一、概要
结合Halcon的阈值分割,仿写X-AnyLabeling标注文件*.json的自动生成
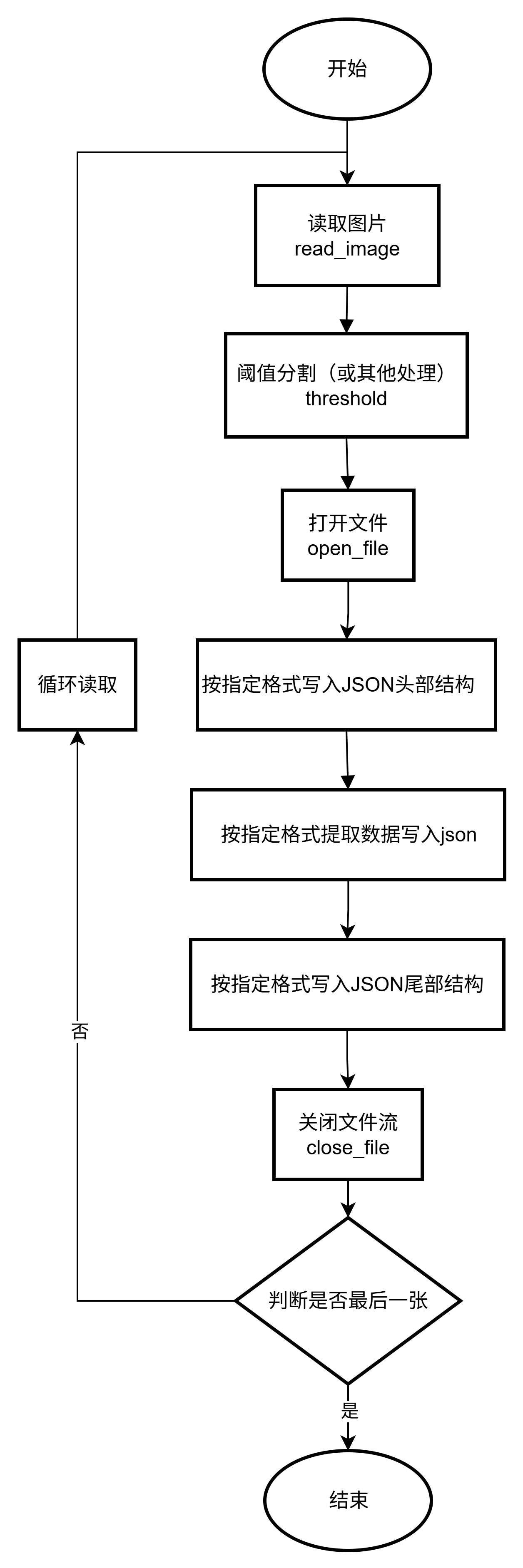
二、整体架构流程
Halcon整体结构框架
三、X-AnyLabeling
X-AnyLabeling 是一款专为深度学习模型训练设计的开源工业级数据标注工具,基于 AnyLabeling 和 Labelme 深度优化,集成了多种前沿 AI 技术,支持图像、视频、文本等多模态数据的自动化标注,尤其适合目标检测、语义分割、OCR 识别、姿态估计等复杂任务。其核心优势在于通过 SOTA 模型(如 Grounding-DINO、SAM、YOLO 系列)实现高效智能标注,显著降低人工成本,提升数据标注效率。

X-AnyLabeling将下图中的黑色轮廓单个标注出来如下图:
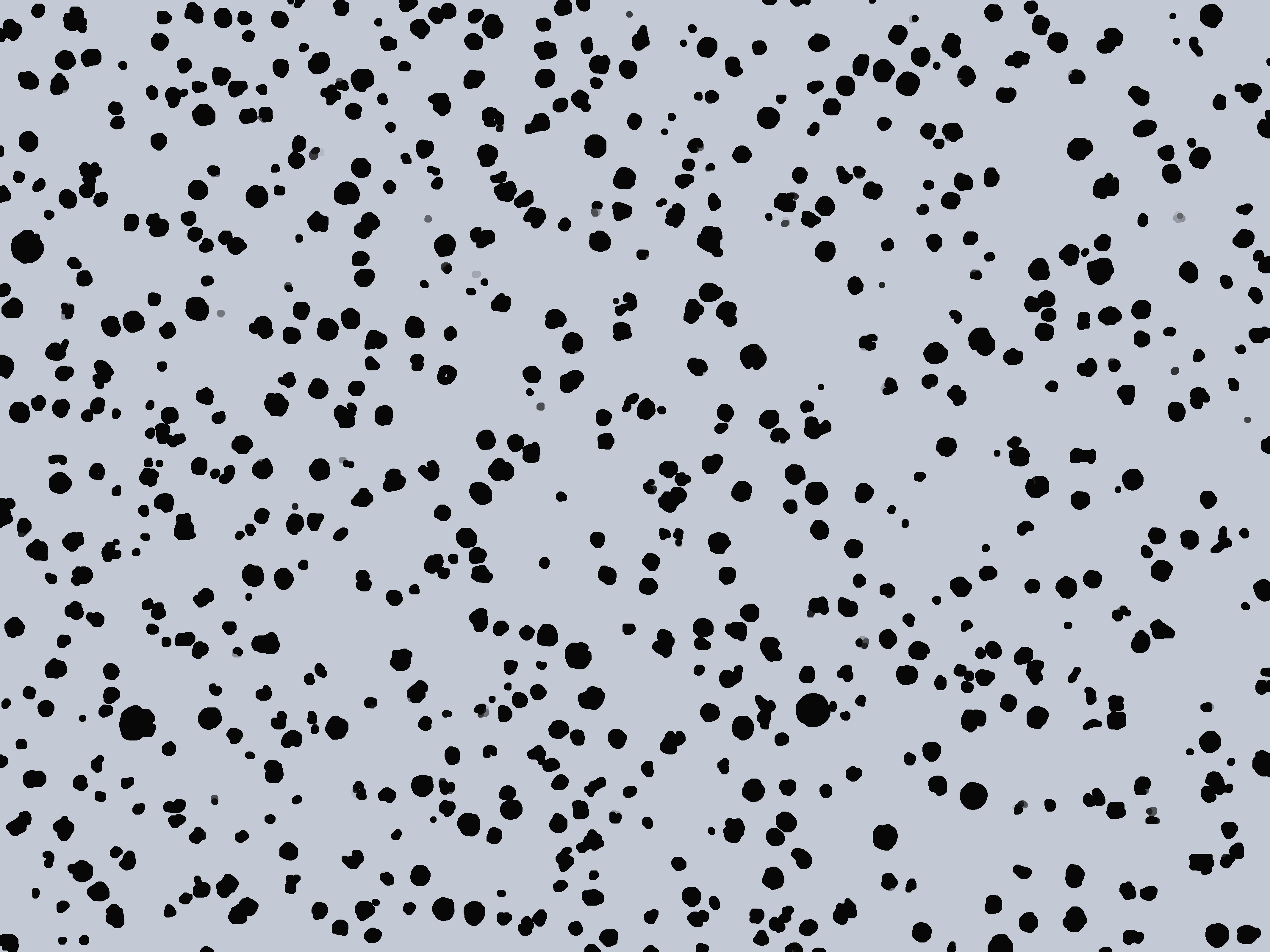

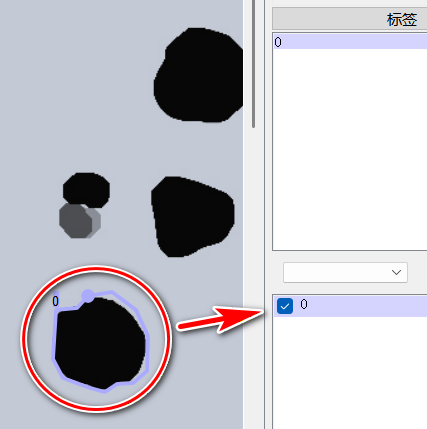
上图标注单个点图片的json文件内容为:
{
"version": "3.2.2",
"flags": {},
"shapes": [
{
"label": "0",
"score": null,
"points": [
[
2007.8095238095239,
773.8095238095239
],
[
1999.079365079365,
783.3333333333334
],
[
1982.4126984126983,
784.9206349206349
],
[
1980.031746031746,
823.8095238095239
],
[
1987.968253968254,
838.8888888888889
],
[
2009.3968253968253,
846.8253968253969
],
[
2021.3015873015872,
850.0
],
[
2030.8253968253969,
843.6507936507936
],
[
2043.5238095238096,
842.8571428571429
],
[
2054.6349206349205,
833.3333333333334
],
[
2055.4285714285716,
805.5555555555555
],
[
2045.904761904762,
784.9206349206349
],
[
2026.857142857143,
770.6349206349206
]
],
"group_id": null,
"description": "",
"difficult": false,
"shape_type": "polygon",
"flags": {},
"attributes": {},
"kie_linking": []
}
],
"imagePath": "标记.jpg",
"imageData": null,
"imageHeight": 3200,
"imageWidth": 4268
}四、全部标注后效果图
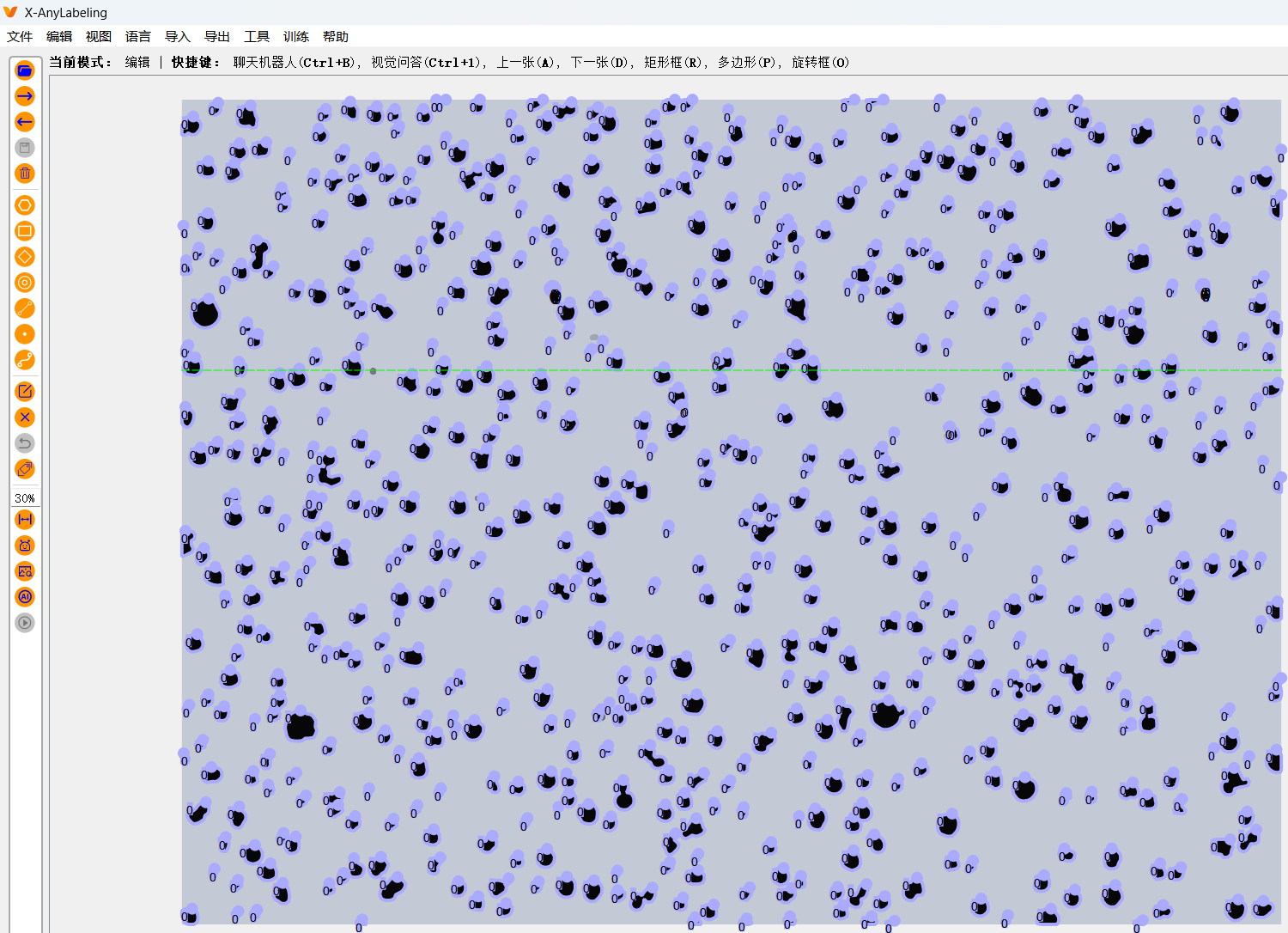
五、json规律
json以下列内容作为开头
{
"version": "3.2.2",
"flags": {},
"shapes": [
json以下列内容作为结尾
其中imagePath为图片名称,imageHeight和imageWidth为当前图片大小
],
"imagePath": "标记.jpg",
"imageData": null,
"imageHeight": 3200,
"imageWidth": 4268
}中间内容为:
*********此处省略*********:为中间点,此处省略,每个区域对应一组这样的
{
"label": "0",
"score": null,
"points": [
[
2007.8095238095239,
773.8095238095239
],
*********此处省略*********
[
2026.857142857143,
770.6349206349206
]
],
"group_id": null,
"description": "",
"difficult": false,
"shape_type": "polygon",
"flags": {},
"attributes": {},
"kie_linking": []
},六、Halcon实现技术细节源码:
结合上述json规律,阈值分割后仿写json文件,实现自动化生成
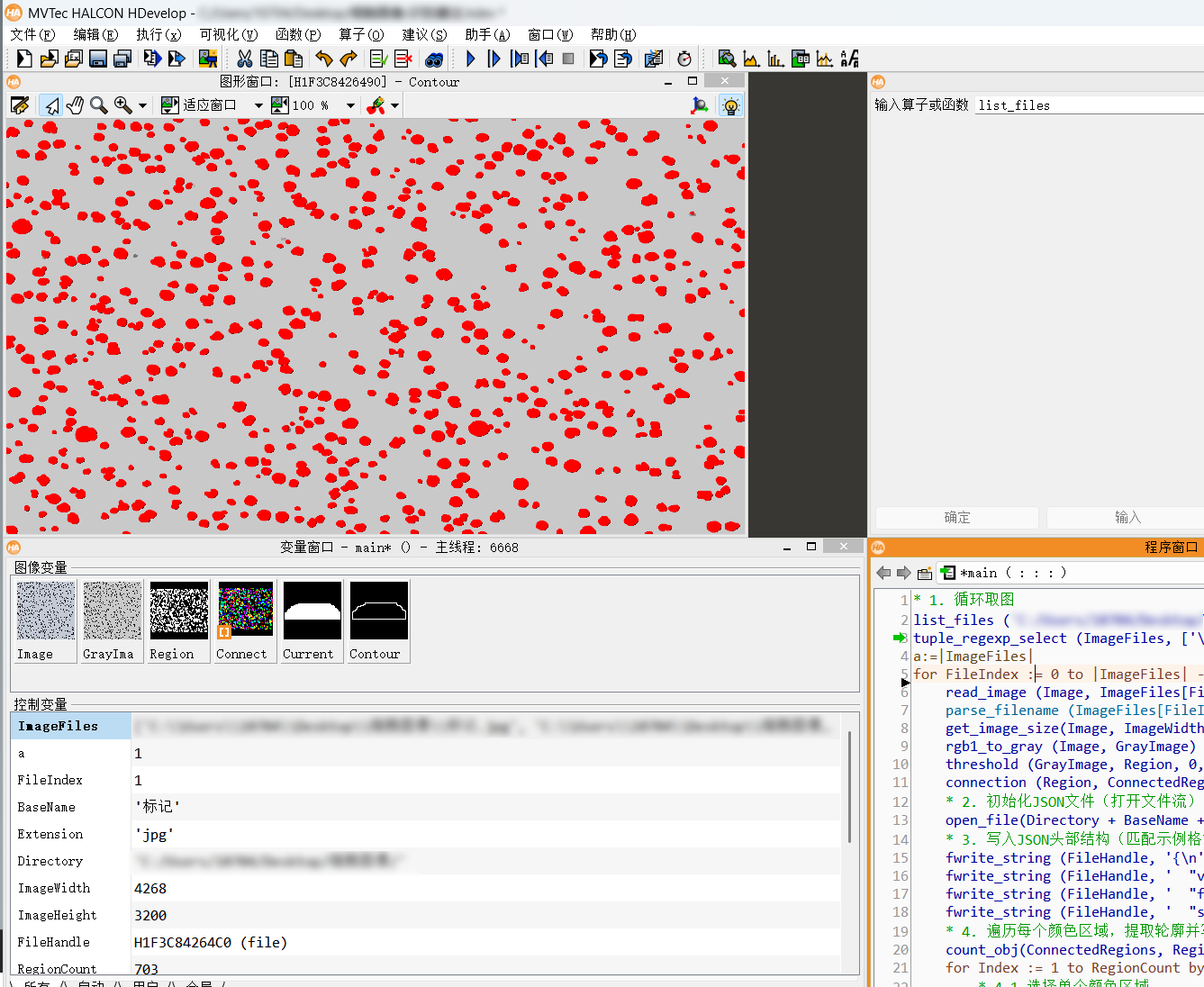
halcon源码:
* 1. 循环取图
list_files ('****你的图片路径****', ['files','follow_links'], ImageFiles)
tuple_regexp_select (ImageFiles, ['\\.(jpg|png|bmp)$','ignore_case'], ImageFiles)
a:=|ImageFiles|
for FileIndex := 0 to |ImageFiles| - 1 by 1
read_image (Image, ImageFiles[FileIndex])
parse_filename (ImageFiles[FileIndex], BaseName, Extension, Directory)
get_image_size(Image, ImageWidth, ImageHeight)
rgb1_to_gray (Image, GrayImage)
threshold (GrayImage, Region, 0, 100)
connection (Region, ConnectedRegions)
* 2. 初始化JSON文件(打开文件流)
open_file(Directory + BaseName + '.json', 'output', FileHandle)
* 3. 写入JSON头部结构(匹配示例格式)
fwrite_string (FileHandle, '{\n')
fwrite_string (FileHandle, ' "version": "3.2.2",\n')
fwrite_string (FileHandle, ' "flags": {},\n')
fwrite_string (FileHandle, ' "shapes": [\n')
* 4. 遍历每个颜色区域,提取轮廓并写入JSON
count_obj(ConnectedRegions, RegionCount)
for Index := 1 to RegionCount by 1
* 4.1 选择单个颜色区域
select_obj(ConnectedRegions, CurrentRegion, Index)
* 4.2 生成区域的边界轮廓(XLD格式,'border'表示区域边界)
gen_contour_region_xld(CurrentRegion, Contour, 'border')
* 4.3 获取轮廓的点坐标(Row=行/垂直方向,Col=列/水平方向)
get_contour_xld(Contour, Row, Col)
PointCount := |Row| // 轮廓点数量
* 4.4 写入单个shape对象(匹配示例字段)
fwrite_string (FileHandle, ' {\n')
fwrite_string (FileHandle, ' "label": "0",\n')
fwrite_string (FileHandle, ' "score": null,\n')
fwrite_string (FileHandle, ' "points": [\n')
* 4.5 写入轮廓点坐标(转换为[Col, Row],匹配JSON的[x,y]格式)
for PointIdx := 0 to PointCount - 1 by 1
ColVal := Col[PointIdx]+0.5 // X轴(水平方向)
RowVal := Row[PointIdx]+0.5 // Y轴(垂直方向)
* 处理最后一个点,避免多余逗号
if (PointIdx == PointCount - 1)
fwrite_string (FileHandle,' [\n')
fwrite_string (FileHandle,' '+ColVal+'.0,\n')
fwrite_string (FileHandle,' '+RowVal+'.0\n')
fwrite_string (FileHandle,' ]\n')
else
tuple_mod (PointIdx, 20, Mod)
if(Mod==0)
fwrite_string (FileHandle,' [\n')
fwrite_string (FileHandle,' '+ColVal+'.0,\n')
fwrite_string (FileHandle,' '+RowVal+'.0\n')
fwrite_string (FileHandle,' ],\n')
endif
endif
endfor
* 4.6 写入shape对象剩余字段
fwrite_string (FileHandle, ' ],\n')
fwrite_string (FileHandle, ' "group_id": null,\n')
fwrite_string (FileHandle, ' "description": "",\n')
fwrite_string (FileHandle, ' "difficult": false,\n')
fwrite_string (FileHandle, ' "shape_type": "polygon",\n')
fwrite_string (FileHandle, ' "flags": {},\n')
fwrite_string (FileHandle, ' "attributes": {},\n')
fwrite_string (FileHandle, ' "kie_linking": []\n')
* 4.7 处理最后一个shape对象,避免多余逗号
if (Index == RegionCount)
fwrite_string (FileHandle, ' }\n')
else
fwrite_string (FileHandle, ' },\n')
endif
endfor
* 5. 写入JSON尾部结构
fwrite_string (FileHandle, ' ],\n')
fwrite_string (FileHandle, ' "imagePath": "'+ BaseName + '.jpg",\n')
fwrite_string (FileHandle, ' "imageData": null,\n')
fwrite_string (FileHandle, ' "imageHeight": '+ImageHeight+',\n')
fwrite_string (FileHandle, ' "imageWidth": '+ImageWidth+'\n')
fwrite_string (FileHandle, '}')
* 6. 关闭文件流
close_file(FileHandle)
endfor- 注意:list_files 的 Directory 参数要输入你自己的路径:类似这样的 'C:/Users/Admin/Desktop/图片'
- 其中 threshold 为最简单应用,可增加其他功能应用,本例为阐述原理所述,非本文重点
七、小结
附件为:
1、测试图片(标记.jpg)
2、对应的X-AnyLabeling生成的json文件(标记.json)
3、halcon源码因版本兼容,txt格式复制粘贴使用
备注:
初写技术博客,内容均为个人技术总结与实践心得。分享出来,一方面是想记录成长,更重要的是希望能为有需要的同行提供一点参考和帮助。文中若有不当之处,恳请大家指出宝贵意见,助力内容完善,在此致谢!
























 607
607

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








