进行评估,得到最好的分支,再从这个分支进行搜索直到目标。这样可以省略大量无畏的搜索路径,提到了效率。在启发式搜索中,利用当前与问题有关的信息作为启发式信息指导搜索,这些信息能够有效省略大量无谓的搜索路径,大大提高了搜索效率。
启发式搜索算法定义了一个估价函数f(n),与问题相关的启发式信息都被计算为一定的 f(n) 的值,引入到搜索过程中。f(n) = g(n) +h(n)其中f(n) 是节点n的估价函数,g(n)是在状态空间中从初始节点到节点n的实际代价,h(n)是从节点n到目标节点最佳路径的估计代价。 在九宫重排问题中,显然g(n)就是从初始状态变换到当前状态所移动的步数,估计函数h(n)估计的是节点n到目标节点的距离,我们可以用欧几里德距离、曼哈顿距离或是两节的状态中数字的错位数来估计。
各个数据结构的定义
九宫格类型
struct NineCell
{
int parentPoint=0;//父节点的下标
char nineCell[3][3] = {' '};//初始化九宫格
int F=0;//F=G+H
int H=0;//从起点到此位置的移动量(层数)
int G=0;//从此位置到终点的移动量(目标与结果位置不同的数字的数量)
bool IsSameNineCell(NineCell other);//判断两个九宫格是否相同
void CopyNineCell(NineCell nineCell);//拷贝九宫格
void PrintNineCell();//打印九宫格
};
创建链表的结点
struct Node
{
NineCell Data;
Node* Next=NULL;
};
创建链表
class List
{
private:
Node* first;
public:
List();//默认构造函数
List(NineCell* p, int n);//带参构造函数
int GetLen();//得到列表中数据的个数
NineCell GetData(int Pos);//得到pos位置的数据
Node* MoveTo(int Pos);//得到pos位置的结点
void Insert(NineCell Data, int Pos);//在pos位置插入数据
void Cout();//输出列表数据
int Search(NineCell Data);//在列表中查找数据返回下标
void Delete(NineCell Data);//删除指定数据
bool Empty();//判断列表是否为空
void Insert(NineCell Data);//在列表末尾插入节点
bool IsContain(NineCell Data);//判断列表是否包含数据
};
创建A星算法实现类
class Astar
{
public:
Astar();//默认构造函数
void PrintNineCell(NineCell nineCell);//打印九宫格
void AstartAlgorthm(NineCell startPoint, NineCell endPoint);//A星算法
private:
List openList;//open表
List closeList;//close表
int CalcH(NineCell startpoint, NineCell endPoint);//计算九宫格的H
int CalcG(NineCell startpoint);//计算九宫格的G
NineCell GetLeastFPoint();//寻找open队列中F的值最小的点
//根据最后得到的close队列追寻之前点的坐标
void Recall(NineCell startPoint, NineCell endPoint);
NineCell* GetDirectionPoint(NineCell startPoint);//得到移动一步空位后的九宫格
};
各项功能具体实现代码
判断两个九宫格是否相同
bool NineCell::IsSameNineCell(NineCell other)
{
//判断两个九宫格是否相同
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
if (this->nineCell[i][j] != other.nineCell[i][j])
{
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
拷贝九宫格
void NineCell::CopyNineCell(NineCell nineCell)
{
//拷贝九宫格
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
this->nineCell[i][j] = nineCell.nineCell[i][j];
}
}
this->H = nineCell.H;
this->F = nineCell.F;
this->G = nineCell.G;
this->parentPoint = nineCell.parentPoint;
}
打印九宫格
void NineCell::PrintNineCell()
{
cout << "九宫格状态为:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
if (this->nineCell[i][j] == '0')
{
cout << ' ';
}
else
{
cout << this->nineCell[i][j];
}
}
}
cout << endl;
}
默认构造函数
List::List()
{
//默认构造函数
this->first = new Node[1];
this->first->Next = NULL;
}
带参构造函数
List::List(NineCell* p, int n)
{
//带参构造函数
this->first = new Node[1];
this->first->Next = NULL;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
Insert(p[i], i + 1);
}
得到列表中数据的个数
int List::GetLen()
{
//得到列表中数据的个数
Node* p = this->first->Next;
int Len = 0;
while (p != NULL)
{
Len++;
p = p->Next;
}
return Len;
}
得到pos位置的数据
NineCell List::GetData(int Pos)
{
//得到pos位置的数据
Node* p = this->first;
for (int i = 0; i < Pos; i++)
p = p->Next;
return p->Data;
}
得到pos位置的结点
Node* List::MoveTo(int Pos)
{
//得到pos位置的结点
Node* p = this->first;
for (int i = 0; i < Pos; i++)
p = p->Next;
return p;
}
//在pos位置插入数据
void List::Insert(NineCell Data, int Pos)
{
//在pos位置插入数据
Node* p = new Node;
p->Data = Data;
Node* q = MoveTo(Pos - 1);
p->Next = q->Next;
q->Next = p;
}
输出列表数据
void List::Cout()
{
//输出列表数据
for (Node* p = this->first->Next; p != NULL; p = p->Next)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
cout << this->first->Data.nineCell[i][j];
}
cout << endl;
}
}
}
在列表中查找数据返回下标
int List::Search(NineCell Data)
{
//在列表中查找数据返回下标
int Pos = 0;
for (Node* p = this->first->Next; p != NULL; p = p->Next)
{
Pos++;
if (p->Data.IsSameNineCell(Data) == true)
{
return Pos;
}
}
return -1;
}
删除指定数据
void List::Delete(NineCell Data)
{
//删除指定数据
int Pos = this->Search(Data);
Node* q = MoveTo(Pos - 1);
Node* p = q->Next;
q->Next = p->Next;
delete p;
}
判断列表是否为空
bool List::Empty()
{
//判断列表是否为空
if (this->first->Next != NULL)
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
在列表末尾插入节点
void List::Insert(NineCell Data)
{
//在列表末尾插入节点
Node* p = new Node;
p->Data = Data;
p->Next = NULL;
Node* q = MoveTo(this->GetLen());
q->Next = p;
}
判断列表是否包含数据
bool List::IsContain(NineCell Data)
{
//判断列表是否包含数据
if (this->Search(Data) != -1)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
计算九宫格的H
int Astar::CalcH(NineCell startpoint, NineCell endPoint)
{
//计算九宫格的H
int samePlaceCount = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
if (startpoint.nineCell[i][j] == endPoint.nineCell[i][j])
{
//当前九宫格和最后目标九宫格中数字位置相同的点的个数
samePlaceCount++;
}
}
}
return 8-samePlaceCount;//得到当前九宫格和最后目标九宫格中数字位置不同的点的个数
}
计算九宫格的G
int Astar::CalcG(NineCell startpoint)
{
//计算九宫格的G
//实际距离为上一个点的距离+1
return startpoint.G + 1;
}
寻找open队列中F的值最小的点
NineCell Astar::GetLeastFPoint()
{
//寻找队列中F最小的点
//F最小点的下标
int index = 1;
for (int i = 2; i < openList.GetLen() + 1; i++)
{
if (openList.GetData(i).F > 0 && openList.GetData(i).F < openList.GetData(index).F)
{
index = i;
}
}
return openList.GetData(index);
}
根据最后得到的close队列追寻之前点的九宫格
void Astar::Recall(NineCell startPoint, NineCell endPoint)
{
//根据最后得到的close队列追寻之前点的九宫格
//以最后目标九宫格进行追溯
NineCell tempPoint = this->closeList.GetData(this->closeList.Search(endPoint));
//创建追溯列表
List coutList;
while (tempPoint.IsSameNineCell(startPoint)==false)
{
//把得到的九宫格插入追溯列表
coutList.Insert(tempPoint);
//追溯的九宫格进行更新
tempPoint = this->closeList.GetData(tempPoint.parentPoint);
}
//插入起始九宫格到列表中
coutList.Insert(startPoint);
//打印记录
for (int i = coutList.GetLen() ; i >0; i--)
{
cout << "step" << coutList.GetLen() - i<<endl;
this->PrintNineCell(coutList.GetData(i));
}
}
得到移动一步空位后的九宫格
NineCell* Astar::GetDirectionPoint(NineCell startPoint)
{
//得到移动一步空位后的九宫格
int nullPlaceX;//九宫格中空白位置的x坐标
int nullPlaceY;//九宫格中空白位置的y坐标
//得到九宫格中空白坐标
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
if (startPoint.nineCell[i][j] == ' ')
{
nullPlaceX = i;
nullPlaceY = j;
}
}
}
NineCell* directionPoint = new NineCell[4];
//根据目标九宫格生成移动空位九宫格
for (int count = 0;count < 4; count++)
{
directionPoint[count].CopyNineCell(startPoint);
}
if (nullPlaceX+1 < 3)
{
//交换右边的数字
directionPoint[0].nineCell[nullPlaceX][nullPlaceY] = directionPoint[0].nineCell[nullPlaceX + 1][nullPlaceY];
directionPoint[0].nineCell[nullPlaceX + 1][nullPlaceY] = ' ';
}
if (nullPlaceX - 1 >= 0 )
{
//交换左边的数字
directionPoint[1].nineCell[nullPlaceX][nullPlaceY] = directionPoint[1].nineCell[nullPlaceX - 1][nullPlaceY];
directionPoint[1].nineCell[nullPlaceX - 1][nullPlaceY] = ' ';
}
if (nullPlaceY + 1 < 3)
{
//交换上边的数字
directionPoint[2].nineCell[nullPlaceX][nullPlaceY] = directionPoint[2].nineCell[nullPlaceX ][nullPlaceY+1];
directionPoint[2].nineCell[nullPlaceX ][nullPlaceY+1] = ' ';
}
if (nullPlaceY - 1 >= 0)
{
//交换下边的数字
directionPoint[3].nineCell[nullPlaceX][nullPlaceY] = directionPoint[3].nineCell[nullPlaceX ][nullPlaceY-1];
directionPoint[3].nineCell[nullPlaceX][nullPlaceY-1] = ' ';
}
return directionPoint;
}
A星算法
void Astar::AstartAlgorthm(NineCell startPoint, NineCell endPoint)
{
//A星算法
//初始化起点的信息
startPoint.G = 0;
startPoint.H = this->CalcH(startPoint, endPoint);
startPoint.F = startPoint.G + startPoint.H;
this->openList.Insert(startPoint);
//this->PrintNineCell(startPoint);
//this->PrintNineCell(endPoint);
while (this->openList.Empty() == false)
{
//寻找开启队列中F最小的点
NineCell minPoint = this->GetLeastFPoint();
//把最小点加入关闭队列
this->closeList.Insert(minPoint);
//得到最小点向四周移动的点
NineCell* directionPoints = this->GetDirectionPoint(minPoint);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
//判断移动点是否超出地图,碰到建筑,或者在关闭队列中
if (directionPoints[i].nineCell!=NULL&&this->closeList.IsContain(directionPoints[i]) == false)
{
//当移动的点不在开启队列中修改其属性
if (openList.IsContain(directionPoints[i]) == false)
{
directionPoints[i].parentPoint = this->closeList.Search(minPoint);
directionPoints[i].G = this->CalcG(minPoint);
directionPoints[i].H = this->CalcH(directionPoints[i], endPoint);
directionPoints[i].F = directionPoints[i].G + directionPoints[i].H;
this->openList.Insert(directionPoints[i]);
}
else
{
//否则则更改在队列中的属性
int tempG = this->CalcG(minPoint);
if (directionPoints[i].G > tempG)
{
directionPoints[i].parentPoint = this->closeList.Search(minPoint);
directionPoints[i].G = this->CalcG(minPoint);
directionPoints[i].F = directionPoints[i].G + directionPoints[i].H;
}
}
}
}
//删除开启队列中的起点
this->openList.Delete(minPoint);
if (closeList.IsContain(endPoint) == true)
{
//追溯打印结果
this->Recall(startPoint, endPoint);
return;
}
}
}
打印九宫格
void Astar::PrintNineCell(NineCell nineCell)
{
//打印九宫格
cout << "九宫格的状态为:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
cout << nineCell.nineCell[i][j];
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << "九宫格的F值为:" << nineCell.F << endl;
cout << "九宫格的G值为:" << nineCell.G << endl;
cout << "九宫格的H值为:" << nineCell.H << endl;
cout << endl;
}
主函数代码
输入九宫格
void InputNineCell(NineCell& point)
{
//输入九宫格
cout << "输入0代表九宫格中的空位" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
cout << "请输入(" << i << "," << j << ")" << "位置的九宫格的值:" ;
cin >> point.nineCell[i][j];
}
}
cout << endl;
}
实验结果
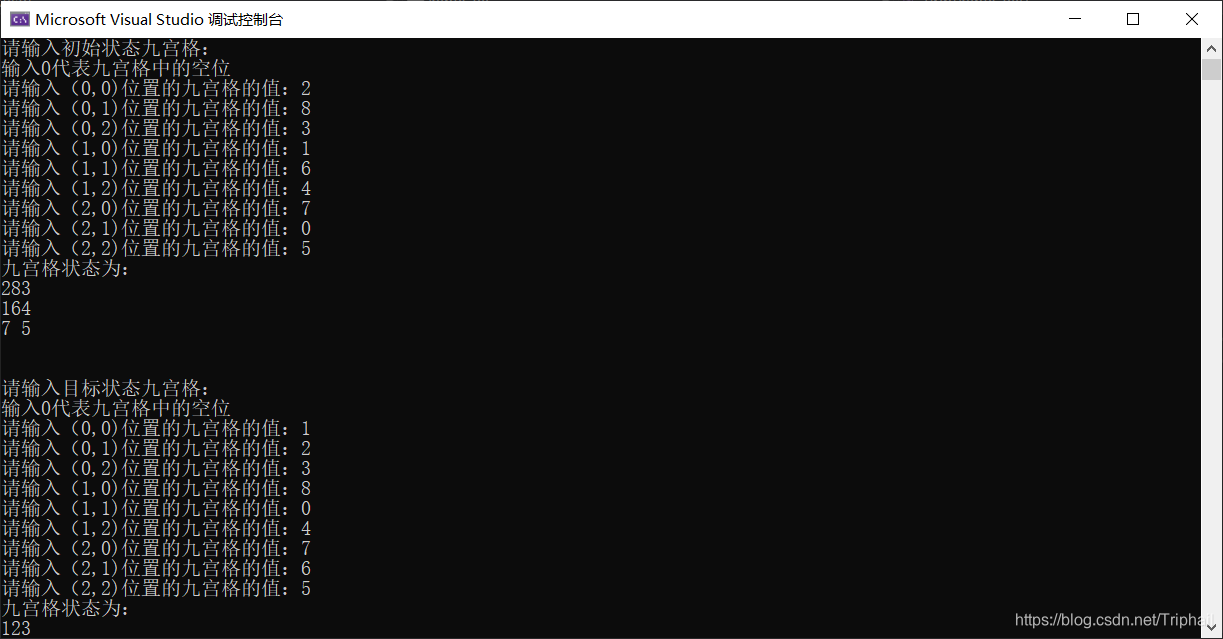
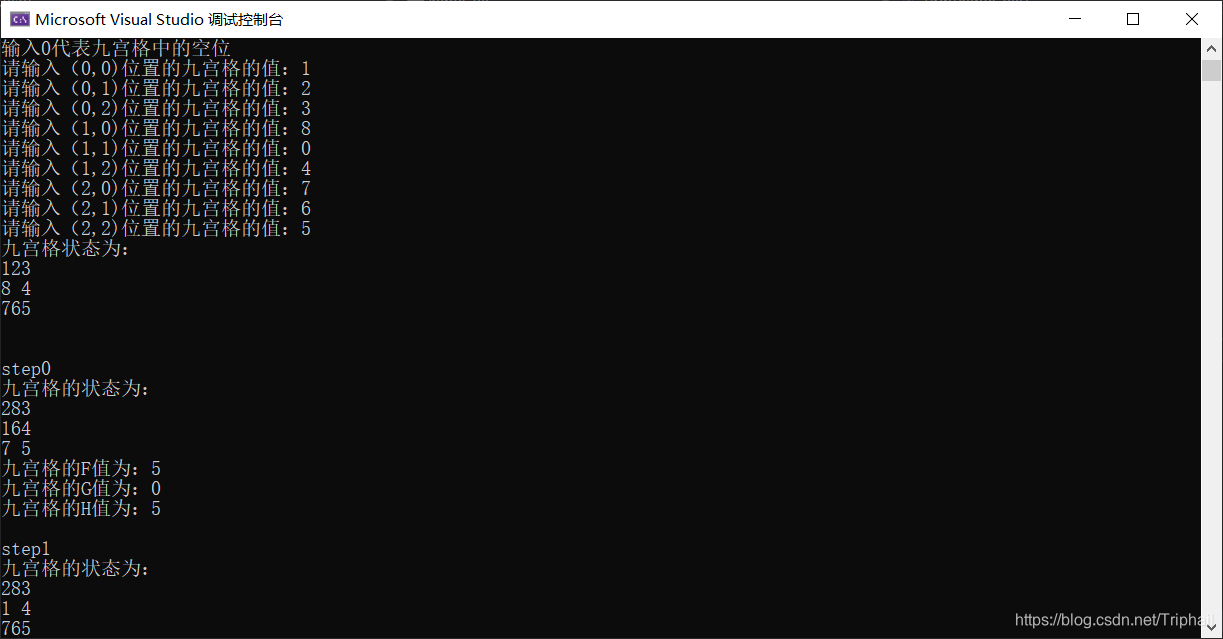





















 583
583

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








