sort函数排序的三种方式使用
1.自带库函数(用的少) 默认从小到大
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
void printArr(int a[],int n)
{
for(int i = 0 ;i < n;i++)
cout << a[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
int a[10] = {9,6,3,4,8,5,2,7,1,0};
sort(a,a+10);
printArr(a,10);
sort(a,a+10,less<int>());
printArr(a,10);
sort(a,a+10,greater<int>());
printArr(a,10);
return 0;
}
输出结果:
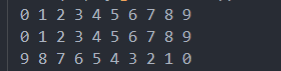
2.自定义比较函数(重点)
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
bool cmp1(int a, int b) {return a < b;}
bool cmp2(int a, int b) {return a > b;}
void printArr(int a[],int n)
{
for(int i = 0 ;i < n;i++)
cout << a[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
int a[10] = {9,6,3,4,8,5,2,7,1,0};
sort(a,a+10);
printArr(a,10);
sort(a,a+10,cmp1);
printArr(a,10);
sort(a,a+10,cmp2);
printArr(a,10);
return 0;
}
输出结果如下:
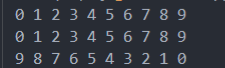
3.配合结构体使用的比较函数(超重点)
== 方式一. 重载小于号 ==
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
struct student
{
int math, english;
bool operator< (const student &b)
{
if(math == b.math)
return english < b.english;
else
return math < b.math;
}
};
student st[100];
int main()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++)
cin >> st[i].math >> st[i].english;
//按数学成绩从小到大,如果相同,按语文成绩从小到大
sort(st, st + 7);
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++)
printf("math = %d, english = %d \n", \
st[i].math, st[i].english);
return 0;
}
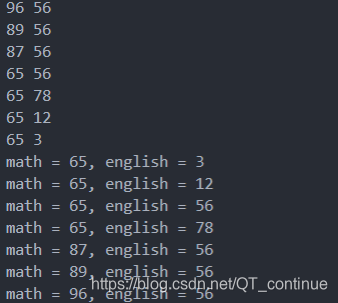
输出结果:
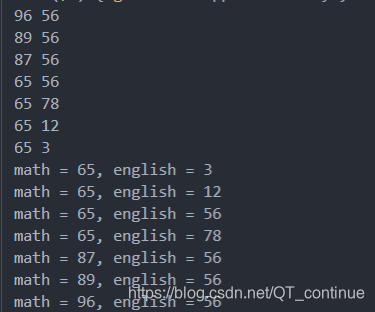
== 方式二. 直接写函数比较 ==
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
struct student
{
int math, english;
};
student st[100];
bool cmp(const student &a, const student &b)
{
if (a.math == b.math)
return a.english < b.english;
else
return a.math < b.math;
}
int main()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++)
cin >> st[i].math >> st[i].english;
//按数学成绩从小到大,如果相同,按语文成绩从小到大
sort(st, st + 7,cmp);
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++)
printf("math = %d, english = %d \n",
st[i].math, st[i].english);
return 0;
}
输出结果:
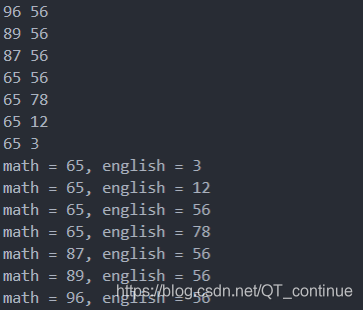
== 方式3. 重载括号、仿函数、用自定义函数对象排序 ==
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
struct student
{
int math, english;
};
student st[100];
struct
{
bool operator()(const student &a, const student &b)
{
if (a.math == b.math)
return a.english < b.english;
else
return a.math < b.math;
}
}cmp;
main()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++)
cin >> st[i].math >> st[i].english;
//按数学成绩从小到大,如果相同,按语文成绩从小到大
sort(st, st + 7, cmp);
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++)
printf("math = %d, english = %d \n",
st[i].math, st[i].english);
return 0;
}
输出结果





 本文详细介绍了C++中sort函数的三种排序方式:1) 使用默认升序排序;2) 自定义比较函数实现升序和降序排序;3) 结合结构体重载运算符或自定义函数对象进行排序。通过实例展示了如何根据需求灵活运用sort函数进行排序操作。
本文详细介绍了C++中sort函数的三种排序方式:1) 使用默认升序排序;2) 自定义比较函数实现升序和降序排序;3) 结合结构体重载运算符或自定义函数对象进行排序。通过实例展示了如何根据需求灵活运用sort函数进行排序操作。
















 2763
2763

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








