案例1:写一篇短文,然后对这篇短文进行打分
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate, MessagesPlaceholder
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnableWithMessageHistory, RunnableLambda
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
llm_zhipu = ChatOpenAI(
temperature=0.9,
model='glm-4-air-0111',
api_key='****',
base_url='https://open.bigmodel.cn/api/paas/v4/'
)
parser = StrOutputParser()
prompt1 = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template('给我写一篇关于{key_word}的{type},字数不超过{count}。')
prompt2 = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template('请简单评价一下这篇短文,如果总分是10分,请给这篇短文打分:{text_context}。')
chain1 = prompt1 | llm_zhipu | StrOutputParser()
#这样组装,不会输出chain1的内容
# chain2 = {'text_context':chain1} | prompt2 | llm_zhipu | StrOutputParser()
def print_chain1(input):
print(input)
print('*'*30)
return {'text_context':input}
chain2 = chain1 | RunnableLambda(print_chain1) | prompt2 | llm_zhipu | parser
print(chain2.invoke({'key_word': '请写一篇关于春天的文章', 'type': '散文', 'count': 500}))
输出:

案例2:根据用户输入的点餐偏好,推荐2-3家餐厅,并给出推荐理由
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate, MessagesPlaceholder
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnableWithMessageHistory, RunnableLambda
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
llm = ChatOpenAI(
temperature=1,
model='deepseek-r1',
api_key='****',
base_url='https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/compatible-mode/v1'
)
parser = StrOutputParser()
user_preperences_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template('用户输入了一些餐厅偏好:\n{user_input}\n,请将用户的偏好总结为清晰的需求:')
recommend_preperences_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template('基于用户的需求:\n{recommend_input}\n,请推荐3家适合的餐厅,并说明推荐的理由:')
summarize_preperences_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template('以下是餐厅推荐和推荐的理由:\n{summarize_input}\n,请总结成2-3句话,供用户参考:')
chain = user_preperences_prompt | llm | recommend_preperences_prompt | llm | summarize_preperences_prompt | llm | parser
print(chain.invoke({'user_input': '我喜欢吃辣,环境要安静点的餐厅,价格要实惠,又好吃的菜'}))
输出:
案例3:用户会问到各个领域的问题,根据不同的领域定义不同的提示词模板,动态的选择合适的任务模板去完成
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser, JsonOutputParser
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate, MessagesPlaceholder
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnableWithMessageHistory, RunnableLambda, RouterRunnable, RunnableSequence
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
llm = ChatOpenAI(
temperature=1,
model='deepseek-r1',
api_key='*****',
base_url='https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/compatible-mode/v1'
)
#用户会问到各个领域的问题,根据不同的领域定义不同的提示词模板,动态的选择合适的任务模板去完成
parser = StrOutputParser()
math_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template('你是一位数学家,擅长分步骤解决各种数学问题,以下是问题的内容:{input}')
physics_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template('你是一位物理教授,擅长用通俗易懂的语言回答各种物理问题,以下是问题的内容:{input}')
history_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template('你是一位历史研究学家,对历史事件和背景很精通,以下是问题的内容:{input}')
computer_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template('你是一位非常自身的计算机科学家,擅长算法,大数据,编程问题,以下是问题的内容:{input}')
default_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template('输入内容无法归类,请直接回答:{input}')
default_chain = default_prompt | llm
computer_chain = computer_prompt | llm
history_chain = history_prompt | llm
physics_chain = physics_prompt | llm
math_chain = math_prompt | llm
def route(input):
"""
根据大模型第一次处理的值输出来,动态判断各种领域的任务
:param input:
:return:
"""
if '物理' in input['type']:
print('1号路由')
return {'key':'physics','input':input['input']}
elif '数学' in input['type']:
print('2号路由')
return {'key':'math','input':input['input']}
elif '历史' in input['type']:
print('3号路由')
return {'key':'history','input':input['input']}
elif '计算机' in input['type']:
print('4号路由')
return {'key':'computer','input':input['input']}
else :
print('5号路由')
return {'key':'default','input':input['input']}
#创建一个路由的节点
route_runnable = RunnableLambda(route)
router = RouterRunnable(runnables={
'physics':physics_chain,
'math':math_chain,
'history': history_chain,
'computer': computer_chain,
'default': default_chain
})
#第一个提示词模板:
first_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(
'不要回答下面用户的问题,只要根据用主呢的输入来判断分类,一共有【物理、历顺、计算机、数学、其他】5种类别\n\n\
用户的输入:{input}\n\n\
最后的输出包含分类的类别和用户输入的内容,输出的格式为json,其中类别的key为type,用户输入内容的key为input'
)
chain1 = first_prompt | llm | JsonOutputParser()
chain2 = RunnableSequence(chain1,route_runnable,router) # chain1 | route_runnable | router
inputs = [
{'input':'什么是黑体辐射?'},
{'input':'1+1真的等于2吗?'},
{'input':'介绍一下第一次世界大战的背景?'},
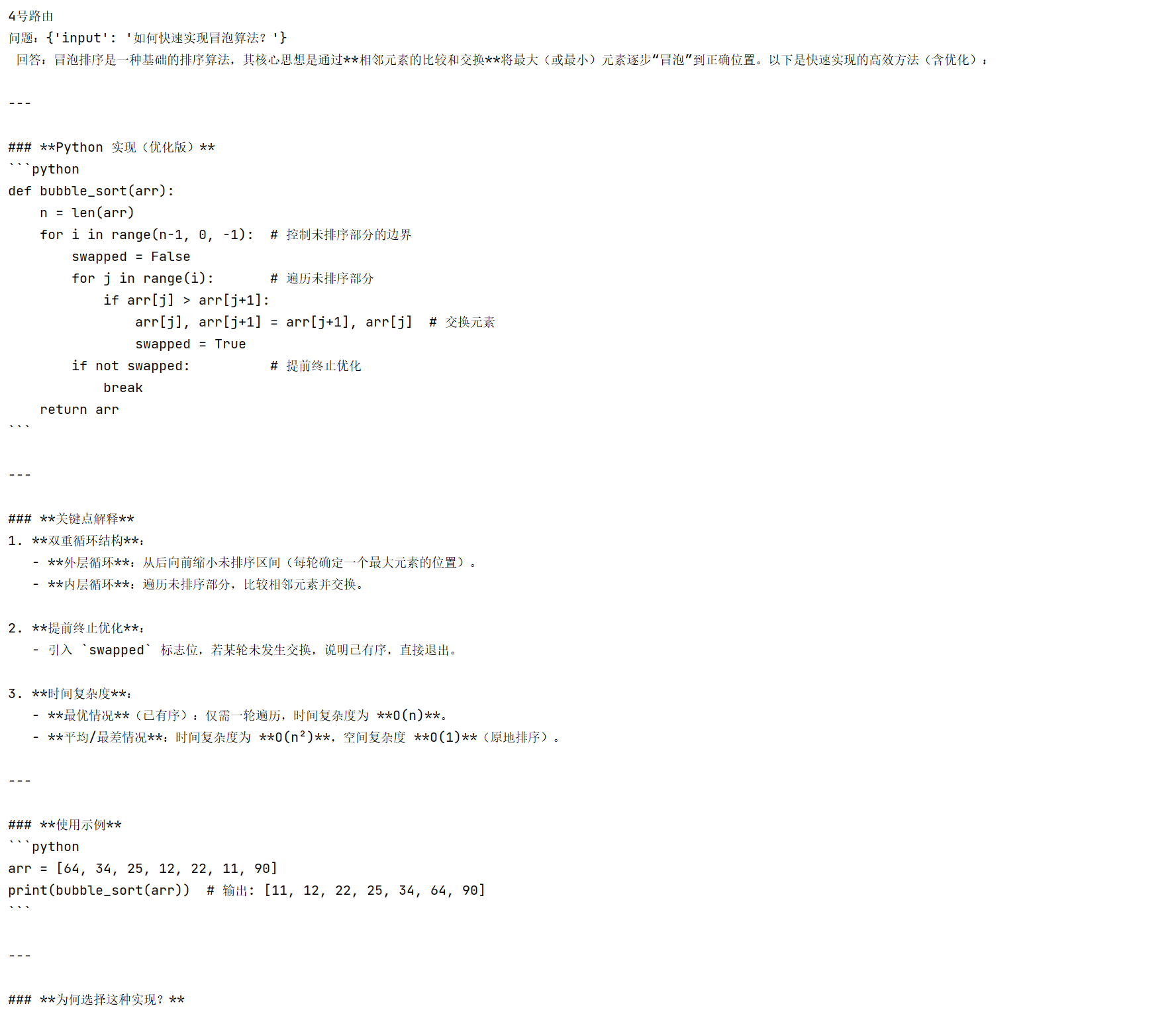
{'input':'如何快速实现冒泡算法?'}
]
for inp in inputs:
result = chain2.invoke(inp)
print(f'问题:{inp}\n 回答:{result.content}\n')
输出:
























 3373
3373

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








