在上篇文章https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/Quellaaa/article/details/83989676中还留下了待补充的知识点——动态加载dll的类。有经验的前辈指点道:尽量用动态链接方式加载dll,因为静态链接方式加载dll要加入lib,当工程庞大时太多lib会加重工程负担,并可能会出现redefine问题。
因此本文章关键词为:动态链接加载、dll、接口类。
一、接口类
1. 接口类的定义
所谓的接口,即将内部实现细节封装起来,外部用户用过预留的接口可以使用接口的功能而不需要知晓内部具体细节。C++中,通过类实现面向对象的编程,而在基类中只给出纯虚函数的声明,然后在派生类中实现纯虚函数的具体定义的方式实现接口,不同派生类实现接口的方式也不尽相同,从而实现多态。
接口类就是只提供接口不提供实现的类,就是接口类,接口类和抽象类对C++而言,没有什么区别。
2. 接口类的特点
1)子类来实现接口类中没有实现的所有接口。
2)接口方法前面有virtual关键词修饰,并且等于0。
注意!析构函数一定记得用virtual修饰,但构造函数不能用virtual修饰,原因如下:
虚函数调用是在部分信息下完成工作的机制,允许我们只知道接口而不知道对象的确切类型。 要创建一个对象,你需要知道对象的完整信息。 特别是,你需要知道你想要创建的确切类型。 因此,构造函数不应该被定义为虚函数。
3)只能被继承,不能独自生成对象。
3. 接口类的目的和优缺点
目的:降低使用接口的用户直接操作数据造成不必要错误的可能性。
优点:将模块的依赖性降到了最低。举个例子,假如客户在使用这些接口的时候,如果这些接口内部的实现细目变更了,客户也不需要再重新编译自己的代码,因为客户只依赖接口声明的头文件。如果客户依赖接口的代码量非常大,那么,这个时候,这样定义接口就非常有必要了,毕竟客户在不修改自己代码的前提下,不需要重新编译自己的代码,这样可以提高客户的效率。
缺点:虽然接口定义在一个类中,但是真正实例化接口类的过程中,编译器会自动替我们生成必需的成员函数(比如构造函数、拷贝构造函数等)。虽然有这样的缺点,但还是瑕不掩瑜。
4. 接口类的代码示例
新建一个类型为dll的工程,该工程包含的文件有:IPerson.h、Student.h、Student.cpp、Teacher.h、Teacher.cpp和main.cpp
IPerson.h
// 这个是接口类,给用户用的
// Q:用户用的类名字要不要和dll名字一样?
// 该接口类简单定义了每个人都会做的事情:有名字性别,要吃饭睡觉
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class IPerson
{
public:
IPerson():m_strName("NULL"), m_strSex("NULL"){};
virtual ~IPerson();
virtual void SetName(string strName)=0;
virtual void SetSex(int nSex) = 0;
virtual void Eat()=0;
virtual void Sleep()=0;
virtual string GetName()=0;
virtual string GetSex()=0;
private:
string m_strName;
string m_strSex;
};上面代码示例验证了接口类只提供接口不实现类。该文件(IPerson.h)是会给到用户的,但用户看了这个代码,也不会知道其成员函数事实上是怎么实现的。这就是我们要的效果。
接口类的实现
Student.h
#pragma once
#ifndef STUDENT_H
#define STUDENT_H
#include "IPerson.h"
class CStudent : public IPerson
{
public:
CStudent();
~CStudent();
void SetName(string strName);
void SetSex(int nSex);
void Sleep();
void Eat();
string GetName();
string GetSex();
private:
string m_strName;
string m_strSex;
};
#endif
Student.cpp
#include "Student.h"
#include <iostream>
CStudent::CStudent()
:m_strName("student_NULL")
,m_strSex("student_null")
{
}
// 析构函数声明了一定要定义
CStudent::~CStudent()
{
}
void CStudent::SetName(string strName)
{
m_strName = strName;
}
void CStudent::SetSex(int nSex)
{
switch(nSex)
{
case 0:
m_strSex = "female";
break;
case 1:
m_strSex = "male";
break;
default:
m_strSex = "null";
}
}
void CStudent::Sleep()
{
cout<<"students sleep\n";
}
void CStudent::Eat()
{
cout<<"students eat\n";
}
std::string CStudent::GetName()
{
return m_strName;
}
std::string CStudent::GetSex()
{
return m_strSex;
}Teacher.h
#pragma once
#ifndef TEACHER_H
#define TEACHER_H
#include "IPerson.h"
class CTeacher : public IPerson
{
public:
CTeacher();
~CTeacher();
void SetName(string strName);
void SetSex(int nSex);
string GetName();
string GetSex();
void Eat();
void Sleep();
private:
string m_strName;
string m_strSex;
};
#endif
Teacher.cpp
#include "Teacher.h"
#include <iostream>
CTeacher::CTeacher()
:m_strName("teacher_null")
,m_strSex("teacher_null")
{
}
CTeacher::~CTeacher()
{
}
void CTeacher::SetName(string strName)
{
m_strName = strName;
}
void CTeacher::SetSex(int nSex)
{
switch(nSex)
{
case 0:
m_strSex = "Female";
break;
case 1:
m_strSex = "male";
break;
default:
m_strSex = "null";
break;
}
}
std::string CTeacher::GetName()
{
return m_strName;
}
std::string CTeacher::GetSex()
{
return m_strSex;
}
void CTeacher::Eat()
{
cout<<"teachers are eating...\n";
}
void CTeacher::Sleep()
{
cout<<"teachers are sleeping...\n";
}main.cpp
#include "Student.h"
#include "Teacher.h"
// 需要导出的函数(用户在外部可以调用的接口)
_declspec(dllexport) bool GetPersonObject(int nID, void **_RtObject)
{
IPerson *pMan = NULL;
pMan = new CStudent();
*_RtObject = (void *)pMan;
return true;
}
_declspec(dllexport) bool ReleasePersonObject(void *RtObject)
{
delete RtObject;
RtObject = NULL;
return true;
}编译后就会生成一个接口函数的dll,其名字为testInterfacePerson.dll
二、使用接口类dll
新建一个类型为exe的工程,首先将IPerson.h和testInterfacePerson.dll放到该工程代码的目录下。
main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <windows.h>
#include "IPerson.h"
using namespace std;
typedef bool (*GetObjectFunc)(void **);
typedef bool (*ReleaseObjectFunc)(void *);
int main()
{
HINSTANCE hIs = LoadLibrary(L"testInterfacePerson.dll");
GetObjectFunc GetPersonObject = (GetObjectFunc)GetProcAddress(hIs, "GetPersonObject");
ReleaseObjectFunc ReleaseObject = (ReleaseObjectFunc)GetProcAddress(hIs, "ReleasePersonObject");
IPerson * person = NULL;
void *pObj = NULL;
if(GetPersonObject(&pObj))
{
person = (IPerson *)pObj;
person->SetName("test");
cout<<person->GetName()<<endl;
person->Eat();
ReleaseObject(pObj);
}
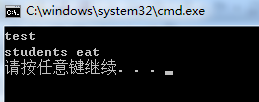
}运行结果如下图所示:










 本文介绍了C++中接口类的概念、特点、目的和优缺点,详细讲解了如何定义接口类及其代码示例。此外,还展示了如何动态加载dll并使用接口类,帮助读者理解动态链接加载dll的方法。
本文介绍了C++中接口类的概念、特点、目的和优缺点,详细讲解了如何定义接口类及其代码示例。此外,还展示了如何动态加载dll并使用接口类,帮助读者理解动态链接加载dll的方法。
















 4万+
4万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








