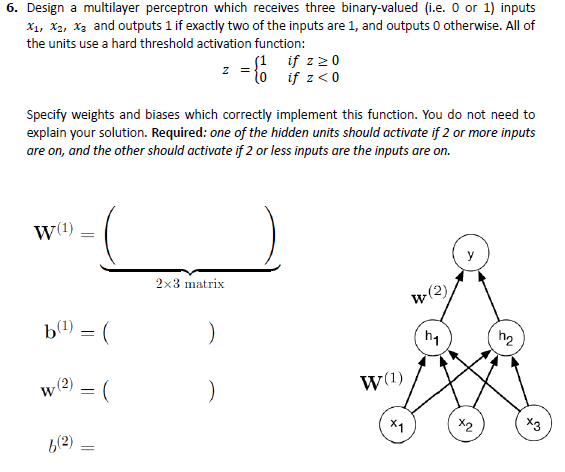
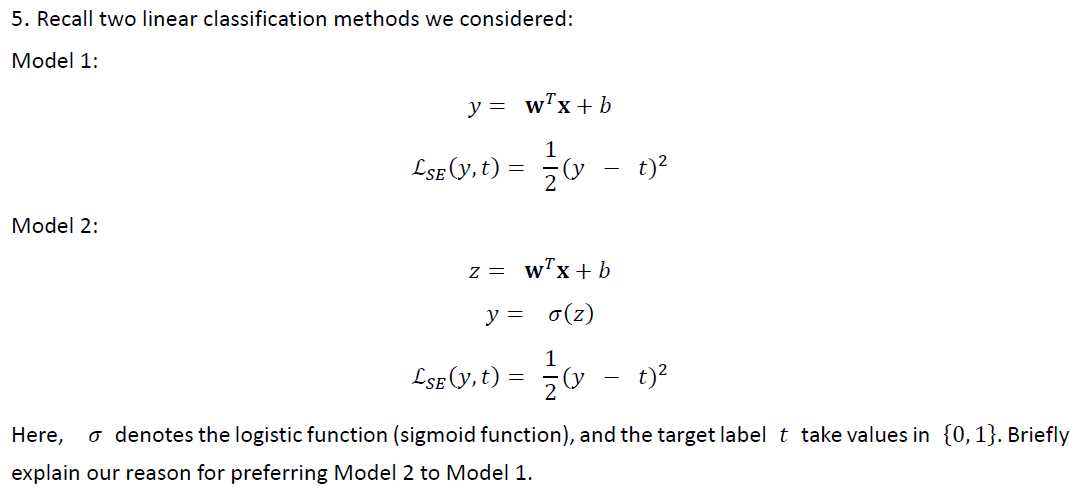
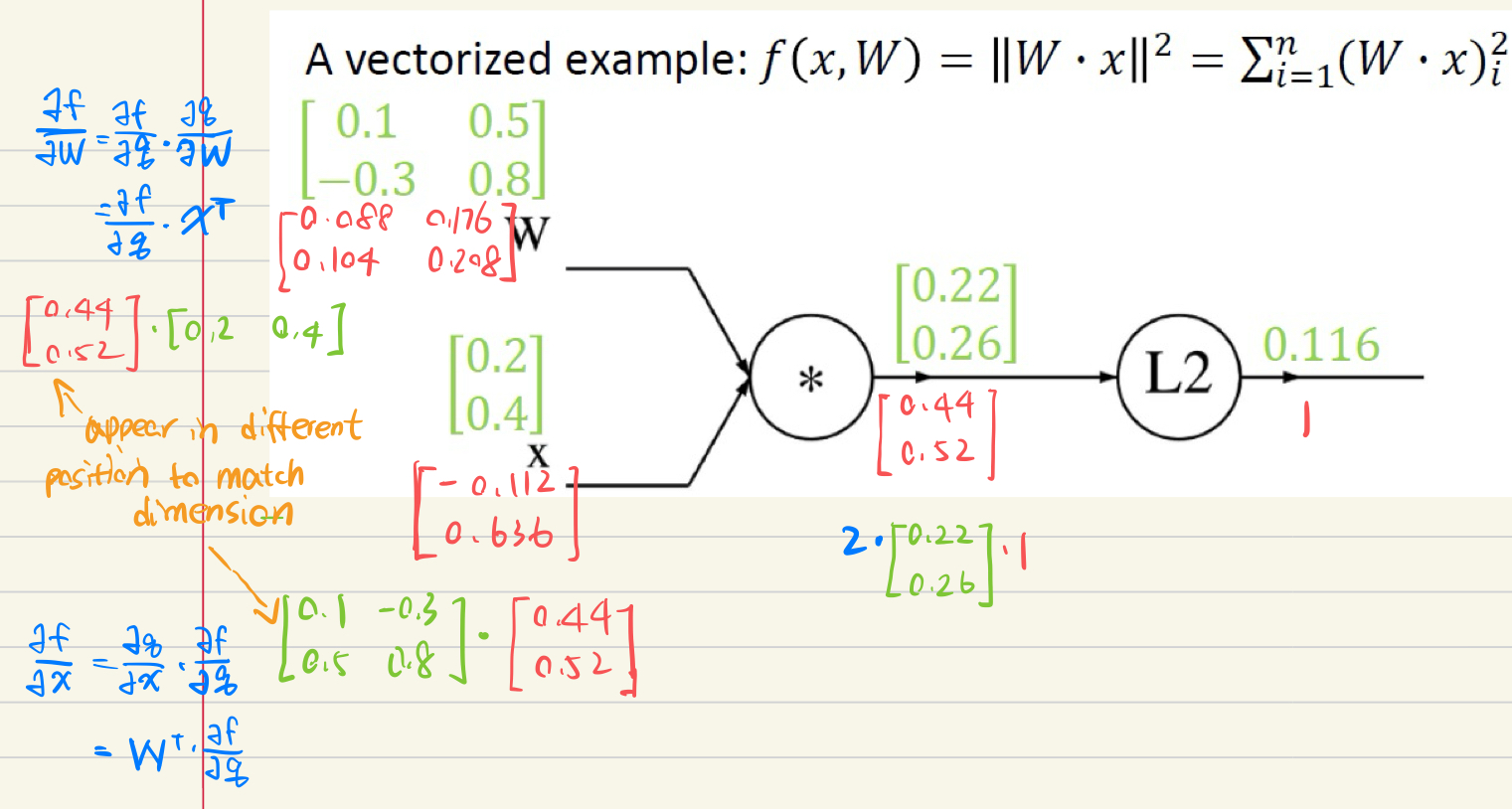
gradient descent
1.
21
1)

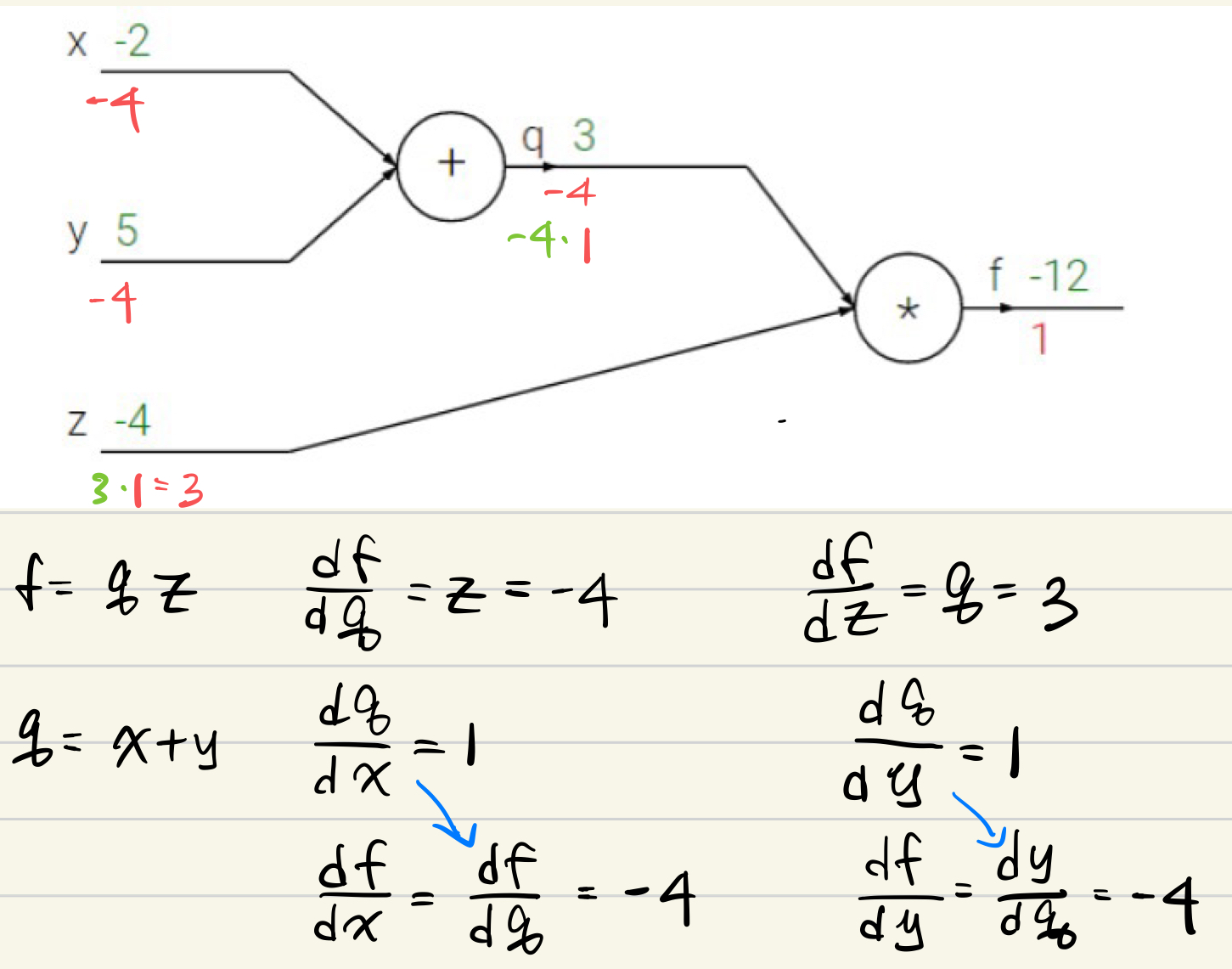
2)
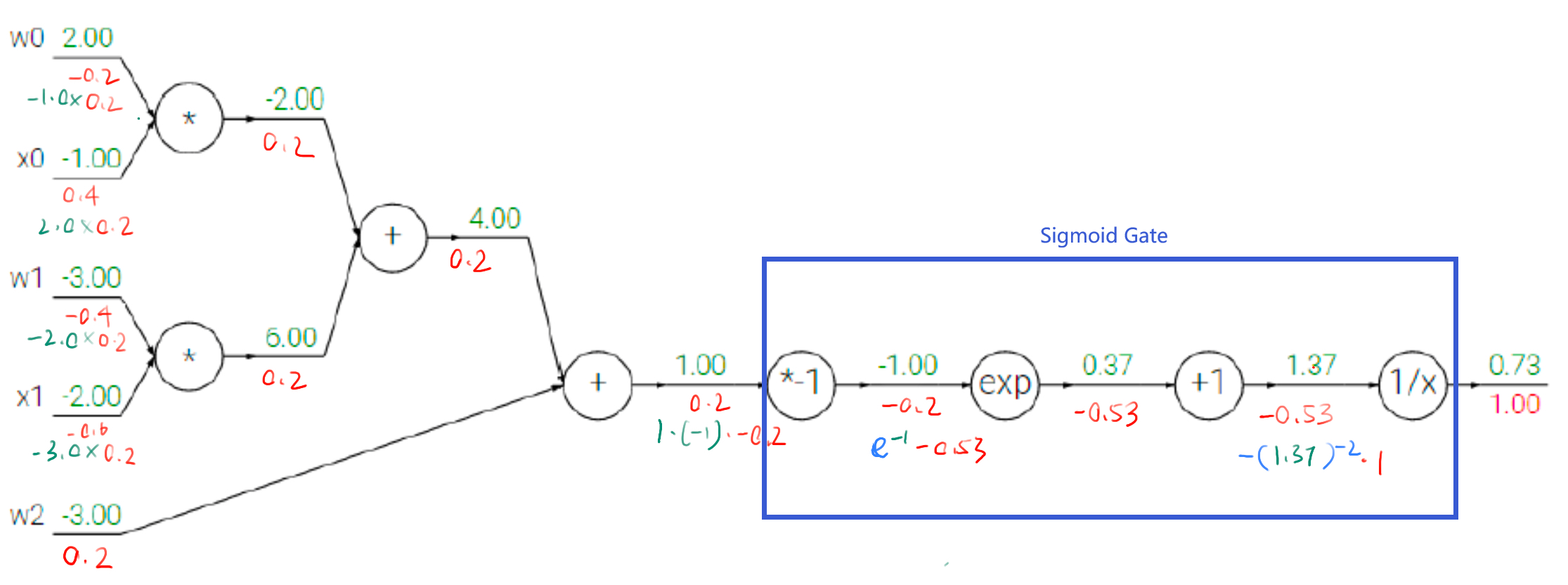

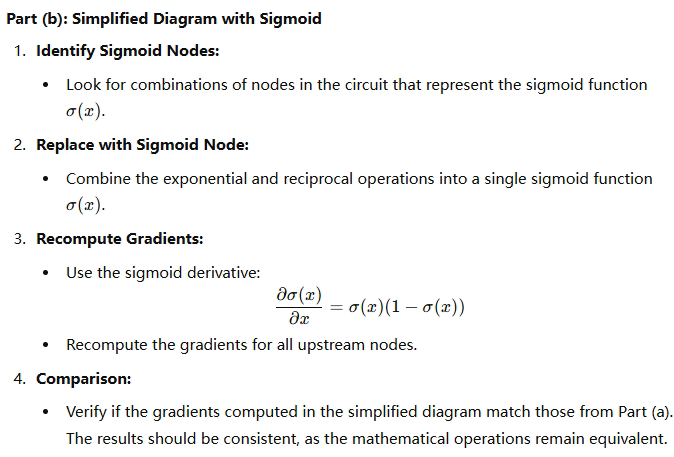
3)
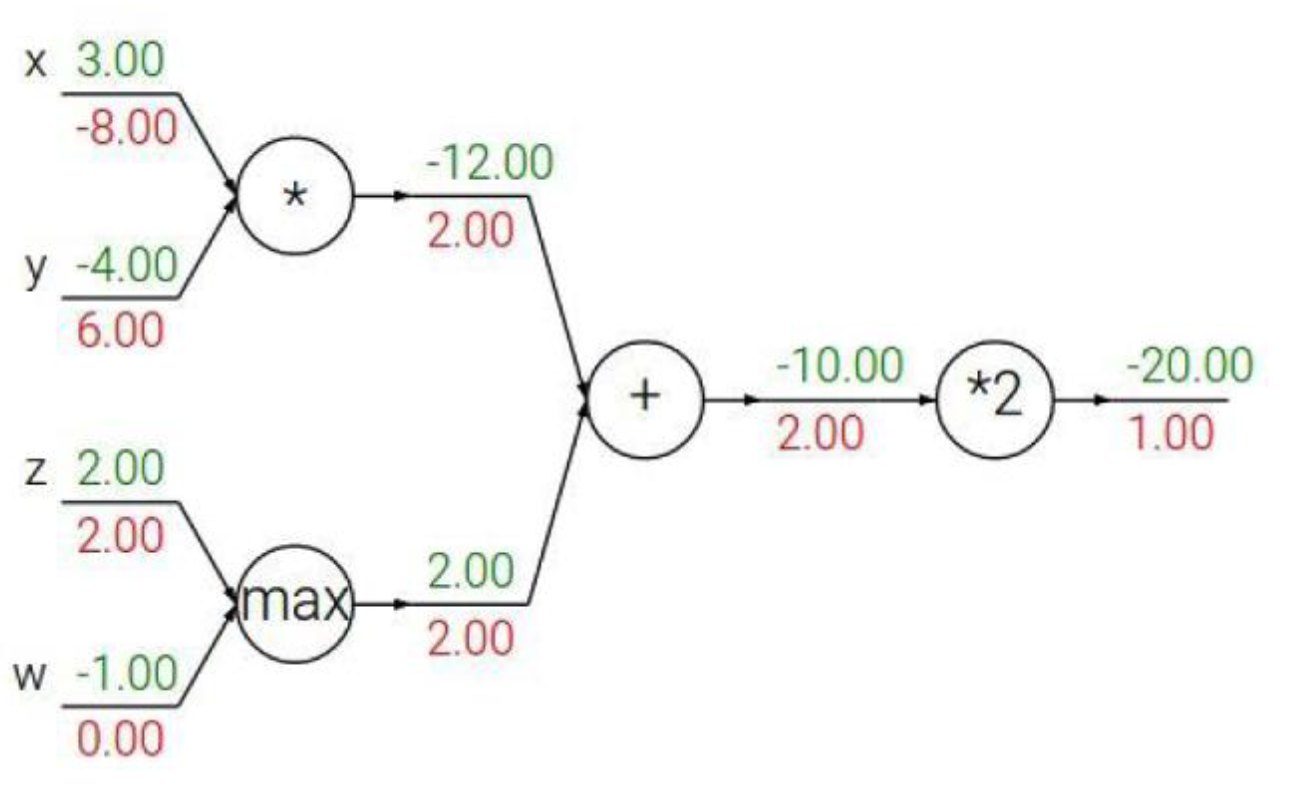
4)
The gradient with respect to a variable should have the same shape as the variable
3.
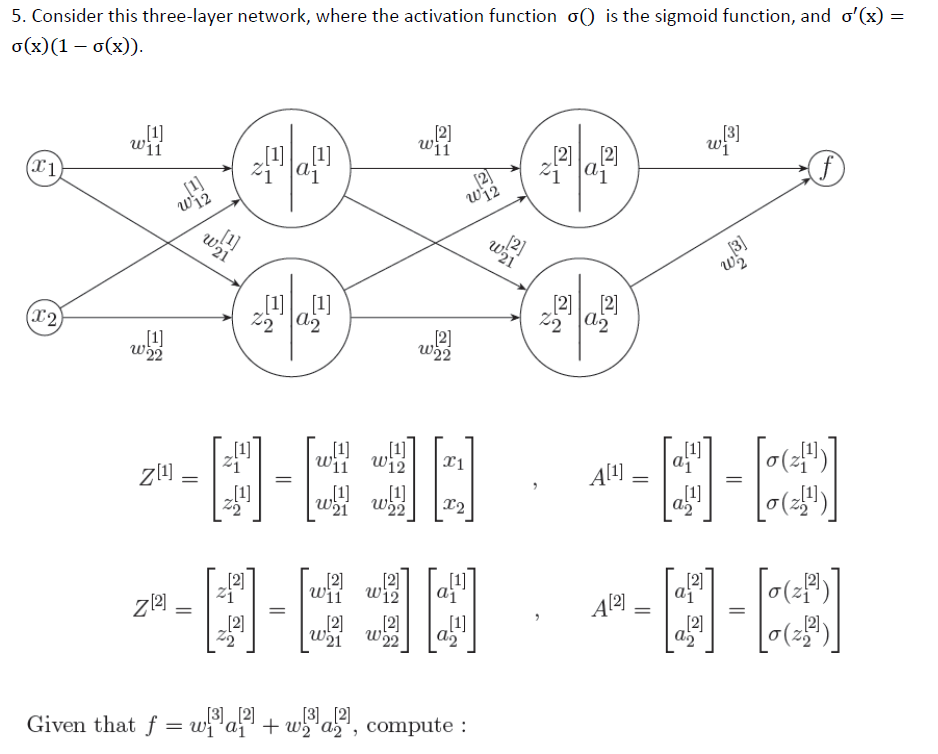

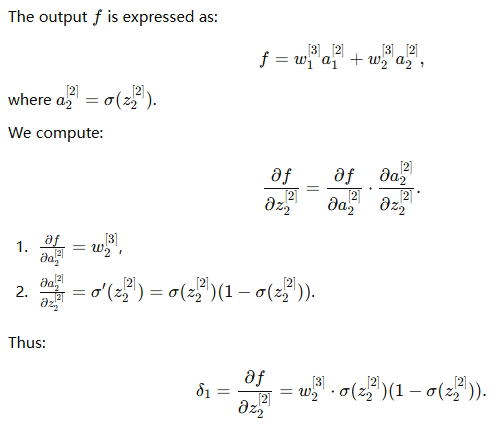


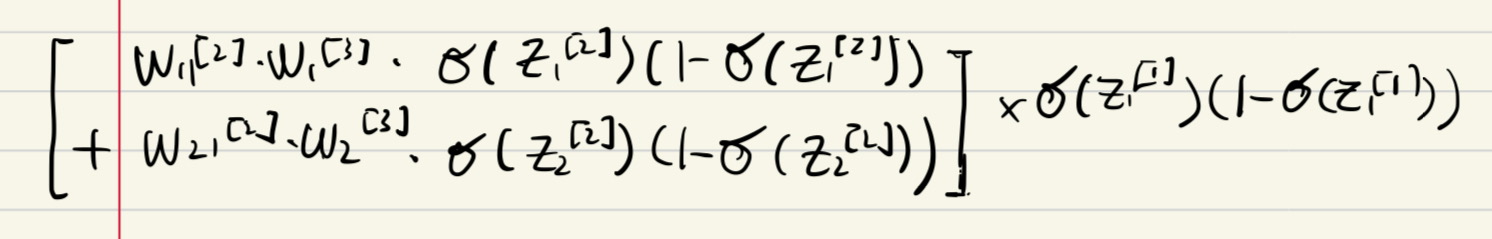


2.
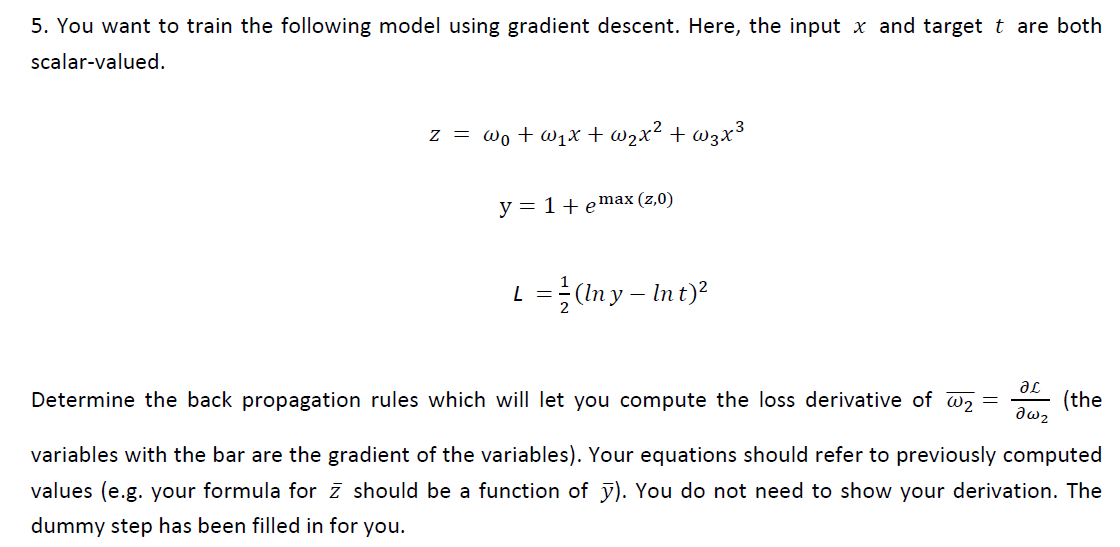
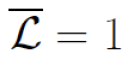

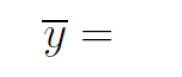

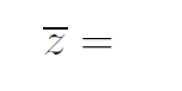
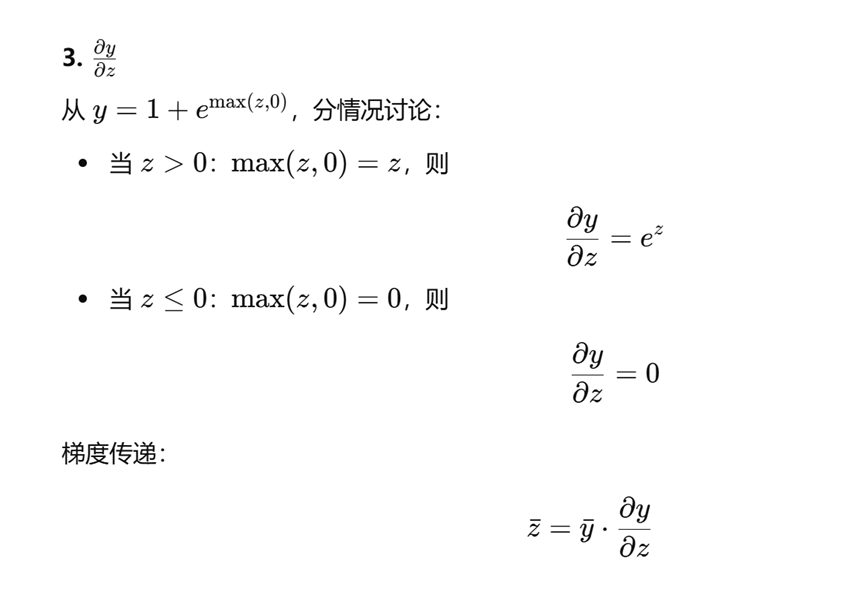
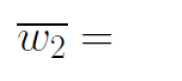

4.
21,22



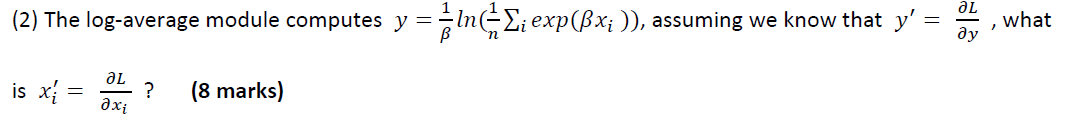

5.
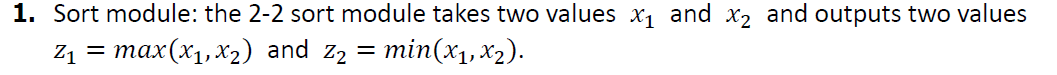
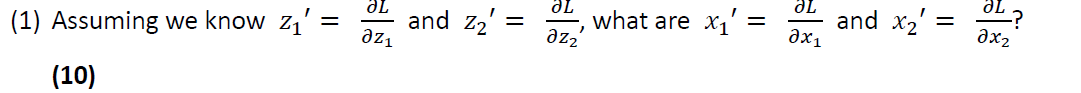
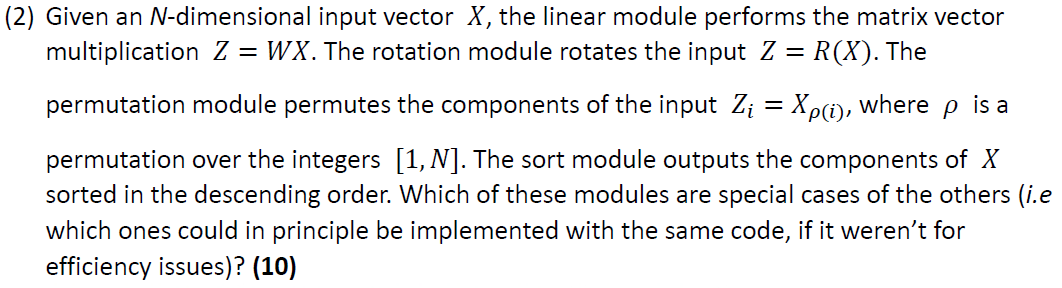

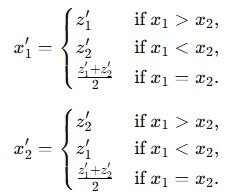
The relationship between permutation modules and sorting modules: A permutation module is a certain reordering of X, while a sorting module is a special case of permutation (i.e., ordering in descending order). Therefore, the sorting module is a special case of the permutation module.
The relationship between linear modules and rotation modules: If W is a rotation matrix (an orthogonal matrix with a determinant of 1), then a linear module can represent a rotation module. Thus, the rotation module is a special case of the linear module.
Therefore, the sorting module is a special case of the permutation module, and the rotation module is a special case of the linear module.
From a theoretical perspective, if we disregard efficiency, the sorting module and the permutation module can be implemented using the same code. Similarly, the linear module and the rotation module can also share the same code, but additional constraints are required to ensure W is a rotation matrix.
6.

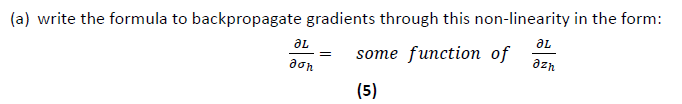
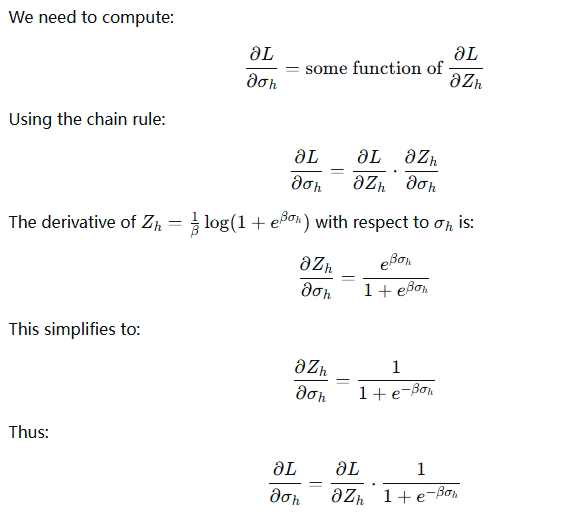

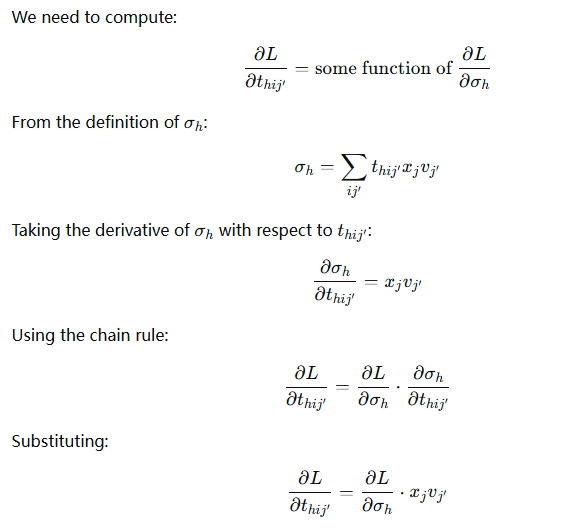
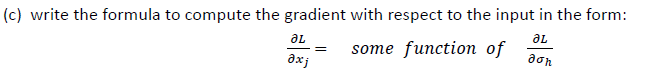
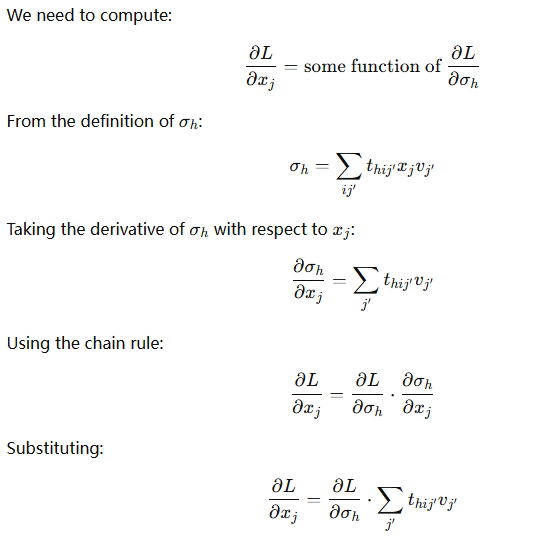
7.


8.


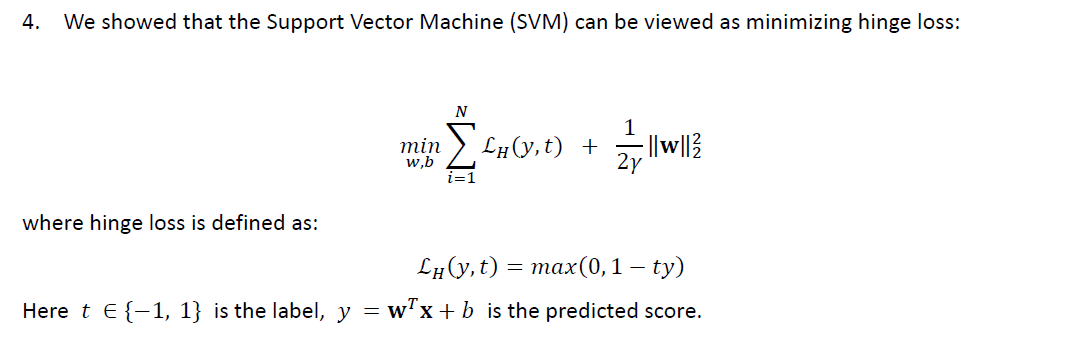
SVM-hinge loss
1.
21

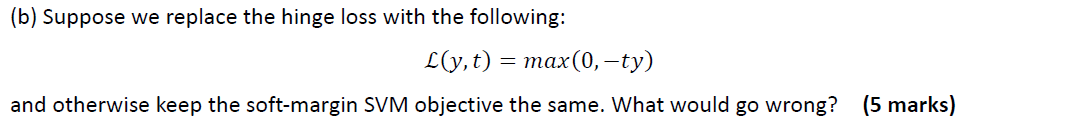

Concept
1.
21,22,23

2.
3.

4.



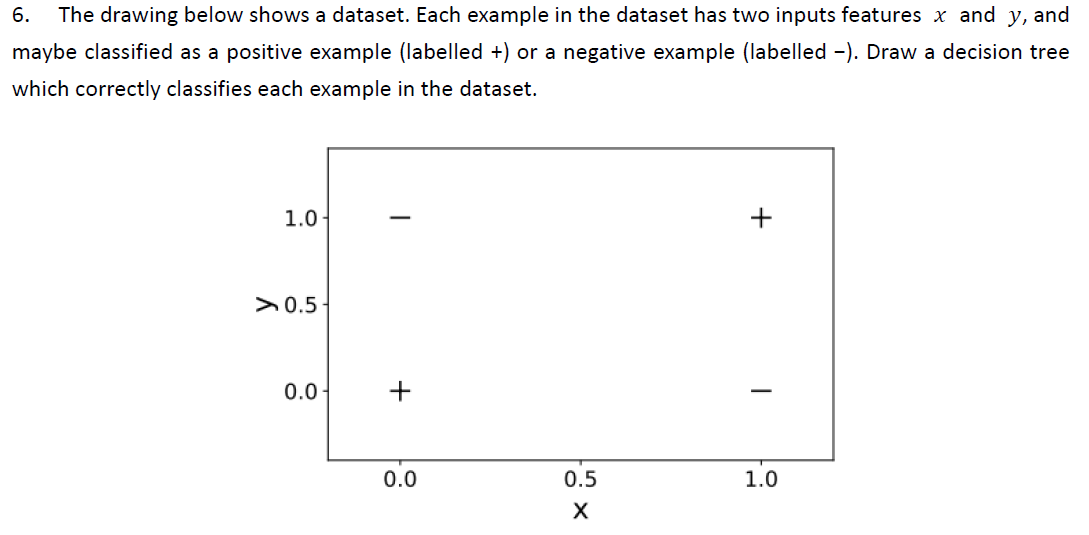
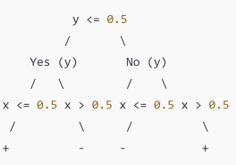
Decision Tree
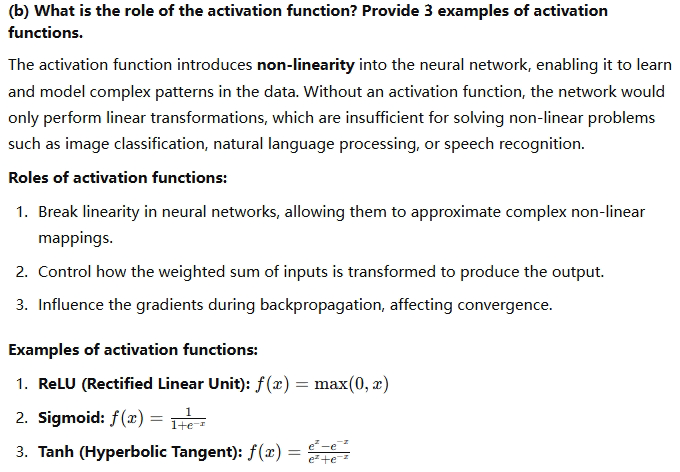
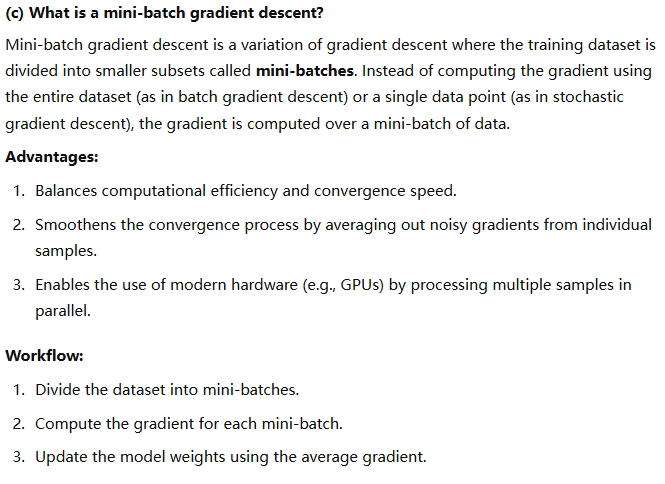
information gain 信息熵
entropy
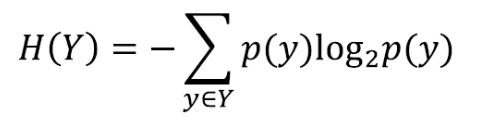
注意这里算的是样本比率!!!!!
P(y): 变量 Y 取值为 y 的概率。
The expected conditional entropy
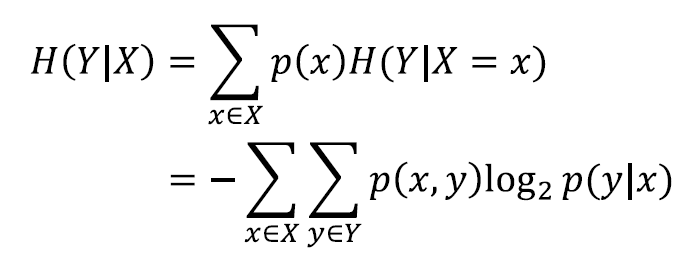
Information Gain 信息增益
Information gain 𝐼𝐺 (𝑌| 𝑋) in 𝑌 due to 𝑋, or the mutual information of 𝑌 and 𝑋

If 𝑋 is completely uninformative about 𝑌: 𝐼𝐺 (𝑌|X) =0
If 𝑋 is completely informative about 𝑌: 𝐼𝐺 (𝑌|X) = H(Y)
1.
21
2.
22
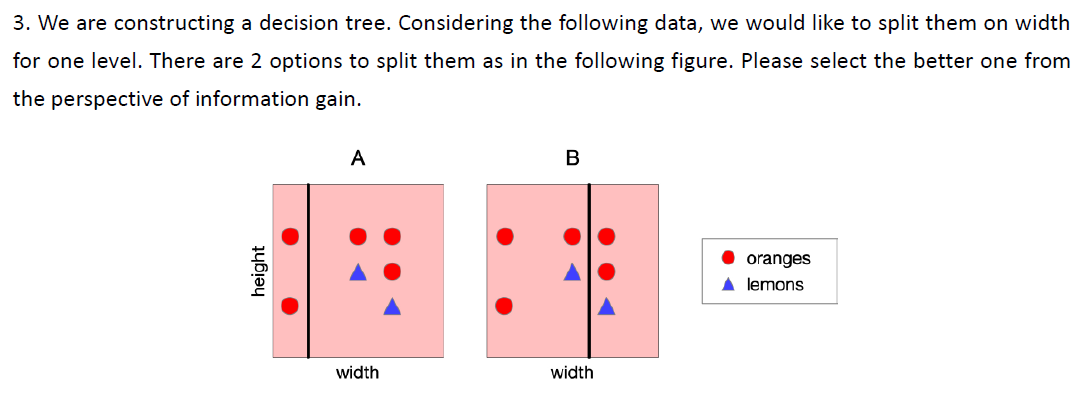
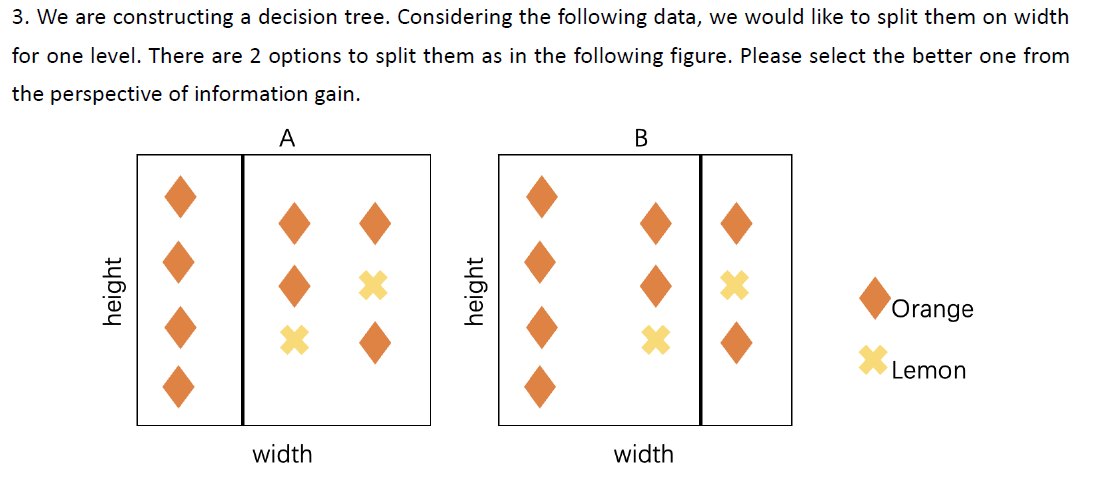
A informative!
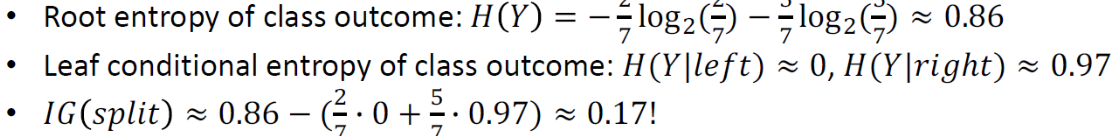
B not terribly informative
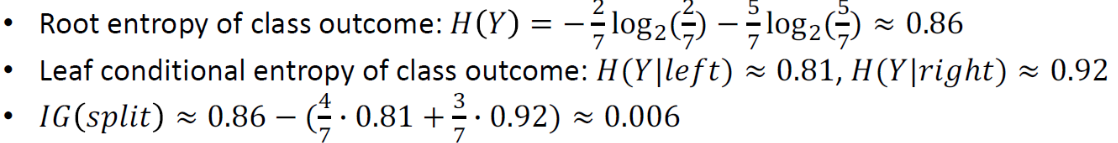
3.
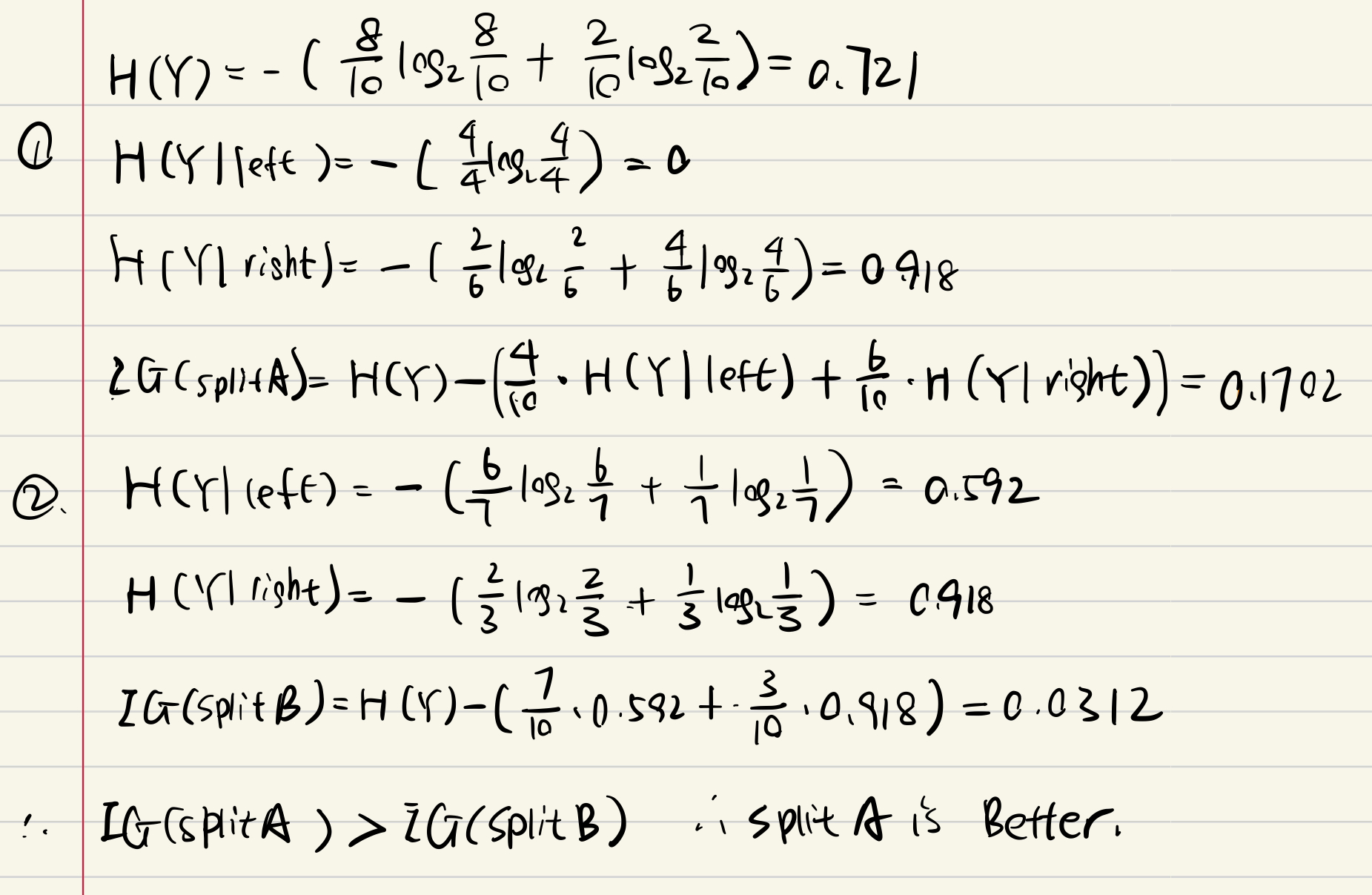
4.
21

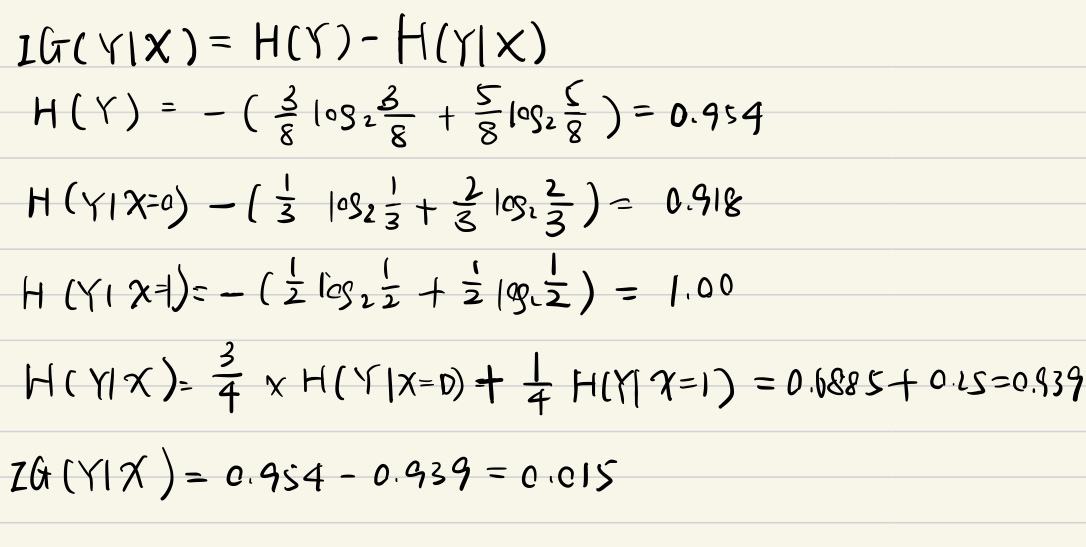
objective function construction
1.
21
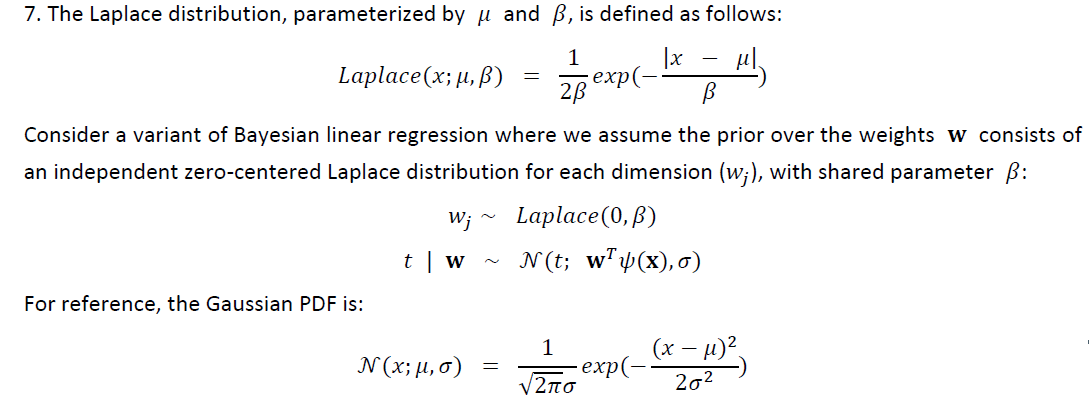



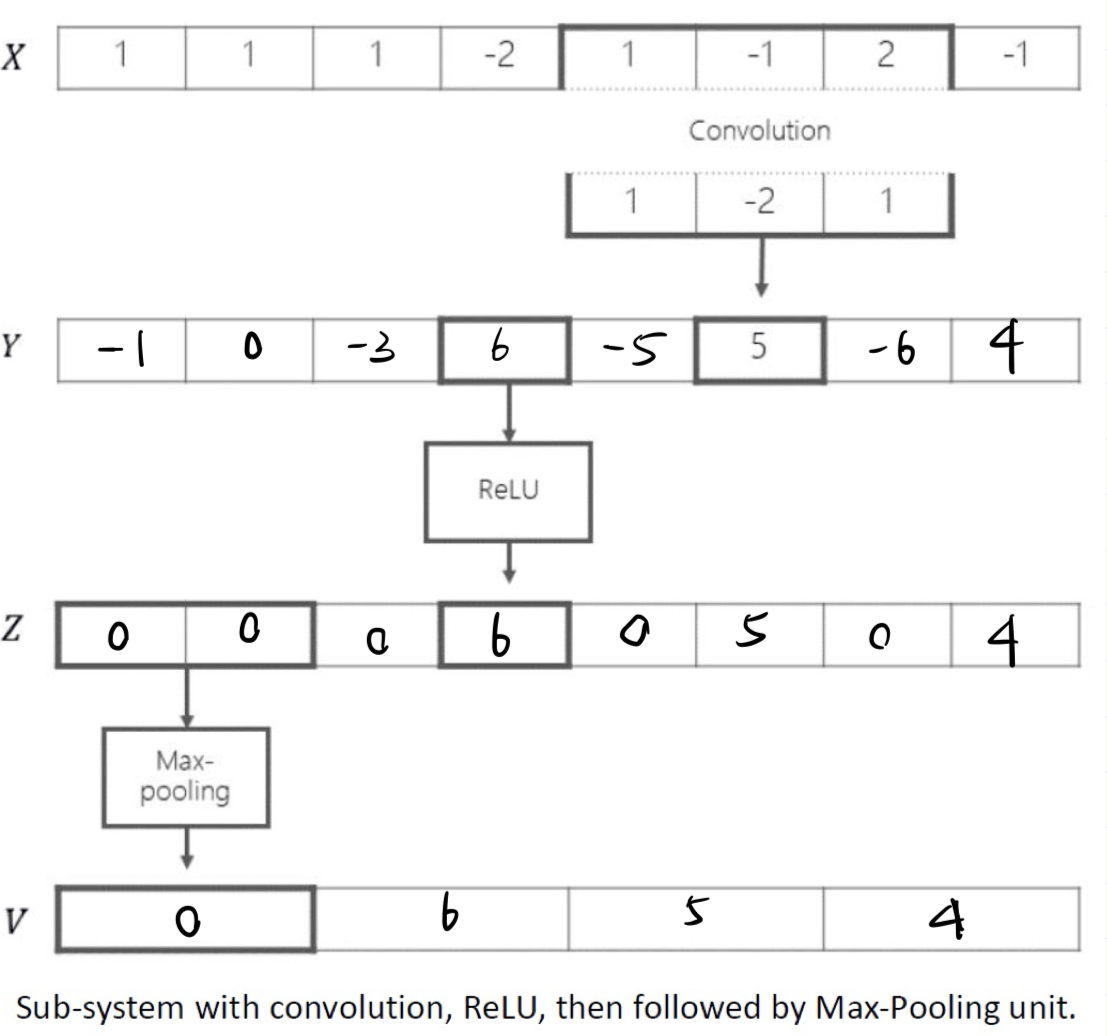
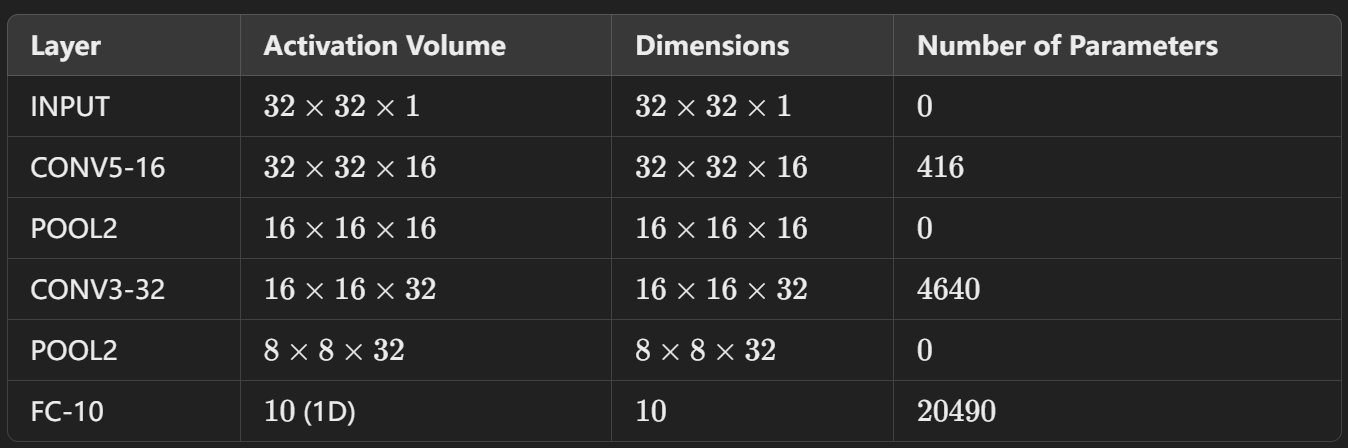
CNN
input size(H,W)
Fliter size(FH, FW)
Outputsize(OH,OW)
padding P
stride S
channel C
The number of filters (also the number of output channels) K
output size
OH = (H+2P-FH)/S +1
OW = (W+2P-FW)/S +1
但是一般情况下其实input,output 和 filter 都是正方形的
so if H =W, FH = FW = F
O = (H + 2P -F)/S +1
parameters
(FH×FW×Cin+1)×K + K
注意这里两个K只在有偏置项的时候加!
The number of parameters is determined by the filter size and the number of filters, regardless of the stride
1.
22

![]()
(FH×FW×Cin+1)×K + K
注意这里两个K只在有偏置项的时候加!
(1*3*1)*1 = 3

1
2.
23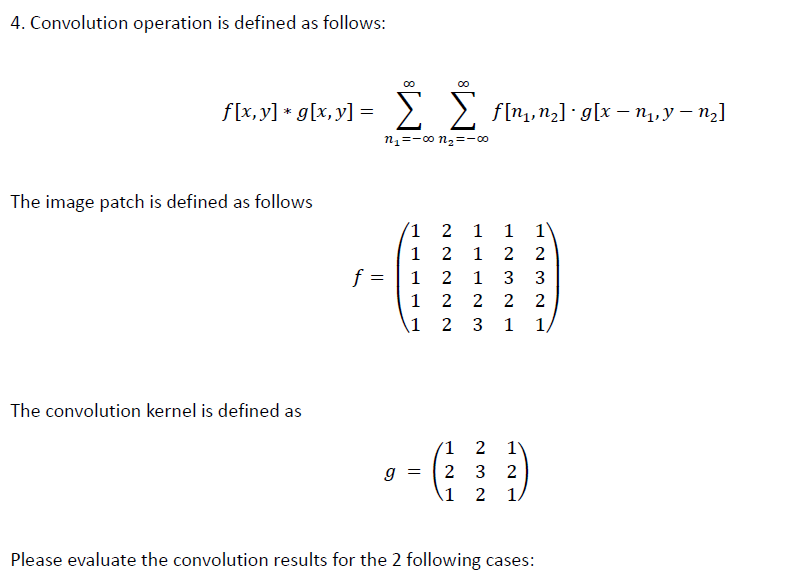
![]()
![]()
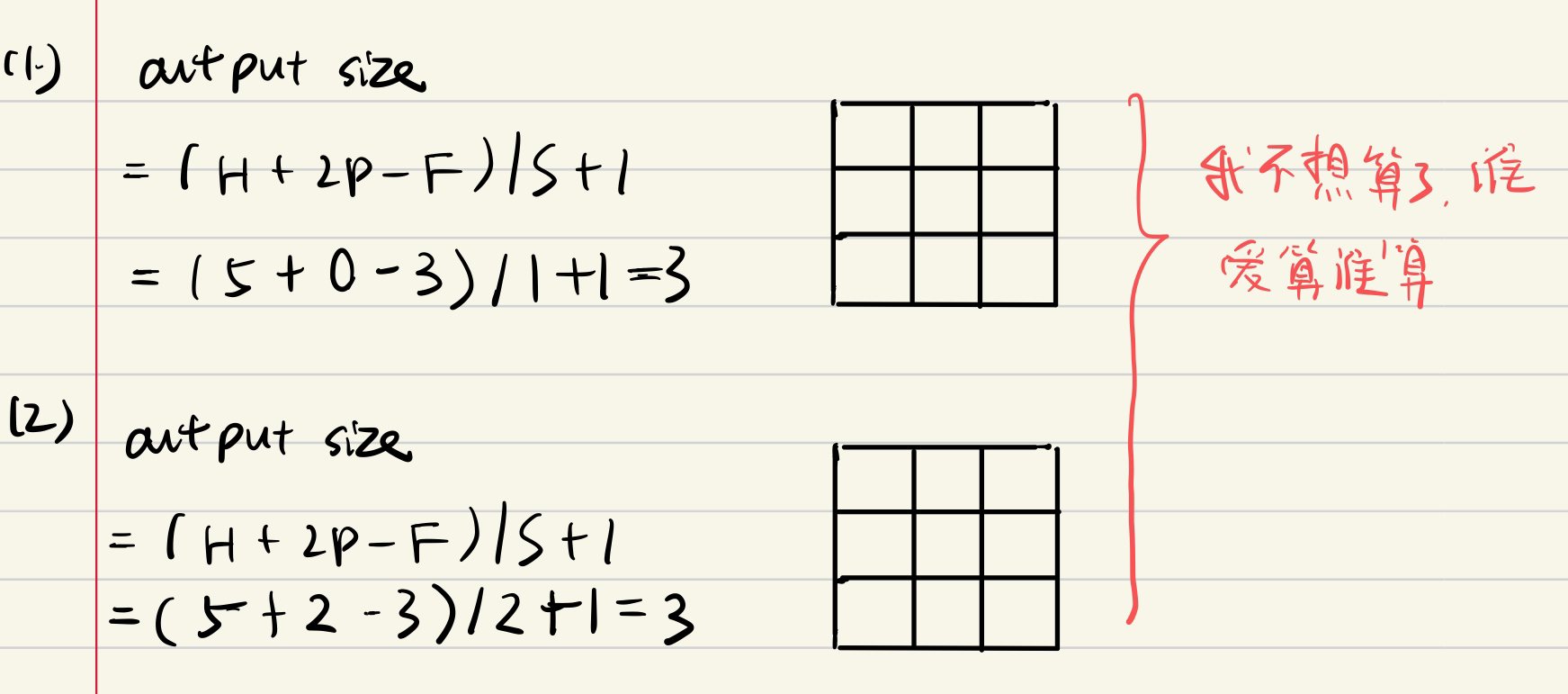
3.
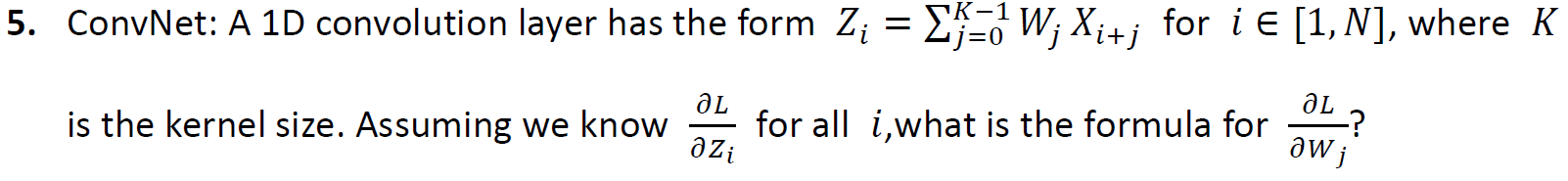

4.

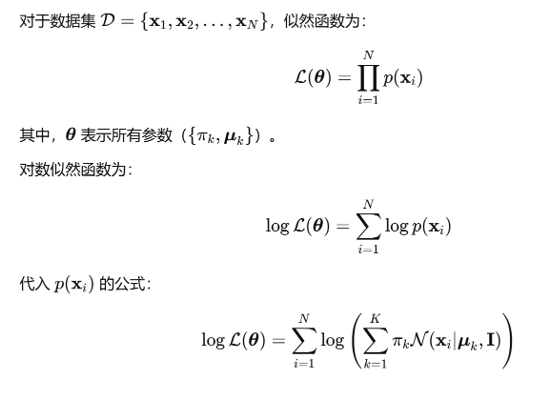
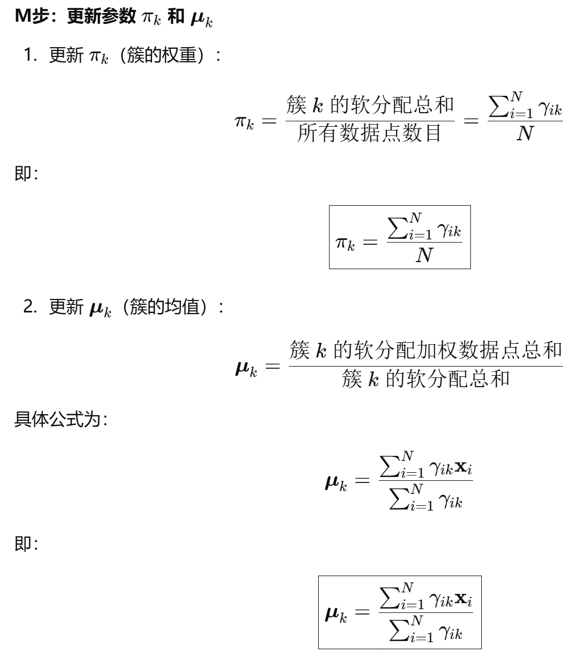
GMM
2.
23
![]()

![]()


![]()






















 1091
1091

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








