Arc of Dream
Time Limit: 2000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65535/65535 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 5059 Accepted Submission(s): 1584
Problem Description
An Arc of Dream is a curve defined by following function:
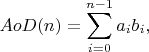
where
a 0 = A0
a i = a i-1*AX+AY
b 0 = B0
b i = b i-1*BX+BY
What is the value of AoD(N) modulo 1,000,000,007?
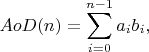
where
a 0 = A0
a i = a i-1*AX+AY
b 0 = B0
b i = b i-1*BX+BY
What is the value of AoD(N) modulo 1,000,000,007?
Input
There are multiple test cases. Process to the End of File.
Each test case contains 7 nonnegative integers as follows:
N
A0 AX AY
B0 BX BY
N is no more than 10 18, and all the other integers are no more than 2×10 9.
Each test case contains 7 nonnegative integers as follows:
N
A0 AX AY
B0 BX BY
N is no more than 10 18, and all the other integers are no more than 2×10 9.
Output
For each test case, output AoD(N) modulo 1,000,000,007.
Sample Input
1 1 2 3 4 5 6 2 1 2 3 4 5 6 3 1 2 3 4 5 6
Sample Output
4 134 1902
Author
Zejun Wu (watashi)
Source
这题就是构造矩阵,链接里的和我的没差,就是顺序不太一样。
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
const LL N = 5;
const LL p = 1e9+7;
struct mx
{
LL a[N+1][N+1];
};
mx cheng(mx a,mx b)
{
mx ans;
for(int i=1;i<=N;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=N;j++)
{
ans.a[i][j]=0;
for(int k=1;k<=N;k++)
{
(ans.a[i][j]+=a.a[i][k]*b.a[k][j])%=p;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
mx qkm(mx base,LL mi)
{
mx ans;
for(LL i=1;i<=N;i++)
{
for(LL j=1;j<=N;j++)
{
ans.a[i][j]=i==j;
}
}
while(mi)
{
if(mi&1) ans=cheng(ans,base);
base=cheng(base,base);
mi>>=1;
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
LL n;
while(~scanf("%lld",&n))
{
LL a0,ax,ay;
LL b0,bx,by;
scanf("%lld %lld %lld %lld %lld %lld",&a0,&ax,&ay,&b0,&bx,&by);
LL x1=ax;
LL x2=bx;
LL y1=ay;
LL y2=by;
if(n==0) printf("0\n");
else if(n==1) printf("%lld\n",a0*b0%p);
else
{
mx base;
base.a[1][1]=1;base.a[1][2]=0; base.a[1][3]=0; base.a[1][4]=0; base.a[1][5]=0;
base.a[2][1]=1;base.a[2][2]=x1*x2%p;base.a[2][3]=0; base.a[2][4]=0; base.a[2][5]=0;
base.a[3][1]=0;base.a[3][2]=y1*x2%p;base.a[3][3]=x2;base.a[3][4]=0; base.a[3][5]=0;
base.a[4][1]=0;base.a[4][2]=y2*x1%p;base.a[4][3]=0; base.a[4][4]=x1;base.a[4][5]=0;
base.a[5][1]=0;base.a[5][2]=y1*y2%p;base.a[5][3]=y2;base.a[5][4]=y1;base.a[5][5]=1;
base=qkm(base,n-1);
LL a1=(x1*a0%p+y1)%p;
LL b1=(x2*b0%p+y2)%p;
LL b2=(x2*b1%p+y2)%p;
LL a2=(x1*a1%p+y1)%p;
// printf("%lld %lld\n",a2,b2);
LL z[6];
z[1]=a0*b0%p;
z[2]=a1*b1%p;
z[3]=b1;
z[4]=a1;
z[5]=1;
LL ans=0;
for(int k=1;k<=5;k++)
{
ans+=z[k]*base.a[k][1];
}
printf("%lld\n",ans%p);
}
}
}






 本文介绍了一种通过构造矩阵的方法来高效计算弧梦曲线在特定点的取值,并提供了一个完整的C++代码实现。该方法适用于处理大规模数据集,尤其当输入参数N非常大时,能够快速准确地计算出弧梦曲线的值。
本文介绍了一种通过构造矩阵的方法来高效计算弧梦曲线在特定点的取值,并提供了一个完整的C++代码实现。该方法适用于处理大规模数据集,尤其当输入参数N非常大时,能够快速准确地计算出弧梦曲线的值。
















 8662
8662

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








