
英文是纯手打的!论文原文的summarizing and paraphrasing。可能会出现难以避免的拼写错误和语法错误,若有发现欢迎评论指正!文章偏向于笔记,谨慎食用
目录
2.4. Multimodal Learning of Brain-Visual-Linguistic Features
2.4.2. Brain, Image and Text Preprocessing
2.4.3. High-Level Overview of the Proposed BraVL Model
2.4.4. Multi-Modality Joint Modeling
2.4.5. Mutual Information (MI) Regularization
2.4.6. Overall Objective and Training
2.5.1. Brain-Visual-Linguistic Datasets
3.1. Product-of-experts formulation
1. 心得
(1)捡到宝了?只能说对TPAMI印象太好了
(2)看到作者给笑的,大家title好多。
(3)xd增补三个数据集模态啊我靠五体投地了
(4)................是个工作量很大也很难的模型
2. 论文逐段精读
2.1. Abstract
①Limitations: a) under-exploitation of multimodal information, b) limited number of paired data
②Their model, BraVL, can be used in trimodal (brain-visual-linguistic) matching tasks
2.2. Introduction
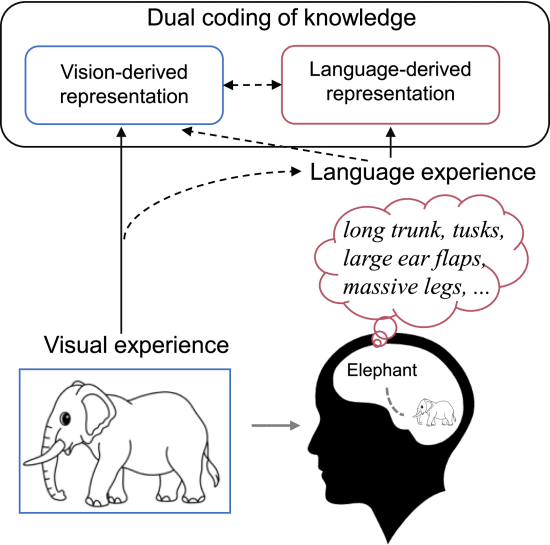
①⭐The authors believed that object names and images have the same impact on brain signals. In terms of artificial intelligence, names and images are aligned
②⭐Therefore, the authors believe that deeper brain information should be explored, such as providing subjects with richer detailed vocabulary or articles:
2.3. Related Work
①Neural decoding usually focus on single modality
②They chose the (c) method to achieve Zero-Shot Learning (ZSL): a) learning instance → semantic projections, b) learning semantic → instance projections, c) learning the projections of instance and semantic spaces to a shared latent space
③They introduce text feature to enhance visual neural decoding
④They prove that inter-modality MI-maximization is equivalent to multimodal contrast learning
2.4. Multimodal Learning of Brain-Visual-Linguistic Features
2.4.1. Problem Definition
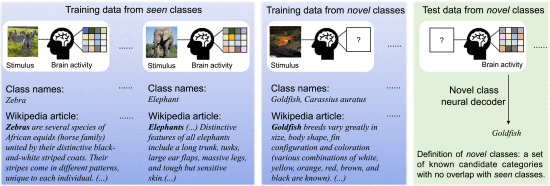
①Provide brain activities, image and text for seen categories, and only image and text for unseen classes
②Seen data:
where denotes brain activity (fMRI) features,
denotes visual features,
denotes textual features,
denotes labels of seen classes
③Novel/unseen data:
where ,
is only available on test
④For any modality subscript , the unimodal feature matrix is:
where ,
denotes sample size,
denotes the feature dimension of modality
2.4.2. Brain, Image and Text Preprocessing
①Process raw input to feature representations:
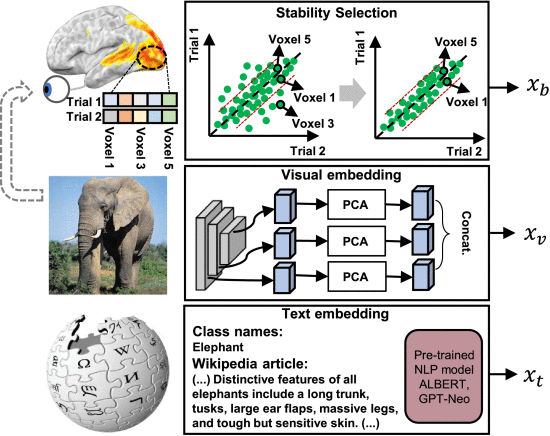
②⭐“为了提高神经解码的稳定性,作者对 fMRI 数据使用了稳定性选择(Pearson),其中选择了在相同视觉刺激的不同试验中激活模式具有最高一致性的体素进行分析”
③Decrease the dimension by discarding unstabled voxels in all the ROIs
④Normalize fMRI data
⑤Applying PCA on fMRI data and doing test
⑥Extracting feature from images by pre trained RepVGG, and futher flatten and normalize data, then apply PCA
⑦Encode text by ALBERT and GPT-Neo, and get sentence embedding by average of token embeddings. “由于 ALBERT 和 GPT-Neo 的输入序列长度受到限制,不能直接将整个 Wikipedia 文章输入到模型中。为了对可以超过最大长度的文章进行编码,也可以将文章文本拆分为部分重叠的 256 个标记序列,其中重叠 50 个标记。连接多个句子嵌入将导致不希望的“维度诅咒”问题。因此,我们使用多个序列的平均池化表示来编码整篇文章。这种平均池化策略也已成功用于最近的语言神经编码研究 。同样,如果一个类在 Wikipedia 中有多个对应的文章,我们将对从每个文章中获得的表示进行平均。有关平均池化下文本特征的异质性程度,请参阅附录。”
文章分割成重叠序列例子: 假设有一篇包含 1000 tokens 的文章。将其分割成以下几个重叠的序列:
第一段:从第 1 到第 256 个 token(共 256 个 token)
第二段:从第 207 到第 462 个 token(共 256 个 token,与第一段有 50 个 token 的重叠)
第三段:从第 413 到第 668 个 token(共 256 个 token,和第二段有 50 个 token 的重叠)
依此类推。
这样,虽然每个片段的长度为 256 个 token,但它们之间有 50 个 token 重叠,这样模型可以理解不同片段之间的联系和上下文。
平均池化例子:假设有3个片段,它们分别通过模型得到了以下嵌入向量:
第一段的嵌入向量:0.1,0.2,0.3
第二段的嵌入向量:0.2,0.3,0.4
第三段的嵌入向量:0.3,0.4,0.5
将这些向量进行平均池化:
平均向量 =
结果是:
平均向量 =
类似多篇文章取平均
2.4.3. High-Level Overview of the Proposed BraVL Model
①Overall framework of BraVL:
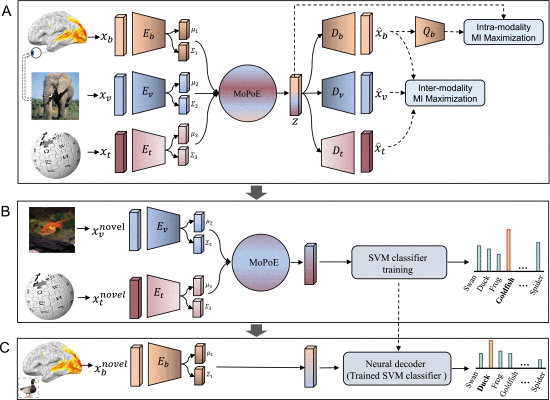
where MoPoE is Mixture-of-Products-of-Experts
2.4.4. Multi-Modality Joint Modeling
①Marginal log-likelihood for single modality :
②Due to the difficult of calculating , variational auto-encoders (VAEs) chose to optimize Evidence Lower BOund (ELBO):
where denotes approximate posterior distribution represented,
is decoder network
③A multimodality ELBO:
where denotes decoders with multi parameters and modalities
. seen
and unseen
,
denotes a possible subset of
,
denotes all
subsets
④Optimization methods:

⑤Parameterized will be easilyd faced with posterior collapse: a) the joint latent variable
is independent from the observed data
, b) the decoder may no longer focus on latent variables
, c) lack of consistency between jointly generated modalities
⑥By MoPoE, the loss can be writen as:
2.4.5. Mutual Information (MI) Regularization
(1)Intra-Modality MI Maximization
①Variational lower bound on MI between samples of the posterior distribution of joint latent variable and observation
:
where is some auxiliary distribution implemented by a deepneural network
②Through InfoGAN, they change the bound by:
③There is
④Intra loss:
(2)Inter-Modality MI Maximization
①The seen inter modality loss:
②They add a χ-upper-bound(CUBO) estimator to limite the upper bound:
③Inter loss for novel class:
2.4.6. Overall Objective and Training
①Total loss:
②Training process:

③Classifier: SVM
2.5. Experiments
2.5.1. Brain-Visual-Linguistic Datasets
①Statistcs of datasets:

②Used EEG signals:
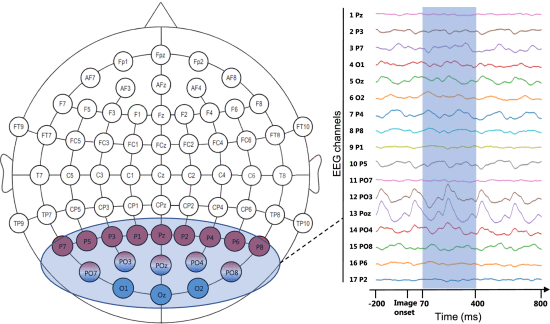
2.5.2. Implementation Detail
①Parameters:
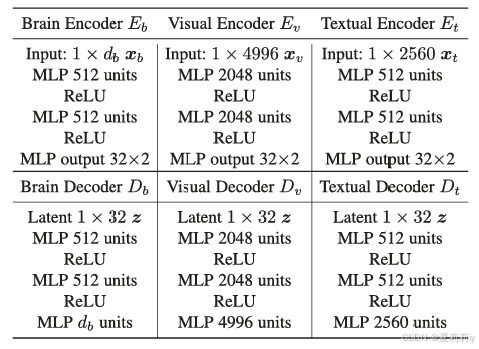
②Stability of ROIs:

2.5.3. Results
(1)Does Language Influence Vision?
①Performance table:

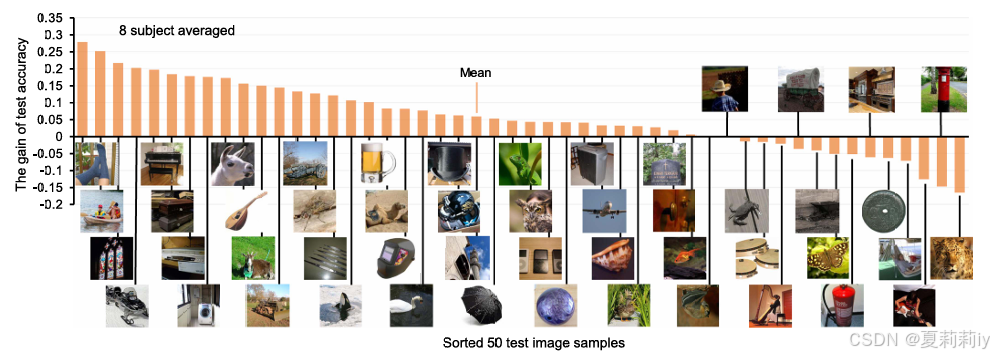
②The benefits brought by text assisted training:
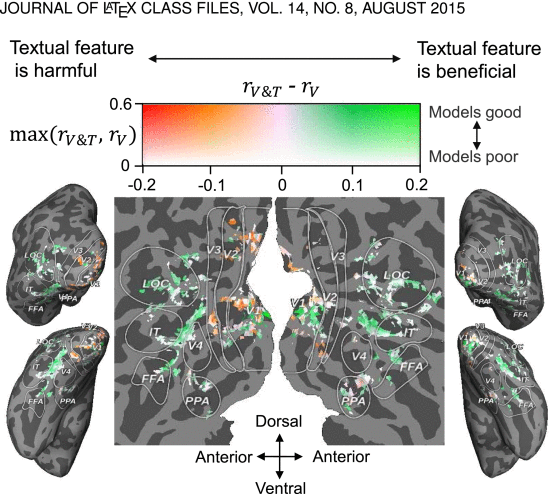
③The impact of text prompts on brain regions:
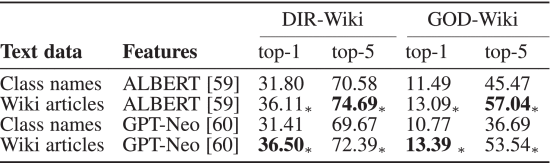
(2)Are Wiki Articles More Effective Than Class Names?
①Decoder ablation:
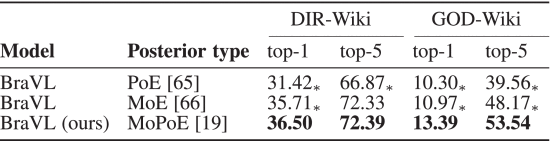
(3)Ablation Study
①Loss ablation:

②Joint posterior approximation ablation:
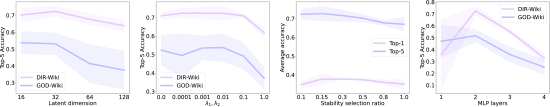
(4)Sensitivity Analysis
①Hyperparameters ablation:
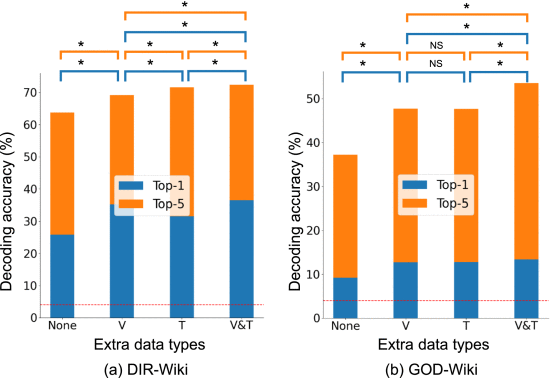
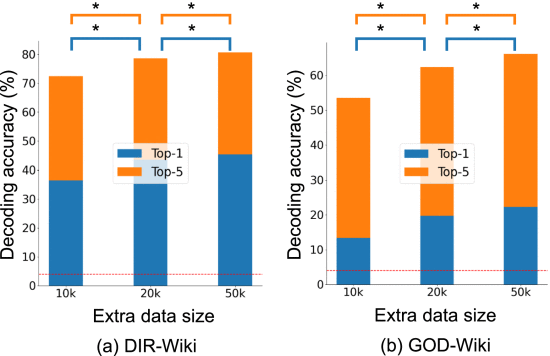
(5)Analyzing the Impact of Extra Data
①Benefits from extra data:
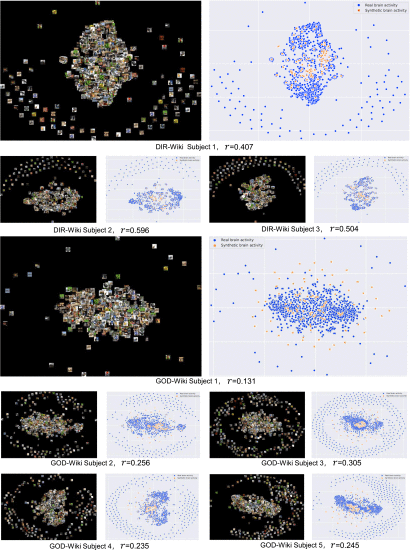
(6)Cross-Modality Generation for Brain Activity
①t-SNE of real (blue) and generated (orange) images:
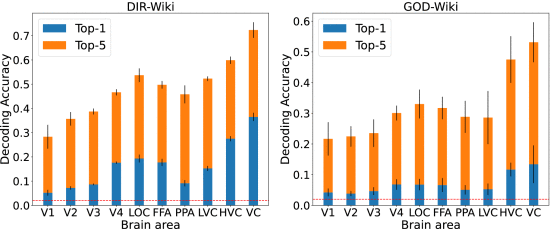
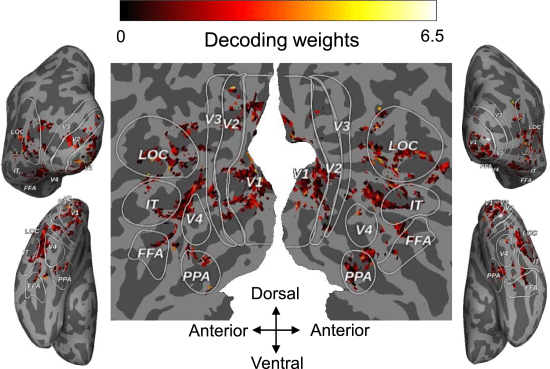
(7)Performance of Different Brain Areas
①ROI ablation:
②Importance of ROIs:
(8)Evaluation on the ThingsEEG-Text Dataset
①Performance on ThingsEEG-Text dataset:

(9)Fine-Tuning the Feature Extractors
①No need
2.6. Discussion
2.7. Conclusion
3. 知识补充
3.1. Product-of-experts formulation
(1)参考学习:Product-of-Experts(PoE) - 知乎
4. Reference
Du, C. et al. (2023) Decoding Visual Neural Representations by Multimodal Learning of Brain-Visual-Linguistic Features, IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 45(9): 10760-10777. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2023.3263181

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








