题目:两数之和
描述:
给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出和为目标值的那 两个 整数,并返回他们的数组下标。你可以假设每种输入只会对应一个答案。但是,数组中同一个元素不能使用两遍。
要求:
编写一个函数 twoSum,该函数接收一个整数向量 nums 和一个整数 target,返回一个包含两个整数的向量,表示在 nums 中和为目标值 target 的两个数的索引。
源代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
unordered_map<int, int> numToIndex;
// 遍历数组
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i) {
int complement = target - nums[i];
// 检查补数是否存在于哈希表中
if (numToIndex.find(complement) != numToIndex.end()) {
// 找到结果,返回两个索引
return { numToIndex[complement], i };
}
// 将当前数字及其索引插入哈希表
numToIndex[nums[i]] = i;
}
// 如果没有找到结果,返回一个空向量(根据题目要求,这种情况不会发生)
return {};
}
int main() {
// 测试用例 1
vector<int> nums1 = { 2, 7, 11, 15 };
int target1 = 9;
vector<int> result1 = twoSum(nums1, target1);
cout << "测试用例 1 输出: [";
for (int index : result1) {
cout << index << " ";
}
cout << "]" << endl;
// 测试用例 2
vector<int> nums2 = { 3, 2, 4 };
int target2 = 6;
vector<int> result2 = twoSum(nums2, target2);
cout << "测试用例 2 输出: [";
for (int index : result2) {
cout << index << " ";
}
cout << "]" << endl;
// 测试用例 3
vector<int> nums3 = { 3, 3 };
int target3 = 6;
vector<int> result3 = twoSum(nums3, target3);
cout << "测试用例 3 输出: [";
for (int index : result3) {
cout << index << " ";
}
cout << "]" << endl;
return 0;
}
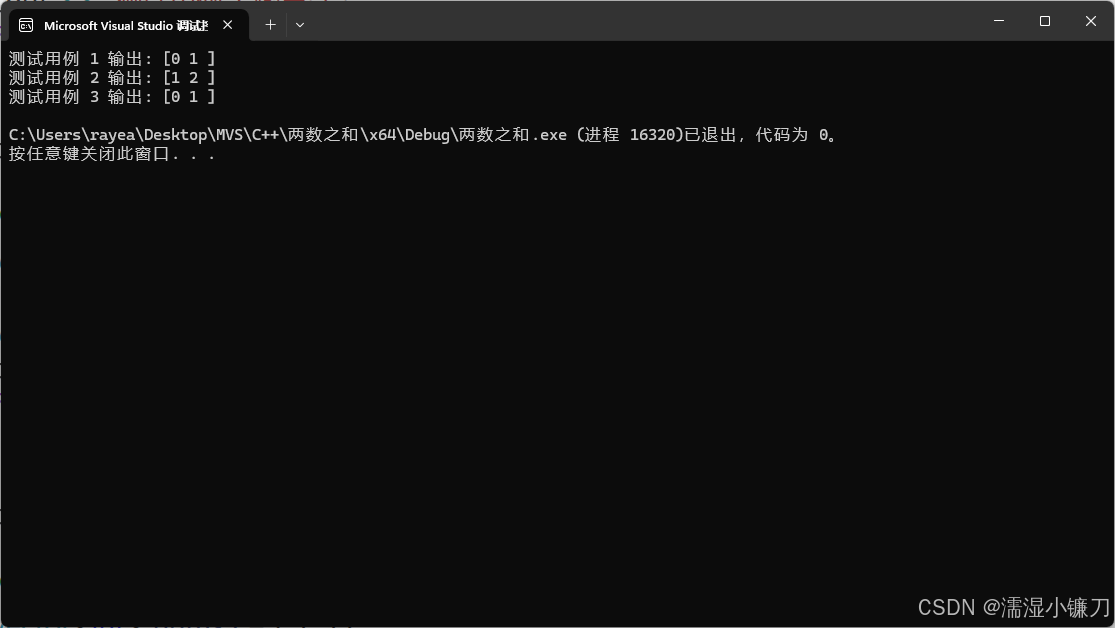
运行截图:





















 206
206

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








