F. Multi-Colored Segments
time limit per test 3 seconds
memory limit per test 256 megabytes
inputstandard input
outputstandard output
题目描述
Dmitry has n segments of different colors on the coordinate axis Ox. Each segment is characterized by three integers li, ri and ci (1≤li≤ri≤109,1≤ci≤n), where li and ri are are the coordinates of the ends of the i-th segment, and ci is its color.
Dmitry likes to find the minimum distances between segments. However, he considers pairs of segments of the same color uninteresting. Therefore, he wants to know for each segment the distance from this segment to the nearest differently colored segment.
The distance between two segments is the minimum of the distances between a point of the first segment and a point of the second segment. In particular, if the segments intersect, then the distance between them is equal to 0.
For example, Dmitry has 5 segments:
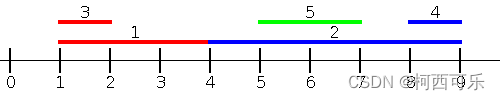
The first segment intersects with the second (and these are segments of different colors), so the answers for them are equal to 0.
For the 3-rd segment, the nearest segment of a different color is the 2-nd segment, the distance to which is equal to 2.
For the 4-th segment, the nearest segment of a different color is the 5-th segment, the distance to which is equal to 1.
The 5-th segment lies inside the 2-nd segment (and these are segments of different colors), so the answers for them are equal to 0.
输入描述
The first line of the input contains an integer t (1≤t≤10^4) — the number of test cases in the test.
The descriptions of the test cases follow.
The first line of description of each test case contains one integer n (2≤n≤2⋅10^5) — the number of segments.
The next n lines contain descriptions of the segments. Each segment is described by three integers li, ri and ci (1≤li≤ri≤109,1≤ci≤n) — coordinates of the left and right ends of i-th segment, as well as the color of this segment. It is guaranteed that there are at least 2 segments of different colors.
It is guaranteed that the sum of n over all test cases does not exceed 2⋅10^5.
输出描述
For each test case, on a separate line print n integers, where the i-th number is equal to the distance from the i-th segment to the nearest segment of a different color.
题意
n 条颜色为 c 的 [l,r] 线段,求每条线段与其它与其颜色不同的任意线段的最短距离(有重合为 0 )
思路1
可以先预处理出 以 l 升序的前缀 r 最右值 以 r 升序的 后缀 l 最左值 并在前后缀中 存前两个颜色的最值 即无论如何都会有一个颜色与要判断的线段颜色不同
二分的时候对于前缀我们只需要找满足 左端点 l 小于等于要求区间的 r 即可
对于后缀我们只需要找满足 右端点 r 大于等于要求区间的 l 即可
Code(思路1)
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define __T int csT;scanf("%d",&csT);while(csT--)
const int mod=1e9+7;
const int maxn=2e5+3;
int n;
struct node{
int id,l,r,c,ans;
}a[maxn];
struct qz{
int l;
int c1,r1,c2,r2;
}q[maxn];
struct hz{
int r;
int c1,l1,c2,l2;
}h[maxn];
int cmpl(node a,node b)
{
return a.l<b.l;
}
int cmpr(node a,node b)
{
return a.r<b.r;
}
int cmpid(node a,node b)
{
return a.id<b.id;
}
int qzl(qz a,qz b)
{
return a.l<b.l;
}
int hzr(hz a,hz b)
{
return a.r<b.r;
}
inline void sol()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)
{
scanf("%d%d%d",&a[i].l,&a[i].r,&a[i].c);
a[i].id=i;
a[i].ans=1e9;
}
//get q
sort(a+1,a+1+n,cmpl);
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)
{
if(i==1)
{
q[i].l=a[i].l;
q[i].c1=a[i].c;
q[i].r1=a[i].r;
q[i].c2=0;
q[i].r2=0;
}
else
{
q[i].l=a[i].l;
q[i].c1=q[i-1].c1;
q[i].r1=q[i-1].r1;
q[i].c2=q[i-1].c2;
q[i].r2=q[i-1].r2;
if(a[i].c==q[i].c1)
{
q[i].r1=max(q[i].r1,a[i].r);
continue;
}
if(a[i].c==q[i].c2)
{
q[i].r2=max(q[i].r2,a[i].r);
continue;
}
if(q[i].r1>=q[i].r2)
{
if(a[i].r>q[i].r2)
{
q[i].c2=a[i].c;
q[i].r2=a[i].r;
}
}//r2小 替换r2
else
{
if(a[i].r>q[i].r1)
{
q[i].c1=a[i].c;
q[i].r1=a[i].r;
}
}//r1小 替换r1
}
}
//get h
sort(a+1,a+1+n,cmpr);
for(int i=n;i>=1;--i)
{
if(i==n)
{
h[i].r=a[i].r;
h[i].c1=a[i].c;
h[i].l1=a[i].l;
h[i].c2=0;
h[i].l2=1e9+7;
}
else
{
h[i].r=a[i].r;
h[i].c1=h[i+1].c1;
h[i].l1=h[i+1].l1;
h[i].c2=h[i+1].c2;
h[i].l2=h[i+1].l2;
if(a[i].c==h[i].c1)
{
h[i].l1=min(h[i].l1,a[i].l);
continue;
}
if(a[i].c==h[i].c2)
{
h[i].l2=min(h[i].l2,a[i].l);
continue;
}
if(h[i].l1<=h[i].l2)
{
if(a[i].l<h[i].l2)
{
h[i].c2=a[i].c;
h[i].l2=a[i].l;
}
}//l2大 替换l2
else
{
if(a[i].l<h[i].l1)
{
h[i].c1=a[i].c;
h[i].l1=a[i].l;
}
}//l1大
}
}
int xb;
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)
{
xb=upper_bound(q+1,q+1+n,qz{a[i].r,0,0,0,0},qzl)-q-1;
if(a[i].c!=q[xb].c1&&q[xb].c1!=0)
{
if(q[xb].r1>=a[i].l)a[i].ans=0;
else
{
a[i].ans=min(a[i].ans,a[i].l-q[xb].r1);
}
}
if(a[i].c!=q[xb].c2&&q[xb].c2!=0)
{
if(q[xb].r2>=a[i].l)a[i].ans=0;
else
{
a[i].ans=min(a[i].ans,a[i].l-q[xb].r2);
}
}
xb=lower_bound(h+1,h+1+n,hz{a[i].l,0,0,0,0},hzr)-h;
if(a[i].c!=h[xb].c1&&h[xb].c1!=0)
{
if(h[xb].l1<=a[i].r)a[i].ans=0;
else
{
a[i].ans=min(a[i].ans,h[xb].l1-a[i].r);
}
}
if(a[i].c!=h[xb].c2&&h[xb].c2!=0)
{
if(h[xb].l2<=a[i].r)a[i].ans=0;
else
{
a[i].ans=min(a[i].ans,h[xb].l2-a[i].r);
}
}
}
sort(a+1,a+1+n,cmpid);
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)
{
printf("%d ",a[i].ans);
}
puts("");
}
int main()
{
__T
sol();
return 0;
}
思路2
若排除掉重合情况的话显然即为排除掉 要求的线段颜色 c 后离左端点最近的线段右端点以及离右端点最近的左端点 重合即判所处的这段区间是否还有线段 故可以通过线段树区间加和区间求和判重以及删颜色判完再加回去
判断不重合部分可以通过线段树上二分 1-1e9 的值域可以采用线段树动态开点 (离散化也不是不行 但映射来去容易写错)
Code(思路2)(先挖个坑吧)





 本文介绍了一种算法问题:计算每条彩色线段与其他颜色线段的最短距离,包括线段重叠的情况。通过预处理线段的左右边界并利用二分查找,实现了高效的解决方案。
本文介绍了一种算法问题:计算每条彩色线段与其他颜色线段的最短距离,包括线段重叠的情况。通过预处理线段的左右边界并利用二分查找,实现了高效的解决方案。

















 747
747

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










