相距为l的一对等量异号点电荷+q和-q,并且它们到观察点P的距离rl。通常的媒质分子在外电场的作用下可以形成这种电偶极子。电偶极子的特征用电偶极矩(或电矩)p=lq表示,l和p的方向规定由-q指向+q。电矩p 的国际制单位为C·m(库·米)。微观物理学中常用的单位为德拜(debye);1德拜=3.336×10C·m,它相当于典型分子内部核间距离的十分之一(约2×10m)同一个电子的电荷e=1.6×10C的乘积。
电偶极子产生的电场+q和-q分别在观察点P(r)产生的电位的代数和即电偶极子产生的电位
式中墷只对P点的坐标变量运算。在P点的电场强度为 。
外电场中的电偶极子若电偶极子+q和-q所在点的外电场的电位为V1和V2,则偶极子的位能W=qV1-qV2=q(l·墷)V=p·墷 V=-p·Eo,式中Eo为点偶极子所在的外电场强度。
偶极子在外电场中受到平移力 F=-墷W=墷(p·Eo)=(p·墷)Eo。
如果外电场均匀,Eo为常量,则F=0。 偶极子在外电场作用下受到的力矩 T=-дW/дθ=pEosinθ或T=p×Eo,它使电矩p同外电场强度Eo的夹角减小。如果p 同Eo平行,则力矩T=0。并可看到p的量值也就是电偶极子在单位外电场(Eo=1)下可能受到的最大力矩,故称电矩。
如果点偶极子 p1 处于另一偶极子 p2 产生的电场E2(r)中,则p1的位能即相互作用能为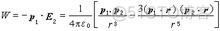 电偶极子
电偶极子
。
电偶极子是电介质理论和原子物理学的重要模型,研究从稳恒到 X光频电磁场作用下电介质的色散和吸收,以及天线的辐射等现象,可以用振荡偶极子poe 电偶极子
电偶极子
来表示。
将偶极子概念加以推广,可有多极子,它是含有2个大小相等的点电荷,其中正负各半数,排列成有规律的点阵。在多极子系列中,n=0时,就是点电荷;n=1,就是电偶极子;n=2,称为四极子;n≥2,统称为高阶多极子。
高阶多级子模型应用于核物理,其中最重要的是四极子。任意点电荷集合或任意分布电荷,如果能够用一个球面包围,则球外的电位V可用集中在球心的点多极子系列的合成电位表示,称为电场的多极子展开。
function varargout = dianoujizi(varargin)
% dianoujizi MATLAB code for dianoujizi.fig
% dianoujizi, by itself, creates a new dianoujizi or raises the existing
% singleton*.
%
% H = dianoujizi returns the handle to a new dianoujizi or the handle to
% the existing singleton*.
%
% dianoujizi('CALLBACK',hObject,eventData,handles,...) calls the local
% function named CALLBACK in dianoujizi.M with the given input arguments.
%
% dianoujizi('Property','Value',...) creates a new dianoujizi or raises the
% existing singleton*. Starting from the left, property value pairs are
% applied to the GUI before dianoujizi_OpeningFcn gets called. An
% unrecognized property name or invalid value makes property application
% stop. All inputs are passed to dianoujizi_OpeningFcn via varargin.
%
% *See GUI Options on GUIDE's Tools menu. Choose "GUI allows only one
% instance to run (singleton)".
%
% See also: GUIDE, GUIDATA, GUIHANDLES
% Edit the above text to modify the response to help dianoujizi
% Last Modified by GUIDE v2.5 03-May-2013 20:22:55
% Begin initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
gui_Singleton = 1;
gui_State = struct('gui_Name', mfilename, ... %GUI结构
'gui_Singleton', gui_Singleton, ...
'gui_OpeningFcn', @dianoujizi_OpeningFcn, ...
'gui_OutputFcn', @dianoujizi_OutputFcn, ...
'gui_LayoutFcn', [] , ...
'gui_Callback', []);
if nargin && ischar(varargin{1})
gui_State.gui_Callback = str2func(varargin{1});
end
if nargout
[varargout{1:nargout}] = gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
else
gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
end
% End initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
% --- Executes just before dianoujizi is made visible.
function dianoujizi_OpeningFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles, varargin)
% This function has no output args, see OutputFcn.
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% varargin command line arguments to dianoujizi (see VARARGIN)
set(handles.a_edit,'String',2); %设置默认值为2
set(handles.b_edit,'String',2); %设置默认值为2
% Choose default command line output for dianoujizi
handles.output = hObject;
% Update handles structure
guidata(hObject, handles);
% UIWAIT makes dianoujizi wait for user response (see UIRESUME)
% uiwait(handles.figure1);
% --- Outputs from this function are returned to the command line.
function varargout = dianoujizi_OutputFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% varargout cell array for returning output args (see VARARGOUT);
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Get default command line output from handles structure
varargout{1} = handles.output;
function a_edit_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to a_edit (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of a_edit as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of a_edit as a double
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function a_edit_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to a_edit (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function b_edit_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to b_edit (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of b_edit as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of b_edit as a double
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function b_edit_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to b_edit (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
% --- Executes on button press in eped_pushbutton.
function eped_pushbutton_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to eped_pushbutton (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
a=str2num(get(handles.a_edit,'String')); %获得默认值
b=str2num(get(handles.b_edit,'String'));
x=-8:0.8:8;
y=x;
q=2e-6; %电荷
k=9e9; %常数
[X,Y]=meshgrid(x,y);
rp=sqrt((X-a).^2+(Y-b).^2); %设置变量求出r-
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
- 51.
- 52.
- 53.
- 54.
- 55.
- 56.
- 57.
- 58.
- 59.
- 60.
- 61.
- 62.
- 63.
- 64.
- 65.
- 66.
- 67.
- 68.
- 69.
- 70.
- 71.
- 72.
- 73.
- 74.
- 75.
- 76.
- 77.
- 78.
- 79.
- 80.
- 81.
- 82.
- 83.
- 84.
- 85.
- 86.
- 87.
- 88.
- 89.
- 90.
- 91.
- 92.
- 93.
- 94.
- 95.
- 96.
- 97.
- 98.
- 99.
- 100.
- 101.
- 102.
- 103.
- 104.
- 105.
- 106.
- 107.
- 108.
- 109.
- 110.
- 111.
- 112.
- 113.
- 114.
- 115.
- 116.
- 117.
- 118.
- 119.
- 120.
- 121.
- 122.
- 123.
- 124.
- 125.
- 126.
- 127.
- 128.
- 129.
- 130.
- 131.
- 132.
- 133.





















 211
211

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








