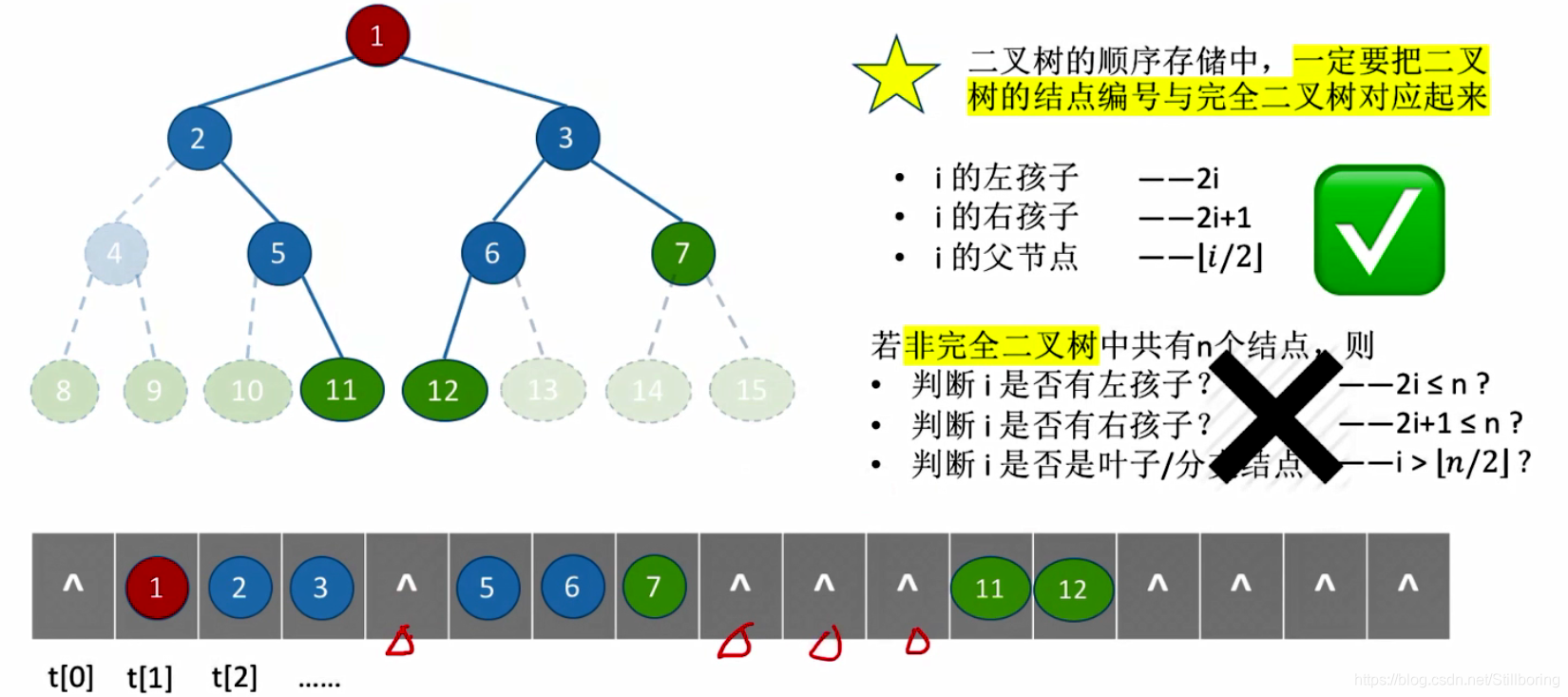
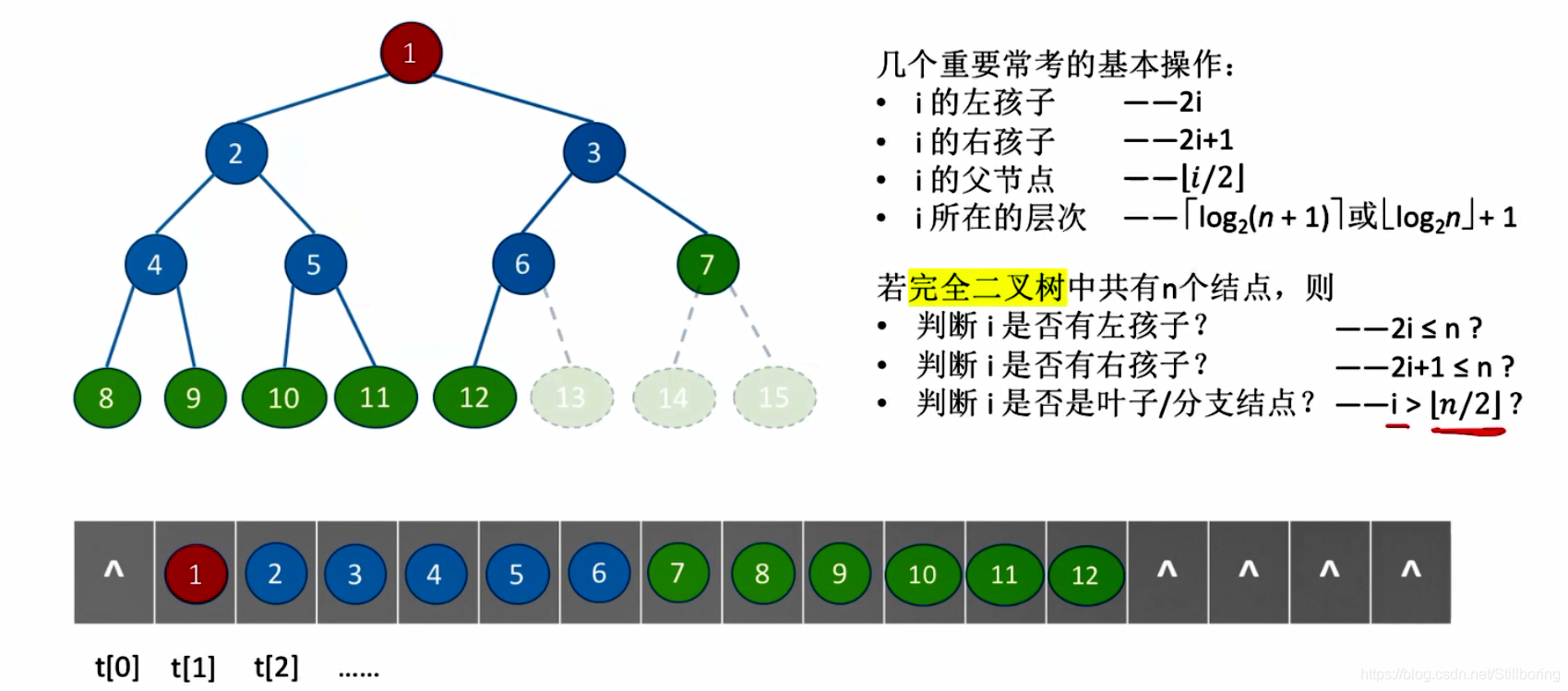
二叉树的顺序存储
定义
从数组中index=1处开始存储。左孩子为2*i,右孩子为2*i+1
#define MaxSize 100
struct TreeNode
{
ElemType value;
bool isEmpty;
};
TreeNode t[MaxSize];对于完全二叉树:
完全二叉树在数组中存储时,结点中间一定不会有缺失值。
对于非完全二叉树:
只能通过isEmpty来查看是否有结点
初始化
void InitTree(TreeNode &t[])
{
for(int i = 0; i < MaxSize; i++)
{
t[i].isEmpty = true;
}
}二叉树的链式存储
定义
typedef struct BiTNode
{
ElemType data;
struct BiTNode *lchild,*rchild;
}BiTNode,*BiTree;先序遍历
void PreOrder(BiTree T)
{
if(T)
{
visit(T);
PreOrder(T->lchild);
PreOrder(T->rchild);
}
}非递归实现:
void preOrder(BTree T)
{
BTree p = T;
while(p||!s.empty())
{
if(p)
{
visit(p);
Push(s,p);
p=p->l;
}
else
{
Pop(s,p);
p=p->r;
}
}
}中序遍历
void InOrder(BiTree T)
{
if(T)
{
InOrder(T->lchild);
visit(T);
InOrder(T->rchild);
}
}非递归实现:
void preOrder(BTree T)
{
BTree p = T;
while(p||!s.empty())
{
if(p)
{
visit(p);
Push(s,p);
p=p->l;
}
else
{
Pop(s,p);
p=p->r;
}
}
}后序遍历
void PostOrder(BiTree T)
{
if(T)
{
PostOrder(T->lchild);
PostOrder(T->rchild);
visit(T);
}
}非递归实现:
void postOrder(BTree T)
{
BTree p = T;
BTree pre = NULL;
while(p||!s.empty())
{
if(p)
{
Push(s,p);
p=p->l;
}
else
{
getTop(s,p);
if(p->r == NULL||p->r == pre)
{
visit(p)
pre = p;
Pop(s,p);
}
else
{
p=p->r;
}
}
}
}
先序遍历、中序遍历、后序遍历遍历的时间复杂度为O(n) n为结点个数
层次遍历
void LevelOrder(BiTree T)
{
LinkQueue Q;
InitQueue(Q);
EnQueue(Q,T);
while(!isEmpty(Q))
{
BiTNode *node;
deQueue(Q,node);
visit(node);
if(node->lchild)
enQueue(node->lchild);
if(node->rchild)
enQueue(node->rchild);
}
}求树的高度
int treeDepth(BiTree T)
{
if(T==NULL)
return 0;
int l = treeDepth(T->lchild);
int r = treeDepth(T->rchild);
return l>r?l+1:r+1;
}线索二叉树
定义
typedef struct ThreadNode
{
ElemType data;
struct ThreadNode *lchild,*rchild;
int ltag,rtag; //当tag=1时表示指针指向的是一个线索,tag=0时表示指针指向的是一个孩子
}ThreadNodem,*ThreadTree;线索化
中序线索化
中序线索化入口,创建一个指针pre用来指向前驱结点。然后执行InThread函数进行中序线索化,InThread函数执行完毕后,最后一个序列的后继结点应该被修改为NULL,同时把rtag修改为1.
//线索化入口
void CreateInThread(ThreadTree T)
{
ThreadTree pre = NULL;
if(T!=NULL)
{
InThread(T,pre);
pre->rchild = NULL;
pre->rtag = 1;
}
}中序线索化操作函数:
先找到最左边的一个结点,因为中序遍历的第一个结点一定是树的最左边的结点。然后把最左边的结点(也就是中序遍历序列中的第一个结点)的左指针指向NULL,对于tag设为1.pre代表当前结点的上一个结点,如果pre此时不为空(也就是当前结点不是第一个结点时)并且pre存在空的右指针,就把pre指向的结点(也就是中序遍历中上一个结点)的右指针指针指向当前结点,并修改对应的rtag。
修改完线索后,将pre指向当前节点,然后再处理当前节点的右子树
void InThread(ThreadTree &T,ThreadTree &pre)
{
if(T)
{
InThread(T->lchild,pre);
if(T->lchild == NULL)
{
T->ltag = 1;
T->lchild = pre;
}
if(pre!=NULL&&pre->rchild == NULL)
{
pre->rchild = T;
pre->rtag = 1;
}
pre = T;
InThread(T->rchild,pre);
}
}为什么这里的pre的类型是引用呢?引用的实质是常指针,也就是一旦初始化指向一个地址后,就无法再改变的指针。实际上也就是一个二级指针。为什么要使用二级指针呢?因为,最后需要把中序遍历序列中的最后一个序列节点的rchild指向空,并修改对应的tag。
如果仅仅pre的类型为指针,在CreateInThread函数中的pre作为实参传入InThread时,C语言会创建一个临时指针,这个指针与pre指向相同的位置。所以在InThread里的pre = T的操作,并不会影响到CreateInThread里的pre,最后令pre->rchild = NULL时的pre是NULL。
如果pre的类型是引用。在CreateInThread函数中的pre作为实参传入InThread时,会创建一个二级指针指向pre,这个二级指针的值为pre的地址。对这个二级指针的操作,都会使它指向的那个指针变化。所以最后CreateInThread函数中执行完InThread函数后,pre指向的是中序遍历序列中最后一个节点。此时pre相当于是一个全局变量
先序线索化
入口函数一样。
void CreatePreThread(ThreadTree T)
{
ThreadTree pre = NULL;
if(T!=NULL)
{
PreThread(T,pre);
pre->rchild = NULL;
pre->rtag = 1;
}
}先序线索化函数有一个地方需要注意:
递归左子树的时候,需要判断当前节点的ltag是否为0。如果ltag为1,说明当前节点左子树为空,并且当前节点的左指针已经被当作线索指针指向了前驱节点。此时如果再进行左子树递归,就会产生无限递归。
void PreThread(ThreadTree &T,ThreadTree &pre)
{
if(T->lchild == NULL)
{
T->lchild = pre;
T->ltag = 1;
}
if(pre!=NULL&&pre->rchild == NULL)
{
pre->rchild = T:
pre->rtag = 1;
}
if(T->ltag == 0)
PreThread(T->lchild,pre);
PreThread(T->rchild,pre);
}后序线索化
入口函数有一点不同:
因为是后序线索化,所以对节点的访问顺序是左右根,根的右儿子不一定为空,所以要判断以下。
前面的先序线索化与中序线索化,对节点的访问顺序分别是根左右和左根右,最后访问的节点一定是一个叶子节点,所以不需要判断pre->rchild是否为空。
void CreatePostThread(ThreadTree T)
{
ThreadTree pre = NULL;
if(T!=NULL)
{
PostThread(T,pre);
if(pre->rchild == NULL)
pre->rtag=1;
}
}后序线索化函数
void PostThread(ThreadTree &T,ThreadTree &pre)
{
PostThread(T->lchild,pre);
PostThread(T->rchild,pre);
if(T->lchild == NULL)
{
T->lchild = pre;
T->ltag = 1;
}
if(pre!=NULL&&pre->rchild == NULL)
{
pre->rchild = T:
pre->rtag = 1;
}
}遍历线索二叉树
找中序前驱结点
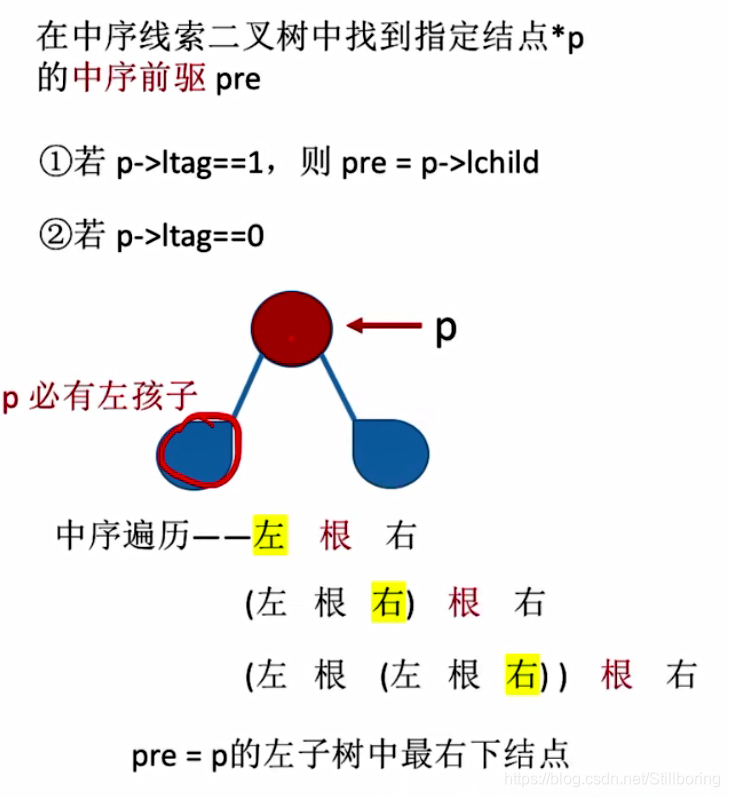
综上所述:
- 若p->ltag=1,则lastNode = p->lchild
- 若p->ltag=0,说明当前结点有左孩子,并且该左孩子不一定是后继。该节点的后继为左子树中序遍历中最后一个出现的结点即最右下方的结点。
ThreadNode *Lastnode(ThreadNode *p)
{
while(p->rtag == 0) p =p->rchild;
return p;
}
ThreadNode *Prenode(ThreadNode *p)
{
if(p->ltag == 0) return Lastnode(p->lchild);
else return p->lchild;
}找中序后继结点
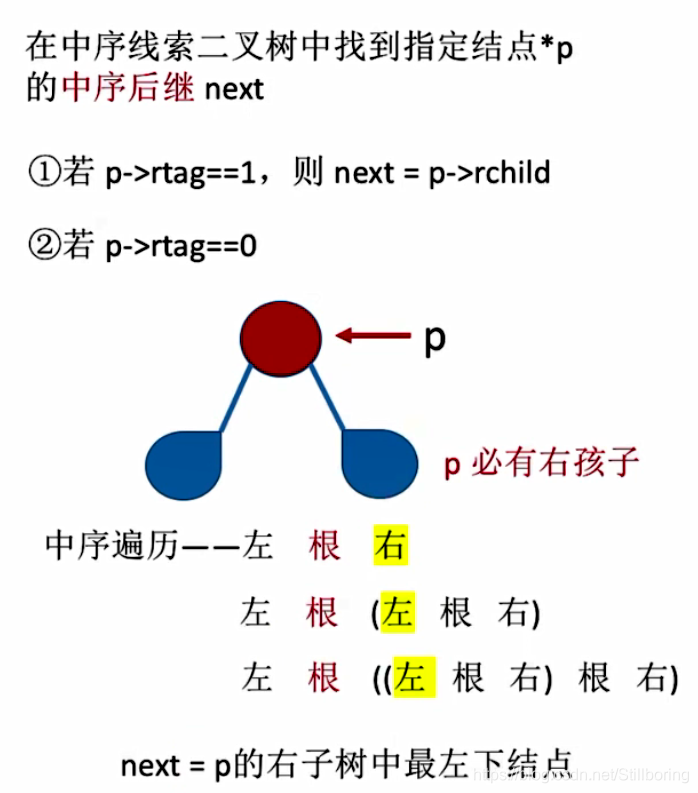
综上所述:
- 若p->rtag=1,则next = p->rchild
- 若p->rtag=0,说明当前结点有右孩子,并且该右孩子不一定是后继。该节点的后继为右子树中序遍历中第一个出现的序列即最左下结点。
ThreadNode * Firstnode(ThreadNode *p)
{
while(p->ltag == 0) //相当于p-lchild!=NULL
p = p->lchild;
return p;
}
ThreadNode *Nextnode(ThreadNode *p)
{
if(p->rtag==0) return Firstnode(p->rchild);
else return p->rchild;
}对中序线索二叉树进行中序遍历
for(ThreadNode *p = Firstnode(T);p!=NULL;p=Nextnode(p))
{
visit(p);
}对中序线索二叉树进行逆向中序遍历
for(ThreadNode *p = Lastnode(T);p!=NULL;p=Prenode(p))
{
visit(p);
}找先序线索二叉树的前驱
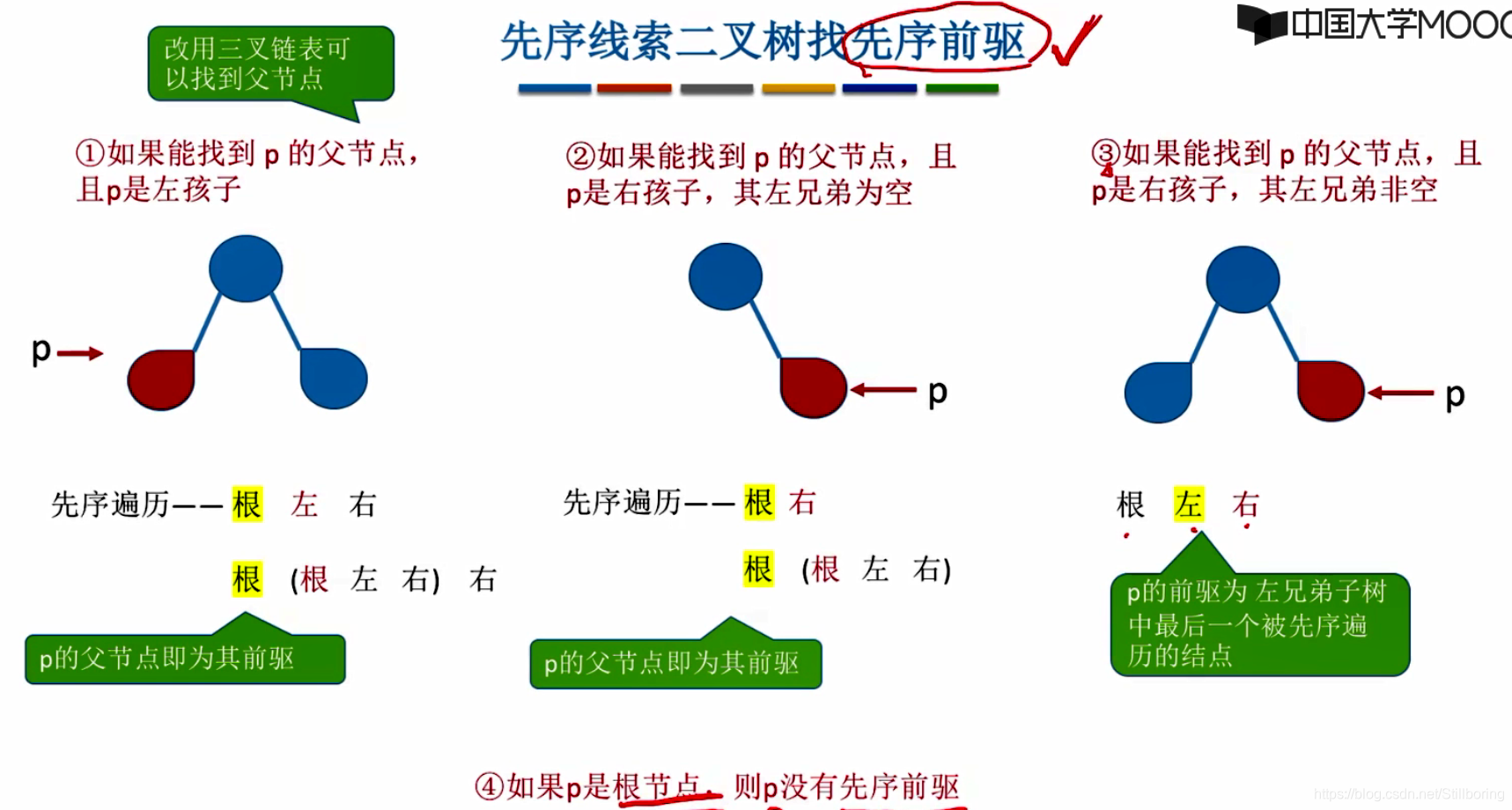
如果没有使用三叉链表,是无法找到前驱的。
找先序线索二叉树的后继
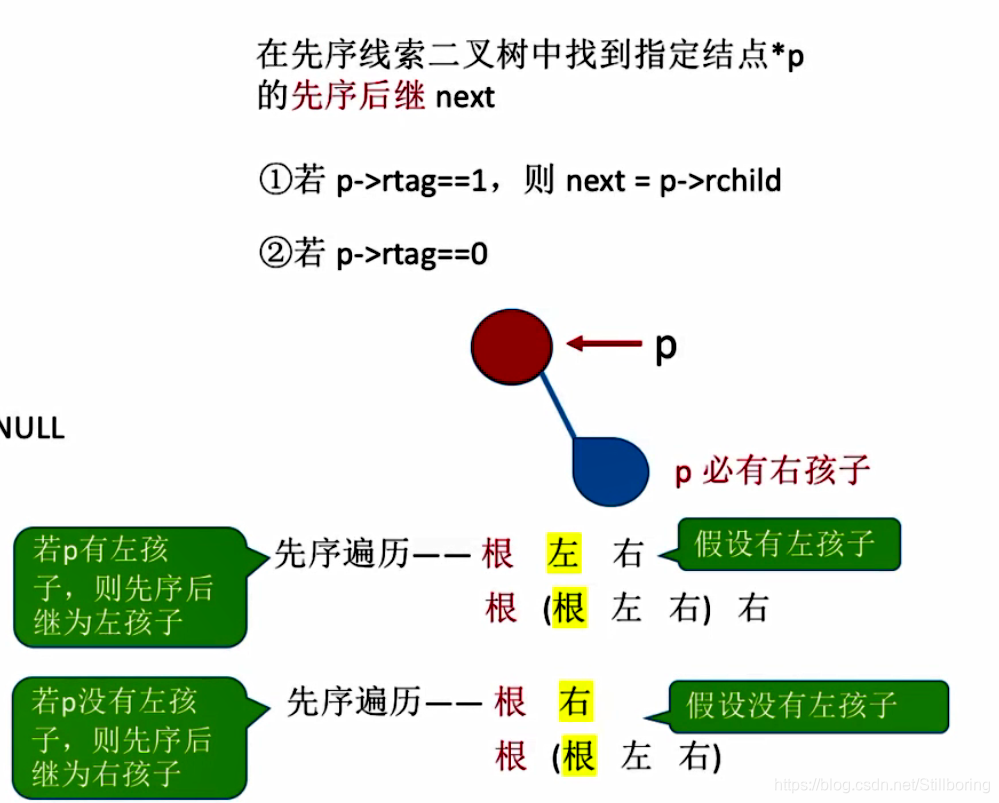
ThreadNode * Firstnode(ThreadNode *p)
{
return p->lchild!=NULL ? p->lchild:p->rchild;
}
ThreadNode *Nextnode(ThreadNode *p)
{
if(p->rtag==0) return Firstnode(p->rchild);
else return p->rchild;
}找后序线索二叉树的前驱结点
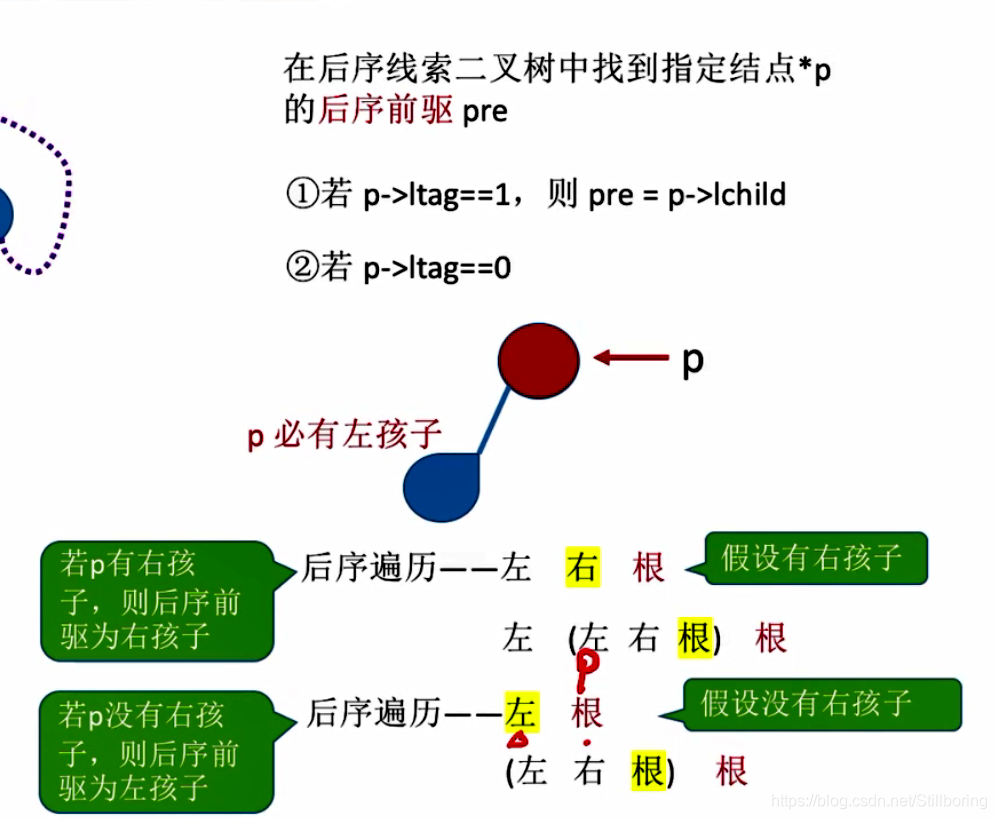
ThreadNode * Lastnode(ThreadNode *p)
{
return p->rchild!=NULL ? p->rchild:p->lchild;
}
ThreadNode *Prenode(ThreadNode *p)
{
if(p->ltag==0) return Lastnode(p);
else return p->lchild;
}找后序线索二叉树的后继结点
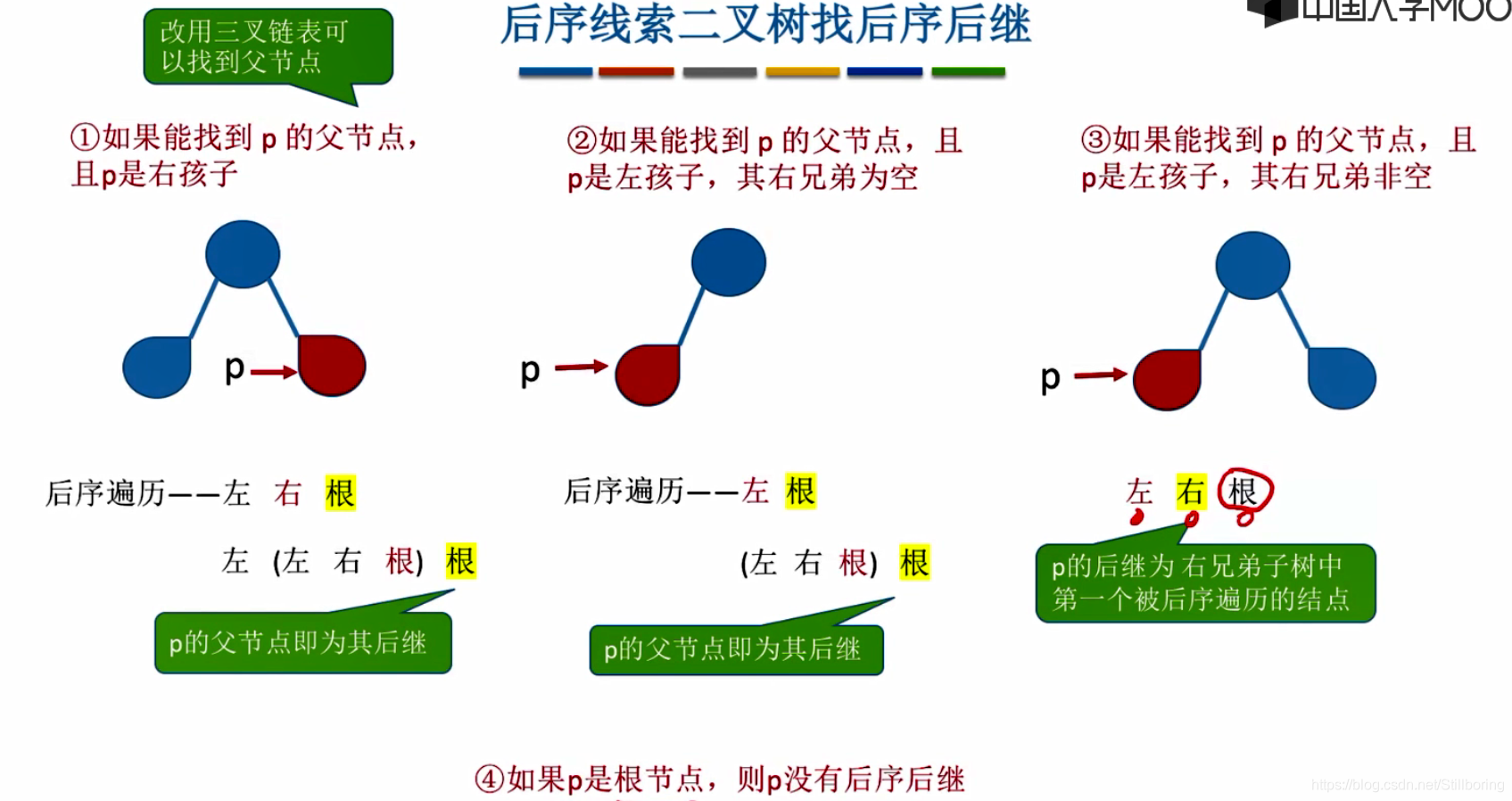
需要使用三叉链表,每个结点存储其父节点的地址。
树的存储结构
双亲表示法(顺序存储)
每个结点保存指向双亲的指针(以数组下标模拟指针)。
优点:查找双亲结点很方便
缺点:查找指定结点的孩子只能从零开始。
数组中的相对位置并没有反应结点的位置(与二叉树的顺序存储不同)
根节点默认数组下标位0,其父节点为-1(代表没有双亲结点)
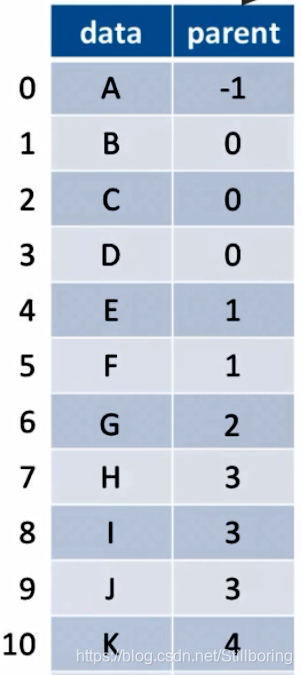
定义
#define MaxSize 100
typedef struct
{
ElemType data;
int parent;
}PTNode;
typedef struct
{
PTNode nodes[MaxSize];
int n;
}PTree;新增结点
直接在数组末尾添加新元素即可。
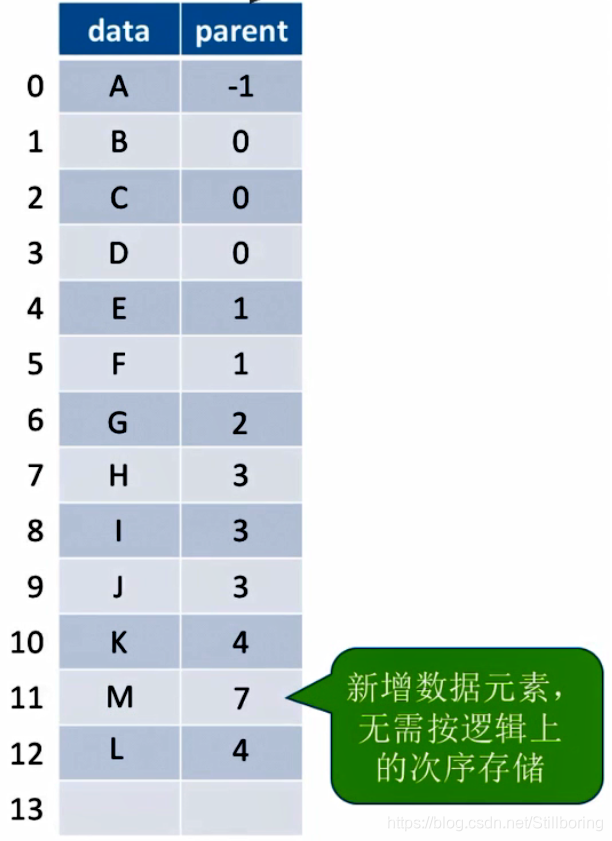
删除结点
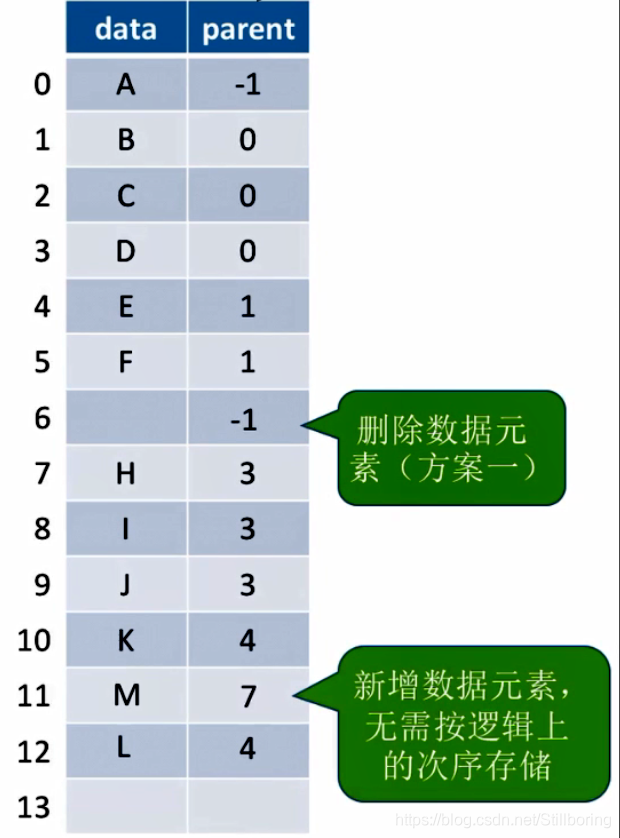
第一种方案,把要删除的结点的父指针设置为-1,并把data清空。
第二种方案,把数组中最后一个元素移到被删除的元素处。
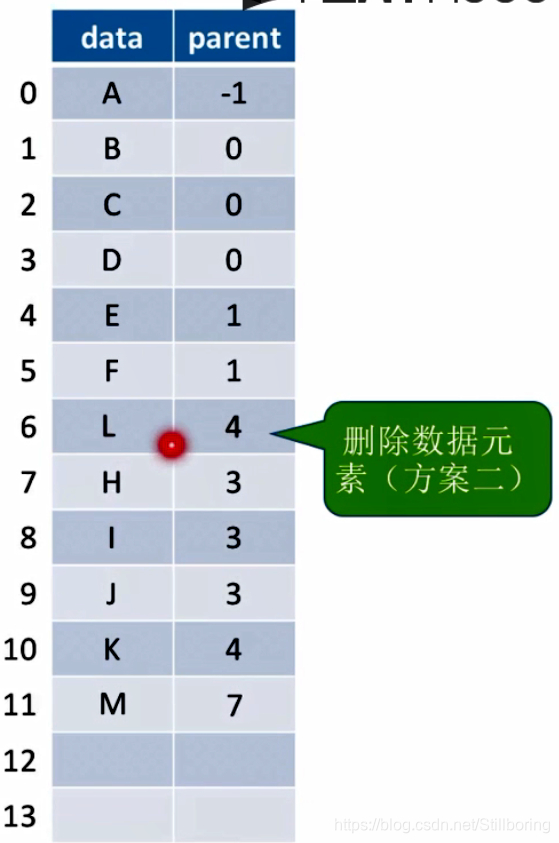
对于树来说,删除一个非叶子节点,也意味着把其子孙全部删除。
孩子表示法(顺序+链式存储)
顺序存储各个结点,每个结点中保存孩子链表头指针。
优点:找孩子很简单
缺点:找双亲会很麻烦
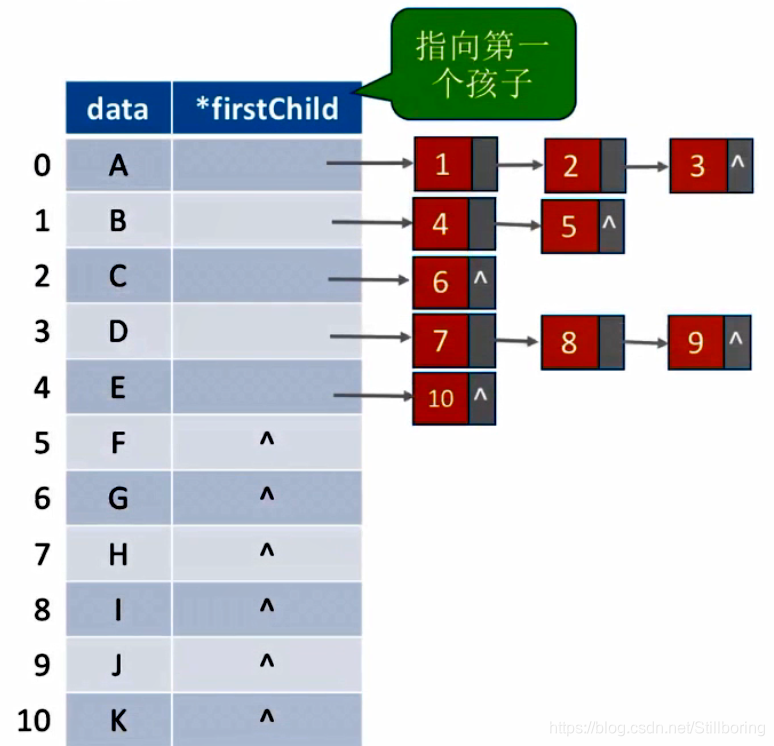
定义
struct CTNode
{
int child;//孩子结点在数组中的位置
struct CTnode *next;//下一个孩子
};
typedef struct
{
ElemType data;
struct CTNode *firstChild;
}CTBox;
typedef struct
{
CTBox nodes[MaxSize];
int n,r; //节点数和根的位置
}孩子兄弟表示法(链表)
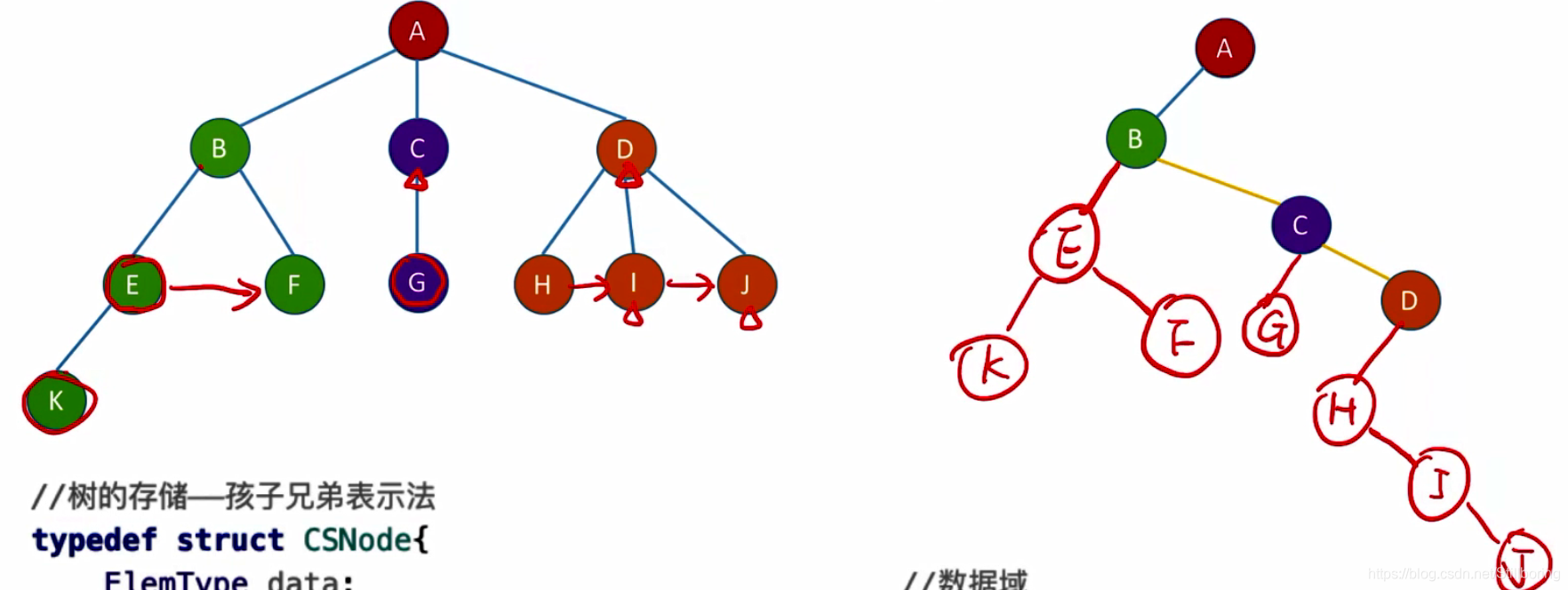
定义
typedef struct CSNode
{
ElemType data;
struct CSNode *firstchild,*nextsibling;
}CSNode,*CSTree;二叉排序树
查找
非递归实现
空间复杂度为O(1),时间复杂度为O(logN)
BSTNode *BST_search(BSTree T,int key)
{
while(T!=NULL&&T->key!=key)
{
if(key<T->key) T=T->lchild;
else T=T->rchild;
}
return T;
}递归实现
空间复杂度为O(h),时间复杂度为O(logN)
BSTNode *BSTSearch(BSTree T,int key)
{
if(T == NULL)
return NULL;
if(T->key == key)
return T;
else if(key<T->key)
return BSTSearch(T->lchild);
else
return BSTSearch(T->rchild);
}插入
待补充。。。
递归插入
int BSTInsert(BSTree &T,int k)
{
if(T==NULL)
{
T = (BSTree)malloc(sizeof(BSTNode));
T->key = k;
T->lchild = T->rchild = NULL;
return 1;//返回1 插入成功
}
else if(k == T->key) //树中存在相同关键字的结点,插入失败
{
return 0;
}
else if(k < T->key)
{
return BSTInsert(T->lchild,k);
}
else
{
return BSTInsert(T->rchild,k);
}
}非递归插入
如果T为空,那么直接在根节点存放key值,如果非空,则设置一个前驱结点parent指向将要连接新插入结点的父节点。
int BSTInsert(BSTree &T,int key)
{
BSTree p = T,parent=NULL;
while(p!=NULL)
{
parent = p;
if(key < p->key)
{
p=p->lchild;
}
else if(key == p->key)
{
return 0;
}
else
{
p=p->rchild;
}
}
if(parent == NULL)
{
T = (BSTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BSTNode));
T->key = key;
T->lchild = T->rchild = NULL;
}
else
{
p = (BSTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BSTNode));
p->key = key;
p->lchild = p->rchild = NULL;
if(key<parent->key)
parent->lchild = p;
else
parent->rchild = p;
}
return 1;
}删除结点
- 删除的是叶子结点,直接删除即可
- 要删除的结点只有左子树或者只有右子树,删除后让其父节点连接它的子树的根节点
- 如果删除的结点z有左右两棵子树,则令z的直接后继(或直接前驱这里的直接后继和直接前驱指的是中序遍历序列的)代替z,然后从二叉排序树中删除这个直接后继,这样就转换成了第一种或第二种情况
平衡二叉树
定义
typedef struct BSTNode
{
int key,h;
struct BSTNode *lchild,*rchild;
}*BSTree,BSTNode;辅助函数
//返回以T为根节点树的高度
int treeDepth(BSTree T)
{
if(T == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
return T->h;
}LL型
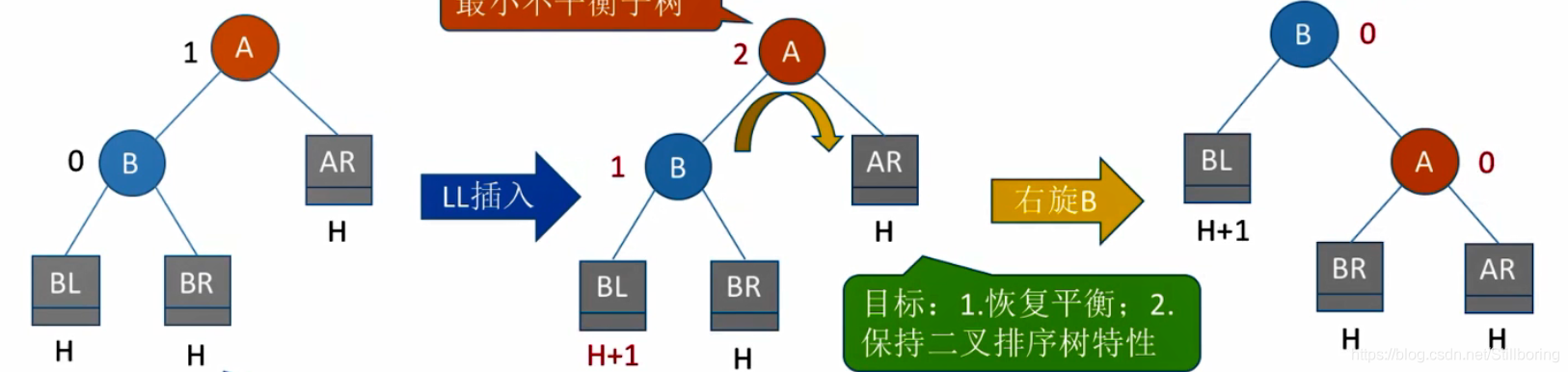
//右旋
void LL(BSTree &T)
{
BSTree Lchild = T->lchild;
T->lchild = Lchild->rchild;
Lchild->rchild = T;
//更新高度
T->h = max(treeDepth(T->rchild),treeDepth(T->lchild))+1;
Lchild->h = max(treeDepth(Lchild->lchild),T->h)+1;
T = Lchild;
}RR型
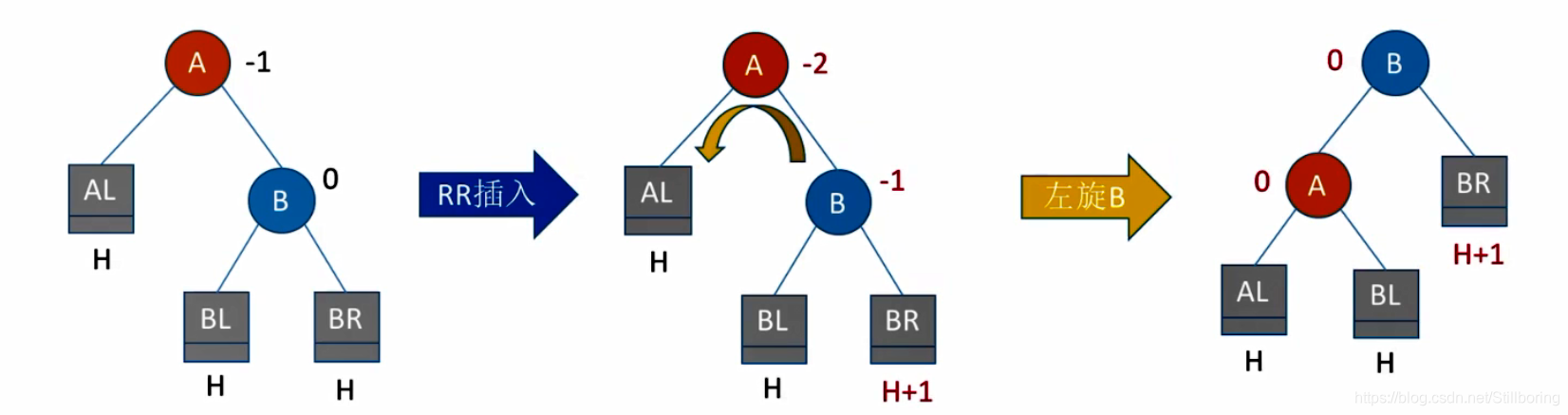
//左旋
void RR(BSTree &T)
{
BSTree Rchild = T->rchild;
T->rchild = Rchild->lchild;
Rchild->lchild = T;
//更新高度
T->h = max(treeDepth(T->rchild),treeDepth(T->lchild))+1;
Rchild->h = max(treeDepth(Rchild->rchild),T->h)+1;
T = Rchild;
}LR型
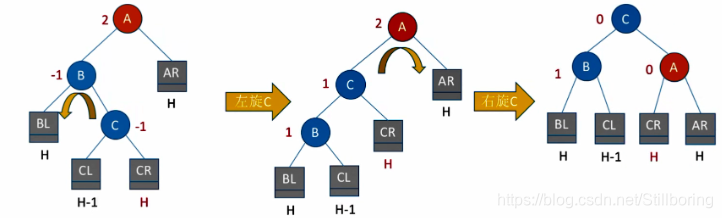
void LR(BSTree &T)
{
RR(T->lchild);
LL(T);
}RL型
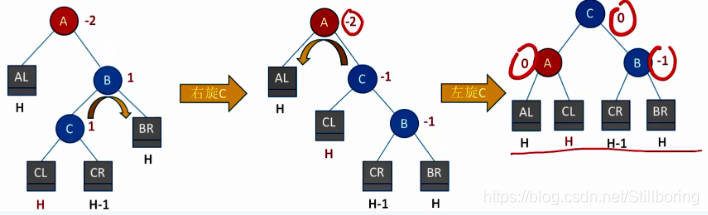
void RL(BSTree &T)
{
LL(T->rchild);
RR(T);
}建立平衡二叉树
void BSTInsert(BSTree &T,int key)
{
if(T==NULL)
{
T = (BSTree)malloc(sizeof(BSTNode));
T->key = key;
T->lchild = T->rchild = NULL;
T->h = 1;
}
else if(key == T->key) //树中存在相同关键字的结点,不插入
{
return ;
}
else if(key < T->key)
{
BSTInsert(T->lchild,key);
if(treeDepth(T->lchild) - treeDepth(T->rchild)>1)
{
if(T->lchild->key>key) //LL
{
LL(T);
}
else if(T->lchild->key<key) //LR
{
LR(T);
}
}
}
else
{
BSTInsert(T->rchild,key);
if(treeDepth(T->rchild)-treeDepth(T->lchild)>1)//为了保证差为正值
{
if(T->rchild->key>key) //RL
{
RL(T);
}
else if(T->rchild->key<key) //RR
{
RR(T);
}
}
}
T->h = max(treeDepth(T->lchild),treeDepth(T->rchild))+1;
}完整代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef struct BSTNode
{
int key,h;
struct BSTNode *lchild,*rchild;
}*BSTree,BSTNode;
int treeDepth(BSTree T)
{
if(T == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
return T->h;
}
//右旋
void LL(BSTree &T)
{
BSTree Lchild = T->lchild;
T->lchild = Lchild->rchild;
Lchild->rchild = T;
//更新高度
T->h = max(treeDepth(T->rchild),treeDepth(T->lchild))+1;
Lchild->h = max(treeDepth(Lchild->lchild),T->h)+1;
T = Lchild;
}
//左旋
void RR(BSTree &T)
{
BSTree Rchild = T->rchild;
T->rchild = Rchild->lchild;
Rchild->lchild = T;
//更新高度
T->h = max(treeDepth(T->rchild),treeDepth(T->lchild))+1;
Rchild->h = max(treeDepth(Rchild->rchild),T->h)+1;
T = Rchild;
}
void LR(BSTree &T)
{
RR(T->lchild);
LL(T);
}
void RL(BSTree &T)
{
LL(T->rchild);
RR(T);
}
void BSTInsert(BSTree &T,int key)
{
if(T==NULL)
{
T = (BSTree)malloc(sizeof(BSTNode));
T->key = key;
T->lchild = T->rchild = NULL;
T->h = 1;
}
else if(key == T->key) //树中存在相同关键字的结点,不插入
{
return ;
}
else if(key < T->key)
{
BSTInsert(T->lchild,key);
if(treeDepth(T->lchild) - treeDepth(T->rchild)>1)
{
if(T->lchild->key>key) //LL
{
LL(T);
}
else if(T->lchild->key<key) //LR
{
LR(T);
}
}
}
else
{
BSTInsert(T->rchild,key);
if(treeDepth(T->rchild)-treeDepth(T->lchild)>1)
{
if(T->rchild->key>key) //RL
{
RL(T);
}
else if(T->rchild->key<key) //RR
{
RR(T);
}
}
}
T->h = max(treeDepth(T->lchild),treeDepth(T->rchild))+1;
}
void InOrder(BSTree T)
{
if(T)
{
InOrder(T->lchild);
cout<<T->key<<" ";
InOrder(T->rchild);
}
}
int main()
{
BSTree T = NULL;
int n,x;
cin>>n;
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++)
{
cin>>x;
BSTInsert(T,x);
}
cout<<T->key<<endl;
return 0;
}
树的其他操作
统计二叉树中度为0的结点个数
int count(BinTree T)
{
if(T)
{
if(T->l==NULL&&T->r==NULL)
return 1;
else
return count(T->l)+count(T->r);
}
else
{
return 0;
}
}统计二叉树中度为1的结点个数
int count(BinTree T)
{
if(T)
{
if(T->l==NULL&&T->r)
return 1+count(T->r);
else if(T->l&&T->r==NULL)
return 1+count(T->l);
else
return count(T->l)+count(T->r);
}
else
{
return 0;
}
}统计二叉树中度为2的结点个数
int count(BinTree T)
{
if(T)
{
if(T->l&&T->r)
return 1+count(T->l)+count(T->r);
else
return count(T->l)+count(T->r);
}
else
{
return 0;
}
}求树的宽度
int treeMaxWidth(BinTree T)
{
BinTree temp[1000];
int front=0,rear=0;
temp[rear++]=T;
int last = rear;
int maxWidth = 1;
while(front!=rear)
{
BinTree p = temp[front++];
cout<<p->data;
if(p->l)
temp[rear++]=p->l;
if(p->r)
temp[rear++]=p->r;
if(front==last)
{
maxWidth = max(maxWidth,rear-front);
last=rear;
}
}
cout<<endl;
return maxWidth;
}前序中序序列建树
void bt(BinTree &T,char a[],char b[],int n) //a是中序遍历序列 b是前序遍历序列
{
if(n<=0)
{
T=NULL;
return ;
}
T=new BinNode;
T->data = a[0];
int i;
for(i = 0;i<n;i++)
{
if(b[i]==a[0])
break;
}
bt(T->l,a+1,b,i);
bt(T->r,a+i+1,b+i+1,n-1-i);
}
/*
9
ABDFGHIEC
FDHGIBEAC
*/删除二叉树中全部叶节点
void deleteLeafs(BinTree T,BinTree &father)
{
if(T)
{
if(T->l==NULL&&T->r==NULL)
{
if(father->l==T)
{
father->l = NULL;
free(T);
}
else
{
father->r = NULL;
free(T);
}
}
else
{
deleteLeafs(T->l,T);
deleteLeafs(T->r,T);
}
}
}求指定指针aim指向的结点的所在层次
int countLevel(BinTree T,BinTree aim)
{
BinTree temp[1000];
int front=0,rear=0;
temp[rear++]=T;
int last = rear;
int level=1;
while(front!=rear)
{
BinTree p = temp[front++];
if(aim==p)
return level;
if(p->l)
temp[rear++]=p->l;
if(p->r)
temp[rear++]=p->r;
if(front==last)
{
level++;
last=rear;
}
}
}交换二叉树中每个结点的子女
递归实现
void change(BinTree &T)
{
if(T)
{
change(T->l);
change(T->r);
BinTree p = T->l;
T->l = T->r;
T->r = p;
}
}非递归实现
使用后序遍历的非递归实现交换两个子树
void changeWithStack(BinTree &T)
{
BinTree stack[100];
int top=0;
BinTree p = T,pre=NULL;
while(p||top!=0)
{
while(p)
{
stack[top++]=p;
p=p->l;
}
if(p==NULL)
{
p = stack[top-1];
if(p->r==NULL||p->r==pre)//后序遍历访问该结点
{
cout<<p->data;
top--;
//交换两个子树
BinNode *temp = p->l;
p->l = p->r;
p->r=temp;
pre=p;
p=NULL;
}
else
{
p=p->r;
}
}
}
}打印根节点到与给定data相等结点的路径
void printPath(BinTree T,char data)
{
BinTree stack[100];
int top=0;
BinNode*p = T,*pre=NULL;
while(p||top!=0)
{
while(p)
{
stack[top++]=p;
p=p->l;
}
p=stack[top-1];
if(p->r==NULL||p->r==pre)//当前结点右子树为空,或者已经访问过时,就访问当前结点
{
//如果当前结点等于待求结点值,此时栈中保存的结点值就是从根到该节点的路径
if(p->data==data)
{
for(int i = 0; i<top; i++)
{
if(i!=top-1)
cout<<stack[i]->data<<"->";
else
cout<<stack[i]->data<<endl;
}
}
top--;
pre=p;
p=NULL;
}
else
{
p=p->r;
}
}
}




















 3041
3041










