一.简介
- thread是允许应用程序并发执行多个任务的一种机制。一个进程(process)可以包含多个线程。同一进程中的所有线程均会独立执行相同程序,并且共享同一份全局内存。
- 进程是CPU分配资源的最小单位,线程是操作系统执行调度的最小单位。
- 线程是轻量级的进程(LWP: Light Weight Process)
- 查看指定进程的 LWP 号 : ps -Lf pid
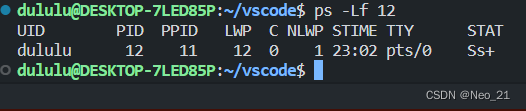
线程和进程的区别:

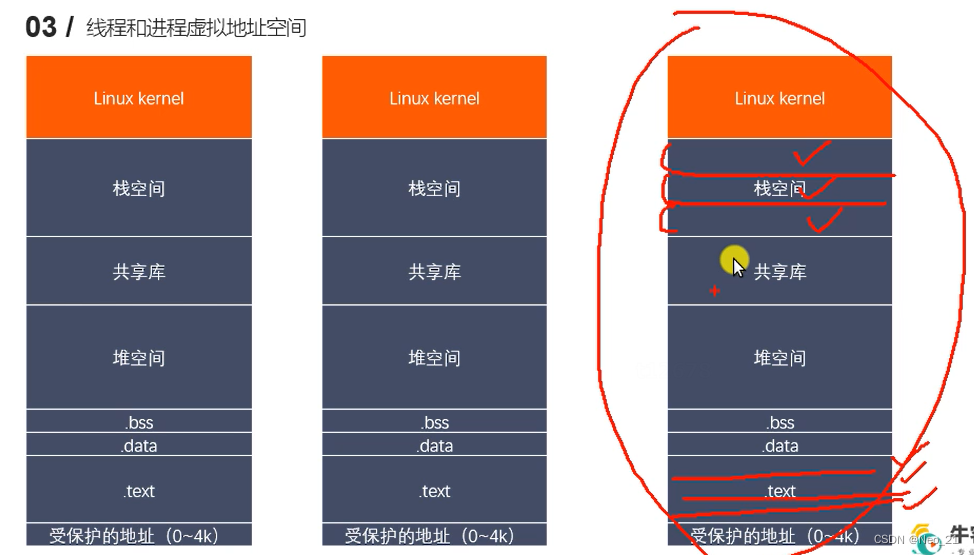
线程之间共享和非共享的资源 二.创建线程
二.创建线程
线程操作:
查看:man thread_create
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_create(pthread_t *thread, const pthread_attr_t *attr,
void *(*start_routine) (void *), void *arg);
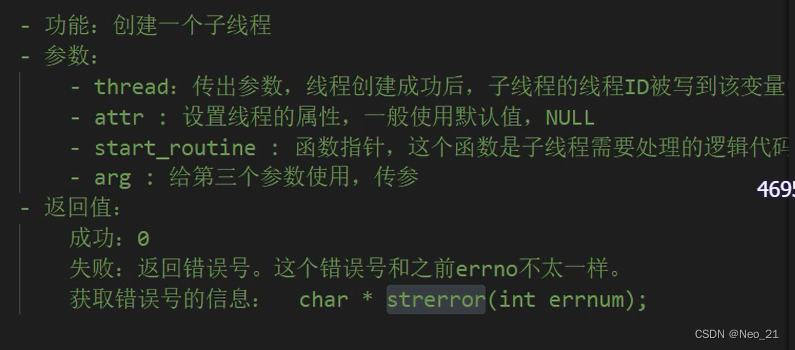
// #include <pthread.h>
// int pthread_create(pthread_t *thread, const pthread_attr_t *attr,
// void *(*start_routine) (void *), void *arg);
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <string.h>
#include<unistd.h>
int main()
{
pthread_t tid;
void *callback(void *arg)
{
printf("child thread .....\n");
printf("arg value: %d\n",*(int *)arg);
return NULL;
}
// 创建一个子线程
int num = 10;
int ret = pthread_create(&tid, NULL, callback,(void *)&num);
if (ret != 0)
{
char *errstr = strerror(ret);
printf("error : %s\n", errstr);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
printf("%d\n", i);
}
sleep(1);
return 0;
}
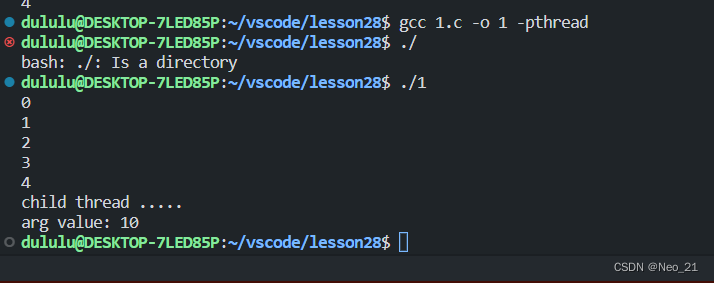
callback 里的是子线程 main 中的是主线程





 线程是操作系统执行调度的最小单位,轻量级进程(LWP)。进程包含多个线程,共享全局内存。文章通过示例展示了如何使用pthread_create在C语言中创建线程,以及线程间的资源共享。
线程是操作系统执行调度的最小单位,轻量级进程(LWP)。进程包含多个线程,共享全局内存。文章通过示例展示了如何使用pthread_create在C语言中创建线程,以及线程间的资源共享。
















 577
577

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








