投稿:ACL
Abstract
通过融合进步的文化理念,仇恨表情包(meme)不断演变,新的表情包不断出现,使得依赖广泛培训的现有方法变得过时或无效。在这项工作中,我们提出了Evolver,通过整合模因的进化属性和上下文信息,通过进化链(CoE)提示融合了大型多模态模型(Large Multimodal Models, LLM)。具体而言,Evolver使用进化配对挖掘模块(evolutionary pair min-ing module)、进化信息提取器(evolutionary information ex-tractor)和语境关联放大器(contextual relevance amplifier),逐步模拟模因和原因通过lmm的进化和表达过程。在公共FHM、MAMI和HarM数据集上进行的大量实验表明,可以将CoE提示合并到现有的LLM中,以提高其性能。更令人鼓舞的是,它可以作为一种解释工具,促进对表情包进化的理解。
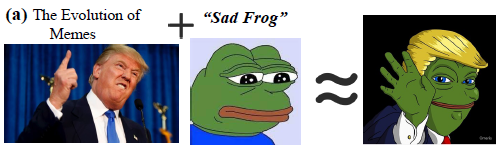
fig1.a 仇恨表情包的融合和进化
Memes evolve by fusing new cultural concepts. The meme of Trump is influenced by the meme of a sad frog in an image and text symbol, which creates a new hateful meme.
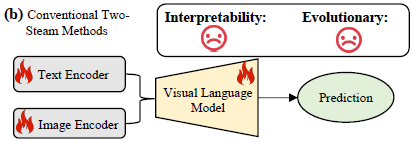
fig1.b 传统的 two-stream 方法:缺点:poor interpretability, over-fitting on training sets and diminished effectiveness in the dynamic and evolving meme landscape
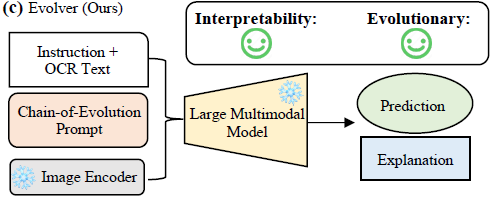
fig1.c 我们的进化方法:captures the evolution and context of memes, utilizing them as prompts for large multimodal models to obtain a comprehensive understanding of memes.
Evolver is an innovative approach in zero-shot hateful meme detection significantly
Main :
-We establish an LMM-based zero-shot hateful meme detection benchmark, which provides a comprehensive evaluation of the application of LMMs in social media.
- We propose a simple yet effective Evolver frame-work, which advances LMMs with Chain-of-Evolution prompting. It expands LMMs with an evolution reasoning ability while offering good interpretability.
- Extensive experiments on commonly used zero-shot hateful meme detection datasets with supe-rior performance validate the efficacy and gen-eralization of our method.
Method
Problem Definition
hateful meme detection 当二分类问题
Meme, in our case, consists of an image-text pair.
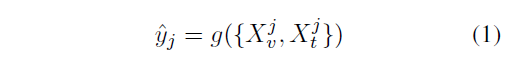
where yˆj denotes the j-th prediction. The pre-diction yˆj ∈ {0, 1} indicates the target image-text pair is hateful or not.
g(·) is the multimodal model.
{Xvj , Xtj } is the j-th image-text paired input.
Large Multimodal Models
Vision Encoder
help language models understand visual content.
leverages frozen pretrained vision models such as CLIP (Radford et al., 2021) and ViT (Dosovitskiy et al., 2020) to encode visual content
![]()
hv is the language embedding tokens
W is the projection to transform visual features into language embedding tokens
Encvis(Xv) denotes the visual feature extracted by pretrained model.
先转化成图像特征然后再把图像特征映射到language embedding tokens
Large Language Model Decoder
是标准 decoder 的生成逻辑 + 多模态输入(文本和图像)
generates a sentence given tokens:
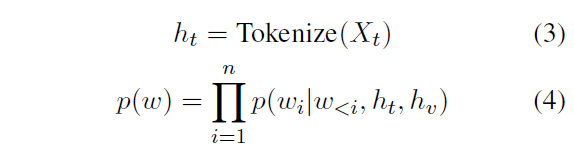
Xt is the input text
Tokenize(·) transform text into tokens
hv is the image tokens
p(w) is the probability of generating a sentence by a language model
p(wi|w<i, ht, hv) is the probability of generating a token at the i-th position given the previously generated tokens, input text, and image tokens.
是典型的 自回归(autoregressive)语言模型,一步一步生成每一个 token
The visual tokens are incorporated with textual tokens and then fed to the language model.
Evolver: Chain-of-Evolution Prompting
找相似 → 抽仇恨特征 → 上下文增强 → LMM推断
we design a novel Chain-of-Evolution (CoE):
evolutionary pair mining 的目标是通过寻找与目标 meme 相关的最接近的 K 个 meme,并从这些 meme 中提取出什么特征是与 hatefulness 相关的。这些提取出来的信息会作为 evolution information,并用来帮助模型理解这些 meme 是如何演变过来的。
然后,这些 evolutionary information 会被输入到 Evolution Information Extractor 中,以提取出与 hatefulness 相关的关键特征。接下来,Contextual Relevance Amplifier 就是对这些提取的信息进行增强,它的作用是将信息进一步调整成对当前任务更有帮助的形式。
最后,在 LMM (Large Multimodal Model) 进行推断时,模型会结合这些增强过的信息来进行最终的判断。你可以理解为 Amplifier 就是通过增强信息和加入明确的指令,来提升整个判断的准确度。
简而言之,信息增强(Amplifier)确实是在第二和第三阶段之间作为一种增强方式,通过这种方式,最终的判断会更加准确,因为它引入了一个对当前任务更加相关的背景信息。
Evolutionary Pair Mining
通过余弦相似度找这个meme 可能的k个衍生/来源
在Qu等人(2023)的推动下,模因的进化被定义为通过融合其他模因或文化观念而出现的新模因。因此,模因的演变与旧模因具有相似的文本和视觉语义规律。我们利用这一特性,根据进化的模因来识别这些旧模因。为此,我们可以利用仇恨表情包的进化来增强lmm的仇恨表情包理解能力
1. CLIP: generate the textual and visual embeddings from an external meme pool and target memes.
external meme pool: (1) do not overlap with the test set. (2) have enough evolutionary information.
training set as the carefully curated meme pools rather than any other dataset, where the memes follow the same definition of hate-fulness/harm/misogyny.
2. fuse the textual and visual embeddings with a fixed ratio
* 现有技术很难确认进化meme的上下来源
use multiple evolutionary memes to find the common characteristics of this evolution:
we retrieve the top-K similar memes using cosine similarity:
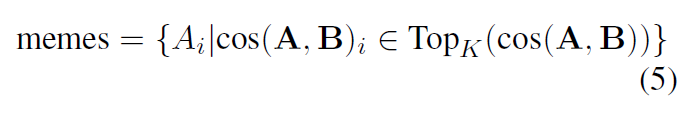
A ∈ Rn×d is embedding of n candidate memes
B ∈ Rd is the d-dimensional vector of the target meme
cos(·) return a similarity vector
TopK(·) returns K highest values given the input vector.
For each evolution meme, we pair K memes that the evolution meme is derived from.
Evolution Information Extractor
To extract the information we are interested in (e.g., hateful component), we summarize paired memes with the help of a large multimodal model.
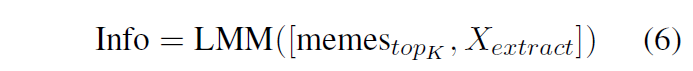
Info stands for our evolutionary information
LMM indicates the large multimodal model.
memesT opK are the T opK memes retrieved in the previous step
Xextract is the instruction to guide the LMM to extract information
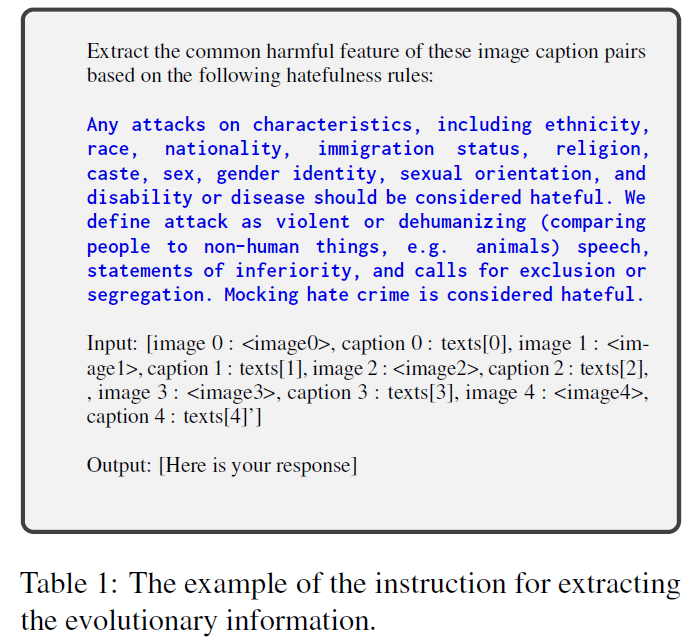
We present the detailed instruction of Xextract as shown in Table 1.
More definitions of hateful memes from different datases are shown in Appendix D.
Contextual Relevance Amplifier
To enhance the in-context hatefulness information, we add a contextual relevance amplifier to the LMM during evolution information extraction and final prediction to increase the search for hateful components
contextual relevance amplifier is the definition of a hateful meme given by the dataset we use
we combine the extracted information and contextual relevance amplifier as the in-context enhancement and feed them to the model:
![]()
yˆ is the final prediction,
Info stands for the information extracted pre-viously,
memesT is the memes we want to detect,
XD is the instruction to ask the large multimodal model to detect hateful memes.
Amp refers to contextual relevance amplifier.
The example of the amplifier is the same as the blue part in Table 1
可不可以理解为先用最接近的k个meme得出什么是hateful的 info,再把这个info放入最后判断,这个amplifier是作为信息增强作为一段instruction加入2,3阶段的?
The Principles of Prompts
principal:
(1) include the hateful meme definition and (2) limit the prompt to 30 words, addressing LMMs’ challenges with long-text comprehension.
We di-rectly applied definitions from the FHM, MAMI, and HarM datasets, summarized to meet this length requirement with the whole prompt using GPT-4. To this end, we do not use any specialized prompt design, highlighting the robustness of our method.
Experiment
Datasets
Facebook Hateful Meme dataset (FHM) (Kiela et al., 2020)
Harmful Meme dataset (HarM) (Pramanick et al., 2021)
Multimedia Automatic Misogyny Identification (MAMI) (Fersini et al., 2022)
Implementation
We implement our Evolver based on the
MMICL:
Evolution Info Extractor:
minimum length for the generation: 50
maximum length for the generation: 80
temperature: 0.2.
final prediction:
minimum length of generation: 1
maximum length for generation: 50
LLaVA-1.5:
both stage:
temperature: 0.2
maxi-mum generated tokens: 1024
embedding size of textual and visual embeddings: N × 768, N is the number of memes
fuse textual and visual embeddings with a fixed ratio of 4:1 by element-wise add in practice.
Baselines
The detailed description of the base-line models including API-based (e.g., GPT-4V) and open-source LMMs (e.g., LLaVA) can be found in Appendix A.
Metrics
We adopt ACC (accuracy) and AUC (area under the ROC curve) as evaluation metrics.
LMM Backbones
We implement our Evolver based on MMICL (Zhao et al., 2023) and LLaVA-1.5 (Liu et al., 2023a). Please refer to the Ap-pendix B for more details.
Result
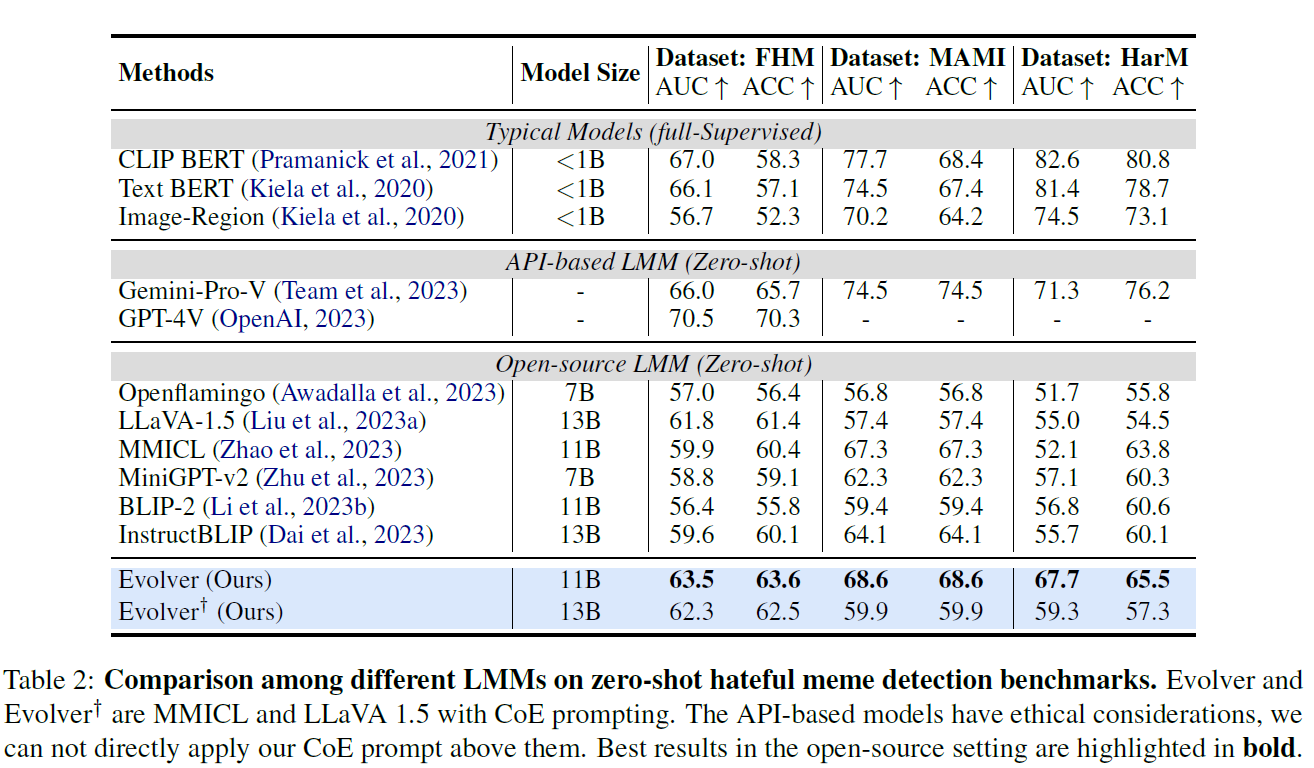
还是有蛮大提升空间的

The origin model (MMICL) without considering the meme’s evolu-tion, predicts non-hateful because it is not easy to detect the boy’s disability or genetic conditions. After obtaining the evolution information like “dis-criminates against individuals with disabilities or genetic conditions.", our Evolver rectify the predic-tion, which supports the rationale of our method.
model size does not necessar-ily lead to a better understanding of hateful memes.
closed-source models still outper-form open-source LMMs in zero-shot results, sug-gesting a significant gap for open-source models to close. (大概指的是那种qwen等开源不如gpt这种闭源)
typical existing training-based mod-els are fully supervised settings, mainly based on CLIP (Radford et al., 2021) and BERT (Devlin, 2018), which can not provide interpretability.
Ablation Study
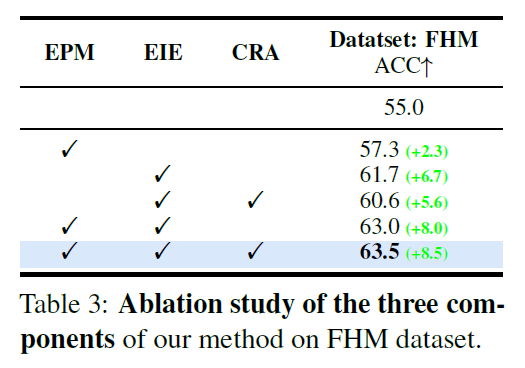
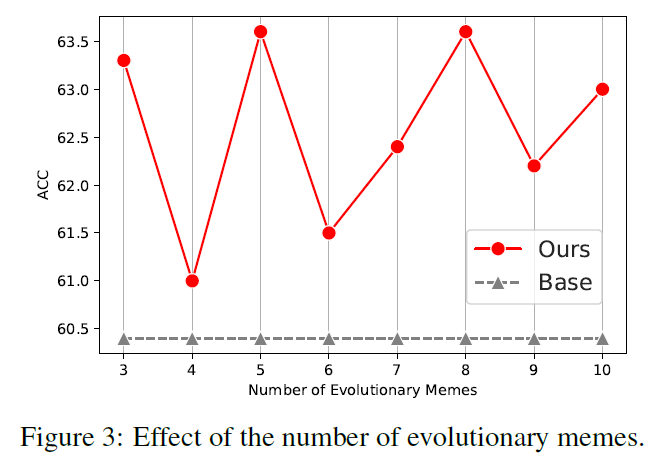
As shown in Figure 3, we show the effect of the number K of the evolutionary memes.
we set the K = 5 to achieve the best
Limitation
First, the effectiveness of our approach relies heav-ily on the quality and diversity of the curated meme pool used for seeking evolutionary memes.
Fur-thermore, biases inherent in these datasets could potentially affect the model’s ability to generalize across different cultural contexts and meme evolution patterns not represented in the related data.
Conclusion
We present Evolver to seamlessly boost LMMs for hateful meme detection via Chain-of-Evolution prompting. By integrating evolution of memes, our method can adapt to unseen memes. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of Evolver.






















 531
531

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








