题目:
Vasya's house is situated in a forest, and there is a mushroom glade near it. The glade consists of two rows, each of which can be divided into n consecutive cells. For each cell Vasya knows how fast the mushrooms grow in this cell (more formally, how many grams of mushrooms grow in this cell each minute). Vasya spends exactly one minute to move to some adjacent cell. Vasya cannot leave the glade. Two cells are considered adjacent if they share a common side. When Vasya enters some cell, he instantly collects all the mushrooms growing there.
Vasya begins his journey in the left upper cell. Every minute Vasya must move to some adjacent cell, he cannot wait for the mushrooms to grow. He wants to visit all the cells exactly once and maximize the total weight of the collected mushrooms. Initially, all mushrooms have a weight of 0. Note that Vasya doesn't need to return to the starting cell.
Help Vasya! Calculate the maximum total weight of mushrooms he can collect.
Input
The first line contains the number n (1 ≤ n ≤ 3·105) — the length of the glade.
The second line contains n numbers a1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 106) — the growth rate of mushrooms in the first row of the glade.
The third line contains n numbers b1, b2, ..., bn (1 ≤ bi ≤ 106) is the growth rate of mushrooms in the second row of the glade.
Output
Output one number — the maximum total weight of mushrooms that Vasya can collect by choosing the optimal route. Pay attention that Vasya must visit every cell of the glade exactly once.
Examples
Input
Copy
3 1 2 3 6 5 4
Output
Copy
70
Input
Copy
3 1 1000 10000 10 100 100000
Output
Copy
543210
Note
In the first test case, the optimal route is as follows:
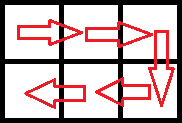
Thus, the collected weight of mushrooms will be 0·1 + 1·2 + 2·3 + 3·4 + 4·5 + 5·6 = 70.
In the second test case, the optimal route is as follows:
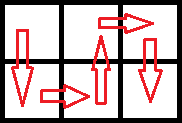
Thus, the collected weight of mushrooms will be 0·1 + 1·10 + 2·100 + 3·1000 + 4·10000 + 5·100000 = 543210.
题意:两排格子, 每个格子会有一个权值, 从左上的格子出发,时间点为零, 每次只能走相邻的格子(上下左右),每次穿越格子花费时间1点,到达每个格子时会得到权值 时间 * 格子权值, 要求走完所有格子且不能走已经走过的格子, 求所得权值的最大值。
题解:首先观察可知一共有n个终点,所以自然想到遍历一遍复杂度应该为O(n),但是要求和,如果不加以处理必定会上升到O(n^2)的复杂度,考虑以下:sum123表示从左到右走到头所摘蘑菇总数,sun321表示从右到左所摘蘑菇总数,sum111表示这一段初始蘑菇总和。我们观察到,不管什么时候开始走sum123+sum321的情况(即一路走到头再从上面回来,中间不转弯),都与原始求的sum123与sum321差一个常数*sum111,因为可把复杂度变为O(n)。
AC代码:
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
long long sum123[2][300001], sum321[2][300001], sum111[2][300001];
int n;
int a[2][300001];
int main()
{
int i, j;
long long sum = 0, res = 0, nres;
scanf("%d", &n);
for(i = 0;i < 2;i++)
for(j = 0;j < n;j++)
scanf("%d", &a[i][j]);
for(i = 0;i < 2;i++){
for(j = n - 1;j >= 0;j--){
sum123[i][j] = sum123[i][j + 1] + j * 1LL * a[i][j];//从i,j一直走到右边端点所摘磨菇数总和
sum321[i][j] = sum321[i][j + 1] + (n - j) * 1LL * a[i][j];//从右端点走到i,j所摘磨菇数总和
sum111[i][j] = sum111[i][j + 1] + a[i][j];//初始磨菇数总和
}
}
for(i = 0, j = 0;j < n;++j, i ^= 1){//学会位运算,k^=1表示:k为偶数k-=1,k为奇数k+=1
nres = sum; //用sum维护左端一直拐弯的蘑菇总和
nres += sum123[i][j] +j * 1LL * sum111[i][j];//补上一个常数(j+1)*sum111的蘑菇数量
nres += sum321[i^1][j] + (j + n - 1) * 1LL * sum111[i ^ 1][j];//补上一个常数(j+n)*sum111的蘑菇数量
res = max(res, nres);//更新总和
sum += a[i][j] * 1LL * (j + j);//更新维护的和
sum += a[i ^ 1][j] * 1LL * (j + j + 1);
}
printf("%I64d\n", res);
return 0;
}





 本文详细解析了CodeForces 1016C蘑菇收集问题,介绍了一个森林中蘑菇生长的特殊场景,通过算法优化实现了在限定时间内收集最大重量蘑菇的目标。
本文详细解析了CodeForces 1016C蘑菇收集问题,介绍了一个森林中蘑菇生长的特殊场景,通过算法优化实现了在限定时间内收集最大重量蘑菇的目标。
















 1148
1148

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








