1.A simple flocking example
之前我们都是在computeshader中计算粒子的位置,然后在顶点片段着色器渲染粒子。通过使用共享的compute buffer。事实上,我们不应该频繁的在cpu和gpu之间传输数据,因为这样非常消耗性能。下面我们使用一个更好的办法来解决这个问题。
首先先介绍一下Boid 算法,我们后面就是参考这个算法来完成我们的粒子系统。
Boid 算法是一种用于模拟群体行为的算法,最早由克雷格·雷诺兹(Craig Reynolds)在 1986 年提出。这个算法最常用来模拟自然界中的群体现象,例如鸟群、鱼群或其他具有集体行为的生物群体。
核心思想
Boid 算法通过定义每个个体(称为 "Boid")的局部行为规则,来产生群体的整体复杂行为。每个 Boid 都基于周围的其他 Boid 做出决策,而不需要全局的群体控制。群体行为通过简单的局部交互自然产生。
三个核心规则
每个 Boid 都遵循以下三条基本规则:
-
分离(Separation):
- 避免与邻近的其他 Boid 发生碰撞或过于接近。
- 这个规则防止群体中的 Boid 挤在一起,避免个体之间的物理重叠。
公式: 计算与所有邻居 Boid 的距离,生成一个方向向量,该向量会将 Boid 推离靠得太近的 Boid。
-
对齐(Alignment):
- 使 Boid 的移动方向与其邻居的方向对齐。
- 这个规则确保群体中的 Boid 朝同样的方向移动,从而产生一致的运动方向。
公式: 计算所有邻居的平均方向向量,调整自己的方向以与邻居一致。
-
凝聚(Cohesion):
- 向邻居的中心靠拢,保持群体的整体凝聚力。
- 这个规则帮助个体保持在群体中,不让它们散开太远。
公式: 计算邻居的平均位置向量,生成一个朝向邻居群体中心的方向向量。
额外的规则
在实际应用中,通常还会加入其他规则,比如:
- 边界处理:Boid 需要避免飞出屏幕或场景边界,通常会引入规则让它们转向场景内部。
- 目标吸引力:Boid 可能需要朝着某个目标点前进,因此加入一个规则,使它们趋向目标。
下面我们就在compute shader完成Boid算法。
首先初始化向量,
separation:用来计算分离向量,避免与邻近的 Boid 过于接近。alignment:用来计算对齐向量,使 Boid 朝着邻居的平均方向移动。cohesion:初始化为flockPosition,最终会计算邻居的平均位置,以产生凝聚力,保持 Boid 朝向邻居群体中心。nearbyCount:用来统计邻居 Boid 的数量,初始值为 1,因为每个 Boid 计算自己时忽略自身。
float3 separation = 0;
float3 alignment = 0;
float3 cohesion = flockPosition;
uint nearbyCount = 1;
然后循环遍历所有Boid,寻找当前Boid的邻居,并且跳过自身。
- 计算邻居关系:
offset:表示当前 Boid 与某个邻居 Boid 的位置差向量。dist:邻居 Boid 与当前 Boid 之间的距离,避免 0 距离(因此使用max(length(offset), 0.00001))。
- 邻居条件:如果距离
dist小于neighbourDistance,则该 Boid 被认为是邻居。然后执行以下操作:separation:计算分离向量,距离越近的邻居产生的分离力越大,推动当前 Boid 远离该邻居。alignment:累加邻居的方向向量,用于后续计算 Boid 的对齐行为。cohesion:累加邻居的位置信息,用于计算凝聚力(即邻居的平均位置)。nearbyCount++:统计有效的邻居数。
for (int i = 0; i < boidsCount; i++)
{
if (i != int(id.x))
{
Boid tempBoid = boidsBuffer[i];
float3 offset = boid.position - tempBoid.position;
float dist = max(length(offset), 0.00001);
if (dist < neighbourDistance)
{
separation += offset * (1.0/dist - 1.0/neighbourDistance);
alignment += tempBoid.direction;
cohesion += tempBoid.position;
nearbyCount++;
}
}
}
接着计算平均向量
alignment:计算邻居的平均方向,将累加的邻居方向向量除以邻居数量nearbyCount。cohesion:计算邻居的平均位置,并生成一个从当前 Boid 指向邻居中心的方向向量。cohesion - boid.position:得到从当前 Boid 到邻居中心的方向。normalize:将方向向量标准化为单位向量。
float avg = 1.0 / nearbyCount;
alignment *= avg;
cohesion *= avg;
cohesion = normalize(cohesion - boid.position);
最后计算最终的移动方向并且进行平滑,并且更新Boid的位置,然后将更新后的Boid写回缓冲区
目前效果:

2.using instanced meshes in the flock
这次我们基于上次的代码继续完善代码,并且使用实例化网格。
首先更改了Boid的构造函数,增加了初始方向以及一个offset(用于后面对速度的变化)
public Boid(Vector3 pos, Vector3 dir, float offset)
{
position.x = pos.x;
position.y = pos.y;
position.z = pos.z;
direction.x = dir.x;
direction.y = dir.y;
direction.z = dir.z;
noise_offset = offset;
}
很明显Boid的初始化方法也要进行修改
这里主要说一下初始方向的设置。
Quaternion rot = Quaternion.Slerp(transform.rotation, Random.rotation, 0.3f);:
- 为 Boid 生成一个平滑插值的随机旋转。
transform.rotation:当前物体的旋转,作为起始旋转方向。Random.rotation:生成一个随机的目标旋转方向。Quaternion.Slerp:以 30% 的比例(即0.3f)将当前旋转transform.rotation平滑过渡到随机旋转Random.rotation。这会生成一个过渡平滑的旋转角度rot。rot.eulerAngles:将四元数rot转换为欧拉角,便于在Boid对象中使用。
private void InitBoids()
{
boidsArray = new Boid[numOfBoids];
for (int i = 0; i < numOfBoids; i++)
{
Vector3 pos = transform.position + Random.insideUnitSphere * spawnRadius;
Quaternion rot = Quaternion.Slerp(transform.rotation, Random.rotation, 0.3f);
float offset = Random.value * 1000.0f;
boidsArray[i] = new Boid(pos, rot.eulerAngles, offset);
}
}
这次还新增了argsBuffer,用于存储绘制参数的计算缓冲区,专门用于间接绘制。
new ComputeBuffer(1, 5 * sizeof(uint), ComputeBufferType.IndirectArguments):
- 创建一个新的
ComputeBuffer对象。 1:指定缓冲区的元素数量。在这种情况下,我们只需要一个元素来存储绘制参数。5 * sizeof(uint):每个元素占用的字节数。这里我们需要存储 5 个uint类型的值,所以总大小是5 * sizeof(uint)。sizeof(uint)是4字节,因此缓冲区总大小是20字节。ComputeBufferType.IndirectArguments:指定缓冲区的类型为间接绘制参数缓冲区。这告诉 GPU 这个缓冲区将用于存储绘制指令。
argsBuffer = new ComputeBuffer(1, 5 * sizeof(uint), ComputeBufferType.IndirectArguments);
-
args[0] = (uint)boidMesh.GetIndexCount(0);:- 获取
boidMesh的索引计数。boidMesh.GetIndexCount(0)返回网格第一个子网格的总索引数,这个值表示绘制每个 Boid 实例所需的索引数量。
- 获取
-
args[1] = (uint)numOfBoids;:- 设置要绘制的 Boid 实例数量。
numOfBoids表示总的 Boid 实例数。
- 设置要绘制的 Boid 实例数量。
if (boidMesh != null)
{
args[0] = (uint)boidMesh.GetIndexCount(0);
args[1] = (uint)numOfBoids;
}
argsBuffer.SetData(args);
然后我们就使用间接绘制技术来高效地渲染多个实例化的对象。
-
boidMesh:- 这是要绘制的网格(Mesh)。在这个例子中,是 Boid 对象的网格。它定义了每个实例的形状。
-
0:- 这是子网格索引,通常是
0,表示第一个子网格。对于包含多个子网格的网格,你可以通过指定不同的子网格索引来绘制特定的子网格。
- 这是子网格索引,通常是
-
boidMaterial:- 这是用来绘制网格的材质(Material)。它定义了渲染时使用的着色器和其他渲染属性。
-
bounds:- 这是一个
Bounds对象,定义了渲染的区域范围。Graphics.DrawMeshInstancedIndirect函数会在这个范围内进行绘制,以确定哪些实例在视图中可见。
- 这是一个
-
argsBuffer:- 这是一个
ComputeBuffer,包含绘制所需的间接绘制参数(如索引计数、实例数量等)。argsBuffer提供了 GPU 进行绘制操作所需的信息,指示 GPU 如何从boidMesh中提取顶点数据并绘制实例。
- 这是一个
Graphics.DrawMeshInstancedIndirect(boidMesh, 0, boidMaterial, bounds, argsBuffer);
然后就是修改我们的compute shader函数。
首先就是增加噪声对速度的影响。
float noise = clamp(noise1(time / 100.0 + boid.noise_offset), -1, 1) * 2.0 - 1.0;
float velocity = boidSpeed * (1.0 + noise * boidSpeedVariation);
然后就是我们的顶点片段着色器,这里我们使用的是表面着色器
surf 是计算表面着色的函数,vert 是自定义的顶点着色器函数。addshadow 使得材质支持阴影,nolightmap 禁用光照贴图
#pragma surface surf Standard vertex:vert addshadow nolightmap
-
#pragma instancing_options:- 这是 Unity 着色器的一个指令,用于控制实例化时的选项。实例化(Instancing)是一种优化技术,用于在场景中绘制大量相似的对象而只需要提交一次绘制调用,从而减少 CPU 到 GPU 的通信开销。
-
procedural:setup:procedural是指设置与程序生成数据(Procedural Data)相关的选项。在实例化过程中,程序生成数据允许你通过代码动态生成实例化数据,而不是仅仅依赖静态的顶点缓冲区。
#pragma instancing_options procedural:setup
好,目前为止,我们运行程序,可以发现mesh始终背对着相机,是因为目前值对顶点进行了位移,我们需要使用旋转矩阵对矩阵进行旋转

创建旋转矩阵的一个方法是需要三个轴, 我们已经拥有了z轴(就是Dir),而且还知道向上的方向(0,1,0),我们可以通过叉积得到一个垂直于这两个向量的向量。
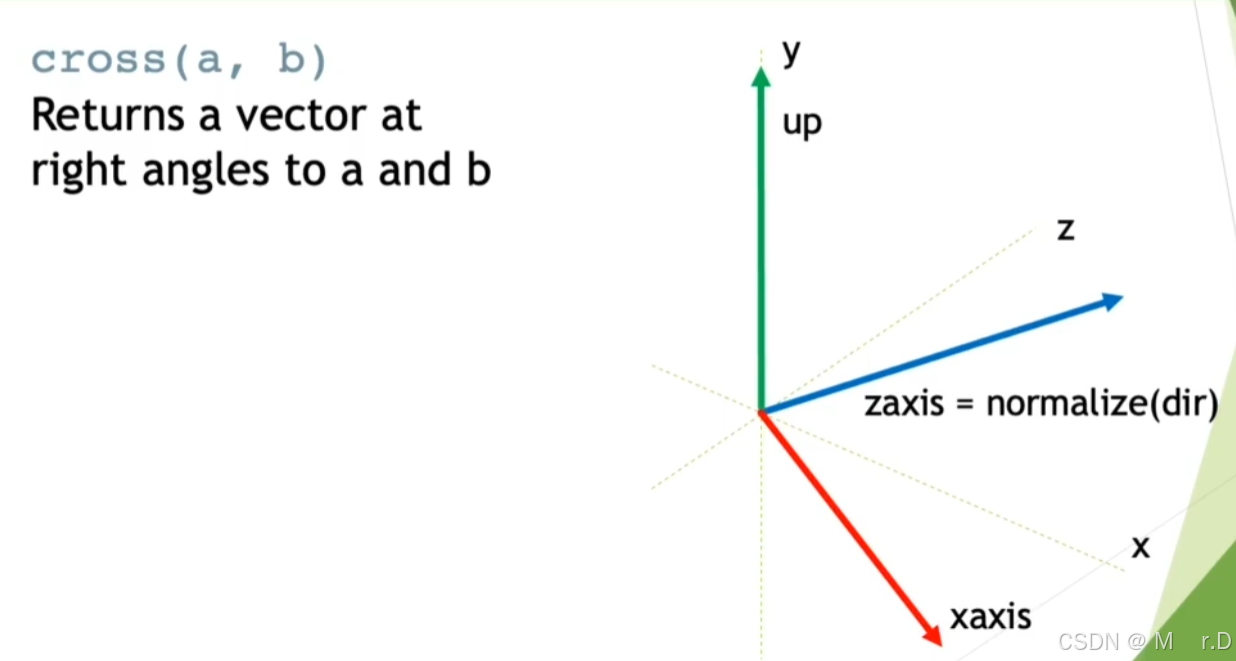
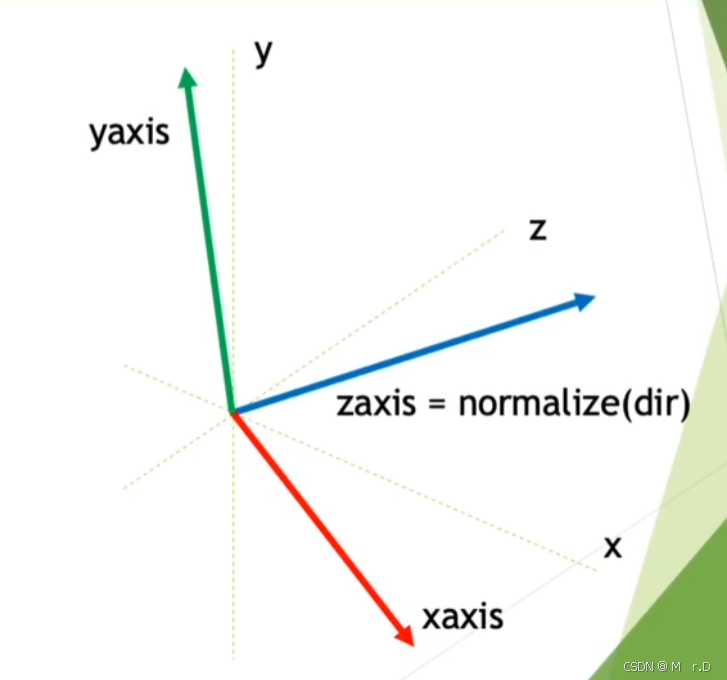
我们先在shader中创建一个函数用来创建矩阵,这里是创建了一个视图矩阵,视图矩阵用于将顶点从世界空间转换到视图空间。视图空间的原点是摄像机的位置,视图矩阵的目的是将世界中的物体映射到摄像机的视图中。矩阵的前 3 列(x 轴、y 轴和 z 轴)分别表示视图空间的方向轴(方向和上方向),而最后一列表示物体在视图空间中的位置(平移),这里忽略了投影矩阵是因为我们进行的是非透视渲染,也就是正交渲染,可以不进行投影变换
float4x4 create_matrix(float3 pos, float3 dir, float3 up) {
float3 zaxis = normalize(dir);
float3 xaxis = normalize(cross(up, zaxis));
float3 yaxis = cross(zaxis, xaxis);
return float4x4(
xaxis.x, yaxis.x, zaxis.x, pos.x,
xaxis.y, yaxis.y, zaxis.y, pos.y,
xaxis.z, yaxis.z, zaxis.z, pos.z,
0, 0, 0, 1
);
}
在每个实例渲染之前,setup() 函数会被调用,以便为每个实例设置其特定的矩阵或其他属性
void setup()
{
#ifdef UNITY_PROCEDURAL_INSTANCING_ENABLED
_BoidPosition = boidsBuffer[unity_InstanceID].position;
//_LookAtMatrix = look_at_matrix(boidsBuffer[unity_InstanceID].direction, float3(0.0, 1.0, 0.0));
_Matrix = create_matrix(boidsBuffer[unity_InstanceID].position, boidsBuffer[unity_InstanceID].direction, float3(0.0, 1.0, 0.0));
#endif
}
最后在顶点函数里将顶点与矩阵相乘就可以进行旋转与位移
void vert(inout appdata_full v, out Input data)
{
UNITY_INITIALIZE_OUTPUT(Input, data);
#ifdef UNITY_PROCEDURAL_INSTANCING_ENABLED
//v.vertex = mul(_LookAtMatrix, v.vertex);
//v.vertex.xyz += _BoidPosition;
v.vertex = mul(_Matrix, v.vertex);
#endif
}
最终效果:
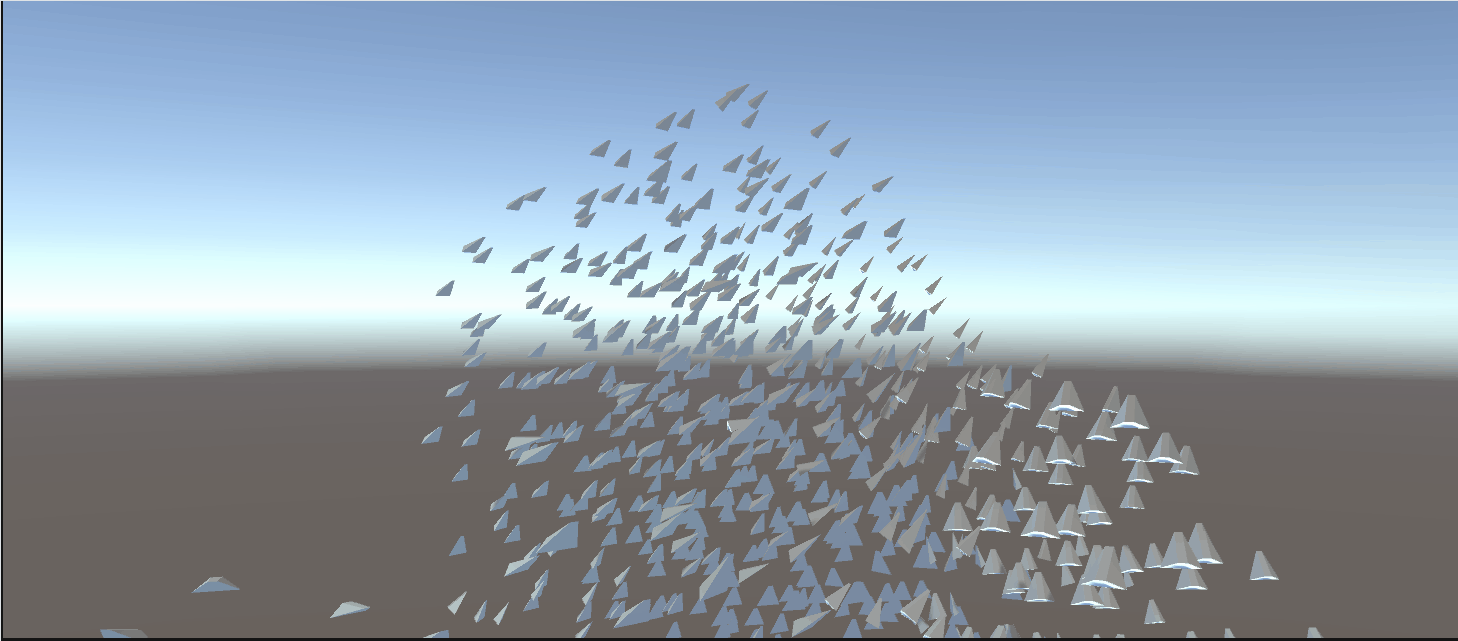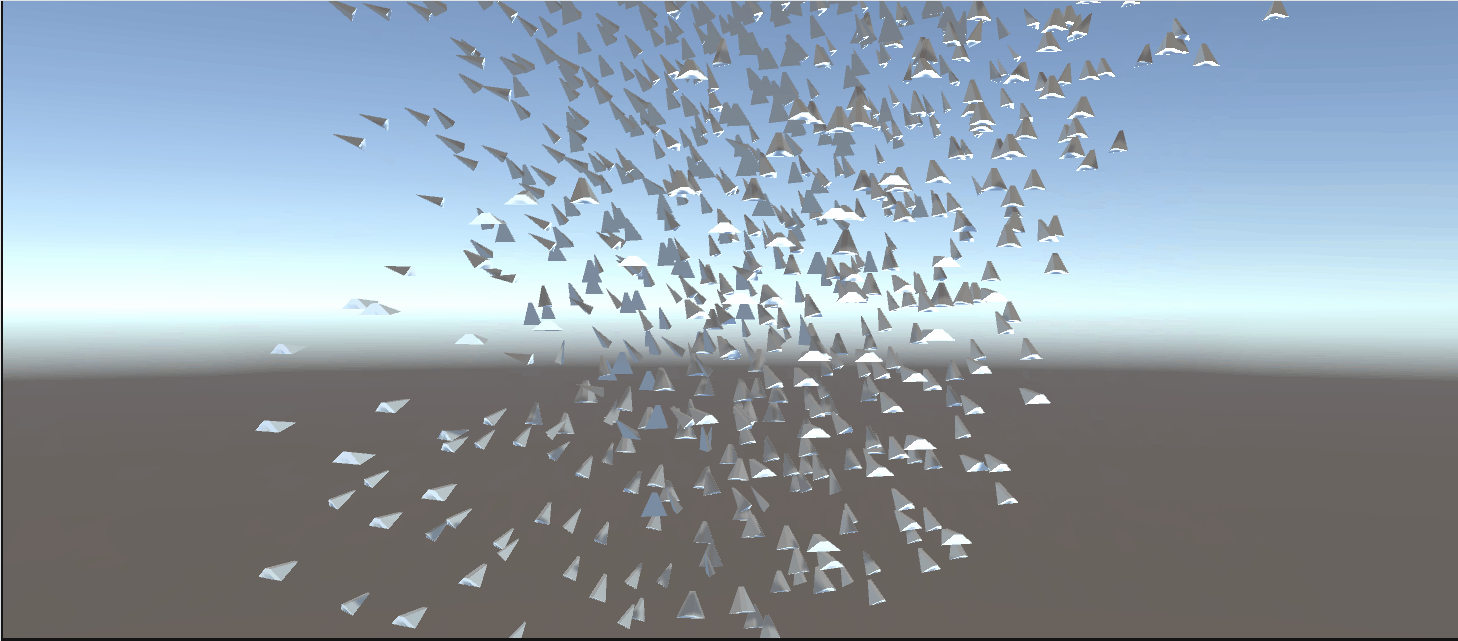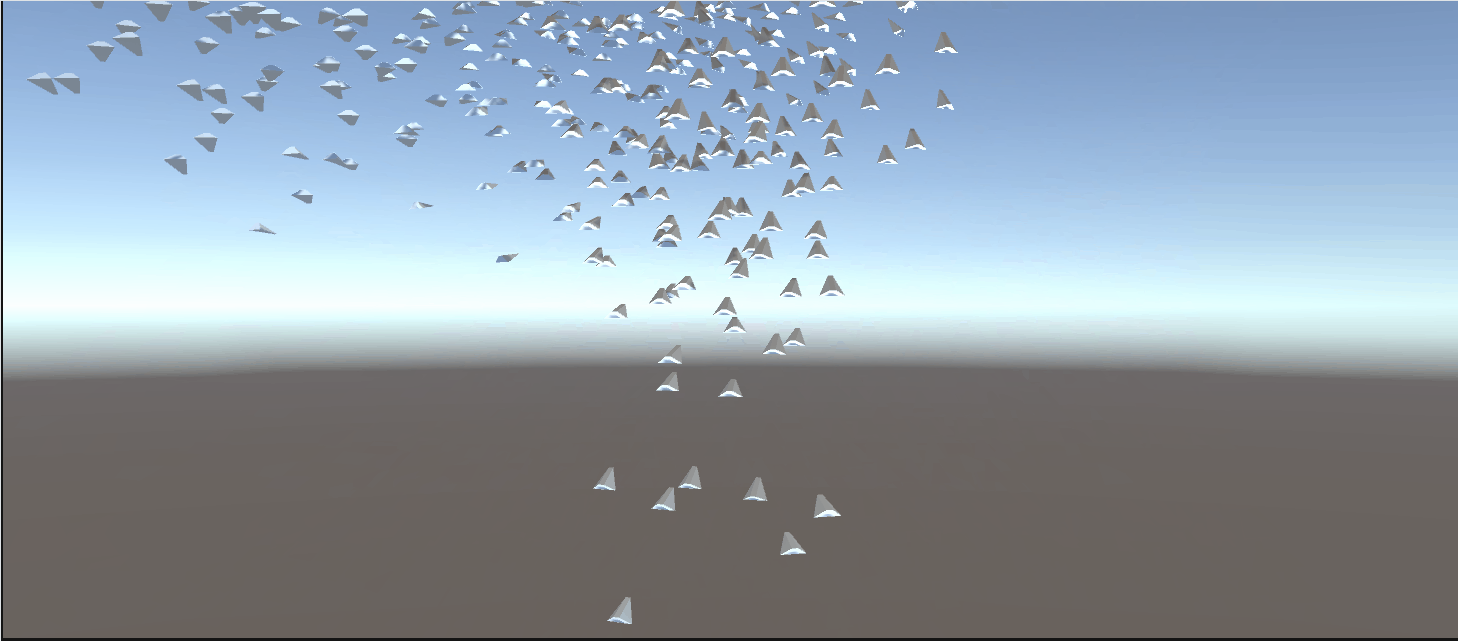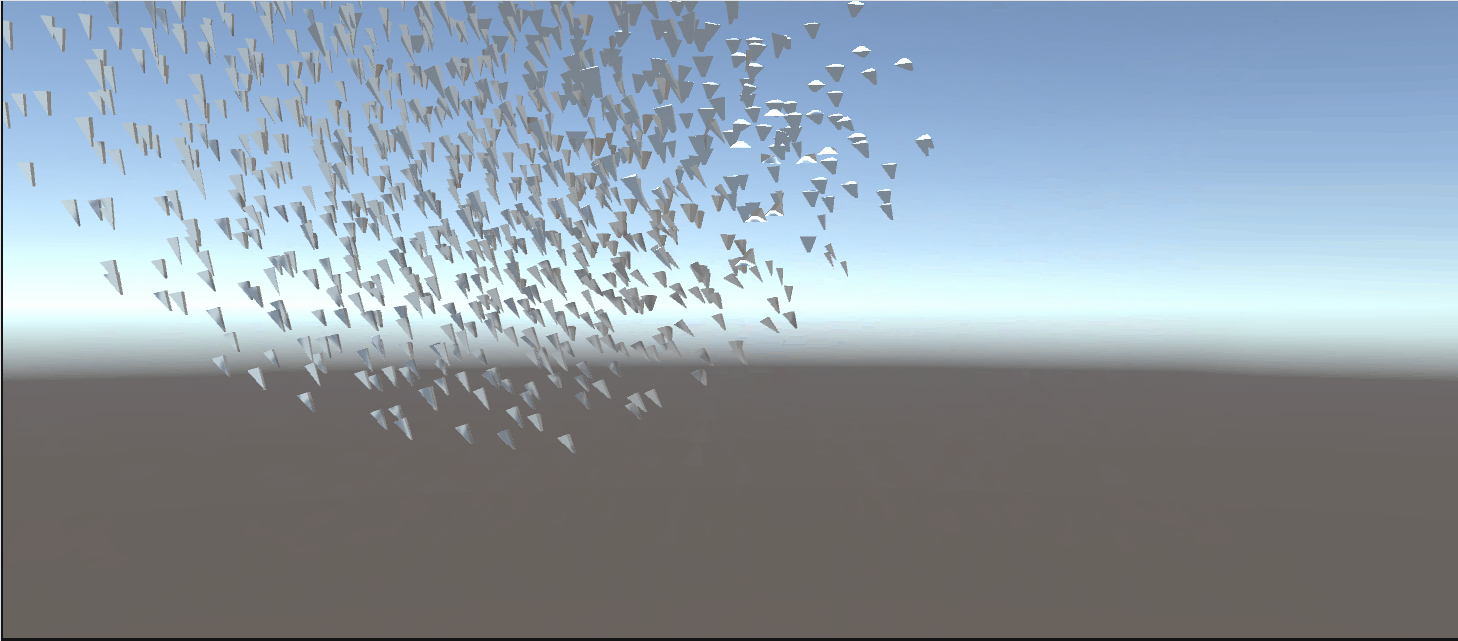
3.5. Using a skinned mesh in the flock
这次我们将基于上次的代码生成飞行的鸟群,并且设置鸟类的动画。
首先增加了一个frame属性,用来选择要显示的动画帧。
public Vector3 position;
public Vector3 direction;
public float noise_offset;
public float frame;
在初始化代码中还添加了可根据 frameInterpolation 变量的值动态地启用或禁用材质中的关键字 FRAME_INTERPOLATION的代码
if (frameInterpolation && !boidMaterial.IsKeywordEnabled("FRAME_INTERPOLATION"))
boidMaterial.EnableKeyword("FRAME_INTERPOLATION");
if (!frameInterpolation && boidMaterial.IsKeywordEnabled("FRAME_INTERPOLATION"))
boidMaterial.DisableKeyword("FRAME_INTERPOLATION");
还添加了GenerateSkinnedAnimationForGPUBuffer()这个函数用来填充vertexAnimationBuffer,这是一个新创建的compute buffer,用来存储静态网格的每一帧顶点动画,下面主要是函数的解析
boidSMR获取了boidObject(包含动画的对象)的SkinnedMeshRenderer组件,用来处理网格的骨骼动画。SkinnedMeshRenderer用于渲染动态变形的网格,通常与骨骼动画(Skinning)系统结合使用。它在运行时根据角色的骨骼(bones)对网格进行实时变形,使其可以进行复杂的动作和动画。boidMesh是获取共享的静态网格数据。共享网格(Shared Mesh) 是指多个对象或组件共享使用同一个网格数据,而不需要为每个对象单独创建一份拷贝。这通常用于节省内存和优化性能。
boidSMR = boidObject.GetComponentInChildren<SkinnedMeshRenderer>();
boidMesh = boidSMR.sharedMesh;
animator 用于控制模型的动画。AnimatorStateInfo 存储当前动画状态的信息
animator = boidObject.GetComponentInChildren<Animator>();
int iLayer = 0;
AnimatorStateInfo aniStateInfo = animator.GetCurrentAnimatorStateInfo(iLayer);
- 这里通过
animationClip的帧率和长度,计算出动画的总帧数,并将帧数调整为最接近的2次幂(提升计算效率)。 -
animationClip.frameRate:- 这是动画片段的帧率,表示每秒播放的帧数。单位是帧每秒(FPS)。
- 比如,
animationClip.frameRate = 30表示动画每秒播放 30 帧。
-
animationClip.length:- 这是动画片段的持续时间,单位是秒。
- 比如,
animationClip.length = 5表示动画片段持续 5 秒
perFrameTime是每帧的时间间隔,用来逐帧采样动画。
numOfFrames = Mathf.ClosestPowerOfTwo((int)(animationClip.frameRate * animationClip.length));
perFrameTime = animationClip.length / numOfFrames;
- 通过
boidSMR.sharedMesh.vertexCount得到网格的顶点数量。 vertexAnimationBuffer是一个ComputeBuffer,用来存储每帧动画的顶点数据。每个顶点用Vector4来存储,包含了x, y, z位置和额外的w分量。
var vertexCount = boidSMR.sharedMesh.vertexCount;
vertexAnimationBuffer = new ComputeBuffer(vertexCount * numOfFrames, 16);
Vector4[] vertexAnimationData = new Vector4[vertexCount * numOfFrames];
- 逐帧采样动画:循环遍历每帧,通过设置
sampleTime来手动播放动画的某一帧,然后使用animator.Update(0f)来更新动画状态。 - 烘焙网格:使用
boidSMR.BakeMesh(bakedMesh)将当前帧的网格状态烘焙到bakedMesh中,确保顶点位置等已经经过骨骼动画计算。 - 记录顶点数据:对于每帧中的每个顶点,获取它的
Vector3位置,存入Vector4数组(vertexAnimationData),其中w分量设置为 1,这样后面进行矩阵乘法的时候可以进行顶点偏移
for (int i = 0; i < numOfFrames; i++)
{
animator.Play(aniStateInfo.shortNameHash, iLayer, sampleTime);
animator.Update(0f);
boidSMR.BakeMesh(bakedMesh);
for(int j = 0; j < vertexCount; j++)
{
Vector4 vertex = bakedMesh.vertices[j];
vertex.w = 1;
vertexAnimationData[(j * numOfFrames) + i] = vertex;
}
sampleTime += perFrameTime;
}
- 通过
vertexAnimationBuffer.SetData将 CPU 计算好的顶点动画数据传递到 GPU。 - 然后,使用
boidMaterial.SetBuffer将这个缓冲区绑定到材质boidMaterial,这样 GPU 在渲染时就可以访问到这些预烘焙的顶点动画数据。
vertexAnimationBuffer.SetData(vertexAnimationData);
boidMaterial.SetBuffer("vertexAnimation", vertexAnimationBuffer);
最后由于烘焙完成后,动画对象的实际网格渲染不再需要,因此将其隐藏,只使用 GPU 进行动画渲染。
boidObject.SetActive(false);
然后我们在compute shader中更新frame,速度越快让它的帧数变化越快,超过帧数上限以后再重置到第0帧
boid.frame = boid.frame + velocity * deltaTime * boidFrameSpeed;
if (boid.frame >= numOfFrames) boid.frame -= numOfFrames;
然后修改表面着色器。
首先要在setup函数中设置当前帧,如果开启了帧插值关键字还要设置下一帧,最后计算出插值系数 ,表示当前帧已经过去了多少秒
void vert(inout appdata_custom v)
{
#ifdef UNITY_PROCEDURAL_INSTANCING_ENABLED
#ifdef FRAME_INTERPOLATION
v.vertex = lerp(vertexAnimation[v.id * numOfFrames + _CurrentFrame], vertexAnimation[v.id * numOfFrames + _NextFrame], _FrameInterpolation);
#else
v.vertex = vertexAnimation[v.id * numOfFrames + _CurrentFrame];
#endif
v.vertex = mul(_Matrix, v.vertex);
#endif
}
最后就是在shader中通过vertexAnimation buffer来修改顶点位置达到顶点动画的效果
void vert(inout appdata_custom v)
{
#ifdef UNITY_PROCEDURAL_INSTANCING_ENABLED
#ifdef FRAME_INTERPOLATION
v.vertex = lerp(vertexAnimation[v.id * numOfFrames + _CurrentFrame], vertexAnimation[v.id * numOfFrames + _NextFrame], _FrameInterpolation);
#else
v.vertex = vertexAnimation[v.id * numOfFrames + _CurrentFrame];
#endif
v.vertex = mul(_Matrix, v.vertex);
#endif
}
最终效果:
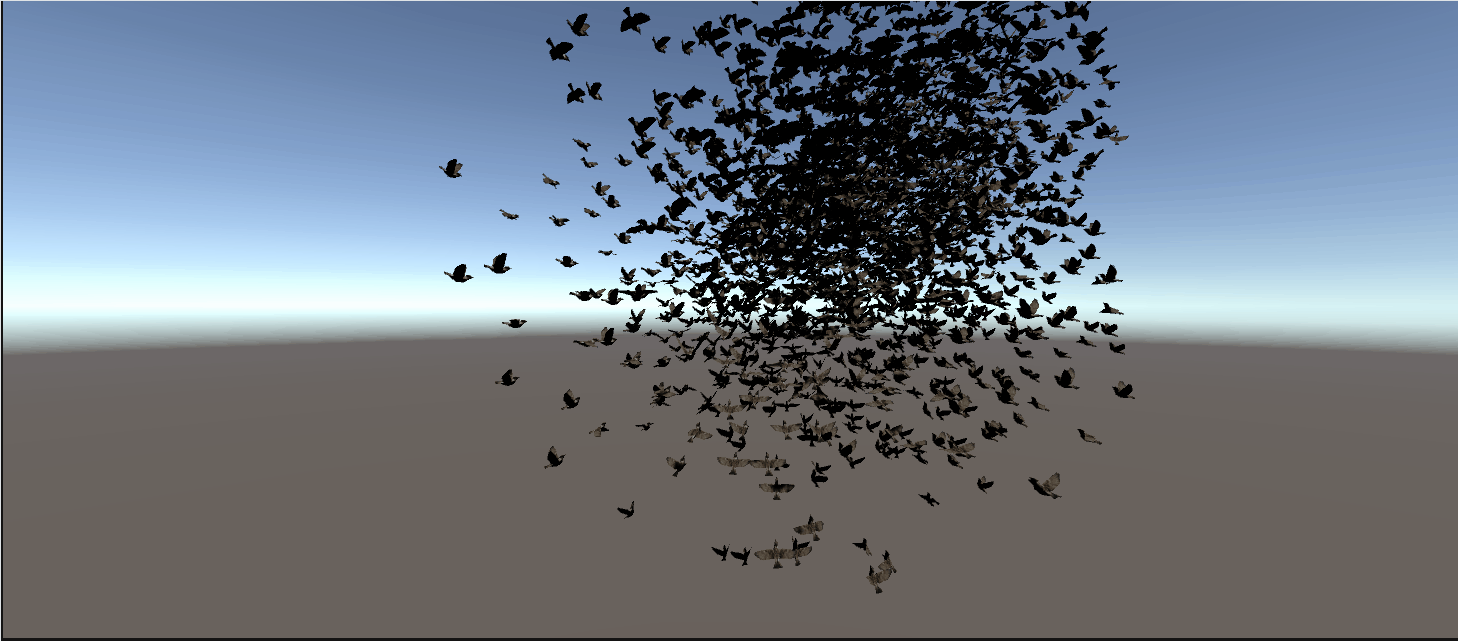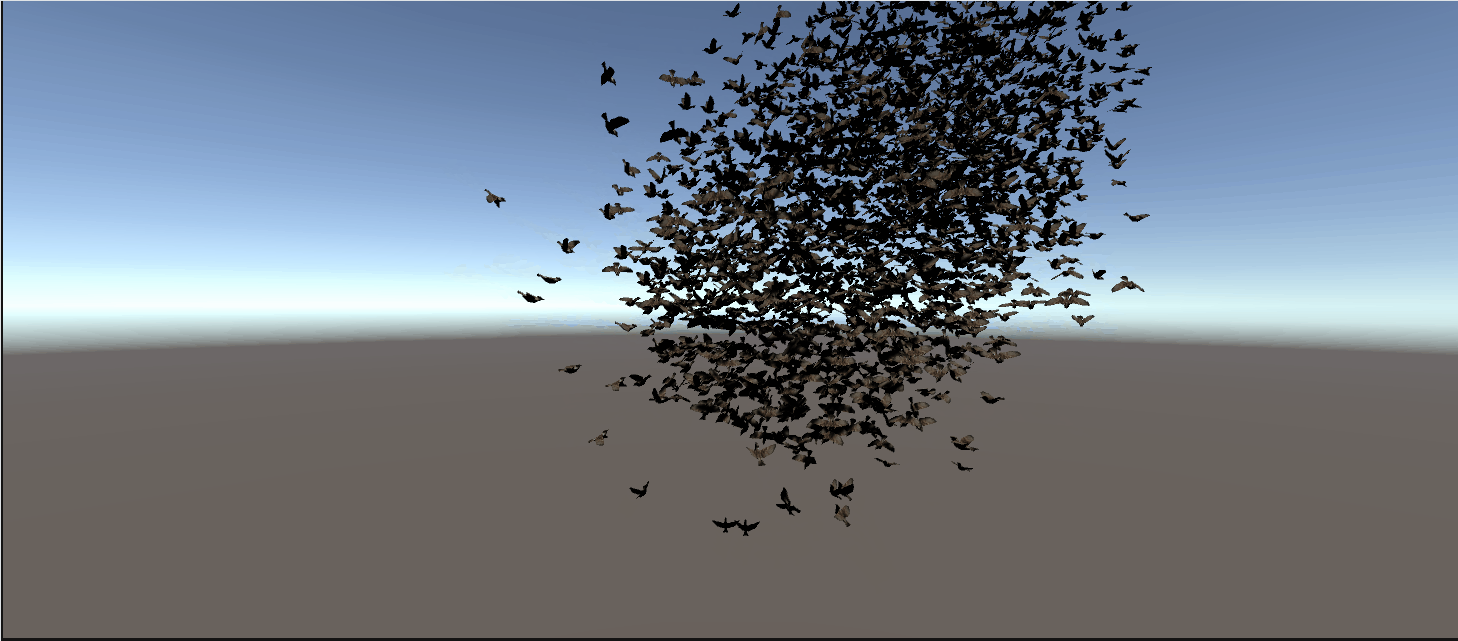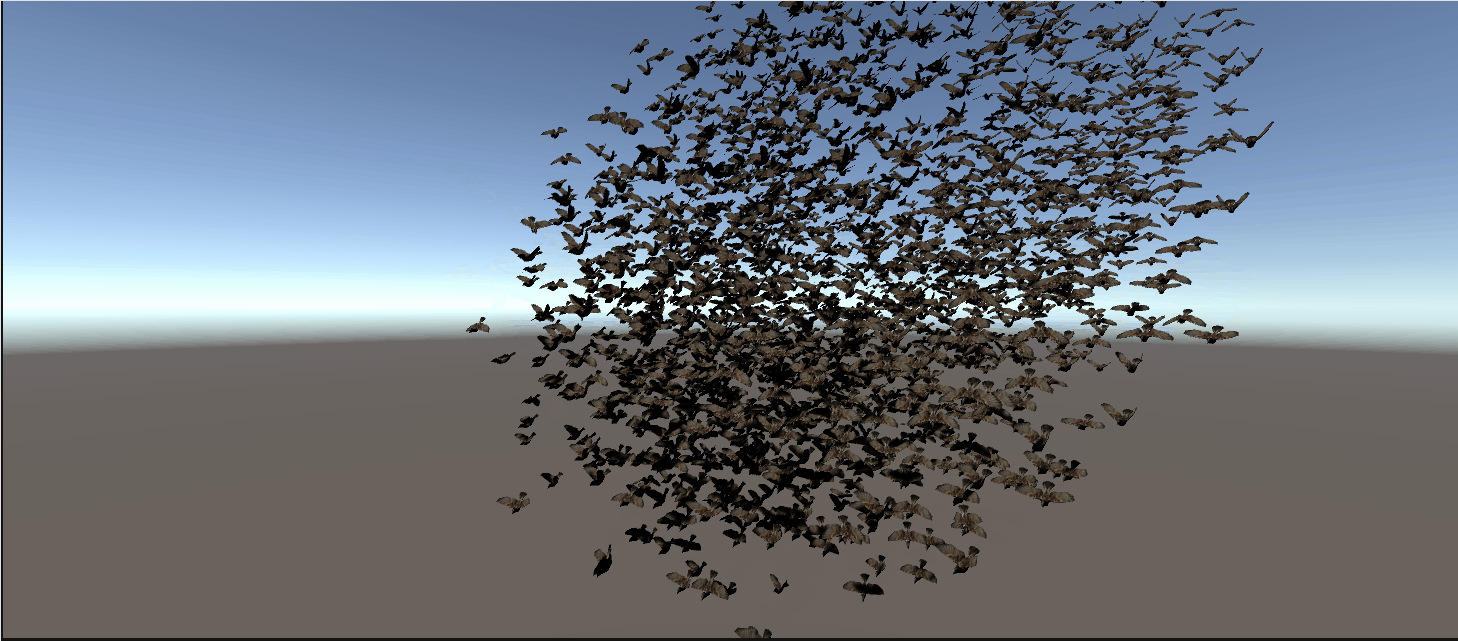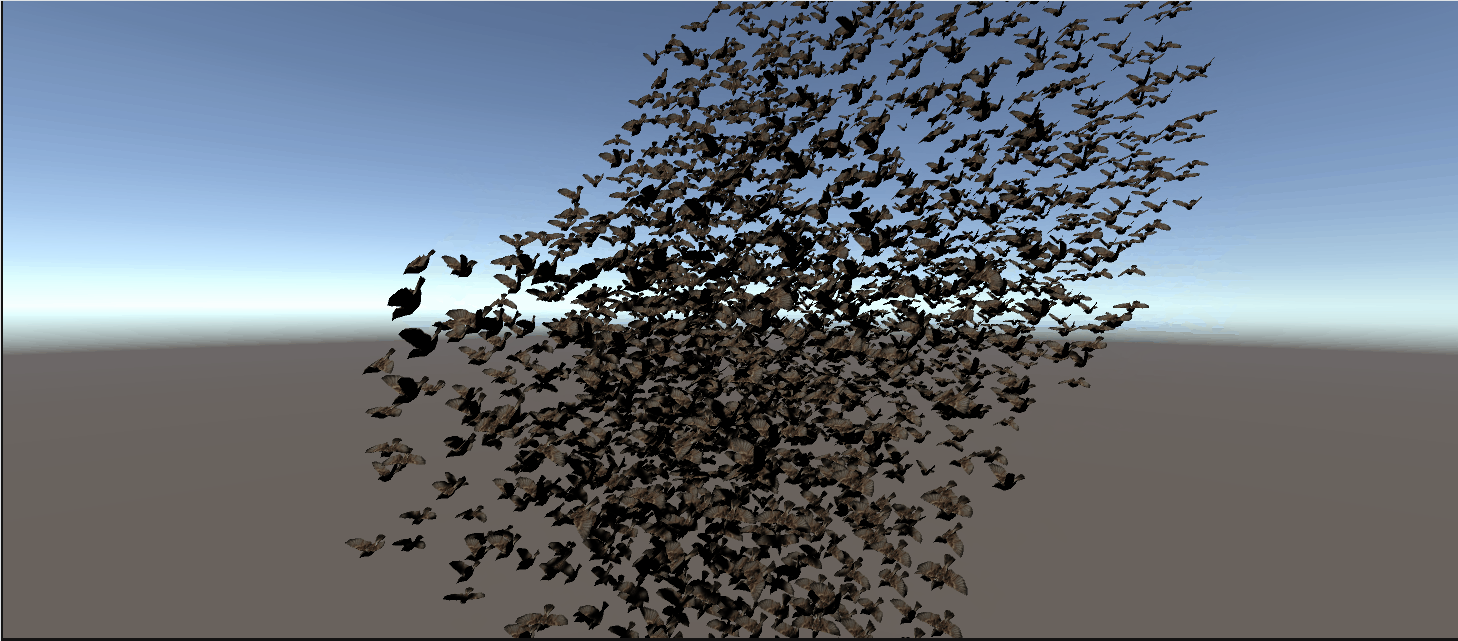
完整代码:
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class SkinnedFlocking : MonoBehaviour {
public struct Boid
{
public Vector3 position;
public Vector3 direction;
public float noise_offset;
public float speed;
public float frame;
public Vector3 padding;
public Boid(Vector3 pos, Vector3 dir, float offset)
{
position.x = pos.x;
position.y = pos.y;
position.z = pos.z;
direction.x = dir.x;
direction.y = dir.y;
direction.z = dir.z;
noise_offset = offset;
speed = frame = 0;
padding.x = 0; padding.y = padding.z = 0;
}
}
public ComputeShader shader;
private SkinnedMeshRenderer boidSMR;
public GameObject boidObject;
private Animator animator;
public AnimationClip animationClip;
private int numOfFrames;
public int boidsCount;
public float spawnRadius;
public Transform target;
public float rotationSpeed = 1f;
public float boidSpeed = 1f;
public float neighbourDistance = 1f;
public float boidSpeedVariation = 1f;
public float boidFrameSpeed = 10f;
public bool frameInterpolation = true;
Mesh boidMesh;
private int kernelHandle;
private ComputeBuffer boidsBuffer;
private ComputeBuffer vertexAnimationBuffer;
public Material boidMaterial;
ComputeBuffer argsBuffer;
MaterialPropertyBlock props;
uint[] args = new uint[5] { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 };
Boid[] boidsArray;
int groupSizeX;
int numOfBoids;
Bounds bounds;
void Start()
{
kernelHandle = shader.FindKernel("CSMain");
uint x;
shader.GetKernelThreadGroupSizes(kernelHandle, out x, out _, out _);
groupSizeX = Mathf.CeilToInt((float)boidsCount / (float)x);
numOfBoids = groupSizeX * (int)x;
bounds = new Bounds(Vector3.zero, Vector3.one * 1000);
// This property block is used only for avoiding an instancing bug.
props = new MaterialPropertyBlock();
props.SetFloat("_UniqueID", Random.value);
InitBoids();
GenerateSkinnedAnimationForGPUBuffer();
InitShader();
}
void InitBoids()
{
boidsArray = new Boid[numOfBoids];
for (int i = 0; i < numOfBoids; i++)
{
Vector3 pos = transform.position + Random.insideUnitSphere * spawnRadius;
Quaternion rot = Quaternion.Slerp(transform.rotation, Random.rotation, 0.3f);
float offset = Random.value * 1000.0f;
boidsArray[i] = new Boid(pos, rot.eulerAngles, offset);
}
}
void InitShader()
{
// Initialize the indirect draw args buffer.
argsBuffer = new ComputeBuffer(
1, 5 * sizeof(uint), ComputeBufferType.IndirectArguments
);
if (boidMesh)//Set by the GenerateSkinnedAnimationForGPUBuffer
{
args[0] = boidMesh.GetIndexCount(0);
args[1] = (uint)numOfBoids;
argsBuffer.SetData(args);
}
boidsBuffer = new ComputeBuffer(numOfBoids, 12 * sizeof(float));
boidsBuffer.SetData(boidsArray);
shader.SetFloat("rotationSpeed", rotationSpeed);
shader.SetFloat("boidSpeed", boidSpeed);
shader.SetFloat("boidSpeedVariation", boidSpeedVariation);
shader.SetVector("flockPosition", target.transform.position);
shader.SetFloat("neighbourDistance", neighbourDistance);
shader.SetFloat("boidFrameSpeed", boidFrameSpeed);
shader.SetInt("boidsCount", numOfBoids);
shader.SetInt("numOfFrames", numOfFrames);
shader.SetBuffer(kernelHandle, "boidsBuffer", boidsBuffer);
boidMaterial.SetBuffer("boidsBuffer", boidsBuffer);
boidMaterial.SetInt("numOfFrames", numOfFrames);
if (frameInterpolation && !boidMaterial.IsKeywordEnabled("FRAME_INTERPOLATION"))
boidMaterial.EnableKeyword("FRAME_INTERPOLATION");
if (!frameInterpolation && boidMaterial.IsKeywordEnabled("FRAME_INTERPOLATION"))
boidMaterial.DisableKeyword("FRAME_INTERPOLATION");
}
void Update()
{
shader.SetFloat("time", Time.time);
shader.SetFloat("deltaTime", Time.deltaTime);
shader.Dispatch(kernelHandle, groupSizeX, 1, 1);
Graphics.DrawMeshInstancedIndirect( boidMesh, 0, boidMaterial, bounds, argsBuffer, 0, props);
}
void OnDestroy()
{
if (boidsBuffer != null) boidsBuffer.Release();
if (argsBuffer != null) argsBuffer.Release();
if (vertexAnimationBuffer != null) vertexAnimationBuffer.Release();
}
private void GenerateSkinnedAnimationForGPUBuffer()
{
boidSMR = boidObject.GetComponentInChildren<SkinnedMeshRenderer>();
boidMesh = boidSMR.sharedMesh;
animator = boidObject.GetComponentInChildren<Animator>();
int iLayer = 0;
AnimatorStateInfo aniStateInfo = animator.GetCurrentAnimatorStateInfo(iLayer);
Mesh bakedMesh = new Mesh();
float sampleTime = 0;
float perFrameTime = 0;
numOfFrames = Mathf.ClosestPowerOfTwo((int)(animationClip.frameRate * animationClip.length));
perFrameTime = animationClip.length / numOfFrames;
var vertexCount = boidSMR.sharedMesh.vertexCount;
vertexAnimationBuffer = new ComputeBuffer(vertexCount * numOfFrames, 16);
Vector4[] vertexAnimationData = new Vector4[vertexCount * numOfFrames];
for (int i = 0; i < numOfFrames; i++)
{
animator.Play(aniStateInfo.shortNameHash, iLayer, sampleTime);
animator.Update(0f);
boidSMR.BakeMesh(bakedMesh);
for(int j = 0; j < vertexCount; j++)
{
Vector4 vertex = bakedMesh.vertices[j];
vertex.w = 1;
vertexAnimationData[(j * numOfFrames) + i] = vertex;
}
sampleTime += perFrameTime;
}
vertexAnimationBuffer.SetData(vertexAnimationData);
boidMaterial.SetBuffer("vertexAnimation", vertexAnimationBuffer);
boidObject.SetActive(false);
}
}
#pragma kernel CSMain
#define GROUP_SIZE 256
float hash( float n )
{
return frac(sin(n)*43758.5453);
}
// The noise function returns a value in the range -1.0f -> 1.0f
float noise1( float3 x )
{
float3 p = floor(x);
float3 f = frac(x);
f = f*f*(3.0-2.0*f);
float n = p.x + p.y*57.0 + 113.0*p.z;
return lerp(lerp(lerp( hash(n+0.0), hash(n+1.0),f.x),
lerp( hash(n+57.0), hash(n+58.0),f.x),f.y),
lerp(lerp( hash(n+113.0), hash(n+114.0),f.x),
lerp( hash(n+170.0), hash(n+171.0),f.x),f.y),f.z);
}
struct Boid
{
float3 position;
float3 direction;
float noise_offset;
float speed;
float frame;
float3 padding;
};
RWStructuredBuffer<Boid> boidsBuffer;
float time;
float deltaTime;
float rotationSpeed;
float boidSpeed;
float boidSpeedVariation;
float3 flockPosition;
float neighbourDistance;
uint boidsCount;
float boidFrameSpeed;
int numOfFrames;
[numthreads(GROUP_SIZE,1,1)]
void CSMain (uint3 id : SV_DispatchThreadID)
{
uint instanceId = id.x;
Boid boid = boidsBuffer[instanceId];
float noise = clamp(noise1(time / 100.0 + boid.noise_offset), -1, 1) * 2.0 - 1.0;
float velocity = boidSpeed * (1.0 + noise * boidSpeedVariation);
float3 boid_pos = boid.position;
float3 boid_dir = boid.direction;
float3 separation = float3(0, 0.0, 0);
float3 alignment = float3(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
float3 cohesion = flockPosition;
uint nearbyCount = 1; // Add self that is ignored in loop
for (uint i = 0; i < boidsCount; i++) {
if (i == instanceId)
continue;
float3 tempBoid_position = boidsBuffer[i].position;
float3 offset = boid.position - tempBoid_position;
float dist = max(length(offset), 0.000001);
if (dist < neighbourDistance)
{
separation += offset * (1.0/dist - 1.0/neighbourDistance);
alignment += boidsBuffer[i].direction;
cohesion += tempBoid_position;
nearbyCount += 1;
}
}
float avg = 1.0 / nearbyCount;
alignment *= avg;
cohesion *= avg;
cohesion = normalize(cohesion - boid_pos);
float3 direction = alignment + separation + cohesion;
float ip = exp(-rotationSpeed * deltaTime);
boid.direction = lerp(direction, normalize(boid_dir), ip);
boid.position += boid.direction * velocity * deltaTime;
boid.frame = boid.frame + velocity * deltaTime * boidFrameSpeed;
if (boid.frame >= numOfFrames) boid.frame -= numOfFrames;
boidsBuffer[id.x] = boid;
}
Shader "Flocking/Skinned" { // StructuredBuffer + SurfaceShader
Properties {
_Color ("Color", Color) = (1,1,1,1)
_MainTex ("Albedo (RGB)", 2D) = "white" {}
_BumpMap ("Bumpmap", 2D) = "bump" {}
_MetallicGlossMap("Metallic", 2D) = "white" {}
_Metallic ("Metallic", Range(0,1)) = 0.0
_Glossiness ("Smoothness", Range(0,1)) = 1.0
}
SubShader {
CGPROGRAM
#include "UnityCG.cginc"
sampler2D _MainTex;
sampler2D _BumpMap;
sampler2D _MetallicGlossMap;
struct appdata_custom {
float4 vertex : POSITION;
float3 normal : NORMAL;
float4 texcoord : TEXCOORD0;
float4 tangent : TANGENT;
uint id : SV_VertexID;
uint inst : SV_InstanceID;
UNITY_VERTEX_INPUT_INSTANCE_ID
};
struct Input {
float2 uv_MainTex;
float2 uv_BumpMap;
float3 worldPos;
};
half _Glossiness;
half _Metallic;
fixed4 _Color;
#pragma multi_compile __ FRAME_INTERPOLATION
#pragma surface surf Standard vertex:vert addshadow nolightmap
#pragma instancing_options procedural:setup
float4x4 _Matrix;
int _CurrentFrame;
int _NextFrame;
float _FrameInterpolation;
int numOfFrames;
#ifdef UNITY_PROCEDURAL_INSTANCING_ENABLED
struct Boid
{
float3 position;
float3 direction;
float noise_offset;
float speed;
float frame;
float3 padding;
};
StructuredBuffer<Boid> boidsBuffer;
StructuredBuffer<float4> vertexAnimation;
#endif
float4x4 create_matrix(float3 pos, float3 dir, float3 up) {
float3 zaxis = normalize(dir);
float3 xaxis = normalize(cross(up, zaxis));
float3 yaxis = cross(zaxis, xaxis);
return float4x4(
xaxis.x, yaxis.x, zaxis.x, pos.x,
xaxis.y, yaxis.y, zaxis.y, pos.y,
xaxis.z, yaxis.z, zaxis.z, pos.z,
0, 0, 0, 1
);
}
void vert(inout appdata_custom v)
{
#ifdef UNITY_PROCEDURAL_INSTANCING_ENABLED
#ifdef FRAME_INTERPOLATION
v.vertex = lerp(vertexAnimation[v.id * numOfFrames + _CurrentFrame], vertexAnimation[v.id * numOfFrames + _NextFrame], _FrameInterpolation);
#else
v.vertex = vertexAnimation[v.id * numOfFrames + _CurrentFrame];
#endif
v.vertex = mul(_Matrix, v.vertex);
#endif
}
void setup()
{
#ifdef UNITY_PROCEDURAL_INSTANCING_ENABLED
_Matrix = create_matrix(boidsBuffer[unity_InstanceID].position, boidsBuffer[unity_InstanceID].direction, float3(0.0, 1.0, 0.0));
_CurrentFrame = boidsBuffer[unity_InstanceID].frame;
#ifdef FRAME_INTERPOLATION
_NextFrame = _CurrentFrame + 1;
if (_NextFrame >= numOfFrames) _NextFrame = 0;
_FrameInterpolation = frac(boidsBuffer[unity_InstanceID].frame);
#endif
#endif
}
void surf (Input IN, inout SurfaceOutputStandard o) {
fixed4 c = tex2D (_MainTex, IN.uv_MainTex) * _Color;
fixed4 m = tex2D (_MetallicGlossMap, IN.uv_MainTex);
o.Albedo = c.rgb;
o.Alpha = c.a;
o.Normal = UnpackNormal (tex2D (_BumpMap, IN.uv_BumpMap));
o.Metallic = m.r;
o.Smoothness = _Glossiness * m.a;
}
ENDCG
}
}





















 4127
4127

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








