一、a.length
作用:输出整形数组的长度
实操:
package 做题;
import java.util.Scanner;
import javax.naming.StringRefAddr;
import org.jcp.xml.dsig.internal.MacOutputStream;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int a[] = new int [10];
System.out.println(a.length);
}
}
二、Arrays.sort()
1、Arrays.sort(a)
实现数组a的升序排列
代码:
package 做题;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.security.PublicKey;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
import javax.naming.StringRefAddr;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
final int N = 10;
String str;
int n = sc.nextInt();
int a[] = new int [n];
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++) a[i] = sc.nextInt();
Arrays.sort(a);
for(int x: a) System.out.printf("%d ",x);
}
}2、Arrays.sort(a,0,n);
实现数组a的升序排列
代码:
package 做题;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.security.PublicKey;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
import javax.naming.StringRefAddr;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
final int N = 10;
String str;
int n = sc.nextInt();
int a[] = new int [n];
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++) a[i] = sc.nextInt();
Arrays.sort(a,0,n);
for(int x: a) System.out.printf("%d ",x);
}
}3、Arrays.sort(a,0,n,(x,y)->{return y - x;});
实现数组a的降序排列
package 做题;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.security.PublicKey;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
import javax.naming.StringRefAddr;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
final int N = 10;
String str;
int n = sc.nextInt();
Integer a[] = new Integer [n];
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++) a[i] = sc.nextInt();
Arrays.sort(a,0,n,(x,y)->{return y - x;});
for(int x: a) System.out.printf("%d ",x);
}
}三、Arrays.fill(int a[], int val);
作用:将数组a中所有元素赋值为val
实操:
一维数组:
package 做题;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.security.PublicKey;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
import javax.naming.StringRefAddr;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
final int N = 10;
int a[] = new int [N];
int n = sc.nextInt();
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++) a[i] = sc.nextInt();
Arrays.fill(a, 5);
for(int x : a) System.out.printf("%d ",x);
}
}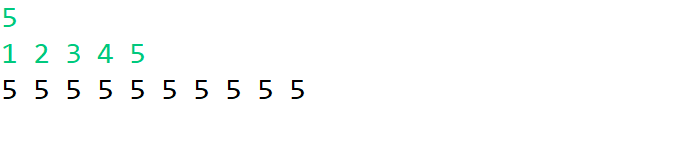
二维数组:
import java.io.*;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
static PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out)));
static math math_myself = new math();
static int INF = (int)1e9;
static int N = (int)2022;
static int g[][] = new int[N][N];
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
int n = rd.nextInt();
int m = rd.nextInt();
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++)
{
for(int j = 1 ; j <= m ; j ++)
{
g[i][j] = rd.nextInt();
}
}
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++) Arrays.fill(g[i],-1);
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++)
{
for(int j = 1 ; j <= m ; j ++)
{
pw.print(g[i][j] + " ");
}
pw.println();
}
pw.flush();
}
}
class rd
{
static BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
static StringTokenizer tokenizer = new StringTokenizer("");
static String nextLine() throws IOException { return reader.readLine(); }
static String next() throws IOException
{
while(!tokenizer.hasMoreTokens()) tokenizer = new StringTokenizer(reader.readLine());
return tokenizer.nextToken();
}
static int nextInt() throws IOException { return Integer.parseInt(next()); }
static double nextDouble() throws IOException { return Double.parseDouble(next()); }
static long nextLong() throws IOException { return Long.parseLong(next()); }
static BigInteger nextBigInteger() throws IOException
{
BigInteger d = new BigInteger(rd.nextLine());
return d;
}
}
class PII
{
int x,y;
public PII(int x, int y)
{
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
class math
{
long gcd(long a,long b)
{
if(b == 0) return a;
else return gcd(b,a % b);
}
long lcm(long a,long b)
{
return a * b / gcd(a, b);
}
// 求n的所有约数
List get_factor(long n)
{
List<Long> a = new ArrayList<>();
for(long i = 1; i <= Math.sqrt(n) ; i ++)
{
if(n % i == 0)
{
a.add(i);
if(i != n / i) a.add(n / i); // 去重 // 避免一下的情况:x = 16时,i = 4 ,x / i = 4的情况,这样会加入两种情况 ^-^复杂度能减少多少是多少
}
}
// 对因子排序(升序)
Collections.sort(a);
return a;
}
}
四、Arrays.toString(int a[])
作用:将整形数组a转换成[1,2,3,4,5]的形式
实操:
package 做题;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.security.PublicKey;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
import javax.naming.StringRefAddr;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
final int N = 10;
String str;
int n = sc.nextInt();
int a[] = new int [n];
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++) a[i] = sc.nextInt();
str = Arrays.toString(a);
System.out.println(str);
}
}





 本文展示了Java中处理整型数组的一些基本操作,包括通过a.length获取数组长度,使用Arrays.sort进行升序和降序排列,以及用Arrays.fill给数组元素赋值和Arrays.toString将数组转化为字符串表示。示例代码详细解释了每个方法的用法。
本文展示了Java中处理整型数组的一些基本操作,包括通过a.length获取数组长度,使用Arrays.sort进行升序和降序排列,以及用Arrays.fill给数组元素赋值和Arrays.toString将数组转化为字符串表示。示例代码详细解释了每个方法的用法。

















 1363
1363

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










