一、前言
本文介绍了使用Spring AI框架深度集成业务系统的方法,实现本地化AI问答功能。主要内容包括:
- 技术选型:基于SpringBoot框架,使用Spring AI接入阿里云百炼平台的deepseek-r1文本模型,配合Elasticsearch向量数据库实现RAG和Redis缓存实现上下文缓存。
- 实现功能:
- 流式输出响应
- 对话上下文管理
- RAG检索增强
- AI工具调用
- 对话日志
- 多租户隔离
- 介绍内容:
- AI提示Prompt
- 结构化输出(代码未实现)
- 多模态(代码未实现,仅概念介绍)
- 聊天记忆,即对话上下文管理
- 工具调用
- MCP模型上下文协议(代码未实现)
- RAG检索增强与向量数据库
文章包含完整的代码示例和配置说明,适合开发者快速实现业务场景的AI对话功能。
注1:文章还记录遇到的问题,代码已完全实现以上介绍的功能,但存在一些BUG,后续会持续更新,如有解决方法还请告知,万分感谢。
注2:如果需要自行改造或进一步理解,请到springAi官网查阅文档。Spring Ai
二、使用技术
基础框架:springboot 3.4.*+
ai框架:springAi
jdk:17
文本模型:阿里云百炼平台的deepseek-r1
向量模型:text-embedding-v4
向量数据库:elasticsearch
缓存数据库:redis
三、代码实现
1、整体目录结构
2、maven坐标
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<groupId>org.dromara</groupId>
<artifactId>ruoyi-modules</artifactId>
<version>${revision}</version>
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>ruoyi-chatai</artifactId>
<description>
openAi模块
</description>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- 前缀为ruoyi的都是若依框架的模块,可替换 -->
<!-- 多租户模块 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.dromara</groupId>
<artifactId>ruoyi-common-tenant</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 鉴权模块 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.dromara</groupId>
<artifactId>ruoyi-common-satoken</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- web模块 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.dromara</groupId>
<artifactId>ruoyi-common-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- mybatis模块 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.dromara</groupId>
<artifactId>ruoyi-common-mybatis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- hutool工具 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.hutool</groupId>
<artifactId>hutool-json</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-codec</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-codec</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- springAi的操作elasticsearch向量数据库依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-elasticsearch-store-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 核心依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-alibaba-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-lang3</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-spring-boot3-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
3、yml配置
spring:
#elasticsearch向量数据库配置
elasticsearch:
uris: http://127.0.0.1:9200
# 本地elasticsearch未开启认证,生产环境必须开启
username: root
password: famsakfdsfx
spring:
ai:
dashscope:
api-key: sk-c7********************* #从阿里云百炼平台获取
chat:
options:
model: deepseek-r1
embedding:
options:
# 嵌入的向量模型
model: text-embedding-v4
vectorstore: #向量相关配置
elasticsearch: #使用elasticsearch作为向量数据库,也可以使用其他的,如redis向量数据库
initialize-schema: true #如果不存在该索引则创建
index-name: spring-ai-rag #索引名称(这里的索引并不是mysql那种索引)
# elasticsearch的向量维度(默认1536),需要和向量模型的维度一致。因为text-embedding-v4向量模型配置维度不生效,只能配置默认的1024
dimensions: 1024
similarity: cosine #相似配置枚举类型
#以上是springAi自身的配置,以下是自定义配置
# ai初始化配置
client:
enabled: false #是否开启初始化
# 系统的默认行为和风格
defaultSystem: 你是一个电子产品回收系统专业的助手。需要做到以下几点:1、在回答问题时,使用表格展示或分点列举的方式,以便用户更容易理解和参考;2、遇到不确定或不明确的信息时,会主动询问用户以获取更多信息;3、拒绝回答与本系统无关的问题。
# 相似度阈值,取值区间:(0,1]
similarity-threshold: 0.3
# 返回匹配的向量文档数量,可以按每个向量文档的token大小来设置,token大,topK则设置小一些,否则会超出ai对话的token长度限制
topK: 50
# 对话上下文记忆条数
chatHistoryWindowSize: 20
knowledgeBasePath: chatai/knowledgeBase
issuePath: chatai/问题提示语.txt
4、ai初始化及配置类
4.1、ai对话配置信息
读取yml配置
/**
* ai对话配置信息
*/
@Data
@Configuration
@ConfigurationProperties("spring.ai.client")
public class ChatClientConfigInfo {
/**
* 是否开启ai
*/
private Boolean enabled;
/**
* 系统的默认行为和风格
*/
private String defaultSystem;
/**
* 相似度阈值,取值区间:(0,1]
*/
private Double similarityThreshold;
/**
* 返回匹配的向量文档数量,可以按每个向量文档的token大小来设置,token大,topK则设置小一些,否则会超出ai对话的token长度限制
*/
private Integer topK;
/**
* 对话上下文记忆条数
*/
private Integer chatHistoryWindowSize;
/**
* 提示词
*/
private List<String> issues;
/**
* 提示词文件路径(可以和提示词共存)
*/
private String issuePath;
/**
* 初始知识库文件路径
*/
private String knowledgeBasePath;
}
4.2、ai初始化
对话上下文缓存具体实现查看 章节 七、聊天记忆,即对话上下文管理
@Slf4j
@Configuration
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class ChatClientConfig {
private final ChatClientConfigInfo chatClientConfigInfo;
private final ChatModel chatModel;
/**
* 初始化AI
*/
@Bean
public ChatClient chatClient() {
return ChatClient.builder(chatModel)
.defaultSystem(chatClientConfigInfo.getDefaultSystem())
// 这里还可以配置一些默认的ai工具、RAG检索、MCP等
.build();
}
/**
* 注册对话上下文缓存
*/
@Bean
public ChatMemory chatMemory() {
return new ChatRedisMemory(chatAiLogService);
}
}
4.3、初始化知识库
将准备好的基本信息文件转化成向量文档存储到向量数据库中,在使用ai时检索与问题相似数据提供给ai。初始化信息可以是:系统介绍、公司介绍、操作手册、业务名称说明、业务表结构说明等等,文件类型推荐文本、word文档、pdf。
@Slf4j
@Configuration
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class SpringAiRunner implements ApplicationRunner {
private final ChatClientConfigInfo chatClientConfigInfo;
private final VectorStoreService vectorStoreService;
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) {
if (chatClientConfigInfo.getEnabled()) {
knowledgeBaseInit();
}
readIssue();
}
/**
* 初始化知识库
*/
public void knowledgeBaseInit() {
List<String> fileNames = new ArrayList<>();
try {
fileNames = FileUtils.getClassPathResourceFileName(chatClientConfigInfo.getKnowledgeBasePath());
} catch (IOException e) {
log.info("无初始化知识库文件!");
}
try {
// 删除旧文档和添加新文档
vectorStoreService.delete(FilterExpressionUtil.in(VectorKey.KEY, fileNames));
for (String fileName : fileNames) {
String filePath = chatClientConfigInfo.getKnowledgeBasePath() + "/" + fileName;
vectorStoreService.saveFile(VectorKey.COMMON,filePath);
}
log.info("初始化 向量知识库 成功!");
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("初始化 向量知识库 失败!原因:\n{}", e.getMessage());
}
}
/**
* 读取【问题提示语.txt】文件添加到chatClientConfigInfo
*/
public void readIssue() {
try {
List<String> issues = FileUtils.readLinesFromFile(chatClientConfigInfo.getIssuePath());
List<String> infoIssues = chatClientConfigInfo.getIssues();
if (infoIssues != null) {
issues.addAll(infoIssues);
}
chatClientConfigInfo.setIssues(issues);
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("读取【{}】文件失败", chatClientConfigInfo.getIssuePath());
}
}
}
例:


5、对话实现
由于ai功能模块化,为了避免耦合,由ai模块提供接口给业务模块,业务模块实现接口,通过实现类将ai工具(tool)传递到ai模块,最后由ai模块实现对话的核心逻辑。这个章节的标题已标注代码是属于ai模块或业务模块。
调用流程为:
ai模块controller->ai模块service接口->业务模块接口实现类(加入ai工具及其它方法作为参数传递)
->ai模块对话实现类
5.1、控制层(ai模块)
@Validated
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/chat/v1")
public class ChatController {
private final ChatService chatService;
private final ChatMemory chatMemory;
/**
* deepSeek
*/
@GetMapping(value = "/deepseek/rag")
public Flux<String> ragChat(String message) {
return chatService.ragChat(message);
}
/**
* 清空上下文
*/
@GetMapping(value = "/deepseek/clearAway")
public R<Void> clearAway() {
chatMemory.clear(LoginHelper.getUserId().toString());
return R.ok();
}
/**
* 中断对话(后续实现)
*/
}
5.2、ai服务接口(ai模块)
提供给外部的接口,业务模块实现该接口,本文是单例实现,可以改造成策略模式达到多实现的目的,使ai更加专注于某一块业务的处理。
/**
* ai服务
*/
public interface ChatService {
/**
* 多轮对话
*/
Flux<String> ragChat(String message);
}
5.3、实现ai服务接口(业务模块)
ai工具调用类具体功能介绍及实现查看章节 八、工具调用
/**
* 回收报价ai服务
*/
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class EsChatService implements ChatService {
//ai工具调用类
private final EquipmentTool equipmentTool;
private final OrderTool orderTool;
private final ChatClientService chatClientService;
private final IEsPriceService esPriceService;
@Override
public Flux<String> ragChat(String message) {
return chatClientService.send(message, esPriceService.priceConsumer(), equipmentTool, orderTool);
}
}
5.4、对话核心实现(ai模块)
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class ChatClientService {
private final ChatClientConfigInfo chatClientConfigInfo;
private final VectorStoreService vectorStoreService;
private final ChatClient chatClient;
private final ChatMemory chatMemory;
/**
* 发送对话
*注:docProcessor 的功能说明及实现示例代码查看下一节 5.5、向量检索后处理实现
*
* @param message 对话信息
* @param docProcessor 向量检索后处理
* @param toolObjects ai对话工具
*/
public Flux<String> send(String message, Function<List<Document>, List<Document>> docProcessor, Object... toolObjects) {
String userId;
try {
userId = LoginHelper.getLoginUser().getUserId().toString();
} catch (Exception e) {
return Flux.just("请先登录!");
}
//先进行数据检索,在知识库中未检索到信息则认为是与本系统无关的问题
// 这里依赖向量数据库的数据库,如果要保留这个操作,需要维护向量数据库的数据
List<Document> documentList = vectorStoreService.search(message);
if (documentList.isEmpty()) {
//未命中知识库
List<String> issues = chatClientConfigInfo.getIssues();
Collections.shuffle(issues);
return Flux.just("我无法回答与系统无关的问题,请换一个问题吧。" +
"\n" + issues.get(0) + "\n" + issues.get(1) + "\n" + issues.get(2)
);
}
if (docProcessor != null) {
documentList = docProcessor.apply(documentList);
}
//把处理后文档拼成上下文,手动塞进 prompt
String context = documentList.stream()
.map(Document::getText)
.collect(Collectors.joining("\n\n"));
return chatClient.prompt()
.system(chatClientConfigInfo.getDefaultSystem() + "请使用以下内容回答用户问题:\n" + context)
.user(message)
.advisors(new MessageChatMemoryAdvisor(chatMemory, userId, chatClientConfigInfo.getChatHistoryWindowSize()))
.tools(toolObjects)
//流式输出,不需要流式输出则将以下代码改为.call().content()
.stream().content();
}
}
5.5、向量检索后处理实现(业务模块)
这个设计的主要目的是用于检索出向量文档后,对向量文档中的数据进一步处理的函数。
**初始化默认的向量检索顾问:**在检索到向量文档后会直接加入到Prompt中,无法做去重、截断、重排序等操作。
**手动查询向量文档:**能灵活的在检索出向量文档后处理数据,处理文档数据后,手动加入到prompt的system()中。
扩展:还可以自定义顾问,在顾问内部留一个函数插槽的方式,对向量检索后数据处理。
public Function<List<Document>, List<Document>> priceConsumer() {
return documentList -> {
List<Document> newDocument = new ArrayList<>();
for (Document oldDoc : documentList) {
Map<String, Object> metadata = oldDoc.getMetadata();
String type = String.valueOf(metadata.get(VectorKey.TYPE));
if ("es_price".equals(type)) {
String text = oldDoc.getText();
JSONObject root = JSON.parseObject(text);
// 修改价格
for (String key : root.keySet()) {
JSONObject memoryObj = root.getJSONObject(key);
for (String memKey : memoryObj.keySet()) {
JSONObject finenessObj = memoryObj.getJSONObject(memKey);
for (String finenessKey : finenessObj.keySet()) {
BigDecimal oldPrice = finenessObj.getBigDecimal(finenessKey);
BigDecimal newPrice = calculatePrice(oldPrice);
finenessObj.put(finenessKey, newPrice);
}
}
}
// 重新生成 Document
String newText = root.toJSONString();
Document newDoc = Document.builder()
.id(oldDoc.getId())
.text(newText)
.metadata(oldDoc.getMetadata())
.build();
newDocument.add(newDoc);
}
}
return newDocument;
};
}
6、ai对话日志
6.1、自定义日志顾问
内部属性无法使用springboot的自动注入,需要在使用时候new一个LoggerAdvisor实例,通过构造方法传入。
/**
* 日志顾问
*/
@Slf4j
public class LoggerAdvisor implements CallAroundAdvisor, StreamAroundAdvisor {
private final IChatAiLogService chatAiLogService;
private final String conversationId;
private final String tenantId;
public LoggerAdvisor(IChatAiLogService chatAiLogService, String tenantId,String conversationId) {
this.chatAiLogService = chatAiLogService;
this.tenantId = tenantId;
this.conversationId = conversationId;
}
// 非流式日志
@Override
public AdvisedResponse aroundCall(AdvisedRequest request, CallAroundAdvisorChain chain) {
List<ChatAiLog> listLog = new ArrayList<>();
ChatAiLog userLog = new ChatAiLog();
userLog.setChatId(conversationId);
userLog.setType(MessageType.USER.getValue());
userLog.setText(request.userText());
userLog.setChatTime(DateUtils.getNowDate());
userLog.setTenantId(tenantId);
listLog.add(userLog);
AdvisedResponse response = chain.nextAroundCall(request);
ChatAiLog systemLog = new ChatAiLog();
systemLog.setChatId(conversationId);
systemLog.setType(MessageType.SYSTEM.getValue());
systemLog.setText(response.response().getResult().getOutput().getText());
systemLog.setChatTime(DateUtils.getNowDate());
systemLog.setTenantId(tenantId);
listLog.add(systemLog);
chatAiLogService.saveBatch(listLog);
return response;
}
// 流式日志
@Override
public Flux<AdvisedResponse> aroundStream(AdvisedRequest request, StreamAroundAdvisorChain chain) {
ChatAiLog userLog = new ChatAiLog();
userLog.setChatId(conversationId);
userLog.setType(MessageType.USER.getValue());
userLog.setText(request.userText());
userLog.setChatTime(DateUtils.getNowDate());
userLog.setTenantId(tenantId);
chatAiLogService.save(userLog);
Flux<AdvisedResponse> responses = chain.nextAroundStream(request);
return new MessageAggregator()
.aggregateAdvisedResponse(responses, res -> {
ChatAiLog systemLog = new ChatAiLog();
systemLog.setChatId(conversationId);
systemLog.setType(MessageType.SYSTEM.getValue());
systemLog.setText(res.response().getResult().getOutput().getText());
systemLog.setChatTime(DateUtils.getNowDate());
systemLog.setTenantId(tenantId);
chatAiLogService.save(systemLog);
}
);
}
@Override
public String getName() {
return "LoggerAdvisor";
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return 100;
}
}
6.2、实体类、Mapper、xml文件、service及impl、controller
简单日志信息的存储和查询,常用的三层架构,可以改成其他的方式。
ai对话日志是为了通过分析更好的调整ai,如用户高频问题,可以编写专门的ai工具调用方法。
/**
* ai对话日志
*/
@Data
@EqualsAndHashCode(callSuper = true)
@TableName("chat_ai_log")
public class ChatAiLog extends BaseEntity {
@Serial
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@TableId(value = "id",type = IdType.AUTO)
private Long id;
/**
* 对话ID(用户ID)
*/
private String chatId;
/**
* 类型(system、user、assistant)
*/
private String type;
/**
* 对话消息
*/
private String text;
/**
* 对话时间
*/
private Date chatTime;
}
public interface ChatAiLogMapper extends BaseMapper<ChatAiLog> {
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="org.dromara.chatai.mapper.ChatAiLogMapper">
</mapper>
public interface IChatAiLogService extends IService<ChatAiLog> {
TableDataInfo<ChatAiLog> queryPageList(ChatAiLog bo, PageQuery pageQuery);
}
@Slf4j
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Service
public class IChatAiLogServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<ChatAiLogMapper, ChatAiLog> implements IChatAiLogService {
@Override
public TableDataInfo<ChatAiLog> queryPageList(ChatAiLog bo, PageQuery pageQuery) {
LambdaQueryWrapper<ChatAiLog> lqw = buildQueryWrapper(bo);
Page<ChatAiLog> result = baseMapper.selectPage(pageQuery.build(), lqw);
return TableDataInfo.build(result);
}
private LambdaQueryWrapper<ChatAiLog> buildQueryWrapper(ChatAiLog bo) {
LambdaQueryWrapper<ChatAiLog> lqw = Wrappers.lambdaQuery();
lqw.orderByAsc(ChatAiLog::getId);
lqw.like(StringUtils.isNotBlank(bo.getType()), ChatAiLog::getType, bo.getType());
lqw.eq(StringUtils.isNotBlank(bo.getText()), ChatAiLog::getText, bo.getText());
return lqw;
}
}
@Validated
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/chat/log")
public class ChatAiLogController {
private final IChatAiLogService chatAiLogService;
/**
* 查询ai对话日志列表
*/
@SaCheckPermission("chat:log:list")
@GetMapping("/list")
public TableDataInfo<ChatAiLog> list(ChatAiLog bo, PageQuery pageQuery) {
return chatAiLogService.queryPageList(bo, pageQuery);
}
/**
* 获取ai对话日志详细信息
*
* @param id 主键
*/
@SaCheckPermission("chat:log:query")
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public R<ChatAiLog> getInfo(@NotNull(message = "主键不能为空") @PathVariable Long id) {
return R.ok(chatAiLogService.getById(id));
}
}
6.3、日志数据库sql
SET NAMES utf8mb4;
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 0;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `chat_ai_log`;
CREATE TABLE `chat_ai_log` (
`id` bigint NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`chat_id` varchar(50) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`type` varchar(20) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`text` text CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci NULL,
`chat_time` datetime NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`create_time` datetime NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`update_time` datetime NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`create_by` bigint NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`update_by` bigint NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`tenant_id` varchar(20) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 36 CHARACTER SET = utf8mb4 COLLATE = utf8mb4_general_ci COMMENT = 'ai对话日志' ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 1;
四、AI提示Prompt
提示(Prompt),实际就是发送给ai的内容,可以包含以下内容:
- system内容,规范ai的行为和规范
- user内容,用户的输入
- 上下文对话内容
- RAG检索内容
- AI工具获取到的内容
- MCP获取到的内容
这些内容显著影响ai的输出,想要ai的输出达到预期效果,设计ai提示(Prompt)是极为重要的。
五、结构化输出(代码未实现)
如标题描述的一样,让ai根据规定的格式进行输出,有两种方式:
- 通过提示词进行规范
- 使用转换器
通过提示词进行规范的方式就是用自然语言告诉ai要按什么格式进行输出,可以提供模版格式,但是使用这种方法并不能百分百保证ai按格式输出。
使用转换器的方法查看SpringAi 结构化输出
六、多模态(代码未实现)
就是配置多种ai模型(文本模型、视觉模型、语言模型),多种模型配合进行问答,功能更加强大。
七、聊天记忆,即对话上下文管理
ai模型并无记忆,要实现连续对话,就得自己记录对话信息,并在每次提问时候将之前的对话记录一并发送给ai。
核心是实现ChatMemory接口
具体怎么保存对话信息可以随意实现,以下介绍的是以redis存储上下信息。
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class ChatEntity implements Serializable {
/**
* 对话ID
*/
private String chatId;
/**
* 类型(system、user、assistant、tool)
*/
private String type;
/**
* 对话消息
*/
private String text;
}
@Slf4j
@Component
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class ChatRedisMemory implements ChatMemory {
private static final String KEY_PREFIX = "chat:history:";
@Override
public void add(String conversationId, Message message) {
ChatMemory.super.add(conversationId, message);
}
@Override
public void add(String conversationId, List<Message> messages) {
String key = KEY_PREFIX + conversationId;
List<ChatEntity> listIn = new ArrayList<>();
for (Message msg : messages) {
//去除think过程
String[] strs = msg.getText().split("</think>");
String text = strs.length == 2 ? strs[1] : strs[0];
ChatEntity ent = new ChatEntity();
ent.setChatId(conversationId);
ent.setType(msg.getMessageType().getValue());
ent.setText(text);
listIn.add(ent);
}
RedisUtils.setCacheList(key, listIn);
RedisUtils.expire(key, Duration.ofMinutes(30));
}
@Override
public List<Message> get(String conversationId, int lastN) {
String key = KEY_PREFIX + conversationId;
List<Message> listOut = new ArrayList<>();
if (!RedisUtils.hasKey(key)) {
return listOut;
}
long size = RedisUtils.getCacheList(key).size();
if (size == 0) {
return listOut;
}
int start = Math.max(0, (int) (size - lastN));
List<Object> listTmp = RedisUtils.getCacheListRange(key, start, -1);
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
for (Object obj : listTmp) {
ChatEntity chat = objectMapper.convertValue(obj, ChatEntity.class);
if (MessageType.USER.getValue().equals(chat.getType())) {
listOut.add(new UserMessage(chat.getText()));
} else if (MessageType.ASSISTANT.getValue().equals(chat.getType())) {
listOut.add(new AssistantMessage(chat.getText()));
} else if (MessageType.SYSTEM.getValue().equals(chat.getType())) {
listOut.add(new SystemMessage(chat.getText()));
}
}
return listOut;
}
@Override
public void clear(String conversationId) {
RedisUtils.deleteObject(KEY_PREFIX + conversationId);
}
}
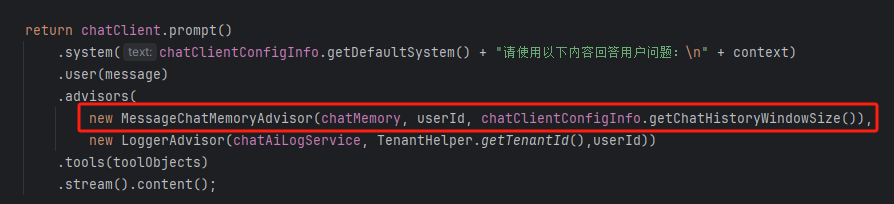
然后在调用ai时通过对话顾问添加到ai中:
八、工具调用
AI工具和MCP的功能有点相似,都是用于扩展ai的功能。
比如检索天气信息、业务数据库信息等。
优缺点对比:
- 上手难度:ai工具极低,MCP需要额外学习
- 功能实现:ai工具需要编码实现,MCP不需要
- 共用性:ai工具仅当前spring应用,MCP可以多服务共用,且不分语言
ai工具实现示例(tool)
核心内容:@Tool和@ToolParam注解,其他可有可无,看业务需要。
只要在方法上加了@Tool注解,那该方法即是ai工具(tool)。
@Tool:使用自然语言描述标记的方法的用处,当ai根据对话内容匹配到时候就会执行该方法。
@ToolParam:使用自然语言描述标记的参数,由ai根据对话内容自动传入。
作用:
作为给ai提供数据的一种方法,或是由ai操作业务的方法,如在订票系统中:帮我订一张xxx的票。(让ai操作业务需要谨慎,ai并不是百分百准确的)
以下为@Tool的使用示例,与ai模块无关。
@Slf4j
@Component
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Description("查询回收设备及价格服务")
public class EquipmentTool {
private final EsEquipmentMapper equipmentMapper;
private final EsPriceMapper priceMapper;
@Tool(name = "查询可回收的产品、设备或型号",
description = """
根据设备的类型(手机、平板等)、品牌(苹果、华为等等)、系列、型号、内存参数查询可回收的设备信息
其中品牌必填
""")
public List<Map<String, String>> productName(@ToolParam(description = "类型") String equipmentType,
@ToolParam(description = "品牌") String brand,
@ToolParam(description = "系列", required = false) String series,
@ToolParam(description = "型号", required = false) String model,
@ToolParam(description = "内存", required = false) String internalStorage) {
return equipmentMapper.getProductNameList(equipmentType, brand, series, model, internalStorage);
}
@Tool(name = "查询价格、回收价格",
description = """
根据设备的类型(手机、平板等)、品牌(苹果、华为等等)、系列、型号、内存参数查询最新价格(回收价格)
其中型号必填
""")
public List<Map<String, String>> selectPrice(@ToolParam(description = "类型", required = false) String equipmentType,
@ToolParam(description = "品牌", required = false) String brand,
@ToolParam(description = "系列", required = false) String series,
@ToolParam(description = "型号") String model,
@ToolParam(description = "内存", required = false) String internalStorage,
@ToolParam(description = "成色", required = false) String fineness) {
return priceMapper.selectPriceListByTableName("es_price", equipmentType, brand, series, model, internalStorage, fineness);
}
@Tool(name = "查询历史价格、回收价格",
description = """
根据设备的类型(手机、平板等)、品牌(苹果、华为等等)、系列、型号、内存参数查询历史价格(回收价格)
其中型号和日期必填必填,日期是Date类型的参数
""")
public List<Map<String, String>> selectHistoryPrice(@ToolParam(description = "类型", required = false) String equipmentType,
@ToolParam(description = "品牌", required = false) String brand,
@ToolParam(description = "系列", required = false) String series,
@ToolParam(description = "型号") String model,
@ToolParam(description = "内存", required = false) String internalStorage,
@ToolParam(description = "成色", required = false) String fineness,
@ToolParam(description = "日期") Date date) {
String dateToStr = DateUtils.parseDateToStr(FormatsType.YYYY_MM_DD_, date);
String tableName = String.format("%s_%s", "es_price", dateToStr);
return priceMapper.selectPriceListByTableName(tableName, equipmentType, brand, series, model, internalStorage, fineness);
}
}
九、MCP模型上下文协议(代码未实现)
mcp是一种标准化协议,mcp服务是遵循mcp协议开发的类似于插件一样的程序,提高ai与外部资源的交互性。
目前市面上已经有大量的mcp服务。
查看SpringAi 模型上下文协议(MCP)
十、RAG检索增强与向量数据库
RAG检索增强是检索向量数据库中的信息,将检索到的信息提供给ai。
向量数据库是一种专用数据库。如常用于缓存数据库的redis,搜索引擎elasticsearch都可以作为向量数据库,不过得用向量数据库版本的。还有很多其他的,具体查看SpringAi 向量数据库
以下是以elasticsearch作为向量数据库的代码实现。
向量数据的存储与检索(核心:VectorStore类)
VectorStore类是没有修改方法的,所以要修改数据的话只能先删除再新增。
注:本文使用elasticsearch作为向量数据库,elasticsearch的下载、安装、使用可以在网上找文章,只需要入门就能使用。
1、向量数据库操作封装类
@Slf4j
@Component
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class VectorStoreService {
private final ChatClientConfigInfo chatClientConfigInfo;
private final VectorStore vectorStore;
private final BatchingStrategy batchingStrategy;
/**
* 数据检索
*
* @param query 检索词
*/
public List<Document> search(String query) {
return search(query, null);
}
/**
* 数据检索
*
* @param query 检索词
* @param expression 过滤表达式
*/
public List<Document> search(String query, Filter.Expression expression) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
expression = buildTenantExpression(expression);
List<Document> documents = vectorStore.similaritySearch(
SearchRequest.builder()
.query(query)
.filterExpression(expression)
.similarityThreshold(chatClientConfigInfo.getSimilarityThreshold())
.topK(chatClientConfigInfo.getTopK())
.build()
);
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("查询向量数据文档数:【{}】,耗时:【{}】毫秒", documents.size(), (endTime - startTime));
return documents;
}
/**
* 删除(这里只封装了根据过滤表达式删除文档的方法,还有一个根据id删除的方法,可以按需使用或封装)
*
* @param expression 过滤表达式
*/
public void delete(Filter.Expression expression) {
expression = buildTenantExpression(expression);
try {
vectorStore.delete(expression);
}catch (IllegalStateException e){
log.error(e.getMessage());
}
}
/**
* 新增
*
* @param key 数据标识
* @param dataType 数据类型
* @param text 新增的数据
*/
public void save(String key, String dataType, String text) {
String tenantId = getTenantId();
Document document = new Document(text, Map.of(VectorKey.KEY, key, VectorKey.TYPE, dataType, VectorKey.TENANT_ID, tenantId));
vectorStore.add(List.of(document));
}
public void saveFile(String dataType, String path) throws IOException {
Resource resource = (new DefaultResourceLoader()).getResource(path);
String text = StreamUtils.copyToString(resource.getInputStream(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
// 获取文件名称
String fileName = Paths.get(path).getFileName().toString();
save(fileName, dataType, text);
}
/**
* 批量添加
*
* @param key 数据标识
* @param dataType 数据类型
* @param data 新增的数据
* @param batchSize 分片数量,为0时不分片,数据量大于一定量时需要分片,否则会超出当个文件token限制
* 注:这个参数一开始是没有6.4的EmbeddingConfig批量新增向量文档配置做的分片手段,需要手动计算token判断是否分片及分片数量,不好控制(可去除)
* @param fun 将需要新增的数据处理成字符串的函数
*/
public <T> void batch(String key, String dataType, List<T> data, int batchSize, Function<List<T>, String> fun) {
String tenantId = getTenantId();
/*
逻辑分片: 在token分片之前,根据业务数据的格式需要进行分片
*/
List<Document> documents = new ArrayList<>();
if (batchSize != 0 && data.size() > batchSize) {
List<List<T>> sharding = ListUtil.sharding(data, batchSize);
for (List<T> s : sharding) {
String text = fun.apply(s);
Document document = new Document(text, Map.of(VectorKey.KEY, key, VectorKey.TYPE, dataType, VectorKey.TENANT_ID, tenantId));
documents.add(document);
}
} else {
String text = fun.apply(data);
Document document = new Document(text, Map.of(VectorKey.KEY, key, VectorKey.TYPE, dataType, VectorKey.TENANT_ID, tenantId));
documents.add(document);
}
/*
token分片
*/
List<List<Document>> batch = batchingStrategy.batch(documents);
for (List<Document> list : batch) {
vectorStore.add(list);
}
}
/**
* 批量添加
*/
public void batch(String key, String dataType, List<String> data, int batchSize) {
batch(key, dataType, data, batchSize, Object::toString);
}
/**
* 租户数据隔离
*/
public Filter.Expression buildTenantExpression(Filter.Expression expression) {
if (expression == null) {
return FilterExpressionUtil.buildTenant(getTenantId());
} else {
Filter.Expression tenantIdExpression = FilterExpressionUtil.buildTenant(getTenantId());
return FilterExpressionUtil.and(expression, tenantIdExpression);
}
}
/**
* 获取租户ID
*
* @return 租户ID
*/
public String getTenantId() {
String tenantId = TenantHelper.getTenantId();
if (tenantId == null || "000000".equals(tenantId)) {
tenantId = VectorKey.COMMON;
}
return tenantId;
}
}
2、向量数据库操作常量
public class VectorKey {
/**
* 来源标识
*/
public final static String KEY = "source_key";
/**
* 来源类型
*/
public final static String TYPE = "source_type";
/**
* 来源租户
*/
public final static String TENANT_ID = "source_tenant_id";
/**
* 公共数据
*/
public final static String COMMON = "common";
}
3、构建向量数据库过滤表达式封装工具类
构建过滤表达式与mysql数据库的where语法差不多。springAi封装的表达式构建方法有三种:
- 字符串,具体语法查看springAi文档中的向量数据库章节。
- new一个Filter.Expression,传入三个参数:表达式类型(等于、不等于、大于、包含等等)、键(使用new Filter.Key(key)包裹)、值(使用new Filter.Value(values)包裹)。
- new一个FilterExpressionBuilder,实际就是第二种的封装。
以下是自主封装第二种构建方法,使用了eq、in、and,如需其他方法可自行添加。
public class FilterExpressionUtil {
public static Filter.Expression eq(String key,Object values){
return new Filter.Expression(Filter.ExpressionType.EQ, new Filter.Key(key), new Filter.Value(values));
}
public static Filter.Expression in(String key, Object... values){
return in(key,List.of(values));
}
public static Filter.Expression in(String key, List<Object> values){
return new Filter.Expression(Filter.ExpressionType.IN, new Filter.Key(key), new Filter.Value(values));
}
public static Filter.Expression and(Filter.Expression expression1,Filter.Expression expression2){
return new Filter.Expression(Filter.ExpressionType.AND, expression1, expression2);
}
public static Filter.Expression buildTenant(String tenantId){
return eq(VectorKey.TENANT_ID,tenantId);
}
}
4、批量新增向量文档配置
以下批量新增配置是SpringAi官方给出的代码示例
@Configuration
public class EmbeddingConfig {
@Bean
public BatchingStrategy customTokenCountBatchingStrategy() {
return new TokenCountBatchingStrategy(
EncodingType.CL100K_BASE,
8000,//单文档最大token数
0.1//保留百分比
);
}
}
5、向量数据库操作封装类的使用示例
search、delete、saveFile在前文中都有使用,sava也不多说,主要是batch批量添加方法。
batch方法的fun参数作用是提供一个构建向量文档数据结构的入口。
构建简单有效的向量文档数据结构,有以下好处:
- 降低成本:采用简洁的数据格式能在相同token消耗下传递更多有效信息,减少向量文档检索的计费开销。
- 提升精度:精简后的数据剔除了冗余内容,使AI检索时更聚焦于关键信息,提高结果准确性。
- 效率增强:简化数据结构直接提升信息传输效率,确保单位时间内处理更多有效内容。
@Async
@Override
public void syncVectorData(String brandName) {
//存在价格变动才更新
if (baseMapper.selectSpreadCount(brandName) > 0) {
EsPriceBo bo = new EsPriceBo();
bo.setName1(brandName);
List<EsPriceVo> vos = baseMapper.mySelectVoList(bo, 0);
Map<String, List<EsPriceVo>> collect = vos.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(
//类型-品牌-系列-型号
vo -> String.format("%s(类型)-%s(品牌)-%s(系列)-%s(型号)", vo.getName0(), vo.getName1(), vo.getName2(), vo.getName3())
));
for (String key : collect.keySet()) {
List<EsPriceVo> data = collect.get(key);
// 先删除之前的再新增,根据key删除
vectorStoreService.delete(FilterExpressionUtil.eq(VectorKey.KEY, key));
/* 数据格式:
{
"name0(类型)-name1(品牌)-name2(系列)-name3(型号)": {
"name4(内存)": {
"finenessName(成色)": "价格"
}
}
}
*/
vectorStoreService.batch(key, "es_price",data, 500, (resData) -> {
// 创建最外层的 JSON 对象
JSONObject resultJson = new JSONObject();
//根据内存分组
Map<String, List<EsPriceVo>> collect4 = data.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(EsPriceVo::getName4));
// 创建内存级别的 JSON 对象
JSONObject name4Json = new JSONObject();
for (String key4 : collect4.keySet()) {
List<EsPriceVo> esEquipmentPriceVos4 = collect4.get(key4);
// 创建成色级别的 JSON 对象
JSONObject finenessJson = new JSONObject();
for (EsPriceVo voF : esEquipmentPriceVos4) {
finenessJson.put(String.format("%s(成色)", voF.getFinenessName()), voF.getPrice());
}
name4Json.put(String.format("%s(内存)", key4), finenessJson);
}
resultJson.put(key, name4Json);
return resultJson.toString();
});
}
}
}
十一、目前存在的问题
1、操作向量数据库时的过滤条件不生效
2、调用ai工具后有概率导致ai报错,非ai工具代码错误。
十二、总结
聊天记忆、ai工具、RAG检索增强、MCP服务等等,一切手段本质上只做了两件事情:
- 规范ai的行为和输出
- 更高效的给ai提供信息
所以,简化ai的调用流程可以描述为:
用户输入->以各种方法检索信息丰富ai的知识库->将用户输入的信息和检索到的附加信息一并发送给ai->ai输出->结束。




















 1349
1349

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








