基本方法:采用队列作为测量数据存储器 , 设队列的长度为 N ,每进行一次测量 ,把测量结果放于队尾 ,而扔掉原来队首的一个数据 ,这样在队列中始终就有 N 个 “最新” 的数据。当计算平均值时 ,只要把队列中的 N 个数据进行算数平均 ,就可得到新的算数平均值。这样每进行一次测量 ,就可得到一个新的算术平均值。
其程序如下所示:
#include <stdio.h>
// 定义滤波数据类型
typedef int filter_type;
// 函数声明
filter_type filter(filter_type value_buf[], filter_type new_value, int num);
// 递推平均滤波函数
filter_type filter(filter_type value_buf[], filter_type new_value, int num)
{
static int i;
int count;
filter_type sum = 0;
value_buf[i++] = new_value;
// 调试信息
/*for (count=0; count<num; count++)
printf("%d ", value_buf[count]);
printf("\n");*/
if (i == num)
i = 0;
for (count=0; count<num; count++)
sum += value_buf[count];
return (filter_type)(sum/num);
}
//打印测试
void main()
{
int i;
filter_type ave, val;
filter_type a[5]= {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
val = 0;
for(i=0; i<3; i++)
{
ave = filter(a, val, sizeof(a)/sizeof(filter_type));
printf("%d\n", ave);
val += 8;
}
}
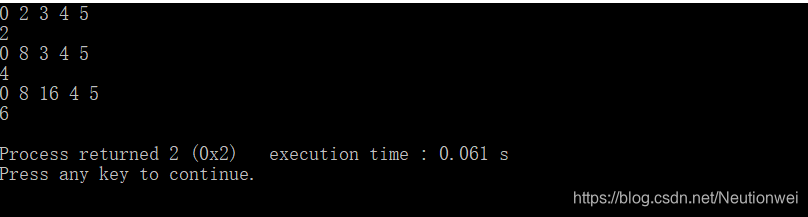
程序结果:
(0+2+3+4+5)/5 = 2.8;(0+8+3+4+5)/5 = 4;(0+8+16+4+5)/5 = 6.6;全部整型输出分别为2、4、6





 本文介绍了一种基于队列的递推平均滤波算法,通过每次更新队列中的数据并计算新平均值来实现数据平滑处理。该算法适用于实时数据处理场景,能够有效减少噪声干扰。
本文介绍了一种基于队列的递推平均滤波算法,通过每次更新队列中的数据并计算新平均值来实现数据平滑处理。该算法适用于实时数据处理场景,能够有效减少噪声干扰。


















 727
727

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










