简单的线性回归
以某产品的温度和产率关系为例,其中产率(y)是温度(x)的函数。请构建模型预测产品产率。
| 温度 | 产率 |
|---|---|
| 100 | 45 |
| 110 | 51 |
| 120 | 54 |
| 130 | 61 |
| 140 | 66 |
| 150 | 70 |
| 160 | 74 |
| 170 | 78 |
| 180 | 85 |
| 190 | 89 |
首先,我们可以先把数据可视化,画个散点图出来。
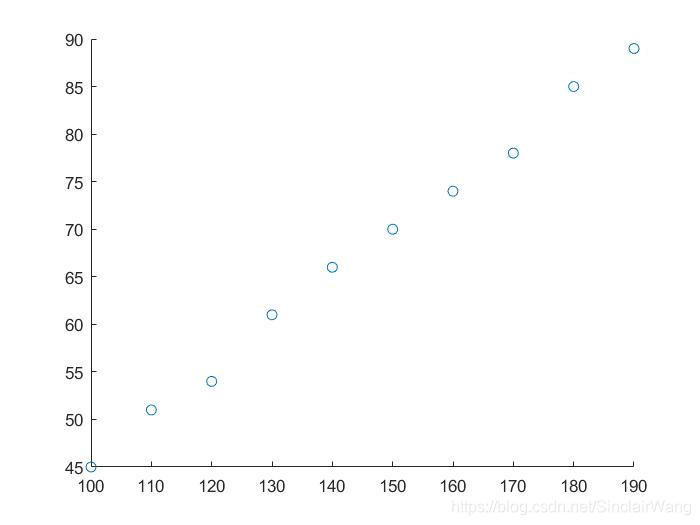
根据散点图可知,数据基本上都在一条直线上,我们可以用一条直线去拟合。
正规方程求解
θ = ( X T X ) − 1 X T Y \theta=(X^TX)^{-1}X^TY θ=(XTX)−1XTY
function [ theta ] = linearReg( )
% 线性回归正规方程求解
% 用130、190作为测试集
train = 8;
X = [1 100;1 110;1 120;1 140;1 150;1 160;1 170;1 180;]
Y = [45; 51 ;54 ;66; 70; 74 ;78; 85];
A = inv(X'*X);
theta = A*X'*Y;
end
解得:
θ
=
(
−
3.1507
0.4851
)
\theta=\begin{pmatrix} -3.1507 \\ 0.4851 \end{pmatrix}
θ=(−3.15070.4851)
散点图拟合情况如下:
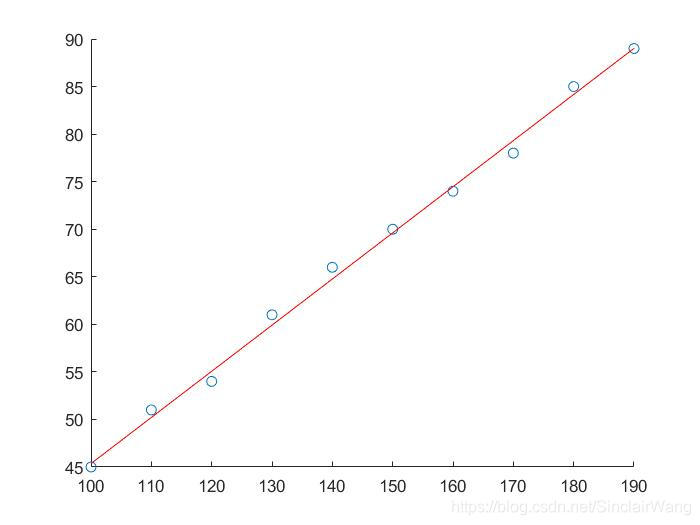
看起来拟合效果还不错
梯度下降求解
假设函数:
h
θ
(
x
)
=
θ
0
+
θ
1
x
h_\theta(x)=\theta_0+\theta_1x
hθ(x)=θ0+θ1x
代价函数:
J
(
θ
0
,
θ
1
)
=
1
2
m
∑
i
=
1
m
(
h
θ
(
x
(
i
)
)
−
y
(
i
)
)
2
J(\theta_0 ,\theta_1)= \frac{1} {2m}\sum_{i=1}^m(h_\theta(x^{(i)})-y^{(i)})^2
J(θ0,θ1)=2m1i=1∑m(hθ(x(i))−y(i))2
梯度下降:(同步更新)
t
e
m
p
0
=
θ
0
−
α
∂
∂
θ
0
J
(
θ
0
,
θ
1
)
temp_0 = \theta_0- \alpha \frac{\partial} {\partial \theta_0}J(\theta_0 ,\theta_1)
temp0=θ0−α∂θ0∂J(θ0,θ1)
t
e
m
p
1
=
θ
1
−
α
∂
∂
θ
1
J
(
θ
0
,
θ
1
)
temp_1 = \theta_1- \alpha \frac{\partial} {\partial \theta_1}J(\theta_0 ,\theta_1)
temp1=θ1−α∂θ1∂J(θ0,θ1)
θ
0
=
t
e
m
p
0
\theta_0 = temp_0
θ0=temp0
θ
1
=
t
e
m
p
1
\theta_1 = temp_1
θ1=temp1
假设函数
function [ res ] = h_func(inputx,theta )
% 预测函数
res = theta(1)+theta(2)*inputx;
end
代价函数
function [ jVal,gradient ] = costFunction2( theta )
% jVal 为 代价值 gradient为梯度
% cost function
% 用130、190作为测试集
x = [100 110 120 140 150 160 170 180]
y = [45 51 54 66 70 74 78 85];
m = size(x,1); % size(x) = [1 8] size(x,1) 表示获取x的行
hypothesis = h_func(x,theta);
delta = hypothesis - y; % 预测误差 向量
jVal= sum(delta.^2); % 损失函数
gradient(1) = sum(delta)/m;
gradient(2) = sum(delta.*x)/m;
end
梯度下降
function [ optTheta,functionVal,exitFlag ] = Gradient_descent()
% 梯度下降
% fminunc 非线性优化
% 找到min f(x) 的 x f(x)是一个返回值为标量的函数,x是一个向量或矩阵
% options 配置选项,'GradObj' 'on' 表示使用自定义的梯度下降函数,'MaxIter',1000 表示最大迭代次数
options = optimset('GradObj','on','MaxIter',1000);
% 需要返回的参数, 需要初始化
initialTheta = zeros(2,1);
[optTheta,functionVal,exitFlag] = fminunc(@costFunction2,initialTheta,options);
end
运行结果:
o
p
t
T
h
e
t
a
=
(
−
3.1507
0.4851
)
optTheta = \begin{pmatrix} -3.1507 \\0.4851 \end{pmatrix}
optTheta=(−3.15070.4851)
f
u
n
c
t
i
o
n
V
a
l
=
6.1996
functionVal = 6.1996
functionVal=6.1996
可见利用正规方程和梯度下降求解出来的参数一样
未完,待续…





 本文通过一个产品温度与产率的关系实例,介绍了如何使用正规方程和梯度下降两种方法进行简单线性回归分析,展示了参数求解过程及模型拟合效果。
本文通过一个产品温度与产率的关系实例,介绍了如何使用正规方程和梯度下降两种方法进行简单线性回归分析,展示了参数求解过程及模型拟合效果。
















 424
424

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








