背景:
在工作时遇到一个要求,将一个Excel表格里的数据写入数据库中。但是手动写sql语句很麻烦,通过网上搜索资料,写了一个Java类来实现。因为本人是小白,所以这篇写的会比较细,方便自己看懂。
读取Excel文件案例:将 测试案例1.xlsx 表格里的两列数据(user,name)插入到info表的user,name字段里。
(表格数据是随机生成的)
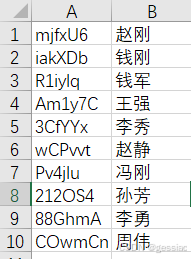
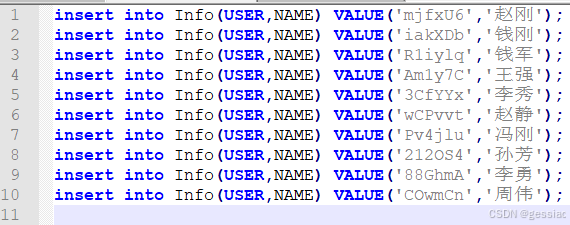
结果:
目录
目标:
- 读取Excel表格中的数据
- 生成SQL语句
项目实现:
1. 依赖:Apache POI
Apache POI(PHP Open Source Integrations)提供了处理 Microsoft Office 格式文件(如 Excel、Word、PowerPoint 等)的 API。其中,用于操作 Excel 文件的两个关键类: HSSF 和 XSSF:
- HSSF:用于读取和写入 Excel 97-2003 格式的文件(.xls 文件)。
- XSSF:用于读取和写入 Excel 2007 及以后版本的文件(.xlsx 文件)。
比如:.xlsx 文件(注意代码第10行和第12行)
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.*;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ExcelReader {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
//创建一个 FileInputStream 对象,尝试打开名为 example.xlsx 的文件
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("example.xlsx");
//创建一个 XSSFWorkbook 对象,将 FileInputStream 中的字节流解析为一个 Excel 工作簿对象
Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(fis)) {
//调用 Workbook 对象的 getSheetAt 方法,根据索引获取指定工作表。
//索引从 0 开始,所以这里获取的是工作簿中的第一个工作表。
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
//遍历工作表中的行和单元格
for (Row row : sheet) {
//遍历该行的每一个单元格
for (Cell cell : row) {
System.out.print(cell.toString() + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}导入maven依赖
<!-- 添加 Apache POI 依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi</artifactId>
<version>4.1.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi-ooxml</artifactId>
<version>4.1.2</version>
</dependency>本来用的5.2.3版本,但是不知道为什么org.apache.poi.ss包导入不进去,所以换了个版本
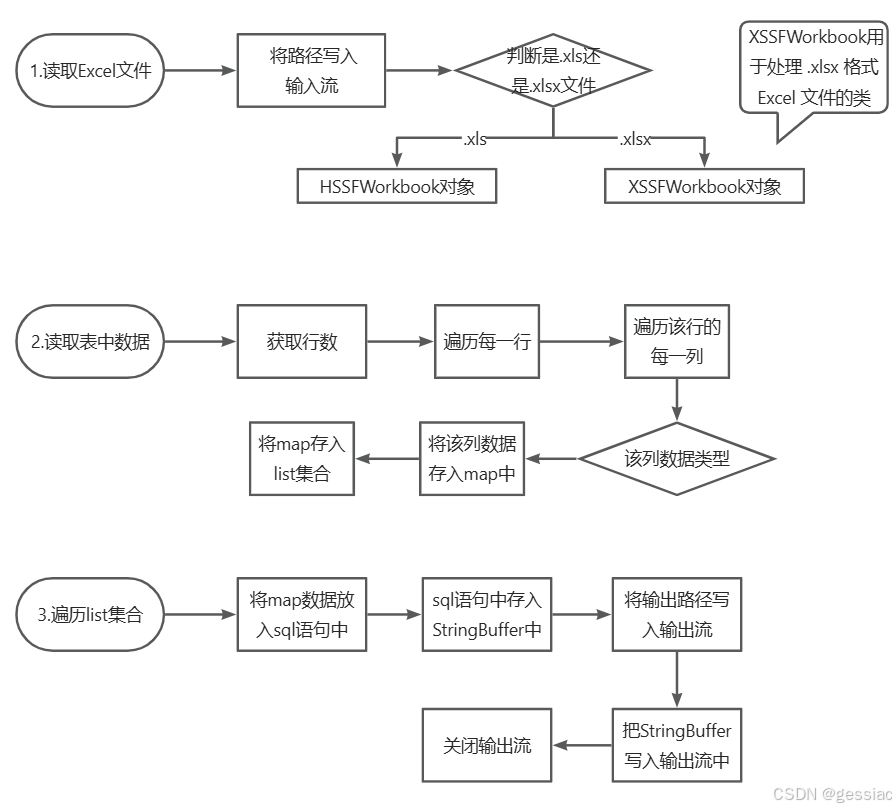
2. 流程
1.读取Excel文件
2.读取表中数据
获取行数遍历
判断每行该列的类型
将数据存入list集合中
3.遍历list集合,生成sql语句
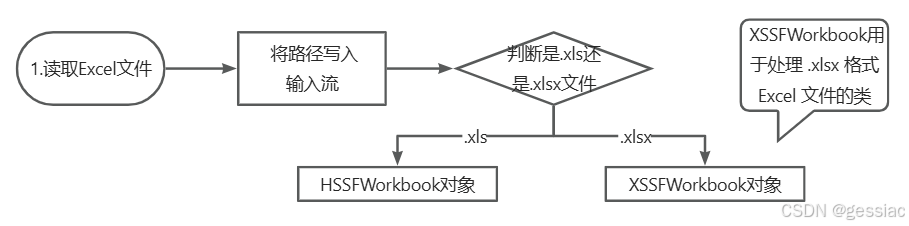
1.读取Excel文件
String filePath = "D:\\TestingData\\测试案例1.xlsx";
System.out.println("开始读取Excel文件..."+ filePath);
Workbook wb = null;
Sheet sheet = null; //用于表示 Excel 工作表的接口
ArrayList<Map<String, String>> list = null;
String columns[] = {"user","name"}; //作为map的key,生成sql语句时使用
//读取Excel文件
wb = readExcel(filePath);
System.out.println("读取Excel文件结束"); //读取Excel
private static Workbook readExcel(String filePath) {
if(filePath == null){
return null;
}
Workbook wb = null;
InputStream is = null;
String substring = filePath.substring(filePath.lastIndexOf("."));
try{
is = new FileInputStream(filePath);
if(".xls".equals(substring)){
return wb = new HSSFWorkbook(is);
}else if(".xlsx".equals(substring)){
//创建一个 XSSFWorkbook 对象 workbook,XSSFWorkbook用于处理 .xlsx 格式 Excel 文件的类
wb = new XSSFWorkbook(is);
}else{
return wb = null;
}
}catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return wb;
}
2.读取表中数据
获取行数遍历
判断每行该列的类型
将数据存入list集合中
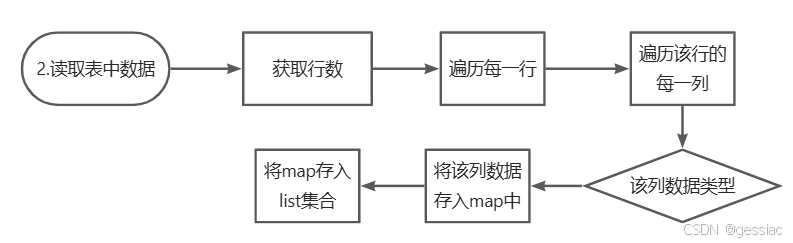
if(wb != null){ //读取表中数据
list = new ArrayList<>();
//获取第一个sheet 获取工作簿中的第一个工作表
sheet = wb.getSheetAt(0);
//获取最大行数
int rows = sheet.getPhysicalNumberOfRows();
System.out.println("最大行数"+rows);
//获取第一行
Row row = sheet.getRow(0);
//获取最大列数
int colnum = row.getPhysicalNumberOfCells();
System.out.println("最大列数"+colnum);
//遍历 表中的每一行
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++){
Map<String, String> map = new LinkedHashMap<>();
//获取当前行
row = sheet.getRow(i);
//遍历每一行的每一列
for (int j = 0; j < colnum; j++){
//row.getCell(j).setCellType(Cell.CELL_TYPE_STRING);
//判断每个单元格信息,强转为String类型,具体依据数据表中该字段类型
String cellData = (String) getCellFormatValue(row.getCell(j)); //第一行的第j列
map.put(columns[j],cellData); //存入map对应的key中
}
if (map.size() > 0){
list.add(map); //将第i行数据存入集合中
}
}
}else {
System.out.println("没有Excel表");
}判断每行该列的类型:
cell:方法的参数,代表一个 Excel 单元格对象
//读取每个单元格信息
private static Object getCellFormatValue(Cell cell) {
Object cellValue = null;
if (cell != null){
//判断cell类型
switch (cell.getCellType()){
case NUMERIC:{
if(DateUtil.isCellDateFormatted(cell)){ //判断是否是日期
cellValue = cell.getDateCellValue().toString();
} else {
cellValue = String.valueOf((int) cell.getNumericCellValue()); //数字类型
}
break;
}
case STRING:{
cellValue = cell.getRichStringCellValue().getString(); //字符串类型
//cellValue = cell.getStringCellValue();
break;
}
case FORMULA:{
cellValue = cell.getCellFormula(); //公式类型
break;
}
case BOOLEAN:{
cellValue = String.valueOf(cell.getBooleanCellValue());
break;
}
default:
cellValue = "";
}
}else {
cellValue = "";
}
return cellValue;
}
3.遍历list集合,生成sql语句
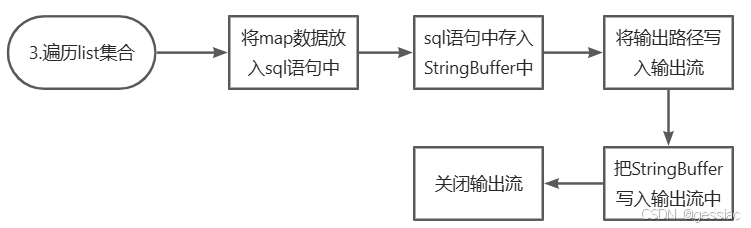
//3.遍历解析出来的list
System.out.println("解析出来的数据为:"+ list);
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
for(Map map : list){
//insert into Lnfo(USER,NAME) VALUE('iakXDb','钱刚')
String sql = "insert into Info(USER,NAME) VALUE('" +map.get("user") + "','" + map.get("name") + "');";
System.out.println(sql);
//将sql语句存入 StringBuffer 中,为了写入到输出文件中
sb.append(sql);
sb.append("\n");
}
try(FileOutputStream fo = new FileOutputStream("D:\\TestingData\\测试案例1.sql")) {
fo.write(sb.toString().getBytes());
System.out.println("写入文件成功");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("写入文件失败");
}
总代码:
package org.example.excel.xlsx;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFWorkbook;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.*;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class ReadExcel {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filePath = "D:\\TestingData\\测试案例1.xlsx";
System.out.println("开始读取Excel文件..."+ filePath);
Workbook wb = null;
Sheet sheet = null; //用于表示 Excel 工作表的接口
ArrayList<Map<String, String>> list = null;
String columns[] = {"user","name"}; //作为map的key,生成sql语句时使用
//1.读取Excel文件
wb = readExcel(filePath);
System.out.println("读取Excel文件结束");
if(wb != null){
//读取表中数据
list = new ArrayList<>();
//获取第一个sheet 获取工作簿中的第一个工作表
sheet = wb.getSheetAt(0);
//获取最大行数
int rows = sheet.getPhysicalNumberOfRows();
System.out.println("最大行数"+rows);
//获取第一行
Row row = sheet.getRow(0);
//获取最大列数
int colnum = row.getPhysicalNumberOfCells();
System.out.println("最大列数"+colnum);
//遍历 表中的每一行
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++){
Map<String, String> map = new LinkedHashMap<>();
row = sheet.getRow(i);
//遍历每一行的每一列
for (int j = 0; j < colnum; j++){
//row.getCell(j).setCellType(Cell.CELL_TYPE_STRING);
//2.判断每个单元格信息,强转为String类型,具体依据数据表中该字段类型
String cellData = (String) getCellFormatValue(row.getCell(j)); //第一行的第一列
map.put(columns[j],cellData); //存入map对应的key中
}
if (map.size() > 0){
list.add(map); //添加到集合中
}
}
}else {
System.out.println("没有Excel表");
}
//3.遍历解析出来的list
System.out.println("解析出来的数据为:"+ list);
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
for(Map map : list){
//insert into Lnfo(USER,NAME) VALUE('iakXDb','钱刚')
String sql = "insert into Info(USER,NAME) VALUE('" +map.get("user") + "','" + map.get("name") + "');";
System.out.println(sql);
//将sql语句存入 StringBuffer 中,为了写入到输出文件中
sb.append(sql);
sb.append("\n");
}
try(FileOutputStream fo = new FileOutputStream("D:\\TestingData\\测试案例1.sql")) {
fo.write(sb.toString().getBytes());
System.out.println("写入文件成功");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("写入文件失败");
}
}
//读取每个单元格信息
private static Object getCellFormatValue(Cell cell) {
Object cellValue = null;
if (cell != null){
//判断cell类型
switch (cell.getCellType()){
case NUMERIC:{
if(DateUtil.isCellDateFormatted(cell)){ //判断是否是日期
cellValue = cell.getDateCellValue().toString();
} else {
cellValue = String.valueOf((int) cell.getNumericCellValue()); //数字类型
}
break;
}
case STRING:{
cellValue = cell.getRichStringCellValue().getString(); //字符串类型
//cellValue = cell.getStringCellValue();
break;
}
case FORMULA:{
cellValue = cell.getCellFormula();
break;
}
case BOOLEAN:{
cellValue = String.valueOf(cell.getBooleanCellValue());
break;
}
default:
cellValue = "";
}
}else {
cellValue = "";
}
return cellValue;
}
//读取Excel
private static Workbook readExcel(String filePath) {
if(filePath == null){
return null;
}
Workbook wb = null;
InputStream is = null;
String substring = filePath.substring(filePath.lastIndexOf("."));
try{
is = new FileInputStream(filePath);
if(".xls".equals(substring)){
return wb = new HSSFWorkbook(is);
}else if(".xlsx".equals(substring)){
//创建一个 XSSFWorkbook 对象 workbook,XSSFWorkbook用于处理 .xlsx 格式 Excel 文件的类
wb = new XSSFWorkbook(is);
}else{
return wb = null;
}
}catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return wb;
}
}




















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








