《C++ Primer Plus》(第6版)第11章编程练习
《C++ Primer Plus》(第6版)第11章编程练习
1. 随机漫步者位置写入文件
修改程序清单11.15,使之将一系列连续的随机漫步者位置写入到文件中。对于每个位置,用步号进行标志。另外,让该程序将初始条件(目标距离和步长)以及结果小结写入到该文件中。该文件的内容与下面类似:
Target Distance: 100, Step Size: 20
0: (x,y) = (0, 0)
1: (x,y) = (-11.4715, 16.383)
2: (x,y) = (-868807, -3.42232)
....
26: (x,y) = (42.2919, -78.2594)
27: (x,y) = (58.6749, -89.7309)
After 27 steps, the subject has the following location:
(x,y) = (58.6749, -89.7309)
or
(m,a) = (107.212, -56.8194)
Average outward distance per step = 3.97081
代码:
vector.h:
#ifndef VECTOR_H_
#define VECTOR_H_
#include <iostream>
namespace VECTOR
{
class Vector
{
public:
enum Mode
{
RECT,
POL
};
private:
double x;
double y;
double mag;
double ang;
Mode mode;
void set_mag();
void set_ang();
void set_x();
void set_y();
public:
Vector();
Vector(double n1, double n2, Mode from = RECT);
void reset(double n1, double n2, Mode from = RECT);
~Vector();
double xval() const { return x; };
double yval() const { return y; };
double magval() const { return mag; };
double angval() const { return ang; };
void polar_mode();
void rect_mode();
Vector operator+(const Vector &b) const;
Vector operator-(const Vector &b) const;
Vector operator-() const;
Vector operator*(double n) const;
friend Vector operator*(double n, const Vector &a);
friend std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const Vector &v);
};
}
#endif // !VECTOR_H_
vector.cpp:
#include "vector.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
namespace VECTOR
{
const double Rad_to_deg = 45.0 / atan(1.0);
void Vector::set_mag()
{
mag = sqrt(x * x + y * y);
}
void Vector::set_ang()
{
if (x == 0 && y == 0)
ang = 0.0;
else
ang = atan2(y, x);
}
void Vector::set_x()
{
x = mag * cos(ang);
}
void Vector::set_y()
{
y = mag * sin(ang);
}
Vector::Vector()
{
x = y = mag = ang = 0.0;
mode = RECT;
}
Vector::Vector(double n1, double n2, Mode from)
{
mode = from;
if (from == RECT)
{
x = n1;
y = n2;
set_ang();
set_mag();
}
else if (from == POL)
{
mag = n1;
ang = n2 / Rad_to_deg;
set_x();
set_y();
}
else
{
cout << "Incorrect 3rd argument to Vector()--";
cout << "vector set to 0\n";
x = y = mag = ang = 0.0;
mode = RECT;
}
}
void Vector::reset(double n1, double n2, Mode from)
{
mode = from;
if (from == RECT)
{
x = n1;
y = n2;
set_mag();
set_ang();
}
else if (from == POL)
{
mag = n1;
ang = n2 / Rad_to_deg;
set_x();
set_y();
}
else
{
cout << "Incorrect 3rd argument to Vector()--";
cout << "vector set to 0" << endl;
x = y = mag = ang = 0.0;
mode = RECT;
}
}
Vector::~Vector()
{
}
void Vector::polar_mode()
{
mode = POL;
}
void Vector::rect_mode()
{
mode = RECT;
}
Vector Vector::operator+(const Vector &b) const
{
return Vector(x + b.x, y + b.y);
}
Vector Vector::operator-(const Vector &b) const
{
return Vector(x - b.x, y - b.y);
}
Vector Vector::operator-() const
{
return Vector(-x, -y);
}
Vector Vector::operator*(double n) const
{
return Vector(n * x, n * y);
}
Vector operator*(double n, const Vector &a)
{
return a * n;
}
ostream &operator<<(ostream &os, const Vector &v)
{
if (v.mode == Vector::RECT)
os << "(x,y) = (" << v.x << ", " << v.y << ")";
else if (v.mode == Vector::POL)
os << "(m,a) = (" << v.mag << ", " << v.ang << ")";
else
os << "Vector object mode is invalid";
return os;
}
}
randwalk.cpp:
#include "vector.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib> //rand(), srand() prototypes
#include <ctime> //time() prototype
#include <fstream>
int main()
{
using namespace std;
using VECTOR::Vector;
ofstream outFile;
outFile.open("randwalker.txt");
srand(time(0));
double direction;
Vector step;
Vector result(0.0, 0.0);
unsigned long steps = 0;
double target;
double dstep;
cout << "Enter target distance (q to quit): ";
while (cin >> target)
{
cout << "Enter step length: ";
if (!(cin >> dstep))
break;
outFile << "Target Distance: " << target << ", Step Size: " << dstep << endl;
while (result.magval() < target)
{
outFile << steps << ": " << result << endl;
direction = rand() % 360;
step.reset(dstep, direction, Vector::POL);
result = result + step;
steps++;
}
outFile << "After " << steps << " steps, the subject has the following location:\n";
outFile << result << endl;
result.polar_mode();
outFile << " or\n"
<< result << endl;
outFile << "Average outward distance per step = " << result.magval() / steps << endl;
steps = 0;
result.reset(0.0, 0.0);
cout << "Enter target distance (q to quit): ";
}
cout << "Bye!\n";
cin.clear();
while (cin.get() != '\n')
continue;
outFile.close();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
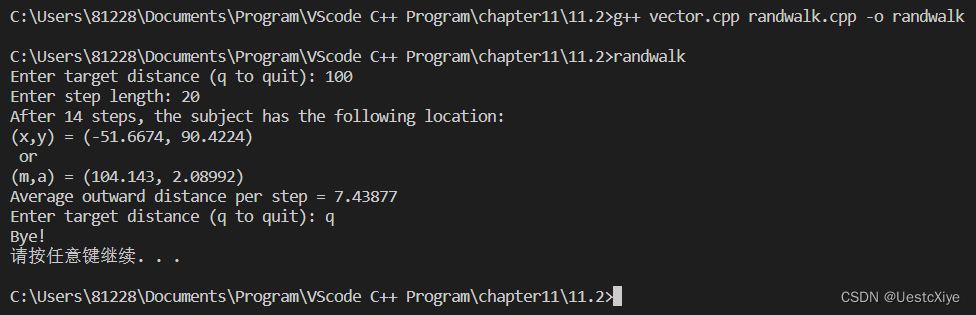
运行结果:

randwalker.txt:
Target Distance: 100, Step Size: 20
0: (x,y) = (0, 0)
1: (x,y) = (-9.38943, 17.659)
2: (x,y) = (9.40442, 10.8185)
3: (x,y) = (9.05537, -9.1784)
4: (x,y) = (6.61799, 10.6725)
5: (x,y) = (-11.9257, 3.18039)
6: (x,y) = (7.9982, 4.9235)
7: (x,y) = (3.15977, -14.4824)
8: (x,y) = (-16.0655, -19.9952)
9: (x,y) = (-26.9582, -3.22175)
10: (x,y) = (-19.7909, 15.4499)
11: (x,y) = (-28.2433, -2.6763)
12: (x,y) = (-37.6327, -20.3352)
13: (x,y) = (-52.2598, -33.9752)
14: (x,y) = (-40.5041, -50.1556)
15: (x,y) = (-29.9057, -67.1165)
16: (x,y) = (-44.5327, -80.7565)
17: (x,y) = (-25.2142, -75.5801)
18: (x,y) = (-5.29033, -73.837)
19: (x,y) = (13.3813, -66.6696)
20: (x,y) = (-4.11112, -56.9734)
21: (x,y) = (0.047114, -37.4105)
22: (x,y) = (-11.1367, -53.9912)
23: (x,y) = (5.0436, -65.7469)
24: (x,y) = (-14.7618, -62.9635)
25: (x,y) = (-10.9456, -43.3309)
26: (x,y) = (4.3753, -30.4752)
27: (x,y) = (-6.51748, -13.7018)
28: (x,y) = (-3.04451, -33.3979)
29: (x,y) = (16.8459, -31.3074)
30: (x,y) = (28.3175, -14.9243)
31: (x,y) = (46.2933, -6.15689)
32: (x,y) = (50.1095, 13.4756)
33: (x,y) = (47.3261, 33.281)
34: (x,y) = (38.5586, 51.2569)
35: (x,y) = (44.4061, 32.1308)
36: (x,y) = (44.7551, 52.1278)
37: (x,y) = (32.1687, 67.6707)
38: (x,y) = (39.9833, 49.2606)
39: (x,y) = (29.3849, 66.2215)
40: (x,y) = (47.9286, 73.7137)
41: (x,y) = (32.6077, 60.8579)
42: (x,y) = (21.1362, 77.241)
43: (x,y) = (11.1362, 59.9204)
44: (x,y) = (-7.88493, 66.1008)
45: (x,y) = (-22.9791, 52.9796)
46: (x,y) = (-15.487, 34.4359)
47: (x,y) = (-5.7908, 51.9283)
48: (x,y) = (6.52243, 36.1681)
49: (x,y) = (26.3734, 38.6055)
50: (x,y) = (20.193, 19.5844)
51: (x,y) = (40.1443, 18.1892)
52: (x,y) = (29.5459, 35.1502)
53: (x,y) = (9.54591, 35.1502)
54: (x,y) = (16.7133, 53.8218)
55: (x,y) = (16.0153, 33.834)
56: (x,y) = (29.6552, 48.4611)
57: (x,y) = (32.0926, 28.6101)
58: (x,y) = (46.7197, 42.2501)
59: (x,y) = (26.9659, 45.3788)
60: (x,y) = (32.8134, 26.2527)
61: (x,y) = (31.7667, 46.2253)
62: (x,y) = (12.3607, 51.0637)
63: (x,y) = (13.7559, 71.015)
64: (x,y) = (10.9724, 90.8204)
65: (x,y) = (16.4852, 71.5951)
66: (x,y) = (-2.64094, 77.4426)
67: (x,y) = (11.5012, 91.5847)
68: (x,y) = (14.9742, 71.8886)
69: (x,y) = (-4.51324, 67.3895)
70: (x,y) = (-24.0006, 62.8905)
71: (x,y) = (-5.59055, 55.0759)
72: (x,y) = (-11.7709, 74.097)
73: (x,y) = (-30.5647, 67.2566)
74: (x,y) = (-45.4276, 53.874)
75: (x,y) = (-42.2989, 34.1202)
76: (x,y) = (-60.5699, 42.255)
77: (x,y) = (-78.0622, 51.9512)
78: (x,y) = (-61.6792, 63.4227)
79: (x,y) = (-53.2268, 81.5488)
80: (x,y) = (-36.2659, 70.9505)
81: (x,y) = (-16.86, 66.112)
82: (x,y) = (-23.3713, 85.0224)
83: (x,y) = (-42.6898, 79.846)
84: (x,y) = (-27.369, 92.7018)
85: (x,y) = (-8.14372, 98.2145)
After 86 steps, the subject has the following location:
(x,y) = (-22.0369, 112.601)
or
(m,a) = (114.737, 1.76406)
Average outward distance per step = 1.33416
2. Vector类:稍作修改
对于Vector类的头文件(程序清单11.13)和实现文件(程序清单11.14)进行修改,使其不再储存矢量的长度和角度,而是在magval()和angval()被调用时计算它们。
应保留公有接口不变(公有方法及其参数不变),但对私有部分(包括一些私有方法)和方法实现进行修改。然后,使用程序清单11.15对修改后的版本进行测试,结果应该与以前相同,因为Vecotr类的公有接口与原来相同。
代码:
vector.h:
#ifndef VECTOR_H
#define VECTOR_H
#include <iostream>
namespace VECTOR
{
class Vector
{
public:
enum Mode
{
RECT,
POL
};
private:
double x;
double y;
Mode mode;
double set_mag();
double set_ang();
void set_x(double mag, double ang);
void set_y(double mag, double ang);
public:
Vector();
Vector(double n1, double n2, Mode from = RECT);
void reset(double n1, double n2, Mode from = RECT);
~Vector();
double xval() const { return x; };
double yval() const { return y; };
double magval() const;
double angval() const;
void polar_mode();
void rect_mode();
Vector operator+(const Vector &b) const;
Vector operator-(const Vector &b) const;
Vector operator-() const;
Vector operator*(double n) const;
friend Vector operator*(double n, const Vector &a);
friend std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const Vector &v);
};
}
#endif
vector.cpp:
#include "vector.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
namespace VECTOR
{
const double Rad_to_deg = 45.0 / atan(1.0);
double Vector::set_mag()
{
double mag;
mag = sqrt(x * x + y * y);
return mag;
}
double Vector::set_ang()
{
double ang;
if (x == 0 && y == 0)
ang = 0.0;
else
ang = atan2(y, x);
return ang;
}
void Vector::set_x(double mag, double ang)
{
x = mag * cos(ang);
}
void Vector::set_y(double mag, double ang)
{
y = mag * sin(ang);
}
Vector::Vector()
{
x = y = 0;
mode = RECT;
}
Vector::Vector(double n1, double n2, Mode from)
{
mode = from;
if (from == RECT)
{
x = n1;
y = n2;
set_mag();
set_ang();
}
else if (from == POL)
{
double mag, ang;
mag = n1;
ang = n2 / Rad_to_deg;
set_x(mag, ang);
set_y(mag, ang);
}
else
{
cout << "Incorrect 3rd argument to Vector()--";
cout << "vector set to 0" << endl;
x = y = 0.0;
mode = RECT;
}
}
void Vector::reset(double n1, double n2, Mode from)
{
mode = from;
if (from == RECT)
{
x = n1;
y = n2;
}
else if (from == POL)
{
double mag, ang;
mag = n1;
ang = n2 / Rad_to_deg;
set_x(mag, ang);
set_y(mag, ang);
}
else
{
cout << "Incorrect 3rd argument to Vector()--";
cout << "vector set to 0" << endl;
x = y = 0.0;
mode = RECT;
}
}
Vector::~Vector()
{
}
double Vector::magval() const
{
double mag;
mag = sqrt(x * x + y * y);
return mag;
}
double Vector::angval() const
{
double ang;
if (x == 0.0 && y == 0.0)
ang = 0.0;
else
ang = atan2(y, x);
return ang;
}
void Vector::polar_mode()
{
mode = POL;
}
void Vector::rect_mode()
{
mode = RECT;
}
Vector Vector::operator+(const Vector &b) const
{
return Vector(x + b.x, y + b.y);
}
Vector Vector::operator-(const Vector &b) const
{
return Vector(x - b.x, y - b.y);
}
Vector Vector::operator-() const
{
return Vector(-x, -y);
}
Vector Vector::operator*(double n) const
{
return Vector(n * x, n * y);
}
Vector operator*(double n, const Vector &a)
{
return a * n;
}
ostream &operator<<(ostream &os, const Vector &v)
{
if (v.mode == Vector::RECT)
os << "(x,y) = (" << v.x << ", " << v.y << ")";
else if (v.mode == Vector::POL)
os << "(m,a) = (" << v.magval() << ", " << v.angval() << ")";
else
os << "Vector object mode is invalid";
return os;
}
}
randwalk.cpp:
#include "vector.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib> //rand(), srand() prototypes
#include <ctime> //time() prototype
using namespace std;
int main()
{
using VECTOR::Vector;
srand(time(0));
double direction;
Vector step;
Vector result(0.0, 0.0);
unsigned long steps = 0;
double target;
double dstep;
cout << "Enter target distance (q to quit): ";
while (cin >> target)
{
cout << "Enter step length: ";
if (!(cin >> dstep))
break;
while (result.magval() < target)
{
direction = rand() % 360;
step.reset(dstep, direction, Vector::POL);
result = result + step;
steps++;
}
cout << "After " << steps << " steps, the subject has the following location:\n";
cout << result << endl;
result.polar_mode();
cout << " or\n"
<< result << endl;
cout << "Average outward distance per step = " << result.magval() / steps << endl;
steps = 0;
result.reset(0.0, 0.0);
cout << "Enter target distance (q to quit): ";
}
cout << "Bye!\n";
cin.clear();
while (cin.get() != '\n')
continue;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
3. 最低、最高和平均步数
代码:
vector.h和vector.cpp同11.1。
randwalk.cpp:
#include "vector.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib> //rand(), srand() prototypes
#include <ctime> //time() prototype
using namespace std;
int main()
{
using VECTOR::Vector;
srand(time(0));
double direction;
Vector step;
Vector result(0.0, 0.0);
unsigned long steps = 0;
double target;
double dstep;
int N = 0;
int max = 0, min = 100000, sum = 0;
double average = 0.0;
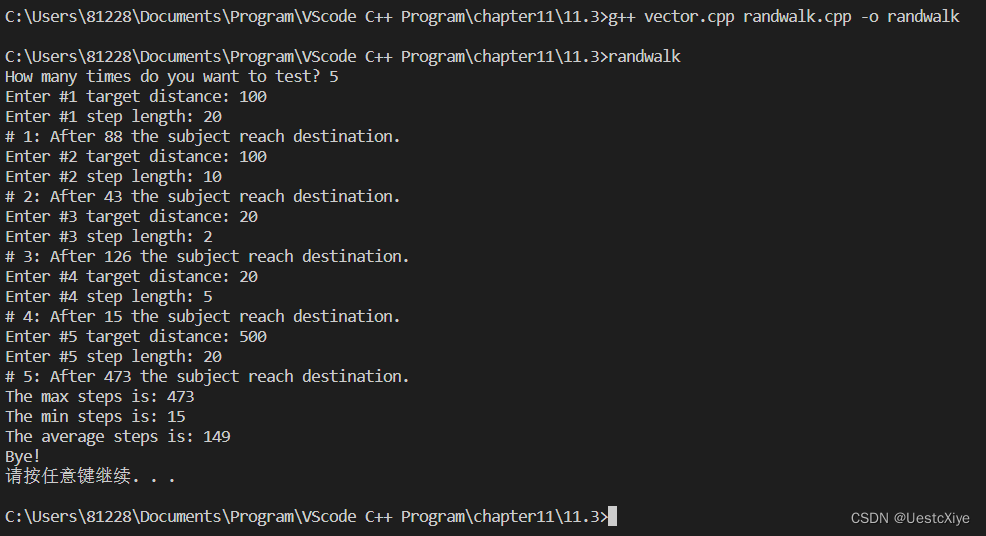
cout << "How many times do you want to test? ";
cin >> N;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
cout << "Enter #"<<i+1<<" target distance: ";
if (!(cin >> target))
break;
cout << "Enter #"<<i+1<<" step length: ";
if (!(cin >> dstep))
break;
while (result.magval() < target)
{
direction = rand() % 360;
step.reset(dstep, direction, Vector::POL);
result = result + step;
steps++;
}
cout << "# " << i + 1 << ": After " << steps << " the subject reach destination.\n";
// cout << result << endl;
// result.polar_mode();
// cout << " or\n"
// << result << endl;
// cout << "Average outward distance per step = " << result.magval() / steps << endl;
if (steps > max)
max = steps;
if (steps < min)
min = steps;
sum += steps;
steps = 0;
result.reset(0.0, 0.0);
}
average = (double)sum / N;
cout << "The max steps is: " << max << endl;
cout << "The min steps is: " << min << endl;
cout << "The average steps is: " << average << endl;
cout << "Bye!\n";
cin.clear();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
4. Time类:使用友元函数来实现所有的重载运算符
重新编写最后的Time类示例(程序清单11.10、程序清单11.11和程序清单11.12),使用友元函数来实现所有的重载运算符。
代码:
mytime.h:
#ifndef MYTIME_H
#define MYTIME_H
#include <iostream>
class Time
{
private:
int hours;
int minutes;
public:
Time();
Time(int h, int m = 0);
void AddMin(int m);
void AddHr(int h);
void Reset(int h = 0, int m = 0);
friend Time operator+(const Time &t1, const Time &t2);
friend Time operator-(const Time &t1, const Time &t2);
friend Time operator*(const Time &t, double mult);
friend Time operator*(double m, const Time &t) { return t * m; }
friend std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const Time &t);
};
#endif
mytime.cpp:
#include "mytime.h"
#include <iostream>
Time::Time()
{
hours = minutes = 0;
}
Time::Time(int h, int m)
{
hours = h;
minutes = m;
}
void Time::AddMin(int m)
{
hours += m;
hours += minutes / 10;
minutes %= 60;
}
void Time::AddHr(int h)
{
hours += h;
}
void Time::Reset(int h, int m)
{
hours = h;
minutes = m;
}
Time operator+(const Time &t1, const Time &t2)
{
Time sum;
sum.minutes = t1.minutes + t2.minutes;
sum.hours = t1.hours + t2.hours + sum.minutes / 60;
sum.minutes %= 60;
return sum;
}
Time operator-(const Time &t1, const Time &t2)
{
Time diff;
int tot1, tot2;
tot1 = t1.minutes + 60 * t1.hours;
tot2 = t2.minutes + 60 * t2.hours;
diff.hours = (tot2 - tot1) / 60;
diff.minutes = (tot2 - tot1) % 60;
return diff;
}
Time operator*(const Time &t, double mult)
{
Time result;
long totalminutes = t.hours * mult * 60 + t.minutes * mult;
result.hours = totalminutes / 60;
result.minutes = totalminutes % 60;
return result;
}
std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const Time &t)
{
os << t.hours << " hours, " << t.minutes << " minutes";
return os;
}
usetime.cpp:
#include "mytime.h"
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
Time aida(3, 35);
Time tosca(2, 48);
Time temp;
cout << "Aida and Tosca:\n";
cout << aida << "; " << tosca << endl;
temp = aida + tosca;
cout << "Aida + Tosca: " << temp << endl;
temp = aida * 1.17;
cout << "Aida * 1.17: " << temp << endl;
cout << "10.0 * Tosca: " << 10.0 * tosca << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:

5. Stonewt类:新增状态成员、重载运算符
重新编写Stonewt类(程序清单11.16和程序清单11.17),使它有一个状态成员,由该状态成员控制对象应转换为英石格式、整数磅格式还是浮点磅格式。重载<<运算符,使用它来替换show_stn()和show_lbs()方法。重载加法、减法和乘法运算符,以便可以对Stonewt值进行加、减、乘运算。编写一个使用所有类方法和友元的小程序,来测试这个类。
代码:
stonewt.h:
#ifndef STONEWT_H
#define STONEWT_H
#include <iostream>
class Stonewt
{
public:
enum Format
{
STONE,
INT_POUND,
DOUBLE_POUND
};
private:
enum
{
Lbs_per_stn = 14
};
Format m_form;
int stone;
double pds_left;
double pounds;
public:
Stonewt(double lbs);
Stonewt(int stn, double lbs);
Stonewt();
~Stonewt();
void SetFormat(Format form);
Stonewt operator+(const Stonewt &s) const;
Stonewt operator-(const Stonewt &s) const;
Stonewt operator*(double n) const;
friend Stonewt operator*(double m, const Stonewt &s) { return s * m; }
friend std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const Stonewt &s);
};
#endif
stonewt.cpp:
#include "stonewt.h"
#include <iostream>
Stonewt::Stonewt(double lbs)
{
stone = int(lbs) / Lbs_per_stn;
pds_left = int(lbs) % Lbs_per_stn + lbs - int(lbs);
pounds = lbs;
m_form = STONE;
}
Stonewt::Stonewt(int stn, double lbs)
{
stone = stn;
pds_left = lbs;
pounds = stn * Lbs_per_stn + lbs;
m_form = INT_POUND;
}
Stonewt::Stonewt()
{
stone = pounds = pds_left = 0;
m_form = DOUBLE_POUND;
}
Stonewt::~Stonewt()
{
}
void Stonewt::SetFormat(Format from)
{
m_form = from;
}
Stonewt Stonewt::operator+(const Stonewt &s) const
{
Stonewt sum;
sum.pounds = pounds + s.pounds;
sum.stone = int(sum.pounds) / Lbs_per_stn;
sum.pds_left = int(sum.pounds) % Lbs_per_stn + sum.pounds - int(sum.pounds);
return sum;
}
Stonewt Stonewt::operator-(const Stonewt &s) const
{
Stonewt diff;
diff.pounds = pounds - s.pounds;
diff.stone = int(diff.pounds) / Lbs_per_stn;
diff.pds_left = int(diff.pounds) % Lbs_per_stn + diff.pounds - int(diff.pounds);
return diff;
}
Stonewt Stonewt::operator*(double n) const
{
double mult;
mult = pounds * n;
return Stonewt(mult);
}
std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const Stonewt &s)
{
if (s.m_form == Stonewt::STONE)
{
os << s.stone << " stone, " << s.pds_left << " pounds\n";
}
else if (s.m_form == Stonewt::INT_POUND)
{
os << int(s.pounds) << " pounds\n";
}
else if (s.m_form == Stonewt::DOUBLE_POUND)
{
os << s.pounds << " pounds\n";
}
else
os << "Stonewt state is invalid";
return os;
}
stone.cpp:
#include "stonewt.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
Stonewt incognito = 275;
Stonewt wolfe(285.7);
Stonewt taft(21, 8);
cout << "The celebrity weighed " << incognito; // STONE
cout << "The detective weighed " << wolfe; // STONE
cout << "The President weighed " << taft << endl; // INT_POUND
Stonewt tf(2);
Stonewt sum, diff, mult;
sum = incognito + tf;
diff = wolfe - tf;
mult = taft * 2;
cout << "The result will display as double_pounds:\n";
cout << "After dinner, the celebrity weighed ";
sum.SetFormat(Stonewt::DOUBLE_POUND);
cout << sum;
cout << "After sport, the detective weighed ";
diff.SetFormat(Stonewt::DOUBLE_POUND);
cout << diff;
cout << "Now,the President weighed ";
mult.SetFormat(Stonewt::DOUBLE_POUND);
cout << mult;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:

6. Stonewt类:重载全部关系运算符
重新编写Stonewt类(程序清单11.16和程序清单11.17),重载全部6个关系运算符。运算符对pounds成员进行比较,并返回一个bool值。编写一个程序,它声明一个包含6个Stonewt对象的数组,并在数组声明中初始化前3个对象。然后使用循环来读取用于设置剩余3个数组元素的值。接着报告最小的元素、最大的元素以及大于或等于11英石的元素的数量(最简单的方法是创建一个Stonewt对象,并将其初始化为11英石,然后将其同其他对象进行比较)。
代码:
stonewt.h:
#ifndef STONEWT_H
#define STONEWT_H
#include <iostream>
class Stonewt
{
public:
enum Format
{
STONE,
INT_POUND,
DOUBLE_POUND
};
private:
enum
{
Lbs_per_stn = 14
};
Format m_form;
int stone;
double pds_left;
double pounds;
public:
Stonewt(double lbs);
Stonewt(int stn, double lbs);
Stonewt();
~Stonewt();
void SetFormat(Format form);
// Stonewt operator+(const Stonewt &s) const;
// Stonewt operator-(const Stonewt &s) const;
// Stonewt operator*(double n) const;
// friend Stonewt operator*(double m, const Stonewt &s) { return s * m; }
friend bool operator>(const Stonewt &s1, const Stonewt &s2);
friend bool operator<(const Stonewt &s1, const Stonewt &s2);
friend bool operator>=(const Stonewt &s1, const Stonewt &s2);
friend bool operator<=(const Stonewt &s1, const Stonewt &s2);
friend bool operator==(const Stonewt &s1, const Stonewt &s2);
friend bool operator!=(const Stonewt &s1, const Stonewt &s2);
friend std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const Stonewt &s);
};
#endif
stonewt.cpp:
#include "stonewt.h"
#include <iostream>
Stonewt::Stonewt(double lbs)
{
stone = int(lbs) / Lbs_per_stn;
pds_left = int(lbs) % Lbs_per_stn + lbs - int(lbs);
pounds = lbs;
m_form = STONE;
}
Stonewt::Stonewt(int stn, double lbs)
{
stone = stn;
pds_left = lbs;
pounds = stn * Lbs_per_stn + lbs;
m_form = INT_POUND;
}
Stonewt::Stonewt()
{
stone = pounds = pds_left = 0;
m_form = DOUBLE_POUND;
}
Stonewt::~Stonewt()
{
}
void Stonewt::SetFormat(Format from)
{
m_form = from;
}
// Stonewt Stonewt::operator+(const Stonewt &s) const
// {
// Stonewt sum;
// sum.pounds = pounds + s.pounds;
// sum.stone = int(sum.pounds) / Lbs_per_stn;
// sum.pds_left = int(sum.pounds) % Lbs_per_stn + sum.pounds - int(sum.pounds);
// return sum;
// }
// Stonewt Stonewt::operator-(const Stonewt &s) const
// {
// Stonewt diff;
// diff.pounds = pounds - s.pounds;
// diff.stone = int(diff.pounds) / Lbs_per_stn;
// diff.pds_left = int(diff.pounds) % Lbs_per_stn + diff.pounds - int(diff.pounds);
// return diff;
// }
// Stonewt Stonewt::operator*(double n) const
// {
// double mult;
// mult = pounds * n;
// return Stonewt(mult);
// }
bool operator>(const Stonewt &s1, const Stonewt &s2)
{
if (s1.pounds > s2.pounds)
return true;
else
return false;
}
bool operator<(const Stonewt &s1, const Stonewt &s2)
{
if (s1.pounds < s2.pounds)
return true;
else
return false;
}
bool operator>=(const Stonewt &s1, const Stonewt &s2)
{
if (s1.pounds >= s2.pounds)
return true;
else
return false;
}
bool operator<=(const Stonewt &s1, const Stonewt &s2)
{
if (s1.pounds <= s2.pounds)
return true;
else
return false;
}
bool operator==(const Stonewt &s1, const Stonewt &s2)
{
if (s1.pounds == s2.pounds)
return true;
else
return false;
}
bool operator!=(const Stonewt &s1, const Stonewt &s2)
{
if (s1.pounds != s2.pounds)
return true;
else
return false;
}
std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const Stonewt &s)
{
if (s.m_form == Stonewt::STONE)
{
os << s.stone << " stone, " << s.pds_left << " pounds\n";
}
else if (s.m_form == Stonewt::INT_POUND)
{
os << int(s.pounds) << " pounds\n";
}
else if (s.m_form == Stonewt::DOUBLE_POUND)
{
os << s.pounds << " pounds\n";
}
else
os << "Stonewt state is invalid";
return os;
}
stone.cpp:
#include "stonewt.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
Stonewt s[6] = {275, 285.7, Stonewt(21, 8.0)};
cout << "Enter the rest three Stonewt:\n";
for (int i = 3; i < 6; i++)
{
double pounds;
cout << "#" << i + 1 << ": ";
cin >> pounds;
s[i] = pounds;
}
Stonewt s_max = s[0], s_min = s[0], flag(11, 0.0);
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
{
cout << "#" << i + 1 << ": " << s[i] << endl;
if (s[i] > s_max)
s_max = s[i];
if (s[i] < s_min)
s_min = s[i];
if (s[i] >= flag)
count++;
}
cout << "The max is " << s_max;
cout << "The min is " << s_min;
if (count > 1)
cout << "There are " << count << " members greater than or equal to 11 stones.\n";
else
cout << "There is " << count << " member greater than or equal to 11 stones.\n";
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:

7.
复数有两个部分组成:实数部分和虚数部分。复数的一种书写方式是:(3.0,4.0),其中,3.0是实数部分,4.0是虚数部分。假设a=(A,Bi),c=(C,Di),则下面是一些复数运算。
- 加法:a+c=(A+C,(B+D)i)。
- 减法:a-c=(A-C,(B-D)i)。
- 乘法:a * c=(A*C-B * D,(A * D+B * C)i)。
- 乘法::x * c=(x * C,x * Di),其中x为实数。
- 共轭:~a=(A,-Bi)。
请定义一个复数类,以便下面的程序可以使用它来获得正确的结果。
#include <iostream>
#include "complex0.h"
using namespace std;
int main(void)
{
complex a(3.0, 4.0);
complex c;
cout << "Enter a complex number (q to quit):\n";
while (cin >> c)
{
cout << "c is " << c << endl;
cout << "complex conjugate is " << ~c << endl;
cout << "a is " << a << endl;
cout << "a + c is " << a + c << endl;
cout << "a - c is " << a - c << endl;
cout << "a * c is " << a * c << endl;
cout << "2 * c is " << 2 * c << endl;
cout << "Enter a complex number (q to quit):" << endl;
}
cout << "Done!" << endl;
return 0;
}
注意。必须重载运算符<<和>>。标准C++使用头文件complex提供了比这个示例更广泛的复数支持,因此应将自定义的头文件命名为complex0.h,以免发生冲突。应尽可能使用const。
下面是该程序的运行情况。
Enter a complex number (q to quit):
real: 10
imaginary: 12
c is (10,12i)
complex conjugate is (10,-12i)
a is (3,4i)
a + c is (13,16i)
a - c is (-7,-8i)
a * c is (-18,76i)
2 * c is (20,24i)
Enter a complex number (q to quit):
real: q
Done!
请注意,经过重载后,cin>>c将提示用户输入实数和虚数部分。
代码:
complex0.h:
#ifndef COMPLEX0_H
#define COMPLEX0_H
#include <iostream>
class complex
{
private:
double real;
double imaginary;
public:
complex();
complex(const double r, const double i);
~complex();
complex operator+(const complex &c) const;
complex operator-(const complex &c) const;
complex operator*(const complex &c) const;
complex operator*(double x) const;
complex operator~() const;
friend complex operator*(double x, const complex &c) { return c * x; };
friend std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const complex &c);
friend std::istream &operator>>(std::istream &is, complex &c);
};
#endif
complex0.cpp:
#include "complex0.h"
#include <iostream>
complex::complex()
{
real = imaginary = 0.0;
}
complex::complex(const double r, const double i)
{
real = r;
imaginary = i;
}
complex::~complex()
{
}
complex complex::operator+(const complex &c) const
{
complex sum;
sum.real = real + c.real;
sum.imaginary = imaginary + c.imaginary;
return sum;
}
complex complex::operator-(const complex &c) const
{
complex diff;
diff.real = real - c.real;
diff.imaginary = imaginary - c.imaginary;
return diff;
}
complex complex::operator*(const complex &c) const
{
complex mult;
mult.real = real * c.real - imaginary * c.imaginary;
mult.imaginary = real * c.imaginary + imaginary * c.real;
return mult;
}
complex complex::operator*(double x) const
{
complex mult;
mult.real = real * x;
mult.imaginary = imaginary * x;
return mult;
}
complex complex::operator~() const
{
return complex(real, -imaginary);
}
std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const complex &c)
{
os << "(" << c.real << "," << c.imaginary << "i)";
return os;
}
std::istream &operator>>(std::istream &is, complex &c)
{
std::cout << "real: ";
if (is >> c.real)
{
std::cout << "imaginary: ";
is >> c.imaginary;
}
return is;
}
main.cpp:
#include "complex0.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
int main()
{
complex a(3.0, 4.0);
complex c;
cout << "Enter a complex number (q to quit):\n";
while (cin >> c)
{
cout << "c is " << c << endl;
cout << "complex conjugate is " << ~c << endl;
cout << "a is " << a << endl;
cout << "a + c is " << a + c << endl;
cout << "a - c is " << a - c << endl;
cout << "a * c is " << a * c << endl;
cout << "2 * c is " << 2 * c << endl;
cout << "Enter a complex number (q to quit):" << endl;
}
cout << "Done!\n";
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:























第11章编程练习&spm=1001.2101.3001.5002&articleId=129496214&d=1&t=3&u=b9bed4e936ab4101aad00b9f029826d2)
 1183
1183

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










