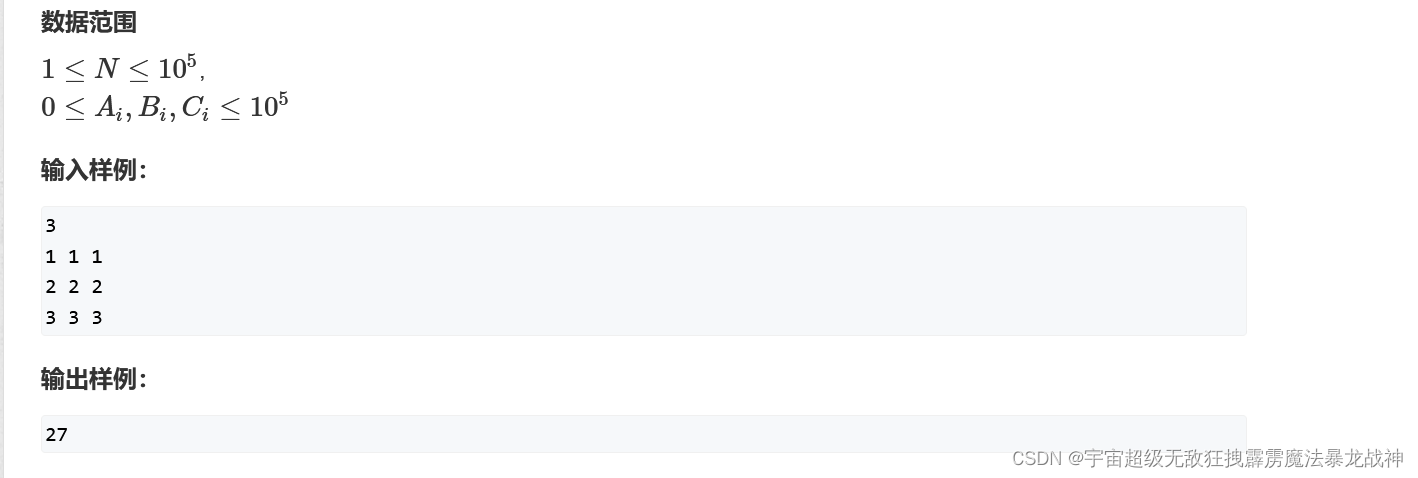
递增三元组:
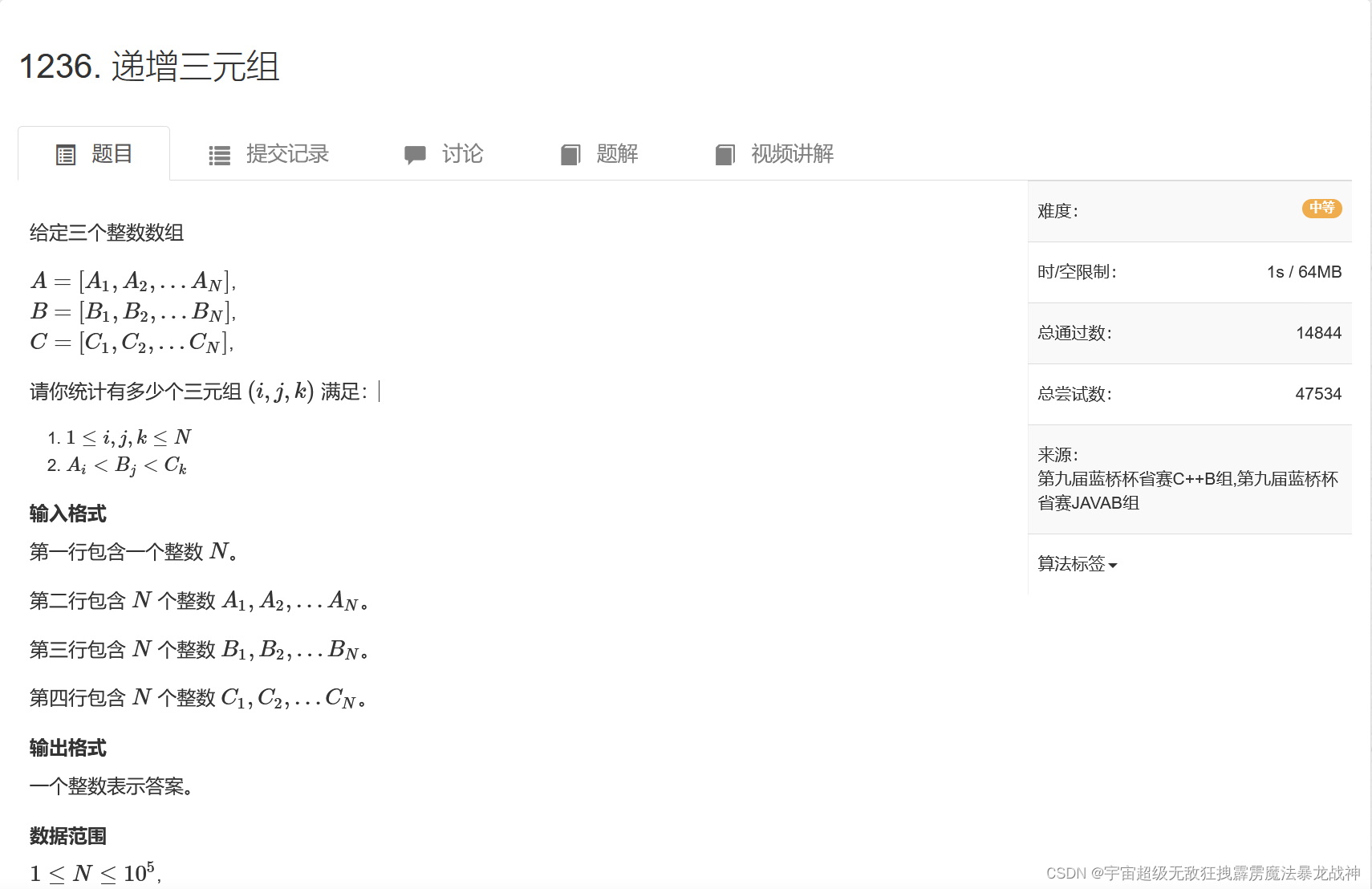
思路:
1、对3个数组分别进行从小到大排序
2、找到a[]数组中最小的大于等于bi的元素位置la,便可知小于bi的个数为num1
3、找到c[]数组中最大的小于等于bi的元素位置lb,便可知大于bi的个数为num2
4、由于a[]和c[]互斥,通过乘法原理可知符合条件的个数为num1 * num2
注意:当la == 0 或者 lb == n + 1时,则表示不符合条件
AC代码:(太优雅了)
import java.io.*;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class Main
{
static PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out)));
static math math_bag = new math();
static int N = (int)1e5 + 10;
static int a[] = new int[N];
static int b[] = new int[N];
static int c[] = new int[N];
static int n;
// 二分的绝妙板子,闭区间寻找
// 寻找左端点,
static int findleft(int l, int r, int x)
{
while(l <= r)
{
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if(a[mid] == x) r = mid - 1;
else if(a[mid] > x) r = mid - 1;
else l = mid + 1;
}
return r + 1; // 找到的时候,r = mid - 1被多执行一次,所以要return r + 1;
}
// 寻找右端点
static int findright(int l ,int r, int x)
{
while(l <= r)
{
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
if(c[mid] == x) l = mid + 1;
else if(c[mid] > x) r = mid - 1;
else l = mid + 1;
}
return l - 1; // 找到的时候,l = mid + 1被多执行一次,所以要return l - 1;
}
public static void main(String[] args ) throws IOException, ParseException
{
n = rd.nextInt();
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++) a[i] = rd.nextInt();
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++) b[i] = rd.nextInt();
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++) c[i] = rd.nextInt();
Arrays.sort(a,0,n);
Arrays.sort(b,0,n);
Arrays.sort(c,0,n);
long res = 0;
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++)
{
int left = findleft(0,n - 1,b[i]);
int right = findright(0,n - 1,b[i]);
res += (long)(left) * (n - right - 1); // left表示小于b[i]的数量,n - right - 1表示大于b[i]的数量,依据乘法原理,每个b[i]能构成的逆序对的数量为(left) * (n - right - 1)
}
pw.println(res);
pw.flush();
}
}
class rd
{
static BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
static StringTokenizer tokenizer = new StringTokenizer("");
static String nextLine() throws IOException { return reader.readLine(); }
static String next() throws IOException
{
while(!tokenizer.hasMoreTokens()) tokenizer = new StringTokenizer(reader.readLine());
return tokenizer.nextToken();
}
static int nextInt() throws IOException { return Integer.parseInt(next()); }
static double nextDouble() throws IOException { return Double.parseDouble(next()); }
static long nextLong() throws IOException { return Long.parseLong(next()); }
static BigInteger nextBigInteger() throws IOException
{
BigInteger d = new BigInteger(rd.nextLine());
return d;
}
}
class math
{
int gcd(int a,int b)
{
if(b == 0) return a;
else return gcd(b,a % b);
}
int lcm(int a,int b)
{
return a * b / gcd(a, b);
}
// 求n的所有约数
List get_factor(int n)
{
List<Long> a = new ArrayList<>();
for(long i = 1; i <= Math.sqrt(n) ; i ++)
{
if(n % i == 0)
{
a.add(i);
if(i != n / i) a.add(n / i); // // 避免一下的情况:x = 16时,i = 4 ,x / i = 4的情况,这样会加入两种情况 ^-^复杂度能减少多少是多少
}
}
// 相同因子去重,这个方法,完美
a = a.stream().distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
// 对因子排序(升序)
Collections.sort(a);
return a;
}
// 判断是否是质数
boolean check_isPrime(int n)
{
if(n < 2) return false;
for(int i = 2 ; i <= n / i; i ++) if (n % i == 0) return false;
return true;
}
}
class PII implements Comparable<PII>
{
int x,y;
public PII(int x ,int y)
{
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public int compareTo(PII a)
{
if(this.x-a.x != 0)
return this.x-a.x; //按x升序排序
else return this.y-a.y; //如果x相同,按y升序排序
}
}
class Edge
{
int a,b,c;
public Edge(int a ,int b, int c)
{
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
this.c = c;
}
}








 该文章描述了一种使用Java解决寻找递增三元组问题的方法,涉及对三个整数数组的排序以及利用二分查找计算满足条件的三元组数量。算法的核心是通过数组的排序和二分查找优化搜索效率。
该文章描述了一种使用Java解决寻找递增三元组问题的方法,涉及对三个整数数组的排序以及利用二分查找计算满足条件的三元组数量。算法的核心是通过数组的排序和二分查找优化搜索效率。

















 5296
5296

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










