本文接上一篇:8.训练自己的数据集(1):TFRecords编写与读取,文件是共享的,不再赘述。
1.先看看训练集与测试集大小:
import tensorflow as tf
import os
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
#查看tfrecords中数据集的大小
def total_sample(tfrecord_name):
sample_nums = 0
for record in tf.python_io.tf_record_iterator(tfrecord_name):
sample_nums += 1
return sample_nums
train_total = total_sample('train.tfrecords')
test_total = total_sample('test.tfrecords')
print(train_total)
print(test_total)

注意,数据集大小在后面是有用的,test_total与train_total都有用。
2.定义相关参数
#定义相关参数
#图片的尺寸
WITH = 40
HEIGHT = 40
#图片总共由3类,用于one_hot标签
classes_num = 3
#每批次训练图片数量
batch_size = 300
#将所有图片训练一轮所需要的总的训练次数
total_batch = int(train_total/batch_size)
#总共循环训练轮数
train_epochs = 50
#定义初始学习率
learning_rate = 0.005
3.构建模型并训练测试
os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = "0,1"
#读取tfrecords中数据方法
def read_tfrecords(tfrecord_name,batch_size):
#将tfrecords读入流中,乱序操作并循环读取
filename_queue = tf.train.string_input_producer([tfrecord_name])
reader = tf.TFRecordReader()
#返回文件名和文件
_, serialized_example = reader.read(filename_queue)
#取出文件中包含image和label的feature对象
features = tf.parse_single_example(serialized_example,
features={
'label': tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64),
'img_raw' : tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string),
})
#将字符串解析成图像对应的像素数组
image = tf.decode_raw(features['img_raw'], tf.uint8)
#改变像素数组的大小,彩图是3通道的
image = tf.reshape(image, [WITH, HEIGHT, 3])
#将像素数组归一化
image = tf.cast(image,tf.float32)*(1./255)-0.5
#读取标签
label = tf.cast(features['label'], tf.int32)
#将标签制成one_hot
label = tf.one_hot(label,depth=classes_num,on_value=1)
#按批次大小乱序读取数据
x_batch, y_batch = tf.train.shuffle_batch([image,label],
batch_size=batch_size,
num_threads=1, capacity=30*batch_size,
min_after_dequeue=15*batch_size)
return x_batch,y_batch
#获取训练集数据
xs_train,ys_train = read_tfrecords('train.tfrecords',batch_size)
#获取测试集数据
xs_test,ys_test = read_tfrecords('test.tfrecords',test_total)
#定义图片和标签的占位符
#None 表示张量的第一维度可以接受任意长度,3表示图片通道数
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,shape = [None,WITH,HEIGHT,3])
#None 表示张量的第一维度可以接受任意长度,class_num表示标签类别个数
y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,shape = [None,classes_num])
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
#定义权重及偏置值变量
W1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(([int(WITH/4)*int(HEIGHT/4)*256,1024])))
b1 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1,shape=[1024]))
W2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(([1024,classes_num])))
b2 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1,shape=[classes_num]))
#定义隐藏层
def hidden_layer(inputs):
#要用激活函数
return tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(inputs,W1)+b1)
#定义权重方法:
def get_filter(shape):
return tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape,stddev=0.1))
#定义偏置值方法:
def get_bias(shape):
return tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1,shape=shape))
w_con1 = get_filter([5,5,3,128])
b_con1 = get_bias([128])
w_con2 = get_filter([5,5,128,256])
b_con2 = get_bias([256])
#第一层卷积输出,输出大小为 batch_size * WITH * HEIGHT * 15:
h_conv1 = tf.nn.conv2d(x,filter=w_con1,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding='SAME')+b_con1
#激活函数:
h1 = tf.nn.relu(h_conv1)
#第一层池化输出,输出大小为 batch_size * (WITH/2) *(HEIGHT/2) * 15:
h_pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(h1,ksize=[1,2,2,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],padding='SAME')
#第二层卷积输出,输出大小为 batch_size * (WITH/2) *(HEIGHT/2) * 30:
h_conv2 = tf.nn.conv2d(h_pool1,filter=w_con2,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding='SAME')+b_con2
#激活函数:
h2 = tf.nn.relu(h_conv2)
#第一层池化输出,输出大小为 batch_size * (WITH/4) *(HEIGHT/4) * 30:
h_pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(h2,ksize=[1,2,2,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],padding='SAME')
#将池化后的输出改变下尺寸,
h_reshape = tf.reshape(h_pool2,[-1,int(WITH/4)*int(HEIGHT/4)*256])
#隐藏层输出,并使用dropout
h3 = hidden_layer(h_reshape)
h_drop1 = tf.nn.dropout(h3,keep_prob)
#预测值,这里不用激活函数,因为等下要用tensorflow定义好的softmax交叉熵函数
pred = tf.matmul(h_drop1,W2) + b2
#定义交叉熵
cross_entropy = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits_v2(logits=pred,labels=y)
#定义总的损失函数
loss = tf.reduce_mean(cross_entropy)
#定义优化器
opt = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(loss)
#以下是测试模型
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(pred,1),tf.argmax(y,1))
#准确率:
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction,tf.float32))
with tf.Session() as sess:
#必写内容
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
coord=tf.train.Coordinator()
threads= tf.train.start_queue_runners(coord=coord)
#开始训练
print("以下是训练模型每轮训练误差:")
for epoch in range(train_epochs):
#定义平均loss值
avg_loss = 0.
#循环所有数据
for i in range(total_batch):
#获取批次训练数据
batch_xs,batch_ys = sess.run([xs_train,ys_train])
_,c,acc = sess.run([opt,loss,accuracy],feed_dict={x:batch_xs,y:batch_ys,keep_prob:0.8})
#平均loss
avg_loss += c / total_batch
#显示每轮的结果
print('Epoch:',epoch+1,', loss:','{:.9f}'.format(avg_loss),', accuracy:','{:.5f}'.format(acc))
print("\n训练模型结束,以下是测试模型准确率:")
#获取测试数据
test_xs,test_ys = sess.run([xs_test,ys_test])
acc = sess.run(accuracy,feed_dict={x:test_xs,y:test_ys,keep_prob:1.0})
print('Accuracy:',acc)
#必写内容
coord.request_stop()
coord.join(threads)
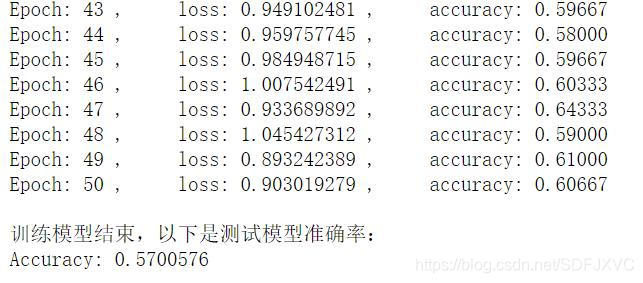
总共训练了50轮,测试正确率57%,很多参数需要调整(比如增加训练次数,添加卷积池化层,改变图片尺寸大小等)。





 本文详细介绍如何使用TensorFlow的TFRecords格式存储和读取数据,构建卷积神经网络(CNN)进行图像分类任务,包括数据预处理、模型构建、训练和测试过程。
本文详细介绍如何使用TensorFlow的TFRecords格式存储和读取数据,构建卷积神经网络(CNN)进行图像分类任务,包括数据预处理、模型构建、训练和测试过程。

















 2292
2292










