人们眼中的天才之所以卓越非凡,并非天资超人一等而是付出了持续不断的努力。1万小时的锤炼是任何人从平凡变成超凡的必要条件。———— 马尔科姆·格拉德威尔

🌟 Hello,我是Xxtaoaooo!
🌈 “代码是逻辑的诗篇,架构是思想的交响”
在AI技术快速发展的今天,MCP(Model Context Protocol)作为Anthropic推出的革命性协议,正在重新定义AI助手与外部工具的交互方式。这个协议的出现解决了一个长期困扰开发者的问题:如何让AI助手能够安全、高效地访问和操作各种外部资源,从数据库查询到文件系统操作,从API调用到复杂的业务逻辑处理。
通过深入研究MCP协议的设计理念和实现机制,我发现它采用了一种优雅的客户端-服务器架构,将AI模型与工具提供者完全解耦。这种设计不仅提高了系统的安全性和可维护性,还为开发者提供了极大的灵活性。与传统的插件系统不同,MCP通过标准化的JSON-RPC通信协议,实现了跨平台、跨语言的工具集成能力。
在实际搭建MCP服务器的过程中,我体验到了这个协议的强大之处。从最基础的文件系统访问工具,到复杂的数据库操作接口,再到自定义的业务逻辑封装,MCP都能够提供统一而简洁的实现方案。特别是在处理敏感数据和权限控制方面,MCP的安全机制设计得相当周到,既保证了功能的完整性,又确保了数据的安全性。
更令人兴奋的是,MCP服务器的扩展性极强。通过模块化的设计,开发者可以轻松地添加新的工具和功能,而无需修改核心代码。这种插件化的架构使得一个MCP服务器可以同时为多个AI助手提供服务,真正实现了"一次开发,多处使用"的理想状态。本文将详细介绍如何从零开始搭建一个功能完整的MCP服务器,包括核心架构设计、工具实现、安全机制和性能优化等关键环节。
一、MCP协议核心概念与架构设计
MCP(Model Context Protocol)是一个开放标准,旨在为AI助手提供安全、可扩展的工具访问能力。它采用客户端-服务器架构,通过标准化的通信协议实现AI模型与外部工具的无缝集成。
1.1 MCP协议基础架构
MCP协议的核心组件包括三个部分:MCP客户端(通常是AI助手)、MCP服务器(工具提供者)和传输层(通信协议)。
// MCP协议基础类型定义
interface MCPMessage {
jsonrpc: "2.0";
id?: string | number;
method?: string;
params?: any;
result?: any;
error?: MCPError;
}
interface MCPError {
code: number;
message: string;
data?: any;
}
// 工具定义接口
interface MCPTool {
name: string;
description: string;
inputSchema: {
type: "object";
properties: Record<string, any>;
required?: string[];
};
}
// 资源定义接口
interface MCPResource {
uri: string;
name: string;
description?: string;
mimeType?: string;
}
// MCP服务器基础类
class MCPServer {
private tools: Map<string, MCPTool> = new Map();
private resources: Map<string, MCPResource> = new Map();
private handlers: Map<string, Function> = new Map();
constructor(private serverInfo: {
name: string;
version: string;
description?: string;
}) {
this.setupDefaultHandlers();
}
// 注册工具
addTool(tool: MCPTool, handler: Function) {
this.tools.set(tool.name, tool);
this.handlers.set(`tools/call/${
tool.name}`, handler);
}
// 注册资源
addResource(resource: MCPResource, handler: Function) {
this.resources.set(resource.uri, resource);
this.handlers.set(`resources/read/${
resource.uri}`, handler);
}
// 设置默认处理器
private setupDefaultHandlers() {
// 初始化处理器
this.handlers.set('initialize', this.handleInitialize.bind(this));
this.handlers.set('tools/list', this.handleToolsList.bind(this));
this.handlers.set('resources/list', this.handleResourcesList.bind(this));
}
// 处理初始化请求
private async handleInitialize(params: any): Promise<any> {
return {
protocolVersion: "2024-11-05",
capabilities: {
tools: {
listChanged: true },
resources: {
subscribe: true, listChanged: true },
prompts: {
listChanged: true }
},
serverInfo: this.serverInfo
};
}
// 处理工具列表请求
private async handleToolsList(): Promise<{
tools: MCPTool[] }> {
return {
tools: Array.from(this.tools.values())
};
}
// 处理资源列表请求
private async handleResourcesList(): Promise<{
resources: MCPResource[] }> {
return {
resources: Array.from(this.resources.values())
};
}
// 处理消息
async handleMessage(message: MCPMessage): Promise<MCPMessage | null> {
try {
if (message.method) {
const handler = this.handlers.get(message.method);
if (handler) {
const result = await handler(message.params);
return {
jsonrpc: "2.0",
id: message.id,
result
};
} else {
throw new Error(`Method not found: ${
message.method}`);
}
}
return null;
} catch (error) {
return {
jsonrpc: "2.0",
id: message.id,
error: {
code: -32603,
message: error instanceof Error ? error.message : "Internal error"
}
};
}
}
}
这个基础实现展示了MCP服务器的核心结构。关键的addTool和addResource方法允许动态注册工具和资源,而handleMessage方法则负责处理所有的JSON-RPC请求。
1.2 MCP通信协议设计
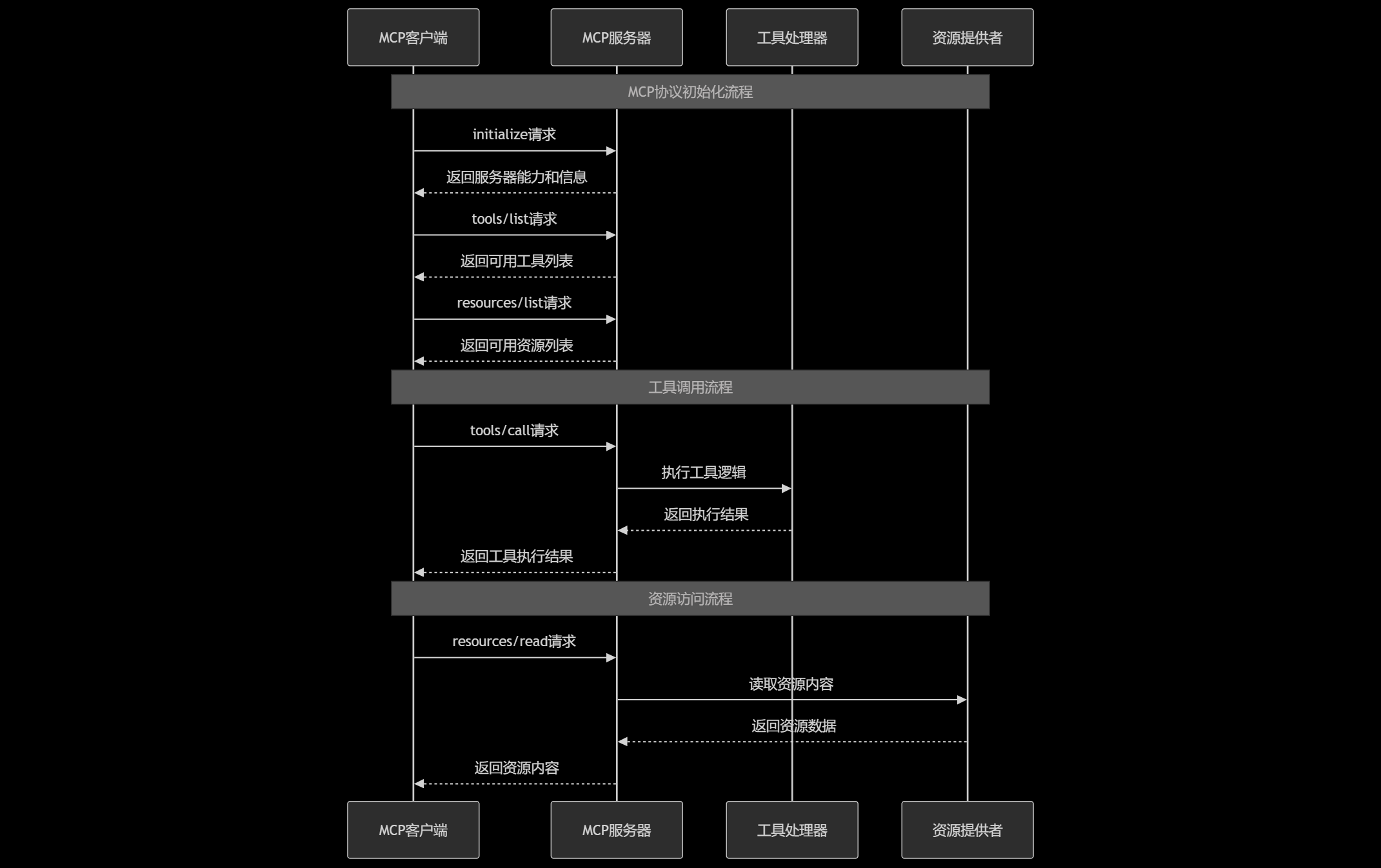
图1:MCP协议通信时序图 - 展示客户端与服务器的完整交互流程
二、核心工具实现与功能扩展
MCP服务器的核心价值在于提供丰富而实用的工具集合。以下是几个关键工具的实现示例。
2.1 文件系统操作工具
文件系统工具是MCP服务器最基础也是最重要的功能之一:
import * as fs from 'fs/promises';
import * as path from 'path';
class FileSystemTools {
private allowedPaths: string[];
constructor(allowedPaths: string[] = []) {
this.allowedPaths = allowedPaths.map(p => path.resolve(p));
}
// 验证路径安全性
private validatePath(filePath: string): boolean {
const resolvedPath = path.resolve(filePath);
return this.allowedPaths.some(allowedPath =>
resolvedPath.startsWith(allowedPath)
);
}
// 注册文件系统工具到MCP服务器
registerTools(server: MCPServer) {
// 读取文件工具
server.addTool({
name: "read_file",
description: "读取指定路径的文件内容",
inputSchema: {
type: "object",
properties: {
path: {
type: "string",
description: "要读取的文件路径"
}
},
required: ["path"]
}
}, this.readFile.bind(this));
// 写入文件工具
server.addTool({
name: "write_file",
description: "将内容写入指定路径的文件",
inputSchema: {
type: "object",
properties: {
path: {
type: "string",
description: "要写入的文件路径"
},
content: {
type: "string",
description: "要写入的文件内容"
}
},
required: ["path", "content"]
}
}, this.writeFile.bind(this));
// 列出目录工具
server.addTool({
name: "list_directory",
description: "列出指定目录下的文件和子目录",
inputSchema: {
type: "object",
properties: {
path: {
type: "string",
description: "要列出的目录路径"
}
},
required: ["path"]
}
}, this.listDirectory.bind(this));
// 创建目录工具
server.addTool({
name: "create_directory",
description: "创建新目录",
inputSchema: {
type: "object",
properties: {
path: {
type: "string",
description: "要创建的目录路径"
}
},
required: ["path"]
}
}, this.createDirectory.bind(this));
}
// 读取文件实现
private async readFile(params: {
path: string }) {
if (!this.validatePath(params.path)) {
throw new Error(`Access denied: ${
params.path}`);
}
try {
const content = await fs.readFile(params.path, 'utf-8');
const stats = await fs.stat(params.path);
return {
content,
size: stats.size,
lastModified: stats.mtime.toISOString(),
encoding: 'utf-8'
};
} catch (error) {
throw new Error(`Failed to read file: ${
error.message}`);
}
}
// 写入文件实现
private async writeFile(params: {
path: string; content: string }) {
if (!this.validatePath(params.path)) {
throw new Error(`Access denied: ${
params.path}`);
}
try {
// 确保目录存在
const dir = path.dirname(params.path);
await fs.mkdir(dir, {
recursive: true });
await fs.writeFile(params.path, params.content, 'utf-8');
const stats = await fs.stat(params.path);
return {
success: true,
size: stats.size,
lastModified: stats.mtime.toISOString()
};
} catch (error) {
throw new Error(`Failed to write file: ${
error.message}`);
}
}
// 列出目录实现
private async listDirectory(params: {
path: string }) {
if (!this.validatePath(params.path)) {
throw new Error(`Access denied: ${
params.path}`);
}
try {
const entries = await fs.readdir(params.path, {
withFileTypes: true });
const items = await Promise.all(
entries.map(async (entry) => {
const fullPath = path.join(params.path, entry.name);
const stats = await fs.stat(fullPath);
return {
name: entry.name,
type: entry.isDirectory() ? 'directory' : 'file',
size: stats.size,
lastModified: stats.mtime.toISOString()
};
})
);
return {
items };
} catch (error) {
throw new Error(`Failed to list directory: ${
error.message}`);
}
}
// 创建目录实现
private async createDirectory(params: {
path: string }) {
if (!this.validatePath(params.path)) {
throw new Error(`Access denied: ${
params.path}`);
}
try {
await fs.mkdir(params.path, {
recursive: true });
return {
success: true, path: params.path };
} catch (error) {
throw new Error(`Failed to create directory: ${
error.message}`);
}
}
}
这个文件系统工具实现了基本的CRUD操作,并包含了重要的安全检查机制。validatePath方法确保只能访问预先配置的安全路径,防止路径遍历攻击。
2.2 数据库操作工具
数据库工具为AI助手提供了强大的数据查询和操作能力:
import {
Pool, PoolClient } from 'pg';
import mysql from 'mysql2/promise';
class DatabaseTools {
private pgPool?: Pool;
private mysqlPool?: mysql.Pool;
constructor(config: {
postgres?: {
host: string;
port: number;
database: string;
user: string;
password: string;
};
mysql?: {
host: string;
port: number;
database: string;
user: string;
password: string;
};
}) {
if (config.postgres) {
this.pgPool = new Pool(config.postgres);
}
if (config.mysql) {
this.mysqlPool = mysql.createPool(config.mysql);
}
}
registerTools(server: MCPServer) {
// SQL查询工具
server.addTool({
name: "execute_sql",
description: "执行SQL查询语句",
inputSchema: {
type: "object",
properties: {
query: {
type: "string",
description: "要执行的SQL查询语句"
},
database: {
type: "string",
enum: ["postgres", "mysql"],
description: "目标数据库类型"
},
params: {
type: "array",
description: "查询参数数组",
items: {
type: "string" }
}
},
required: ["query", "database"]
}
}, this.executeSQL.bind(this));
// 获取表结构工具
server.addTool({
name: "describe_table",
description: "获取数据表的结构信息",
inputSchema: {
type: "object",
properties: {
tableName: {
type: "string",
description: "表名"
},
database: {
type: "string",
enum: ["postgres", "mysql"],
description: "数据库类型"
}
},
required: ["tableName", "database"]
}
}, this.describeTable.bind(this));
}
// 执行SQL查询
private async executeSQL(params: {
query: string;
database: 'postgres' | 'mysql';
params?: string[];
}) {
// 安全检查:禁止危险操作
const dangerousKeywords = ['DR




 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章


















 559
559

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










