JUC
- juc 是java.util.concurrent包下的并发功能包
回顾
- 线程有几个状态
public enum State {
//新生
NEW,
//运行
RUNNABLE,
//阻塞状态
BLOCKED,
//无限期等待
WAITING,
//限时等待
TIMED_WAITING,
//结束
TERMINATED;
}
-
wait & sleep 区别
-
1、来自不同类
-
所有对象都有wait
-
Thread才有sleep
常用的休眠方法:使用java.util.concurrent里的TimeUnit
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); TimeUnit.DAYS.sleep(2);
-
-
2、锁的释放
- wait 会释放锁 sleep带锁睡
-
3、范围不同
- wait 需要在同步代码块
- sleep 可以在任何地方睡
即有synchronized修饰符修饰的语句块,被该关键词修饰的语句块,将加上内置锁。实现同步。
例:synchronized(Object o ){}
-
4、是否需要捕获异常
- wait 不需要捕获异常(除中断异常)
- sleep 必须捕获异常
-
Lock
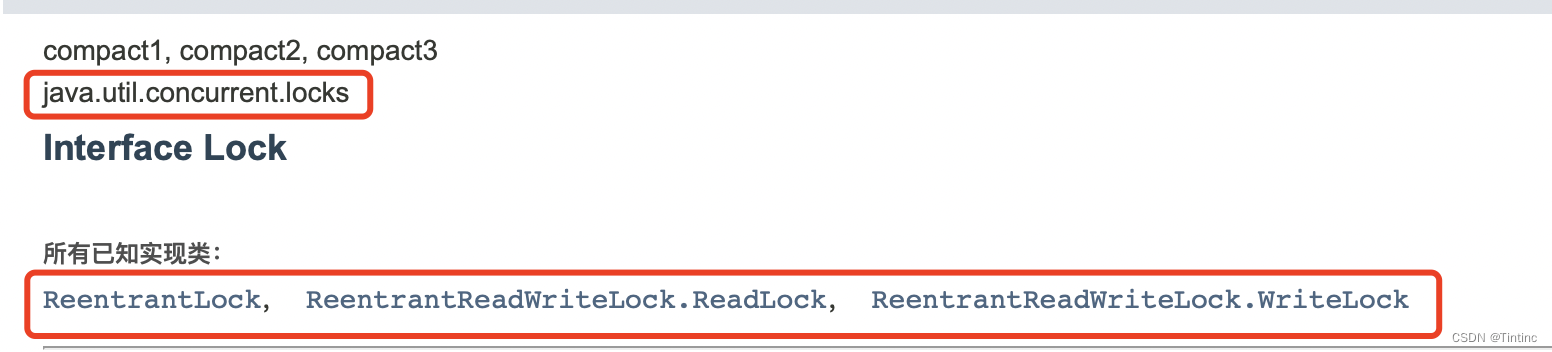
Synchronized和Lock区别:
- Synchronized 内置的java关键字,Lock 是一个Java类
- Synchronized 无法判断获取锁的状态,Lock 可以判断是否获取到锁
- Synchronized 会自动释放锁,lock 必须手动释放锁
- Synchronized 线程1(获得锁,阻塞)、线程2(等待,傻等);Lock 不一定会一直等待下去
- Synchronized 可重入错、不可以中断、非公平锁;Lock 可重入、可判断锁、默认非公平锁
- Synchronized 适合锁少量代码同步问题; Lock 适合锁大量同步代码
卖票
- Synchronized版
@SpringBootTest
class JucApplicationTests {
@Test
void contextLoads() {
final ticket ticket = new ticket();
new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) ticket.sale();}, "A").start();
new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) ticket.sale();}, "B").start();
new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) ticket.sale();}, "C").start();
new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) ticket.sale();}, "D").start();
}
}
class ticket{
int num = 100;
public synchronized void sale(){
if(num > 0){
num--;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "卖出了一张票,剩余" + num);
}
}
}
- Lock版
@SpringBootTest
class JucApplicationTests {
@Test
void contextLoads() {
final ticket ticket = new ticket();
new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) ticket.sale();}, "A").start();
new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) ticket.sale();}, "B").start();
new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) ticket.sale();}, "C").start();
new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) ticket.sale();}, "D").start();
}
}
class ticket{
//创建锁
private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
int num = 100;
public void sale(){
try {
//开启锁
lock.lock();
if(num > 0){
num--;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "卖出了一张票,剩余" + num);
}
}finally {
//释放锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
生产者消费者
- synchroniczed
class ProducerAndConsunmer{
int num = 0;
synchronized void produce(){
try {
// 必须使用while
while (num != 0){
this.wait();
}
num ++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "=>" + num);
this.notifyAll();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
synchronized void consumer(){
try {
// 必须使用wile
while (num == 0){
this.wait();
}
num --;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "=>" + num);
this.notifyAll();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
- JUC版
public class ProducerAndConsumer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ProducerAndConsunmer2 pc = new ProducerAndConsunmer2();
new Thread(() -> { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) pc.produce(); }, "producer1").start();
new Thread(() -> { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) pc.produce(); }, "producer2").start();
new Thread(() -> { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) pc.consumer(); }, "consumer1").start();
new Thread(() -> { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) pc.consumer(); }, "consumer2").start();
}
}
// 判断 方法内容 唤醒
class ProducerAndConsunmer2{
int num = 0;
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Condition condition = lock.newCondition();
void produce(){
try {
lock.lock();
//
while (num != 0){
condition.await();
}
num ++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "=>" + num);
condition.signalAll();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
void consumer(){
try {
lock.lock();
//
while (num == 0){
condition.await();
}
num --;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "=>" + num);
condition.signalAll();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
Condition精确唤醒
public class JucLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Data data = new Data();
new Thread(() -> { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) data.A(); }, "A").start();
new Thread(() -> { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) data.B(); }, "B").start();
new Thread(() -> { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) data.C(); }, "C").start();
}
}
class Data{
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Condition condition1 = lock.newCondition();
Condition condition2 = lock.newCondition();
Condition condition3 = lock.newCondition();
int num = 1; //1=>A 2=>B 3=>C
public void A(){
lock.lock();
try {
// 判断
if (num != 1){
condition1.await();
}
// 执行任务
num ++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "----执行");
// 唤醒
condition2.signal();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void B(){
lock.lock();
try {
//判断
if (num != 2){
condition2.await();
}
//执行
num ++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "----执行");
//唤醒
condition3.signal();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void C(){
lock.lock();
try {
//判断
if (num != 3) {
condition3.await();
}
// 执行
num = 1;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "----执行");
//唤醒
condition1.signal();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
关于锁的八个问题
package com.fang.lock8;
import java.sql.Time;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* 8锁,就是关于锁的8个问题
* 1.标准情况下是先发短信还是打电话 //sms call
* 2.发短信方法延迟4秒 //sms call
*/
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Phone phone = new Phone(); //锁的是调用的对象
new Thread(()->{
phone.sendSms();
},"A").start();
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); //juc里面的休眠方法
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
new Thread(()->{
phone.call();
},"B").start();
}
}
class Phone{
//synchronized锁的对象是方法的调用者
//两个方法用的是同一个锁,谁先拿到谁先执行
public synchronized void sendSms() {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("sendSms");
}
public synchronized void call() {
System.out.println("call");
}
}
package com.fang.lock8;
import java.sql.Time;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* 3.增加一个普通方法,是先执行发短信还是hello(1秒钟输出hello,4秒后输出发短信) //hello msm
* 4.两个对象,两个同步方法,先打电话,再发短信(两个不同的对象,两把锁) //call msm
*/
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Phone2 phone = new Phone2(); //两个不同的对象,两把锁
Phone2 phone2 = new Phone2();
new Thread(()->{
phone.sendSms();
},"A").start();
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
new Thread(()->{
phone2.call();
},"B").start();
}
}
class Phone2{
//synchronized锁的对象是方法的调用者
//两个方法用的是同一个锁,谁先拿到谁先执行
public synchronized void sendSms() {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("sendSms");
}
public synchronized void call() {
System.out.println("call");
}
public void hello() { //这里没有锁,不是同步方法,不受锁的影响
System.out.println("hello");
}
}
package com.fang.lock8;
import java.sql.Time;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* 5.增加两个静态同步方法,只有一个对象(先发短信,再打电话) // sms call
* 6.两个对象,增加两个静态同步方法(先发短信,再打电话) // sms call
*/
public class Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Phone3 phone = new Phone3(); //两个对象的class模板只有一个,static,锁的是class
Phone3 phone2 = new Phone3();
new Thread(()->{
phone.sendSms();
},"A").start();
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
new Thread(()->{
phone2.call();
},"B").start();
}
}
class Phone3{
//synchronized锁的对象是方法的调用者
//static 静态方法 类一加载就有了!class模板,锁的是class对象Class<Phone3> phone3Class = Phone3.class;
//两个方法用的是同一个锁
public static synchronized void sendSms() { //锁的是class
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("sendSms");
}
public static synchronized void call() {
System.out.println("call");
}
}
package com.fang.lock8;
import java.sql.Time;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* 7.一个静态同步方法,一个普通的同步方法,一个对象(先普通方法)
* 8.两个对象(先普通方法)
*/
public class Test4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Phone4 phone = new Phone4();//两个对象的class模板只有一个,static,锁的是class普通方法不受锁
Phone4 phone2 = new Phone4();
new Thread(()->{
phone.sendSms();
},"A").start();
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
new Thread(()->{
phone2.call();
},"B").start();
}
}
class Phone4{
//锁的是class类模板
//static 静态方法 类一加载就有了!class模板,锁的是class对象Class<Phone3> phone3Class = Phone3.class;
//两个方法用的是同一个锁
public static synchronized void sendSms() {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("sendSms");
}
//普通的同步方法,锁的是调用者
public synchronized void call() {
System.out.println("call");
}
}
CopyOnWriteArrayList
// List 出现java.util.ConcurrentModificationException(并发修改异常)
public class UnsafeList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
//Vector<String> list = new Vector<>();
//public synchronized boolean add 用的是 synchronized 效率低
CopyOnWriteArrayList<String> list = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
// public boolean add 底层用的是lock.lock(); 效率较高
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
list.add(UUID.randomUUID().toString().substring(0, 5));
System.out.println(list);
}
}).start();
}
}
}
CopyOnWriteArraySet
// ConcurrentModificationException
public class UnsafeSet {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();//出现并发修改异常 ConcurrentModificationException
// Set<String> set = Collections.synchronizedSet(new HashSet<String>()); 效率较低
CopyOnWriteArraySet<String> set = new CopyOnWriteArraySet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
set.add(UUID.randomUUID().toString().substring(0, 5));
System.out.println(set);
}).start();
}
}
}
- HashSet的底层是HashMap
public boolean add(E e) {
return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
}
ConcurrentHashMap
// ConcurrentModificationException
public class UnsafeMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
// Map<String, Object> map = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap<String, Object>());
ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
map.put(UUID.randomUUID().toString().substring(0,5), UUID.randomUUID().toString().substring(0,5));
System.out.println(map);
}).start();
}
}
}
Callable 方法创建线程
- 回顾
// 启动线程的三种方法
// 第一种继承Thread
public class CallableTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(new Mythread2()).start();
}
}
class Mythread2 extends Thread{
@Override
public void run(){
System.out.println("extends Thread");
}
}
// 第二种实现Runnable
public class CallableTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(new Mythread()).start();
}
}
class Mythread implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("hello");
}
}
// 实现Callable
public class CallableTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(new FutureTask<String>(new Mythread3())).start();
}
}
class Mythread3 implements Callable<String> {
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("Implements Callable");
return "Callable";
}
}
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-ZkbJFNyX-1669883207772)(note.assets/image-20221128104549189.png)]](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/blog_migrate/5db55933fea41840342ceeaacb3de314.png)
常工具类(必会)
CountDownLatch(倒计时锁)
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
CountDownLatch count = new CountDownLatch(6); //初始化计数器
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "Go out");
count.countDown(); //计数器-1
}).start();
}
count.await(); // 等待计数器归零
System.out.println("Close door");
}
Cyclicbarrier(循环屏障)
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
CyclicBarrier cycliBarrier = new CyclicBarrier(7, () -> {
System.out.println("集齐七颗龙珠召唤神龙");
});
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
int finalI = i;
new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println("收集个数->" + finalI);
try {
cycliBarrier.await(); // 相当于计数器+1
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (BrokenBarrierException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}).start();
}
}
Semaphore(计数信号量)
public static void main(String[] args) {
Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(3);
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
semaphore.acquire(); //占用资源
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "获得车位");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
semaphore.release(); //释放资源
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}, String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
}
ReadWriteLock
public class ReadAndWriteLockDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyCache myCache = new MyCache();
for (int i = 0; i < 15; i++) {
int finalI = i;
new Thread(() -> {
myCache.write(finalI + "", finalI + "");
}).start();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 15; i++) {
int finalI = i;
new Thread(() -> {
myCache.read(finalI + "");
}).start();
}
}
}
// 独占锁(写锁) 一次只能被一个线程占有
// 共享锁(读锁) 可以同时被多个线程占有
class MyCache{
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
ReadWriteLock rw = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
void write(String key, String value){
rw.writeLock().lock();
System.out.println("写入" + key);
map.put(key, value);
System.out.println("写入" + key + "完成");
rw.writeLock().unlock();
}
void read(String key){
rw.readLock().lock();
System.out.println("--读取" + key);
System.out.println("--读取" + key + "--->" + map.get(key));
System.out.println("--读取" + key + "完成");
rw.readLock().unlock();
}
}
BlockingQueue
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-4fx1Vac9-1669883207772)(note.assets/image-20221128145542777.png)]](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/blog_migrate/98ed72a5e5e982a0bf9fdba067abb5d0.png)
- 四种Api
| 方式 | 抛出异常 | 不抛出异常 | 阻塞等待(无返回值) | 超时等待 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 添加 | add | offer | put | offer(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) |
| 移除 | remove | poll | Take | pool(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) |
| 判断队首元素 | element | peek | - | - |
- 异常抛出
public static void test1(){
ArrayBlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);
System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("a"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("b"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("c"));
// System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("d")); // IllegalStateException: Queue full
//System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());
// System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove()); // NoSuchElementException
System.out.println(blockingQueue.element()); // 查询队首元素 NoSuchElementException
}
- 有返回值,不抛出异常
public static void test2(){
ArrayBlockingQueue<Object> blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("a"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("b"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("c"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("d")); // false
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll()); // null
System.out.println(blockingQueue.peek()); // 查看队首元素 null
}
- 一直等待
public static void test3(){
ArrayBlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);
try {
blockingQueue.put("a");
blockingQueue.put("b");
blockingQueue.put("c");
// blockingQueue.put("d"); //一直等待
System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.take()); //一直等待
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
- 设置等待的时间
public static void test4() throws InterruptedException {
ArrayBlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("a", 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("b", 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("c", 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("d", 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS)); //false
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS)); // null
}
- synchronousQueue 同步队列
// 只能存一个
public static void test5(){
SynchronousQueue<String> synchronousQueue = new SynchronousQueue<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
int finalI = i;
new Thread(() -> {
try {
synchronousQueue.put("put -->" + String.valueOf(finalI));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}).start();
}
new Thread(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
System.out.println(synchronousQueue.take());
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
System.out.println(synchronousQueue.take());
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
System.out.println(synchronousQueue.take());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}).start();
}
线程池(重点)
-
池化技术及线程池的使用
程序的运行,本质:占用系统的资源!优化资源的使用
线程池,连接池,内存池,对象池
池化技术:事先准备好一些资源,有人要用就来拿,用完之后归还 -
线程池的好处
1、降低资源的消耗
2、提高响应速度
3、方便管理
线程可以复用,可以控制最大并发量,管理线程线程池:三大方法,7大参数,4种拒绝策略
三大方法
//Executors工具类,三大方法
// ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();//单个线程
// ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);//创建一个固定大小得线程池
// ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();//可伸缩,线程数可变
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService threadpool = null;
try {
// threadpool = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor(); // 开启单个线程池
// threadpool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(100); // 开启指定个数线程池
threadpool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); // 开启可伸缩线程池
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
threadpool.execute(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
threadpool.shutdown();
}
}
7大参数
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService threadPool = null;
try {
// executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor(); // 开启单个线程池
// executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(100); // 开启指定个数线程池
// executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); // 开启可伸缩线程池
threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
2, // 核心线程数
5, // Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors(),
2, // 保持活跃时间
TimeUnit.SECONDS, //时间单位
new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(3), // 阻塞队列类型以及大小 ArrayBlockingQueu
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
//new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy() // 超过 最大线程数 + 阻塞队列就会抛出异常
//new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy() // 丢弃新来的线程
//new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy() // 退回
new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy() // 丢弃旧的线程
);
for (int i = 1; i <= 15; i++) {
int finalI = i;
threadPool.execute(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "---->" +finalI);
});
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
threadPool.shutdown();
}
}
4种拒绝策略
threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
2,// 核心线程数
5,// 最大线程数 Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors(), // 见扩展部分
2,// 持续时间
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(3),
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
//new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy() // 超过 最大线程数 + 阻塞队列就会抛出异常
//new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy() // 丢弃新来的线程
//new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy() // 退回
new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy() // 丢弃旧的线程
);
// 扩展
最大线程池应该如何定义
1.cpu密集行,12条线程同时执行,几核心就是几,可以保证cpu的效率最高
2.io密集型>判断你的程序中十分耗io的线程
程序 15个大型任务 io十分暂用资源
System.out.println(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors());//获得cpu的核心数
四大函数式接口(重点)
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-rD4fOz5i-1669883592976)(note.assets/image-20221129101133909.png)]](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/blog_migrate/f47485269086d017e3fad235628eb3d0.png)
Function
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-dkbNtsK8-1669883207773)(note.assets/image-20221129095133417.png)]](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/blog_migrate/35d79f6ae47f3707a9951ce5183618ed.png)
/*
* Function 有一个输入 有一个输出
* 只要是函数式接口就可以使用lambda表达式
* */
public class functionDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Function<String, String> function1 = new Function<String, String>() {
@Override
public String apply(String o) {
return "function";
}
};
// 使用lambda表达式
Function<String, String> function2 = (str) -> {return "function"; };
}
}
Predicate 断言
// 判断式接口
public class PredicateDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Predicate<String>() {
@Override
public boolean test(String str) {
return str.isEmpty();
}
};
// 使用lambda表达式
Predicate<String> predicate = (str) -> { return str.isEmpty(); };
}
}
Consumer 消费型接口
// 消费型函数接口,只有输入没有输出
public class ConsumerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Consumer<String> consumer1 = new Consumer<String>() {
@Override
public void accept(String str) {
System.out.println(str);
}
};
Consumer<String> consumer2 = (str) -> { System.out.println(str); };
consumer2.accept("123");
}
}
Supplier 供给型接口
// 供给型接口:只有返回值没有输入
public class SupplierDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Supplier<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer get() {
return 1024;
}
};
// 使用lambda表达式
Supplier<Integer> supplier = () -> { return 1024; };
}
}
Stream流式计算
public static void main(String[] args) {
User user1 = new User(1,21,"zhang3");
User user2 = new User(2,23,"4");
User user3 = new User(3,29,"5");
User user4 = new User(4,18,"zhao6");
User user5 = new User(5,33,"tian7");
User user6 = new User(6,31,"8");
List<User> list = Arrays.asList(user1, user2, user3, user4, user5, user6);
list.stream()
.filter((u) -> { return u.getId() % 2 == 0; }) // 返回 id 为2的倍数的user
.filter((u) -> { return u.getAge() > 21; }) // 返回 age > 21
.map((u) -> {return u.getName().toUpperCase(); }) // 名字大写
.sorted((u1, u2) -> { return u1.compareTo(u2); }) // 排序
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
ForkJoin
- 需要实现RecursiveTask
- 使用ForkJoinPool.submit()调用,submit.get()获取结果
public class DemoMain {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
new DemoMain().test1();//1743
new DemoMain().test2();//730
new DemoMain().test3();//166
}
public void test1(){
Long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Long sum = 0L;
for (int i = 0; i <= 10_0000_0000; i++) {
sum += i;
}
Long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(sum + "---运行时间:" + (end -start));
}
public void test2() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
Long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
ForkJoinPool forkJoinPool = new ForkJoinPool();
ForkJoinTask<Long> forkJoinDemo = new ForkJoinDemo(0L, 10_0000_0000L);
ForkJoinTask<Long> submit = forkJoinPool.submit(forkJoinDemo);
Long sum = submit.get();
Long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(sum + "运行时间:" + (end -start));
}
public void test3(){
Long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
long reduce = LongStream.rangeClosed(0L, 10_0000_0000).parallel().reduce(0, Long::sum);
Long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(reduce + "---运行时间:" + (end -start));
}
}
public class ForkJoinDemo extends RecursiveTask<Long> {
private Long start;
private Long end;
private Long temp = 1_0000L;
public ForkJoinDemo(Long start, Long end) {
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
}
@Override
protected Long compute() {
if ((end-start) < temp){
Long sum = 0L;
for (Long i = start; i <= end; i++) {
sum += i;
}
return sum;
}else {
Long middle = (end + start)/2;
ForkJoinDemo task1 = new ForkJoinDemo(start, middle);
task1.fork(); //拆分任务压入栈
ForkJoinDemo task2 = new ForkJoinDemo(middle +1, end);
task2.fork(); //拆分任务压入栈
//System.out.println("---" + task1.join() + task2.join());
return task1.join() + task2.join(); //合并结果返回
}
}
}
异步回调
- 无返回值类型
- CompletableFuture.runAsync() //异步任务
- 主线
- completableFuture.get()获取异步结果
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
// 无返回值类型
CompletableFuture<Void> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "---run");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
});
System.out.println("Go on");
completableFuture.get(); // 获取异步调用结果
}
- 有返回值类型
- CompletableFuture.supplyAsync() //
- completableFuture.whenComplete() // 获取异步执行结果
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
// int i =1/0;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "run");
return "1024";
});
completableFuture.whenComplete((t, u) -> {
System.out.println(t); // 正常得到异步返回对结果
System.out.println(u); // 若有异常,打印异常信息;正常为null
}).exceptionally((e) -> {
System.out.println(e.getMessage()); // 打印异常信息
return "500"; //异常返回的结果
}).get();
}
JMM(Java Memory Model)
volatile是java虚拟机提供的轻量级的同步机制
1.保证可见性
2.不保证原子性
3.由于内存屏障,禁止指令重排
什么是JMM
JMM:java的内存模型,不存在的东西,概念,约定
关于JMM的一些同步的约定:
1.线程解锁前,必须把共享变量立刻刷回主存
2.线程枷锁前,必须读取主存中的最新值到工作的内存中
3.加锁和解锁是同一把锁
线程:工作内存 ,主内存
Volititle
可见性
public class VolitileDemo {
// public static int num = 0;
public volatile static int num = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(() -> { // 启动线程
while (num == 0){ } // 保证线程一直运行
}).start();
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); //为了保证上面的线程先启动
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
num = 1; // 未加volititle时,更改num后,上面的thread不回停止
System.out.println("num = " + num);
}
}
不保证原子性
public class VolitileDemo {
// public static int num = 0;
public volatile static AtomicInteger num = new AtomicInteger(); // AtomicInteger可以解决
public static void add(){ // 加synchronized可以解决
// num ++; // ++ 不是一个原子性操作
num.getAndIncrement();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
new Thread(() -> { // 启动线程
for (int j = 0; j < 1000; j++) {
add();
}
}).start();
}
while (Thread.activeCount() > 2){ // main gc
Thread.yield(); // 等待所有线程执行完
}
System.out.println("num = " + num);
}
}
保证指令不被重排
volitale可以避免指令重排:
内存屏障.cpu指令.作用
1.保证特定的操作执行循序
2.可以保证某些变量的内存可见性(利用这些特性,保证valitale实现了可见性)
单例模式
- 饿汉式
public class Hungry {
private static Hungry hungry = new Hungry();
private Hungry(){
}
public static Hungry getHungry(){
return hungry;
}
public void test(){
System.out.println("1");
}
}
class main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println(Hungry.getHungry());
}).start();
}
}
}
- 懒汉式
public class Lazy {
private volatile static Lazy instance; // 禁止指令重排 实时更新instance值
private Lazy lazy(){
return instance;
}
public static Lazy getInstance(){
if (instance == null){ // 第一重锁 如果已经创建有instance 就不必进来经过synchronize 浪费时间
synchronized (Lazy.class){
if (instance == null){ // 第二重锁 再次判断 以防synchronize外有线程等待
return instance = new Lazy();
}
return instance;
}
}
return instance;
}
}
class test{
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println(Lazy.getInstance());
}).start();
}
}
}
- 静态内部类(推荐使用)
public class Lazy2 {
//构造器私有化
private Lazy2(){
}
// 静态内部类
private static class Lazy2Instance{
private static final Lazy2 INSTANCE = new Lazy2();
}
public static Lazy2 getLazy2(){
return Lazy2Instance.INSTANCE; // 这里调用才触发实例化
}
}
- 枚举(推荐)
public enum Singleton {
INSTANCE;
public void hello(){
System.out.println("hello");
}
}
class test2{
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Singleton.INSTANCE.hashCode());
System.out.println(Singleton.INSTANCE.hashCode());
Singleton.INSTANCE.hello();
}
}
各种锁的理解
公平锁,非公平锁
公平锁:非常公平,不能够插队,必须先来后到
非公平锁:非常不公平,可以插队,(默认都是非公平如sychronized,lock,rentrantlock)
可重入锁
又名递归锁(拿到大门的锁,就可以拿到房间的锁)





















 1076
1076


 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?







