

后序遍历(Postorder Traversal)指的是先遍历子节点,再遍历根节点。对于 N 叉树,这意味着对于每个节点,先递归遍历它的所有子节点,最后访问该节点本身。
代码实现:
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, val=None, children=None):
self.val = val
self.children = children if children is not None else []
class Solution:
def postorder(self, root: 'Node') -> list[int]:
if not root:
return []
result = []
def dfs(node):
if not node:
return
for child in node.children:
dfs(child)
result.append(node.val)
dfs(root)
return result
迭代解法:
class Solution:
def postorder(self, root: 'Node') -> list[int]:
if not root:
return []
stack, result = [root], []
while stack:
node = stack.pop()
result.append(node.val)
stack.extend(node.children) # 先加入子节点
return result[::-1] # 逆序得到后序遍历
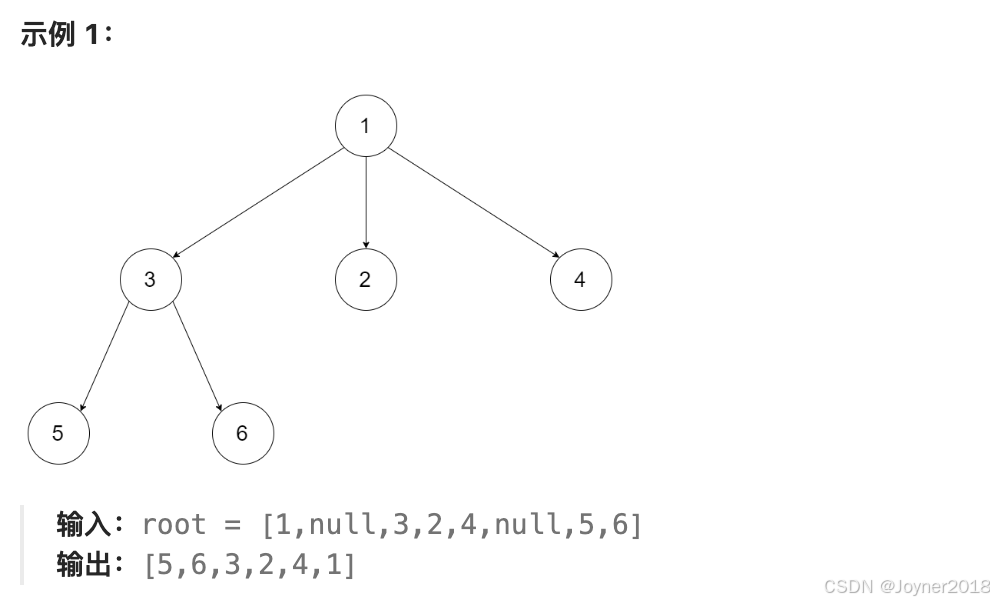
示例:
输入:
1
/|\
3 2 4
/ \
5 6
序列化表示: [1, 3, 2, 4, 5, 6, null, null, null, null, null]
输出: [5, 6, 3, 2, 4, 1]
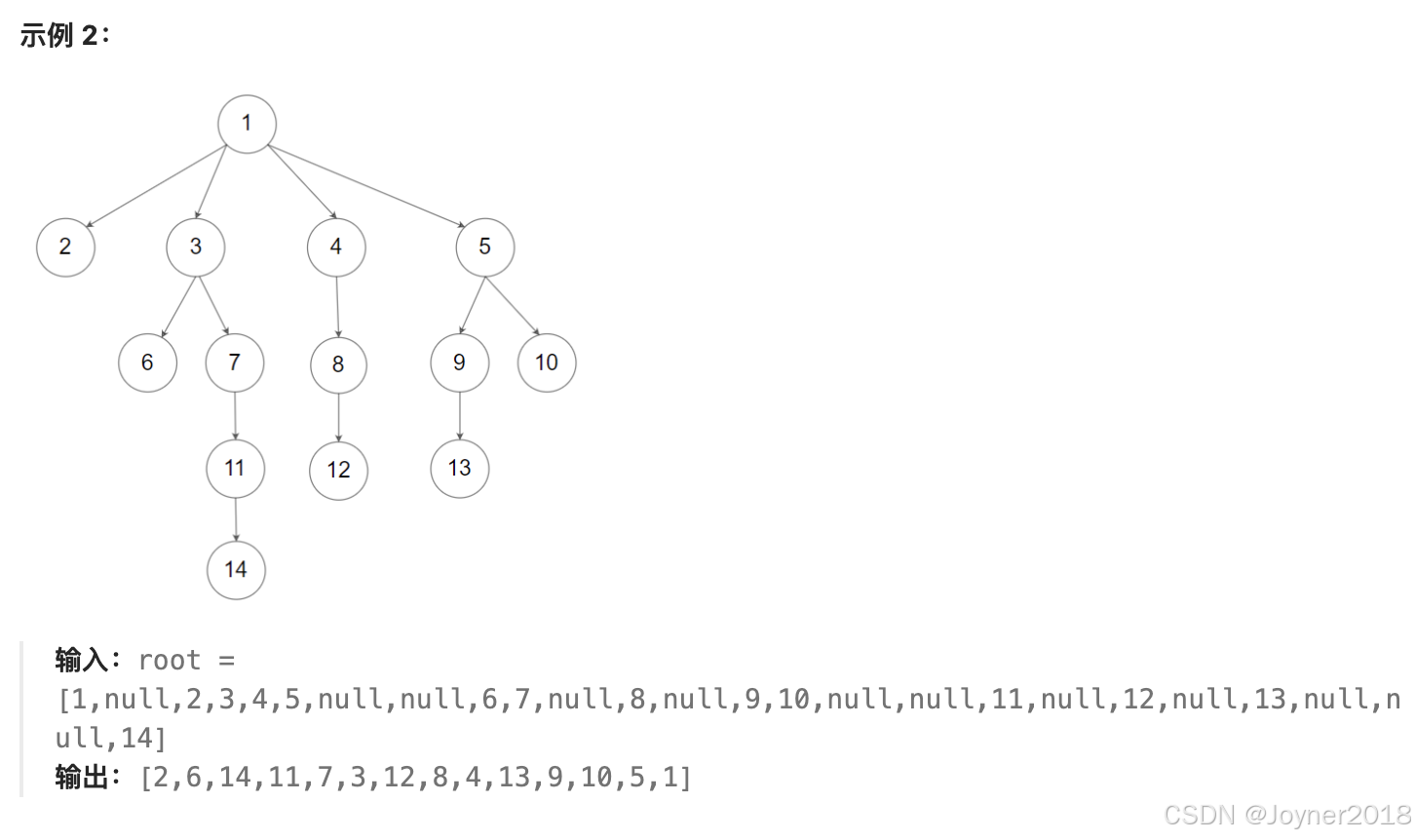
这两种方法都能正确返回 n 叉树的后序遍历结果。





















 1166
1166

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








