真的好久没写博客了
之前是考试周就没怎么做题
后来考试后回家 去厦门玩耍了三四天
19号回学校 20号开始集训
emmmm 结束碎碎念 开始进入正题吧~
目录
鸽巢定理:
容斥定理:
鸽巢定理:
也叫 抽屉定理, 抽屉原理的一般含义为:“如果每个抽屉代表一个集合,每一个苹果就可以代表一个元素,假如有n+1个元素放到n个集合中去,其中必定有一个集合里至少有两个元素。”
第一抽屉原理:
原理1: 把多于n+1个的物体放到n个抽屉里,则至少有一个抽屉里的东西不少于两件。
原理2 :把多于mn(m乘n)+1(n不为0)个的物体放到n个抽屉里,则至少有一个抽屉里有不少于(m+1)的物体。
原理3 :把无穷多件物体放入n个抽屉,则至少有一个抽屉里 有无穷个物体。
第二抽屉原理:
把(mn-1)个物体放入n个抽屉中,其中必有一个抽屉中至多有(m—1)个物体
(例如,将3×5-1=14个物体放入5个抽屉中,则必定有一个抽屉中的物体数少于等于3-1=2)。
POJ 2356
Find a multiple
| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 65536K | |||
| Total Submissions: 9020 | Accepted: 3870 | Special Judge | ||
Description
The input contains N natural (i.e. positive integer) numbers ( N <= 10000 ). Each of that numbers is not greater than 15000. This numbers are not necessarily different (so it may happen that two or more of them will be equal). Your task is to choose a few of given numbers ( 1 <= few <= N ) so that the sum of chosen numbers is multiple for N (i.e. N * k = (sum of chosen numbers) for some natural number k).
Input
The first line of the input contains the single number N. Each of next N lines contains one number from the given set.
Output
In case your program decides that the target set of numbers can not be found it should print to the output the single number 0. Otherwise it should print the number of the chosen numbers in the first line followed by the chosen numbers themselves (on a separate line each) in arbitrary order.
If there are more than one set of numbers with required properties you should print to the output only one (preferably your favorite) of them.
Sample Input
5
1
2
3
4
1
Sample Output
2
2
3题目大意:
给出N以及N个数,从这N个数中任意选择1个或多个数,使得其和是N的倍数。
其实可以用暴力求解 但是很费时间 所以就用抽屉原理来做
PS:也是看了别人的博客才懂的 但是写了详细的注解
#include <stdio.h>
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string.h>
int sum[10005],a[10005],mod[10005];
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int t;
while (~scanf("%d",&t))
{
memset(mod,-1,sizeof (mod));//每执行一次样例 对mod数组重置-1
for (int i=0; i<t; i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
}
for (int i=0; i<t; i++)
{
sum[i+1]=sum[i]+a[i];
if (sum[i+1]%t==0)//若某个sum值是t的倍数 直接输出a[0]~a[i]
{
int j;
printf("%d\n",i+1);//个数
for (j=0; j<=i; j++)
printf("%d\n",a[j]);
break;
}
if (mod[sum[i+1]%t]!=-1)//若出现有相同的余数的值 则依次输出
{
int j;
printf("%d\n",i-mod[sum[i+1]%t]);//个数
for (j=mod[sum[i+1]%t]+1; j<=i; j++)
printf("%d\n",a[j]);
break;
}
mod[sum[i+1]%t]=i;//将相应余数存到mod中
}
}
return 0;
}
加上一题 (类似的 也是求前缀和 然后得到几个数组成的某个数的倍数)
POJ 3370 && HDU 1808
Halloween treats
Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 1221 Accepted Submission(s): 479
Special Judge
Problem Description
Every year there is the same problem at Halloween: Each neighbour is only willing to give a certain total number of sweets on that day, no matter how many children call on him, so it may happen that a child will get nothing if it is too late. To avoid conflicts, the children have decided they will put all sweets together and then divide them evenly among themselves. From last year's experience of Halloween they know how many sweets they get from each neighbour. Since they care more about justice than about the number of sweets they get, they want to select a subset of the neighbours to visit, so that in sharing every child receives the same number of sweets. They will not be satisfied if they have any sweets left which cannot be divided.
Your job is to help the children and present a solution.
Input
The input contains several test cases.
The first line of each test case contains two integers c and n (1 ≤ c ≤ n ≤ 100000), the number of children and the number of neighbours, respectively. The next line contains n space separated integers a1 , ... , an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 100000 ), where ai represents the number of sweets the children get if they visit neighbour i.
The last test case is followed by two zeros.
Output
For each test case output one line with the indices of the neighbours the children should select (here, index i corresponds to neighbour i who gives a total number of aisweets). If there is no solution where each child gets at least one sweet, print "no sweets" instead. Note that if there are several solutions where each child gets at least one sweet, you may print any of them.
Sample Input
4 5 1 2 3 7 5 3 6 7 11 2 5 13 17 0 0
Sample Output
3 5 2 3 4
题目大意:
给你两个整数C和N,再给你N个正数的序列,从中找到若干数,使得其和刚好是 C的倍数。输出这些数的序号。
PS:
样例给出的结果 只是其中的一个解 (存在多解)
要注意的是 要求输出的是 序号 而不是 数组内的数字 (与上一题有点不同)
题目中说 C < N 即人数小于邻居的数量,所以必存在一种结果
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int a[100005];
int mod[100005];
//标记余数出现的位置
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
int n,m;int sum;
while (~scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)&&n)
{
memset(a,0,sizeof a);
memset(mod,-1,sizeof (mod));
sum=0;
for (int i=1; i<=m; i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
a[i]=a[i]%n;
}
for (int i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
sum=(sum+a[i])%n;
if (!sum)
{
printf("%d",1);
for (int j=2;j<=i;j++)
printf(" %d",j);
printf("\n");
break;
}
else if (mod[sum]!=-1)
{
printf("%d",mod[sum]+1);
for (int j=mod[sum]+2;j<=i;j++)
printf(" %d",j);
printf("\n");
break;
}
mod[sum]=i;
}
}
return 0;
}
容斥定理:
在计数时,必须注意没有重复,没有遗漏。为了使重叠部分不被重复计算,人们研究出一种新的计数方法,这种方法的基本思想是:先不考虑重叠的情况,把包含于某内容中的所有对象的数目先计算出来,然后再把计数时重复计算的数目排斥出去,使得计算的结果既无遗漏又无重复,这种计数的方法称为容斥原理。
如果被计数的事物有A、B、C三类,那么,A类和B类和C类元素个数总和= A类元素个数+ B类元素个数+C类元素个数—既是A类又是B类的元素个数—既是A类又是C类的元素个数—既是B类又是C类的元素个数+既是A类又是B类而且是C类的元素个数。(A∪B∪C = A+B+C - A∩B - B∩C - C∩A + A∩B∩C)
以下是从百度百科偷来的公式图:
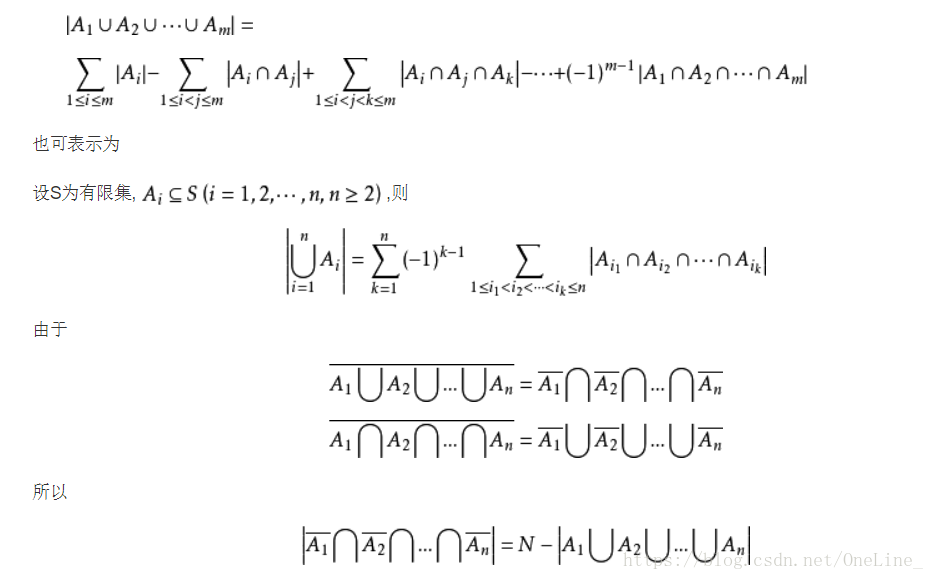
HDU 1796
How many integers can you find
Time Limit: 12000/5000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 10406 Accepted Submission(s): 3109
Problem Description
Now you get a number N, and a M-integers set, you should find out how many integers which are small than N, that they can divided exactly by any integers in the set. For example, N=12, and M-integer set is {2,3}, so there is another set {2,3,4,6,8,9,10}, all the integers of the set can be divided exactly by 2 or 3. As a result, you just output the number 7.
Input
There are a lot of cases. For each case, the first line contains two integers N and M. The follow line contains the M integers, and all of them are different from each other. 0<N<2^31,0<M<=10, and the M integer are non-negative and won’t exceed 20.
Output
For each case, output the number.
Sample Input
12 2
2 3
Sample Output
7
题目大意:
给出N和M个数,求不超过N 且可以被M个数中任意一个整除的数有多少个。
先求出能被单个因子整除的数目 之后 求出被多个因子整除的数目 ——> 奇加偶减
#include <stdio.h>
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string.h>
#include <cmath>
#define ll long long
ll a[20];
using namespace std;
ll gcd(ll a,ll b)//计算最大公约数
{
return b?gcd(b,a%b):a;
}
int main()
{
ll n,m;
while (~scanf("%lld%lld",&n,&m))
{
n=n-1;
int h=1;
for (int i=1; i<=m; i++)
{
scanf("%lld",&a[h]);
if (a[h]!=0)h++;
}
m=h-1;
ll ans=0,k,id;
for (int i=1; i<(1<<m); i++)// << 是移位运算 二进制左移一位 相当于i<2^m
{
k=1;
id=0;
for (int j=0; j<m; j++)
if (i&(1<<j))//二进制控制因子
{
id++;
k=(a[j+1]/gcd(a[j+1],k)*k);
}
if (id&1)//且运算 判断id的末位是否为1
//相当于判断奇偶 id%2==1 (奇加偶减)
ans+=n/k;
else ans-=n/k;
}
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}
上面的代码运用到了位运算 对此不了解的可以自行百度
或者自己走一遍程序 走一遍就能懂了( ̄m ̄)
欧克 七月的第一篇也是最后一篇~
明天也要加油鸭!!!








 本文探讨了鸽巢定理和容斥定理在算法竞赛中的应用,通过解析POJ 2356、POJ 3370、HDU1808和HDU1796等题目,详细解释了如何使用这两种数学原理解决实际问题。
本文探讨了鸽巢定理和容斥定理在算法竞赛中的应用,通过解析POJ 2356、POJ 3370、HDU1808和HDU1796等题目,详细解释了如何使用这两种数学原理解决实际问题。
















 877
877

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








