Numpy的使用(1)
1.首先导入numpy
import numpy as np
1.向量及矩阵的创建方法
1.1创建向量
vector = np.array([1,6,9,3])
print(vector)
print(vector.shape)
[1 6 9 3]
(4,) #一维的四元素向量
1.2创建矩阵
matrix = np.array([[1,3,6],[8,5,6],[4,1,6]])
print(matrix)
print(matrix.shape)
[[1 3 6]
[8 5 6]
[4 1 6]]
(3, 3) #3行3列矩阵
其中一对中括号表示一维向量,两对中括号表示二维矩阵,之后以此类推。
1.3其他方法
(1)向量矩阵互相转换方法
#创建向量:
a = np.array(range(10))
#或者 a = np.arange(10)
print(a)
[0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9]
#将向量转换成(2行5列)矩阵2
a = a.reshape(2,5)
print(a)
[[0 1 2 3 4]
[5 6 7 8 9]]
#再将矩阵转换成5行的矩阵,列数由系统自动算出
a = a.reshape(5,-1)
print(a)
[[0 1]
[2 3]
[4 5]
[6 7]
[8 9]]
#再将矩阵变回向量:
a = a.ravel()
print(a)
[0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9]
(2)其他创建向量方法
#创建[0,10)的向量:
a = np.arange(10)
print(a)
[0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9]
#创建区间[0,10),间隔为2的向量:
b = np.arange(0,10,2)
print(b)
[0 2 4 6 8]
#创建区间为[-1,1],包含10个随机数的向量:
c = np.random.random(10)
print(c)
[0.72959019 0.17969815 0.51343456 0.57307246 0.91541017 0.3133263
0.43194521 0.22442532 0.93384748 0.64065607]
#创建区间为[-1,1],包含10个随机数的2行3列矩阵:
d = np.random.random((2,3))
print(d)
[[0.86979165 0.7390673 0.76586189]
[0.53886312 0.54597965 0.18002876]]
#创建区间为[0,10],均等分成5份的向量
m = np.linspace(0,10,5)
print(m)
[ 0. 2.5 5. 7.5 10. ]
#将向量m中的值全部向下取整:
n = np.floor(m)
print(n)
[ 0. 2. 5. 7. 10.]
1.4初始化矩阵
(1)np.ones和np.zeros用法
#初始化2行3列的全0矩阵:
a = np.zeros((2,3))
print(a)
[[0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0.]]
#初始化3行2列的全1矩阵:
b = np.ones((3,2))
print(b)
[[1. 1.]
[1. 1.]
[1. 1.]]
#初始化2行3列的全1 字符型 矩阵:
c = np.ones((2,3),dtype=str)
print(c)
[[‘1’ ‘1’ ‘1’]
[‘1’ ‘1’ ‘1’]]
#初始化2行3列的全1 整型 矩阵:
d = np.ones((3,2),dtype=int)
print(d)
[[1 1]
[1 1]
[1 1]]
2.array注意事项
(1)数据类型一致性
通过numpy.array转换后,其中的数据类型会变得一致!
list0 = [1,2,3,4]
list1 = [1,2,3,4.]
list2 = [1,2,3,'4']
list3 = [1,2.,3,'str']
array0 = np.array(list0)
array1 = np.array(list1)
array2 = np.array(list2)
array3 = np.array(list3)
print(array0)
print(array0.dtype)
print(array1)
print(array1.dtype)
print(array2)
print(array2.dtype)
print(array3)
print(array3.dtype)
[1 2 3 4]
int32
[1. 2. 3. 4.]
float64
[‘1’ ‘2’ ‘3’ ‘4’]
<U11
[‘1’ ‘2.0’ ‘3’ ‘str’]
<U32
(2)数据类型修改方法
list0 = ['2','8','77']
array0 = np.array(list0)
print(array0.dtype)
print(array0)
<U2
[‘2’ ‘8’ ‘77’]
#将数据类型改成int型
array0 = array0.astype(int)
print(array0.dtype)
print(array0)
int32
[ 2 8 77]
3.判断特定值是否在array中
vector = np.array([1,6,9,3])
print(3 == vector)
print(3 in vector)
print(10 in vector)
[False False False True]
True
False
#返回vector中索引为True的值:
print(vector[3 == vector])
print(vector[10 ==vector])
print(vector[ [True,False,True,False] ])
[3]
[]
[1 9]
4.numpy之随机数的生成
4.1 生成0~1的均匀分布
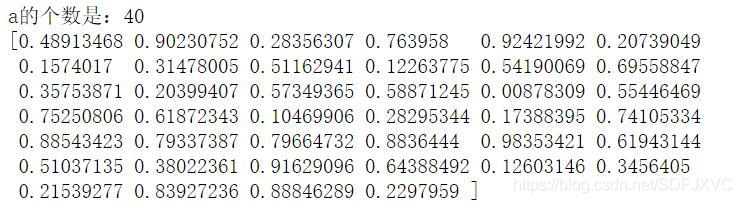
a = np.random.rand(40)
print('a的个数是:%s' % len(a))
print(a)
或者:
#生成10个0~1均匀分布的数
a = np.random.random(10)
#生成5个0~1均匀分布的数
b = np.random.ranf(5)
print(a)
print(b)

4.2 在***指定区间内***随机生成一个整数 或 一个包含指定个数的整数列表。
(1)随机生成一个在0~15之间的整数:
a = np.random.randint(15)
print(a)
11
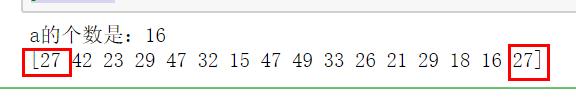
(2)随机生成一个区间在15~50,包含16个整数的列表:
(注意:因为是随机生成的,所以可能会有重复哦)
a = np.random.randint(15,50,16)
print('a的个数是:%s' % len(a))
print(a)
4.3 正态分布
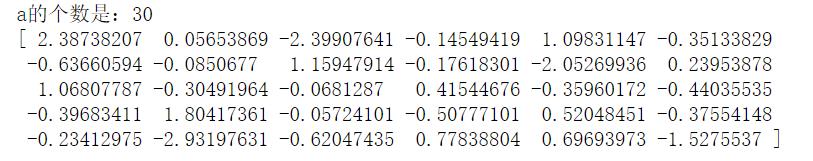
(1)生成30个符合标准正态分布的数:
a = np.random.randn(30)
print('a的个数是:%s' % len(a))
print(a)
(2)生成2行3列符合标准正态分布的矩阵:
a = np.random.randn(2,3)
print('a的shape是:',end='')
print(a.shape)
print(a)

(3)生成15个满足 期望值为2,标准差为4 的正态分布 的数
a = np.random.normal(2,4,15)
print(a)

(4)生成一个3行4列,且满足 期望值为3,标准差为2 的正态分布 的矩阵
a = np.random.normal(3,2,(3,4))
print(a)






 本文介绍了Numpy库在Python中的基本使用,包括向量和矩阵的创建,如np.ones和np.zeros初始化,数据类型的转换与一致性,以及如何在数组中查找特定值。同时,讲解了如何生成不同分布的随机数,如均匀分布和正态分布。
本文介绍了Numpy库在Python中的基本使用,包括向量和矩阵的创建,如np.ones和np.zeros初始化,数据类型的转换与一致性,以及如何在数组中查找特定值。同时,讲解了如何生成不同分布的随机数,如均匀分布和正态分布。
















 3万+
3万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








